Components of periodontal ligament.pptx
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes91 views
The periodontal ligament is a complex connective tissue that surrounds the tooth root and attaches the tooth to the alveolar bone. It is composed of collagen fibers, ground substance, blood vessels, nerves and cells. The principal collagen fibers resist various forces on the tooth and help transmit these forces to the bone. The periodontal ligament provides nutrition to surrounding structures, allows for remodeling and repair, and has proprioceptive functions through its nerve endings.
1 of 39
Download to read offline






















Ad
Recommended
tooth supporting structures and its influence in periodontology
tooth supporting structures and its influence in periodontologyssuserbe13a5
╠²
The document provides an overview of the periodontal ligament (PDL), detailing its structure, development, composition, and functions. It explains the various categories of PDL fibers and cells, as well as their roles in supporting teeth and transmitting occlusal forces. Additionally, it discusses clinical considerations, including the variations in PDL thickness and pathologies such as granulomas and apical cysts that can arise due to inflammatory diseases.1 periodontal ligament in periodontics and dentistry
1 periodontal ligament in periodontics and dentistryssuserbe13a5
╠²
The document discusses the periodontal ligament (PDL), which connects teeth to the jawbone and supports them during function. It details the development, microscopic structure, and functional aspects of the PDL, including its composition, fiber types, and roles in tooth stability and sensory functions. The document also addresses clinical considerations regarding the PDL, highlighting its significance in oral health and potential pathological conditions.pdl.ppt periodontal ligament ppt from periodontics
pdl.ppt periodontal ligament ppt from periodonticsssuserbe13a5
╠²
The document discusses the periodontal ligament (PDL), its definition, evolution, development, and functions, emphasizing its role as a connective tissue that supports teeth. It details the structure of PDL, including its cellular composition, types of fibers, and reaction to occlusal forces through various theories. The significance of maintaining the PDL and surrounding alveolar bone for dental health is highlighted, along with the challenges in regenerating these tissues once damaged.Periodontal ligament in health and diseases
Periodontal ligament in health and diseasesnewknightarise
╠²
periodontal ligament in health and diseasesPERIODONTAL LIGAMENT (PDL)
PERIODONTAL LIGAMENT (PDL)ssuseraf61fb
╠²
The periodontal ligament (PDL) is a connective tissue that surrounds tooth roots, connecting them to the surrounding bone, and is composed of various cell types including osteoblasts, fibroblasts, and cementoblasts. It plays essential roles in tooth support, force transmission, sensory function, and nutrient supply to adjacent structures, while constantly undergoing remodeling. The PDL's width varies based on factors like age and tooth stress, with a normal width of approximately 0.25mm.Pdl
PdlD Venkatesh Kumar
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a specialized connective tissue that connects teeth to the alveolar bone of the jaws. It is composed of cells, collagen fibers, blood vessels and nerves. The collagen fibers are arranged in bundles and attach to both the cementum covering the tooth root and the overlying alveolar bone. The periodontal ligament functions to attach teeth, absorb chewing forces, maintain the position of teeth, and allow limited tooth movement through the remodeling of its collagen fibers.Periodontal ligament - Part 2
Periodontal ligament - Part 2ORAL PATHOLOGY, SRM DENTAL COLLEGE
╠²
The document discusses the periodontal ligament, including its definition, composition, functions, development, and involvement in various diseases and clinical considerations. Specifically, it notes that the periodontal ligament is a specialized connective tissue that anchors the tooth to the alveolar bone and transmits occlusal forces. It consists of collagen fibers embedded in a ground substance containing proteoglycans and glycoproteins. The periodontal ligament serves important supportive, nutritive, sensory and remodeling functions for the tooth.Periodontal ligament, fibers, functions, blood supply
Periodontal ligament, fibers, functions, blood supplynehadeshpande52
╠²
The document outlines the structures and functions of the periodontal ligament, which connects teeth to the alveolar bone and plays a crucial role in supporting dental health. It details the composition, principal fibers, and functions of the periodontal ligament, as well as its importance in the transmission of forces, nourishment, and sensory perception. Additionally, it emphasizes clinical considerations related to the ligament's shock-absorbing properties and the implications for periodontal disease.Periodontal ligament.pptx by Dr. Ira Gupta
Periodontal ligament.pptx by Dr. Ira GuptaRama Dental College Hospital and Research Center
╠²
The document provides an overview of the periodontal ligament (PDL). It discusses the development, cells, extracellular substances like fibers and ground substance, structures present, and functions of the PDL. The PDL is a soft connective tissue that surrounds tooth roots and attaches them to the alveolar bone. It is derived from the dental follicle during root formation and contains fibroblasts, cementoblasts, osteoblasts and other cells. Collagen fibers are the main component and help attach the PDL to cementum and bone. The PDL acts to support teeth, absorb chewing forces, and allow limited movement.Periodontal ligament
Periodontal ligamentAlbie Kamait
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the periodontal ligament, its structure, and functions, highlighting its role in connecting teeth to the alveolar bone and maintaining oral health. It discusses the development, composition, and various fiber types of the periodontal ligament, as well as the clinical implications associated with its health and disease. Additionally, it covers the biological mechanisms involved in its regulation and the impact of pathological conditions on the periodontal space.periodontal ligament
periodontal ligamentshruti lendhey
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a connective tissue that connects the cementum of teeth to the alveolar bone. It contains principal collagen fibers, fibroblasts that produce the fibers, undifferentiated cells, and a ground substance of proteoglycans and glycoproteins. The principal fibers develop in stages from the cementum to bone and resist various forces on teeth. The periodontal ligament plays an important role in tooth support and is vital for tooth function.Periodontal ligament
Periodontal ligamentDrPrasoonPurwar
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a complex connective tissue that surrounds the tooth root and connects it to the alveolar bone. It is composed of collagen fibers, cells like fibroblasts and cementoblasts, blood vessels and nerves. The PDL develops from the dental follicle during root formation and ranges in width from 0.15-0.38mm. It contains principal fibers that extend obliquely from cementum to bone and adapt to functional changes in teeth. The PDL maintains homeostasis between the hard tissues of cementum and bone through regulatory molecules and cells.Periodontal ligament
Periodontal ligamentRitam Kundu
╠²
The periodontium is the connective tissue that surrounds and supports the teeth. It consists of gingiva, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone. The periodontal ligament is a soft, vascular connective tissue that joins the cementum and alveolar bone. It contains collagen fibers that provide support and flexibility to the teeth. The ligament is populated by fibroblasts that synthesize collagen fibers, as well as other cells like cementoblasts and osteoblasts that maintain the hard tissues.Periodontal ligament - Part 1
Periodontal ligament - Part 1ORAL PATHOLOGY, SRM DENTAL COLLEGE
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a soft, vascular connective tissue that connects tooth roots to the alveolar bone socket. It develops from the dental follicle during root formation and tooth eruption. The periodontal ligament contains principal collagen fiber bundles oriented in different directions, as well as fibroblasts, cementoblasts, osteoblasts, and progenitor cells. It maintains homeostasis through a balance of synthetic and resorptive cells and extracellular substances. The unique structure and cellular composition of the periodontal ligament allow it to function in tooth attachment and as a sensory organ.PERIODONTAL LIGAMENT-Dr.Mary Joseph.pptx
PERIODONTAL LIGAMENT-Dr.Mary Joseph.pptxRoyal Dental College Library
╠²
The document summarizes the key components and functions of the periodontium, which provides support to teeth. It consists of the periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone. The periodontal ligament is a complex connective tissue that surrounds the tooth root and connects it to the alveolar bone. It contains principal fiber groups that help distribute forces. The periodontium provides physical support, plays a role in remodeling, and provides sensory and nutritional functions to maintain teeth. Age changes and diseases can impact the periodontium and tooth support. Regenerative therapies are being explored to repair periodontal ligament destruction.Periodontal ligament
Periodontal ligamentMohd Enamur Rashid Biju
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a fibrous connective tissue that attaches the tooth to the alveolar bone. It is composed of fibers, cells, blood vessels and ground substance. The fibers are arranged in bundles that provide support, resist displacement, and allow movement. The principal fiber groups include gingival fibers around the neck of the tooth and dento-alveolar fibers along the root. Blood supply comes from the superior and inferior alveolar arteries.Periodontal ligament future
Periodontal ligament futureddert
╠²
The document discusses the anatomy and functions of the periodontal ligament, a dense connective tissue between teeth and alveolar bone. It details its components, structural groups of fibers, cellular makeup, blood and nerve supply, as well as its various roles including supportive, sensory, nutritive, formative, and protective functions. Additionally, it touches on changes seen in the periodontal ligament with age and the formation of cementicles.P D L ║▌║▌▀Żshare.ppt
P D L ║▌║▌▀Żshare.pptRoyal Dental College Library
╠²
The document discusses the periodontal ligament. It describes the periodontal ligament as the connective tissue that surrounds the root and connects it to the alveolar bone. It is made up of principal fibers, cells, ground substance, blood vessels and nerves. The principal fibers are organized into groups like the alveolar crest fibers, horizontal fibers, oblique fibers, and apical fibers that provide support and resist various forces on the teeth. The periodontal ligament also contains cells like fibroblasts, cementoblasts and osteoblasts that allow for remodeling of the tissues. It carries out functions like shock absorption and sensation in addition to attachment of teeth to bone.Periodontium
PeriodontiumMaryam Bahrami
╠²
The document defines and describes the periodontium, which refers to the tissues that surround and support teeth. It has four main components: gingiva, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone. The document then provides detailed descriptions of each component, including their development, composition, functions, and classifications. It focuses particularly on describing the development and classifications of cementum, which covers tooth roots, and the periodontal ligament, which is the connective tissue between cementum and bone.Pdl and its clinical considerations (2)
Pdl and its clinical considerations (2)nandinibhardwaj7
╠²
The periodontal ligament is composed of complex vascular and highly cellular connective tissue that surrounds the tooth root and connects it to the inner wall of alveolar bone. It develops from the dental follicle and is composed of fibroblasts, osteoblasts, cementoblasts and other cells embedded in collagen fibers and ground substance. The principal fiber groups help resist various forces on the tooth. The periodontal ligament plays an important role in maintaining homeostasis and provides shock absorption for teeth.Periodontal ligament
Periodontal ligamentDr.Malvika Thakur
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a connective tissue that connects the tooth to the alveolar bone. It contains collagen fibers, fibroblasts, cementoblasts, osteoblasts and other cells. The principal collagen fibers of the periodontal ligament originate on the cementum and insert into the alveolar bone in different orientations to provide structural support to the tooth and resist various forces. The periodontal ligament is essential for functions such as tooth eruption and maintains the space between the tooth and bone.Perioontal ligament lecture
Perioontal ligament lecturedentistry
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a dense connective tissue that occupies the space between the root of a tooth and the alveolar bone. It contains collagen fibers, cells, blood vessels, and nerves. The fibers are arranged in different groups to support the tooth and allow movement during mastication while protecting the underlying bone. The periodontal ligament provides nutrition to cementum and bone, senses pressure, and facilitates tooth movement during orthodontic treatment by stimulating bone remodeling through fiber tension and compression. It also protects the tooth and bone by distributing forces and containing mechanoreceptors.ž¦ž▒ž©žĘž® ž¦┘ä┘äž½ž® ž¦┘ä┘ģž▒žŁ┘äž® ž¦┘äž«ž¦┘ģž│ž® žĘž© ž¦┘䞦ž│┘垦┘å ž▓
ž¦ž▒ž©žĘž® ž¦┘ä┘äž½ž® ž¦┘ä┘ģž▒žŁ┘äž® ž¦┘äž«ž¦┘ģž│ž® žĘž© ž¦┘䞦ž│┘垦┘å ž▓dod084
╠²
ž¦ž▒ž©žĘž® ž¦┘ä┘äž½ž® Periodontium
PeriodontiumUE
╠²
The periodontium consists of cementum, the periodontal ligament (PDL), alveolar bone, and gingiva surrounding the tooth. The PDL is a specialized connective tissue between cementum and alveolar bone that functions to support the teeth, absorb chewing forces, provide sensory feedback, and enable nutrient transport. It contains collagen fiber bundles arranged to withstand forces. Cementum is a hard, avascular tissue covering roots that provides attachment for collagen fibers. The alveolar bone forms the tooth sockets and contains the PDL. Molecular factors regulate tissue development and regeneration.9.periodontal ligament ppt
9.periodontal ligament pptpunitnaidu07
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a specialized connective tissue that connects the cementum of teeth to the alveolar bone. It develops from the dental follicle during root formation and tooth eruption. The periodontal ligament is composed of collagen fibers, fibroblasts, blood vessels and nerves. The principal collagen fibers are arranged in bundles and attach to the cementum and bone. The periodontal ligament helps maintain homeostasis between the teeth and surrounding tissues and allows for tooth mobility.Periodontal ligaments
Periodontal ligamentsGovernment Dental College and Hospital, Shimla
╠²
This document provides an overview of the periodontal ligament (PDL). It describes the PDL's extent, shape, width and cellular components. The PDL contains principal collagen fibers that connect cementum to alveolar bone in different orientations. It is made up of fibroblasts, osteoblasts, cementoblasts and other cells. The PDL helps anchor teeth, withstand forces from chewing and allows limited movement.BIOLOGY OF TOOTH MOVEMENT.ppt
BIOLOGY OF TOOTH MOVEMENT.pptCmenonMenon
╠²
This document discusses the biology of tooth movement. It begins by classifying tooth movement into physiological, pathological, and orthodontic categories. It then discusses the historical studies on tooth movement dating back to the early 1900s. The bulk of the document describes the relevant biological structures - cementum, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone, and their cells and composition. It explains the fiber groups within the periodontal ligament. Finally, it discusses the biological events and tissue reactions that occur during orthodontic tooth movement.Periodantal ligament
Periodantal ligamentParth Thakkar
╠²
The periodontal ligament (PDL) is a soft connective tissue located between the cementum on the root of a tooth and the alveolar bone. It consists of collagen fibers, cells like fibroblasts and cementoblasts, blood vessels, and nerves. The principal fibers of the PDL are arranged in groups to help support the tooth, resist movement, and absorb forces during chewing. The PDL transmits occlusal forces to the bone, attaches the tooth, and maintains the gingiva.RESECTIVE OSSEOUS SURGERY.pptx
RESECTIVE OSSEOUS SURGERY.pptxMaria Antony Dhivyan
╠²
Resective osseous surgery aims to eliminate periodontal pockets and create physiological bone contours and gingival architecture to facilitate plaque control. It involves osteoplasty to reshape bone and ostectomy to remove bone. Key principles are using a full-thickness flap, contouring bone to match healthy gingival form, and leaving a positive bone architecture. Techniques are used to modify defects like craters, ledges, and furcations. Studies found minimal bone loss with healing. The main objective is achieving periodontal architecture to enable self-oral hygiene.IMPLANT RELATED COMPLICATIONS.pptx
IMPLANT RELATED COMPLICATIONS.pptxMaria Antony Dhivyan
╠²
This document discusses various complications that can occur with dental implants. It begins by defining implant success and failure, then describes potential complications organized by classification. Complications are discussed at each stage of implant treatment from pre-operative planning issues to post-operative infections or failures. Specific complications involving the maxillary sinus are also covered. The document provides details on causes, diagnostic criteria and management approaches for many common implant complications.More Related Content
Similar to Components of periodontal ligament.pptx (20)
Periodontal ligament.pptx by Dr. Ira Gupta
Periodontal ligament.pptx by Dr. Ira GuptaRama Dental College Hospital and Research Center
╠²
The document provides an overview of the periodontal ligament (PDL). It discusses the development, cells, extracellular substances like fibers and ground substance, structures present, and functions of the PDL. The PDL is a soft connective tissue that surrounds tooth roots and attaches them to the alveolar bone. It is derived from the dental follicle during root formation and contains fibroblasts, cementoblasts, osteoblasts and other cells. Collagen fibers are the main component and help attach the PDL to cementum and bone. The PDL acts to support teeth, absorb chewing forces, and allow limited movement.Periodontal ligament
Periodontal ligamentAlbie Kamait
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the periodontal ligament, its structure, and functions, highlighting its role in connecting teeth to the alveolar bone and maintaining oral health. It discusses the development, composition, and various fiber types of the periodontal ligament, as well as the clinical implications associated with its health and disease. Additionally, it covers the biological mechanisms involved in its regulation and the impact of pathological conditions on the periodontal space.periodontal ligament
periodontal ligamentshruti lendhey
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a connective tissue that connects the cementum of teeth to the alveolar bone. It contains principal collagen fibers, fibroblasts that produce the fibers, undifferentiated cells, and a ground substance of proteoglycans and glycoproteins. The principal fibers develop in stages from the cementum to bone and resist various forces on teeth. The periodontal ligament plays an important role in tooth support and is vital for tooth function.Periodontal ligament
Periodontal ligamentDrPrasoonPurwar
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a complex connective tissue that surrounds the tooth root and connects it to the alveolar bone. It is composed of collagen fibers, cells like fibroblasts and cementoblasts, blood vessels and nerves. The PDL develops from the dental follicle during root formation and ranges in width from 0.15-0.38mm. It contains principal fibers that extend obliquely from cementum to bone and adapt to functional changes in teeth. The PDL maintains homeostasis between the hard tissues of cementum and bone through regulatory molecules and cells.Periodontal ligament
Periodontal ligamentRitam Kundu
╠²
The periodontium is the connective tissue that surrounds and supports the teeth. It consists of gingiva, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone. The periodontal ligament is a soft, vascular connective tissue that joins the cementum and alveolar bone. It contains collagen fibers that provide support and flexibility to the teeth. The ligament is populated by fibroblasts that synthesize collagen fibers, as well as other cells like cementoblasts and osteoblasts that maintain the hard tissues.Periodontal ligament - Part 1
Periodontal ligament - Part 1ORAL PATHOLOGY, SRM DENTAL COLLEGE
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a soft, vascular connective tissue that connects tooth roots to the alveolar bone socket. It develops from the dental follicle during root formation and tooth eruption. The periodontal ligament contains principal collagen fiber bundles oriented in different directions, as well as fibroblasts, cementoblasts, osteoblasts, and progenitor cells. It maintains homeostasis through a balance of synthetic and resorptive cells and extracellular substances. The unique structure and cellular composition of the periodontal ligament allow it to function in tooth attachment and as a sensory organ.PERIODONTAL LIGAMENT-Dr.Mary Joseph.pptx
PERIODONTAL LIGAMENT-Dr.Mary Joseph.pptxRoyal Dental College Library
╠²
The document summarizes the key components and functions of the periodontium, which provides support to teeth. It consists of the periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone. The periodontal ligament is a complex connective tissue that surrounds the tooth root and connects it to the alveolar bone. It contains principal fiber groups that help distribute forces. The periodontium provides physical support, plays a role in remodeling, and provides sensory and nutritional functions to maintain teeth. Age changes and diseases can impact the periodontium and tooth support. Regenerative therapies are being explored to repair periodontal ligament destruction.Periodontal ligament
Periodontal ligamentMohd Enamur Rashid Biju
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a fibrous connective tissue that attaches the tooth to the alveolar bone. It is composed of fibers, cells, blood vessels and ground substance. The fibers are arranged in bundles that provide support, resist displacement, and allow movement. The principal fiber groups include gingival fibers around the neck of the tooth and dento-alveolar fibers along the root. Blood supply comes from the superior and inferior alveolar arteries.Periodontal ligament future
Periodontal ligament futureddert
╠²
The document discusses the anatomy and functions of the periodontal ligament, a dense connective tissue between teeth and alveolar bone. It details its components, structural groups of fibers, cellular makeup, blood and nerve supply, as well as its various roles including supportive, sensory, nutritive, formative, and protective functions. Additionally, it touches on changes seen in the periodontal ligament with age and the formation of cementicles.P D L ║▌║▌▀Żshare.ppt
P D L ║▌║▌▀Żshare.pptRoyal Dental College Library
╠²
The document discusses the periodontal ligament. It describes the periodontal ligament as the connective tissue that surrounds the root and connects it to the alveolar bone. It is made up of principal fibers, cells, ground substance, blood vessels and nerves. The principal fibers are organized into groups like the alveolar crest fibers, horizontal fibers, oblique fibers, and apical fibers that provide support and resist various forces on the teeth. The periodontal ligament also contains cells like fibroblasts, cementoblasts and osteoblasts that allow for remodeling of the tissues. It carries out functions like shock absorption and sensation in addition to attachment of teeth to bone.Periodontium
PeriodontiumMaryam Bahrami
╠²
The document defines and describes the periodontium, which refers to the tissues that surround and support teeth. It has four main components: gingiva, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone. The document then provides detailed descriptions of each component, including their development, composition, functions, and classifications. It focuses particularly on describing the development and classifications of cementum, which covers tooth roots, and the periodontal ligament, which is the connective tissue between cementum and bone.Pdl and its clinical considerations (2)
Pdl and its clinical considerations (2)nandinibhardwaj7
╠²
The periodontal ligament is composed of complex vascular and highly cellular connective tissue that surrounds the tooth root and connects it to the inner wall of alveolar bone. It develops from the dental follicle and is composed of fibroblasts, osteoblasts, cementoblasts and other cells embedded in collagen fibers and ground substance. The principal fiber groups help resist various forces on the tooth. The periodontal ligament plays an important role in maintaining homeostasis and provides shock absorption for teeth.Periodontal ligament
Periodontal ligamentDr.Malvika Thakur
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a connective tissue that connects the tooth to the alveolar bone. It contains collagen fibers, fibroblasts, cementoblasts, osteoblasts and other cells. The principal collagen fibers of the periodontal ligament originate on the cementum and insert into the alveolar bone in different orientations to provide structural support to the tooth and resist various forces. The periodontal ligament is essential for functions such as tooth eruption and maintains the space between the tooth and bone.Perioontal ligament lecture
Perioontal ligament lecturedentistry
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a dense connective tissue that occupies the space between the root of a tooth and the alveolar bone. It contains collagen fibers, cells, blood vessels, and nerves. The fibers are arranged in different groups to support the tooth and allow movement during mastication while protecting the underlying bone. The periodontal ligament provides nutrition to cementum and bone, senses pressure, and facilitates tooth movement during orthodontic treatment by stimulating bone remodeling through fiber tension and compression. It also protects the tooth and bone by distributing forces and containing mechanoreceptors.ž¦ž▒ž©žĘž® ž¦┘ä┘äž½ž® ž¦┘ä┘ģž▒žŁ┘äž® ž¦┘äž«ž¦┘ģž│ž® žĘž© ž¦┘䞦ž│┘垦┘å ž▓
ž¦ž▒ž©žĘž® ž¦┘ä┘äž½ž® ž¦┘ä┘ģž▒žŁ┘äž® ž¦┘äž«ž¦┘ģž│ž® žĘž© ž¦┘䞦ž│┘垦┘å ž▓dod084
╠²
ž¦ž▒ž©žĘž® ž¦┘ä┘äž½ž® Periodontium
PeriodontiumUE
╠²
The periodontium consists of cementum, the periodontal ligament (PDL), alveolar bone, and gingiva surrounding the tooth. The PDL is a specialized connective tissue between cementum and alveolar bone that functions to support the teeth, absorb chewing forces, provide sensory feedback, and enable nutrient transport. It contains collagen fiber bundles arranged to withstand forces. Cementum is a hard, avascular tissue covering roots that provides attachment for collagen fibers. The alveolar bone forms the tooth sockets and contains the PDL. Molecular factors regulate tissue development and regeneration.9.periodontal ligament ppt
9.periodontal ligament pptpunitnaidu07
╠²
The periodontal ligament is a specialized connective tissue that connects the cementum of teeth to the alveolar bone. It develops from the dental follicle during root formation and tooth eruption. The periodontal ligament is composed of collagen fibers, fibroblasts, blood vessels and nerves. The principal collagen fibers are arranged in bundles and attach to the cementum and bone. The periodontal ligament helps maintain homeostasis between the teeth and surrounding tissues and allows for tooth mobility.Periodontal ligaments
Periodontal ligamentsGovernment Dental College and Hospital, Shimla
╠²
This document provides an overview of the periodontal ligament (PDL). It describes the PDL's extent, shape, width and cellular components. The PDL contains principal collagen fibers that connect cementum to alveolar bone in different orientations. It is made up of fibroblasts, osteoblasts, cementoblasts and other cells. The PDL helps anchor teeth, withstand forces from chewing and allows limited movement.BIOLOGY OF TOOTH MOVEMENT.ppt
BIOLOGY OF TOOTH MOVEMENT.pptCmenonMenon
╠²
This document discusses the biology of tooth movement. It begins by classifying tooth movement into physiological, pathological, and orthodontic categories. It then discusses the historical studies on tooth movement dating back to the early 1900s. The bulk of the document describes the relevant biological structures - cementum, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone, and their cells and composition. It explains the fiber groups within the periodontal ligament. Finally, it discusses the biological events and tissue reactions that occur during orthodontic tooth movement.Periodantal ligament
Periodantal ligamentParth Thakkar
╠²
The periodontal ligament (PDL) is a soft connective tissue located between the cementum on the root of a tooth and the alveolar bone. It consists of collagen fibers, cells like fibroblasts and cementoblasts, blood vessels, and nerves. The principal fibers of the PDL are arranged in groups to help support the tooth, resist movement, and absorb forces during chewing. The PDL transmits occlusal forces to the bone, attaches the tooth, and maintains the gingiva.More from Maria Antony Dhivyan (9)
RESECTIVE OSSEOUS SURGERY.pptx
RESECTIVE OSSEOUS SURGERY.pptxMaria Antony Dhivyan
╠²
Resective osseous surgery aims to eliminate periodontal pockets and create physiological bone contours and gingival architecture to facilitate plaque control. It involves osteoplasty to reshape bone and ostectomy to remove bone. Key principles are using a full-thickness flap, contouring bone to match healthy gingival form, and leaving a positive bone architecture. Techniques are used to modify defects like craters, ledges, and furcations. Studies found minimal bone loss with healing. The main objective is achieving periodontal architecture to enable self-oral hygiene.IMPLANT RELATED COMPLICATIONS.pptx
IMPLANT RELATED COMPLICATIONS.pptxMaria Antony Dhivyan
╠²
This document discusses various complications that can occur with dental implants. It begins by defining implant success and failure, then describes potential complications organized by classification. Complications are discussed at each stage of implant treatment from pre-operative planning issues to post-operative infections or failures. Specific complications involving the maxillary sinus are also covered. The document provides details on causes, diagnostic criteria and management approaches for many common implant complications.GENETICS & periodontal disease.pptx
GENETICS & periodontal disease.pptxMaria Antony Dhivyan
╠²
Genetics is the science of heredity and variation in living organisms. Basic units of inheritance are called genes, which are segments of DNA that encode specific functions. Modern genetics studies not only inheritance but also gene functions and behaviors. Genetic epidemiology examines the roles of genes and their interactions with the environment in disease occurrence in human populations. Objectives include determining risks associated with gene variants, mapping genomic regions linked to disease susceptibility, and identifying susceptibility genes.Gingival connective tissue.pptx
Gingival connective tissue.pptxMaria Antony Dhivyan
╠²
The lamina propria of the gingiva contains fibroblasts, mast cells, macrophages, and other cellular elements embedded in an extracellular matrix. The matrix contains collagen, elastin, proteoglycans and glycoproteins that provide structure and regulate cellular functions like adhesion, migration and organization. Blood vessels and nerves innervate the lamina propria. Collagen fibers like dentogingival, alveologingival and circular fibers provide strength and stability. The lamina propria has protective and supportive roles and maintains tissue homeostasis through cellular synthesis and remodeling.PERIO ŌĆō ORTHO RELATIONSHIP.pptx
PERIO ŌĆō ORTHO RELATIONSHIP.pptxMaria Antony Dhivyan
╠²
The document discusses the interactions between orthodontic and periodontal treatments. It notes that the aim of orthodontic treatment is to provide functional and aesthetic tooth movements while preserving the supportive periodontal tissues. Periodontal and orthodontic interactions require establishing an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan to enable coordinated therapy. Orthodontic patients can be classified into three categories based on their oral health status. The document outlines various orthodontic tooth movements and considerations for periodontal health during orthodontic treatment, emphasizing the need for regular hygiene, maintenance of gingival health, and close monitoring of patients with reduced periodontal support.CLASSIFICATION OF PERIODONTAL DISEASE 1.pptx
CLASSIFICATION OF PERIODONTAL DISEASE 1.pptxMaria Antony Dhivyan
╠²
This document summarizes the history and evolution of periodontal disease classification systems. It discusses early classification schemes from the 19th century that categorized periodontal diseases based on their presumed etiology and clinical characteristics. In the 1950s-1960s, studies demonstrated the role of dental plaque in gingivitis. The 1999 international classification workshop established the modern scheme that distinguishes between chronic periodontitis, aggressive periodontitis, periodontitis associated with systemic diseases, and other conditions. The classification aims to facilitate diagnosis and treatment by grouping diseases with similar etiologies and presentations.chronic periodontitis.pptx
chronic periodontitis.pptxMaria Antony Dhivyan
╠²
Chronic periodontitis is an inflammatory disease that causes the destruction of the tissues that support the teeth. It is caused by bacterial plaque accumulating at and below the gumline. It is characterized by pocket formation, attachment loss, and bone loss. The disease progresses slowly over time and is generally classified as slight, moderate, or severe depending on the amount of attachment loss. A clinical diagnosis involves measuring pocket depths and looking for signs of inflammation, recession, and bone loss. Radiographs can also help assess bone level changes over time. Risk factors include poor oral hygiene, smoking, diabetes, and genetic factors. Treatment involves nonsurgical debridement or surgical procedures to reduce pockets and regenerate lost tissues.RED COMPLEX ORGANISMS.docx
RED COMPLEX ORGANISMS.docxMaria Antony Dhivyan
╠²
1. Periodontal diseases are caused by complex biofilms containing multiple bacterial species that interact with host tissues. A key group is the "red complex" comprising Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola, and Tanerella forsythia.
2. These bacteria employ various virulence factors to adhere to surfaces, acquire nutrients, and evade the host immune response in order to colonize and cause disease. Important factors include fimbriae, proteases, and capsules that aid adhesion and facilitate tissue destruction.
3. P. gingivalis possesses specific fimbriae, proteases, and a capsule that help it adhere, acquire iron through hemolAd
Recently uploaded (20)
Anesthetic Evaluation & Management in Pregnancy with APH.pdf
Anesthetic Evaluation & Management in Pregnancy with APH.pdfDr Anik Roy Chowdhury
╠²
Dr. Anik Roy Chowdhury
MBBS, BCS (Health), DA, MD Resident
Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College Hospital (ShSMCH)How to be and stay healthy: Live Wire Not a Couch Potato
How to be and stay healthy: Live Wire Not a Couch PotatoBiljanaPipovic
╠²
Live Wire, Not a Couch Potato was an engaging international eTwinning project aimed at promoting physical activity among youth by blending creativity, tradition, and competition. Founded by teachers from Serbia and Portugal, with partners from Turkey and Greece, the project encouraged students to explore the importance of staying active through fun and meaningful challenges. Working within their local contexts, students from all four countries participated in physical activities at school and in their communities. They documented their experiences through photos, videos, and written reflections, which they shared on TwinSpace. The project helped transform exercise from a routine task into an enjoyable, culturally rich experience, while fostering teamwork, creativity, and international exchange.Drmohamedaslam_resident_copd2025_fm.pptx
Drmohamedaslam_resident_copd2025_fm.pptxAslam
╠²
COPD :LATEST GUIDELINES 2025
REFERENCE: HarrisonŌĆÖs Principles of Internal Medicine
GOLD -2025 Guidelines
It highlights updated diagnostic criteria, pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment options, and current best practices for resident doctors and healthcare professionals.
Ideal for medical students, residents, and practitioners seeking an up-to-date, evidence-based reference.
¤æē Download, share, and feel free to reach out for related study material!Tuberculosis Nepal 2025 National Plan.pptx
Tuberculosis Nepal 2025 National Plan.pptxDr. Anu Marhatta
╠²
The presentation contains preventive therapy, the DOTS program, and the national program of Nepal. This material is intended for educational purposes only.RCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient Care
RCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient CarePVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair, Sumanta Kumar Pal, MD, FASCO, David F. McDermott, MD, and Tian Zhang, MD, MHS, prepared useful Practice Aids pertaining to renal cell carcinoma for this CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£RCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient Care.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/4brGF4h. CME/MOC/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until June 30, 2026.Tonsil anatomy, diseases and treatment options
Tonsil anatomy, diseases and treatment optionsManu Babu
╠²
a brief decription of tonsil related pathologyDrug use in Peptic Ulcer_A complete review.pptx
Drug use in Peptic Ulcer_A complete review.pptxBaasir Umair Khattak
╠²
Open PPT for detail description: Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
Peptic ulcer disease refers to mucosal erosions equal to or greater than 5 mm in the stomach or proximal duodenum, caused primarily by an imbalance between gastric acid/pepsin secretion and mucosal defense mechanisms. The most common etiologies include Helicobacter pylori infection, chronic use of NSAIDs, and physiological stress.
Classification of Peptic Ulcers
¤ö╣ Based on Location
Gastric Ulcers ŌĆō Occur in the stomach lining.
Duodenal Ulcers ŌĆō Occur in the first part of the small intestine (duodenum).
¤ö╣ Based on Etiology
H. pyloriŌĆōAssociated Ulcers
NSAID-Induced Ulcers
Stress-Related Mucosal Disease (SRMD)
ZollingerŌĆōEllison Syndrome (gastrinoma-related)
CushingŌĆÖs Ulcer (due to intracranial injury)
CurlingŌĆÖs Ulcer (seen in burn patients)
Pharmacological Management
¤ö╣ 1. Acid Suppression Therapy
Class Examples Mechanism
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) Omeprazole, Pantoprazole Irreversibly inhibit H+/K+ ATPase pump
H2-Receptor Antagonists Ranitidine, Famotidine Block histamine-mediated gastric acid secretion
¤ö╣ 2. Mucosal Protective Agents
Class Examples Mechanism
Prostaglandin Analogues Misoprostol Increases mucus & bicarbonate; decreases acid; protects mucosa
Mucosal Coating Agents Sucralfate Forms protective barrier over ulcer site
Bismuth Compounds Bismuth subsalicylate Antimicrobial, mucosal protective, and anti-inflammatory
¤ö╣ 3. Eradication Therapy (for H. pylori)
Combination of:
PPI + Two Antibiotics (e.g., amoxicillin + clarithromycin OR metronidazole + tetracycline)
Duration: 7ŌĆō14 days depending on local guidelines
See BNF regimens above for detailed protocols
¤ö╣ 4. Cytoprotective/Adjunctive Agents
Class Examples Role in PUD
Somatostatin Analogues Octreotide Used in bleeding ulcers; reduces splanchnic blood flow and gastric secretions
Antacids Magnesium hydroxide, Aluminium hydroxide Neutralize gastric acid; provide symptomatic relief
Non-Pharmacologic Measures
Avoid NSAIDs, smoking, alcohol, and spicy foods
Small, frequent meals in symptomatic patients
Stress reduction
Endoscopic therapy in case of bleeding or perforation
Surgical Indications (rarely needed)
Perforated ulcer
Gastric outlet obstruction
Refractory ulcers not responding to medical therapy
Severe bleeding unresponsive to endoscopic management
Ō£ģ Summary
Peptic ulcer disease is primarily driven by H. pylori infection and NSAID use, with duodenal ulcers more common than gastric. Treatment is tailored based on etiology and includes acid suppression, H. pylori eradication, and mucosal protection. Advanced cases may require somatostatin analogues for hemorrhage control or surgery for complications. Prostaglandin analogues like misoprostol are especially valuable in preventing NSAID-induced ulcers.Bias, Cofounding Bias, Matching , Blinding
Bias, Cofounding Bias, Matching , BlindingDr. Anu Marhatta
╠²
The slide contains small sippets about the bias, confounding bias, and the ways by which we can remove them. Like by using the methods such as matching and blinding. This slide can be useful as a reference for students in MBBS. Aspirin powder or Acetyl salicylic acid powder.docx
Aspirin powder or Acetyl salicylic acid powder.docxkopalsharma85
╠²
pharmacy exercise on aspirin powderIrradiation to prevent TA-GvHD by Dr. Abrar Kabir Shishir.pptx
Irradiation to prevent TA-GvHD by Dr. Abrar Kabir Shishir.pptxAbrarKabir3
╠²
This presentation discusses the role of irradiation in preventing transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease (TA-GvHD). Covers pathophysiology, risk factors, investigation, prevention strategies, and irradiation procedures. Includes visuals and real-life context from Dhaka Medical College.Mastering the Review Article: Structure, Strategy & Success
Mastering the Review Article: Structure, Strategy & SuccessRajendra Dev Bhatt
╠²
A scoping search identified various types of review articles. For this training, most common types were selected, highlighting their key features, strengths, weaknesses, and uses.Design of cosmeceuticals products;sunprotection,sunscreens
Design of cosmeceuticals products;sunprotection,sunscreensSwami ramanand teerth marathwada university
╠²
Design of cosmeceuticals products and improving the skin to protection sun burning, used sunscreens, sunprotections Viddha karma in Ayurveda-Dr Mahesh Kumar.pdf
Viddha karma in Ayurveda-Dr Mahesh Kumar.pdfCBPACS, Khera Dabar, Najafgarh New Delhi- 73
╠²
Ayurveda have description of various treatment modalities. Viddhakarma is ayurvedic treatment method described in ancient ayurveda literature. Its actually a Vedhana karma.
Application of Viddha karma in clinical practice is now popular.INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS.pptx
INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS.pptxEliLawluvi
╠²
THE DOCUMENT SUMMARIZES THE KEY COMPONENTS OF INTERPRETING FULL BLOOD CUNTBiography and Professional Career of Dr. Seth Eidemiller
Biography and Professional Career of Dr. Seth EidemillerDr. Seth Eidemiller
╠²
Dr. Seth A. Eidemiller is a board-certified emergency physician whose professional journey began on a fourth-generation dairy farm in Idaho. Early on, he gained experience through farming, wildfire suppression, and construction work, which gave him a strong foundation in practical skills and resilience. After completing degrees in International Studies and Spanish, he returned to Boise to fulfill the prerequisites for medical school and study laboratory sciences. He then attended the University of Nevada, Reno School of Medicine, and continued his training with a residency in emergency medicine in Fresno. Today, he serves as Vice Chair of the Chico Emergency Medicine Physician Group.clinical approach to a woman with gynecological problem.ppt
clinical approach to a woman with gynecological problem.pptFaculty of Medicine
╠²
clinical approach to a woman with gynecological problemComputer aided formulation development optimization
Computer aided formulation development optimizationSwami ramanand teerth marathwada university
╠²
Concept of optimization, optimization parameters, factorial design, optimization technology & screening design. Clinical Signs Overview: PICCKLE Mnemonic
Clinical Signs Overview: PICCKLE MnemonicDr Aman Suresh Tharayil
╠²
This presentation provides a concise yet comprehensive review of common clinical signs and their diagnostic significance, summarized under the acronym PICCKLE ŌĆō Pallor, Icterus, Clubbing, Cyanosis, Koilonychia, Lymphadenopathy, and Edema. Each condition is defined, followed by key causes, pathophysiology, diagnostic techniques, and clinical relevance. The content is tailored for undergraduate and postgraduate students in medicine and pharmacy, as well as early-career clinicians seeking to reinforce their clinical examination skillsJUNE 2025 ONCOLOGY CARTOONS BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRO
JUNE 2025 ONCOLOGY CARTOONS BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATROKanhu Charan
╠²
JUNE 2025 ONCOLOGY CARTOONS BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRORCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient Care
RCC Treatment Innovations in Practice: Preparing for Individualized Patient CarePVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Design of cosmeceuticals products;sunprotection,sunscreens
Design of cosmeceuticals products;sunprotection,sunscreensSwami ramanand teerth marathwada university
╠²
Ad
Components of periodontal ligament.pptx
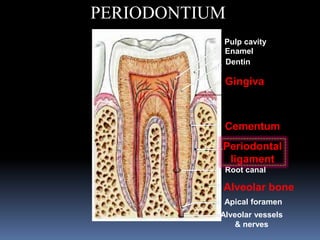
- 3. PERIODONTIUM Cementum Periodontal ligament Alveolar bone Apical foramen Pulp cavity Enamel Dentin Gingiva Root canal Alveolar vessels & nerves
- 4. DEFINITION ’é¦ Periodontal ligament is composed of soft complex vascular and highly cellular connective tissue that surrounds the tooth roots and connects it to the inner wall of the alveolar bone.
- 5. Other terms which were previously used for periodontal ligament are:- 1. Desmondont 2. Gomphosis 3. Pericementum 4. Dental Periosteum 5. Alveolodental ligament 6. Periodontal membrane
- 6. STRUCTURE ’é¦ In the coronal direction it is continuous with lamina propria of gingiva & is demarcated by the alveolar crest fibers. ’é¦ PDL has the shape of an hour glass and is narrowest at the mid root level. ’é¦ It ranges in width from 0.15-0.38mm.-beertsen etal 1997
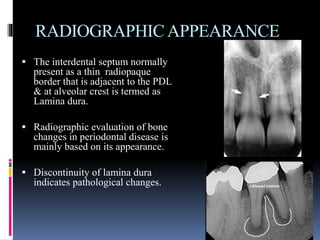
- 7. RADIOGRAPHICAPPEARANCE ’é¦ The interdental septum normally present as a thin radiopaque border that is adjacent to the PDL & at alveolar crest is termed as Lamina dura. ’é¦ Radiographic evaluation of bone changes in periodontal disease is mainly based on its appearance. ’é¦ Discontinuity of lamina dura indicates pathological changes.
- 8. DEVELOPMENT
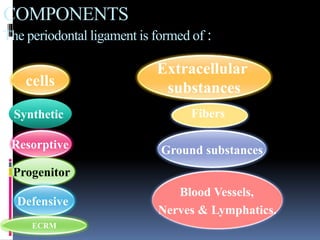
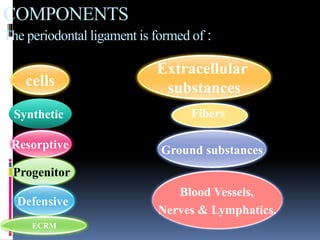
- 9. cells COMPONENTS The periodontal ligament is formed of : Fibers Extracellular substances Synthetic Resorptive Progenitor Defensive Ground substances Blood Vessels, Nerves & Lymphatics. ECRM
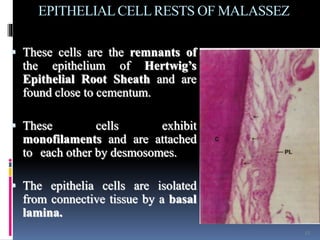
- 13. EPITHELIALCELLRESTS OF MALASSEZ ’é¦ These cells are the remnants of the epithelium of HertwigŌĆÖs Epithelial Root Sheath and are found close to cementum. ’é¦ These cells exhibit monofilaments and are attached to each other by desmosomes. ’é¦ The epithelia cells are isolated from connective tissue by a basal lamina. 13
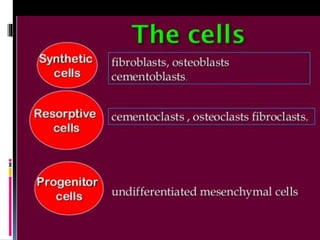
- 14. cells COMPONENTS The periodontal ligament is formed of : Fibers Extracellular substances Synthetic Resorptive Progenitor Defensive Ground substances Blood Vessels, Nerves & Lymphatics. ECRM
- 15. FIBERS ’é¦ Principal fibers ’é¦ Elastic-oxytalan ’é¦ Indifferent fiber plexus
- 16. COLLAGEN ’é¦ Synthesized by fibroblasts, chondroblasts, osteoblasts & other cells ’é¦ Contain 2 unique amino acid hydroxy proline and hydroxy lysine along with glycine & proline (Carneiro J, Fava de Moraes F , 1955) ’é¦ The amount of collagen in a tissue is determined by its hydroxy proline content. ’é¦ There are at least 19 recognized collagen species encoded by at least 25 separate genes, dispersed among 12 chromosomes (Embery et al 2000) Collagen classes a. Principal fibers ---- Type I b. Basement membrane ---- Type IV c. Reticular fibers ---- Type III d. Tooth development ---- Type XII
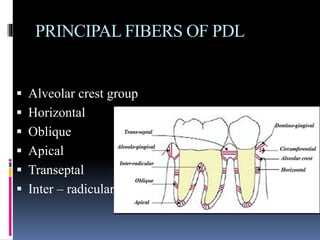
- 17. PRINCIPAL FIBERS OF PDL ’é¦ Alveolar crest group ’é¦ Horizontal ’é¦ Oblique ’é¦ Apical ’é¦ Transeptal ’é¦ Inter ŌĆō radicular
- 18. Alveolar crest group: radiate from the cementum over the alveolar crest & to the fibrous layer of periosteum covering the alveolar bone. Function ŌĆō prevents extrusion of the tooth & resist lateral tooth movement Horizontal group: The fiber bundles run from the cementum to the bone at right angle to the long axis of the tooth. Function - resists horizontal and tipping forces Bone Dentin
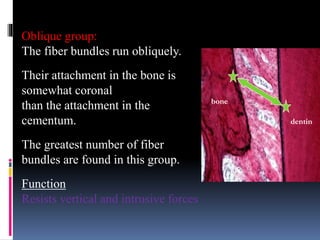
- 19. Oblique group: The fiber bundles run obliquely. Their attachment in the bone is somewhat coronal than the attachment in the cementum. The greatest number of fiber bundles are found in this group. Function Resists vertical and intrusive forces bone dentin
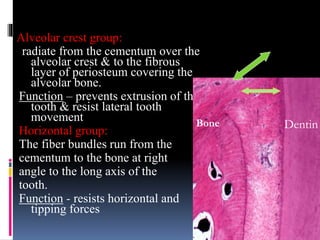
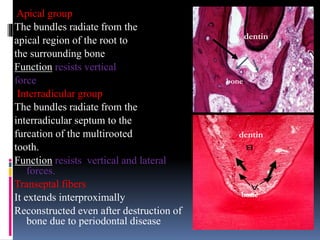
- 20. Apical group The bundles radiate from the apical region of the root to the surrounding bone Function resists vertical force Interradicular group The bundles radiate from the interradicular septum to the furcation of the multirooted tooth. Function resists vertical and lateral forces. Transeptal fibers It extends interproximally Reconstructed even after destruction of bone due to periodontal disease dentin bone dentin bone
- 21. ELASTIN FIBERS ’é¦ PDL fibers do not contain mature elastin but two immature forms are found oxytalan and eulanin ’é¦ Run in apico-coronal direction to bend and attach at cervical third of root (Fulmer et al. 1974) ’é¦ Function - regulate vascular flow - play a role in tooth support - guides cell migration
- 22. GROUND SUBSTANCE ’é¦ Fills the space between the fibers and cells Composition ’é¦ Consists of a biochemically complex, highly hydrated, semisolid gel. ’é¦ Water content of 70% ’é¦ Glycosaminoglycan's ŌĆō hyaluronic acid, proteoglycans( versican , decorin ) ’é¦ Glycoproteins -- fibronectin , laminin , vibronectin , tenascin ’é¦ cementicles
- 23. FUNCTIONS ŌĆó PHYSICAL ŌĆó FORMATIVE AND REMODELING ŌĆó NUTRITIVE ŌĆó SENSORY ŌĆó PDL HOMEOSTASIS
- 24. PHYSICAL 1. Provision for a soft tissue ŌĆśCASINGŌĆÖ to protect the vessels and nerves from injury by mechanical forces . 2. Transmission of occlusal forces to the bone 3. Attachment of teeth to bone. 4. Maintenance of gingival tissues in their proper relationship to the teeth. 5. Resistance to impact of occlusal forces SHOCK ABSORPTION : Tensional theory & Viscoelastic theory
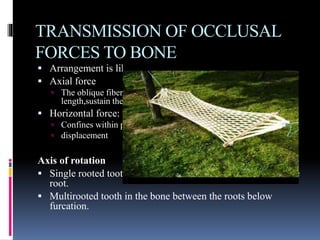
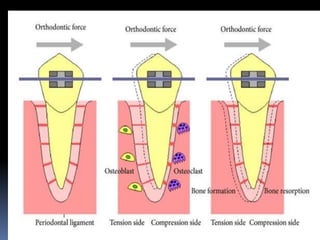
- 27. TRANSMISSION OF OCCLUSAL FORCES TO BONE ’é¦ Arrangement is like suspension bridge or hammock. ’é¦ Axial force ’ā║ The oblique fibers alter their wavy pattern and attain full length,sustain the major part of the axial force ’é¦ Horizontal force: ’ā║ Confines within pdl ’ā║ displacement Axis of rotation ’é¦ Single rooted tooth at junction of middle and apical 3rd of the root. ’é¦ Multirooted tooth in the bone between the roots below furcation.
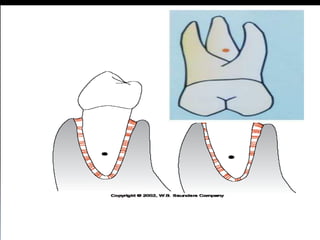
- 28. Distribution of faciolingual forces (arrow) around the axis of rotation (black circle on root) in a mandibular premolar. The periodontal ligament fibers are compressed in areas of pressure
- 30. FORMATIVEAND REMODELING ’é¦ Cells have the capacity to resorb & synthesize the extracellular substance of the CT ligament, alveolar bone & cementum. ’é¦ Participate in physiologic tooth movement & in repair of injuries. ’é¦ PDL is constantly undergoing remodeling old cells and fibers are broken down and replaced by new ones. ’é¦ Radio autographic studies indicate a very high turnover rate of collagen in PDL. A rapid turnover of sulfated GAGs in the cells and amorphous ground substances also occur. Sodek (1977), Muhlemann; 1954)
- 31. NUTRITIVE ’é¦ PDL supplies nutrients to the cementum , bone, and gingiva by way of blood vessels and provides lymphatic drainage. ’é¦ Rich vascular plexus at apex & in the cervical part of the ligament ’é¦ Rich network of arcades are more evident in the PDL space adjacent to the bone than to cementum
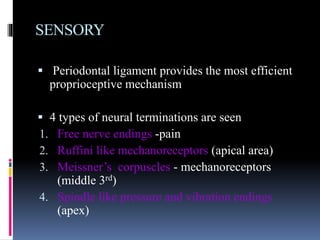
- 32. SENSORY ’é¦ Periodontal ligament provides the most efficient proprioceptive mechanism ’é¦ 4 types of neural terminations are seen 1. Free nerve endings -pain 2. Ruffini like mechanoreceptors (apical area) 3. MeissnerŌĆÖs corpuscles - mechanoreceptors (middle 3rd) 4. Spindle like pressure and vibration endings (apex)
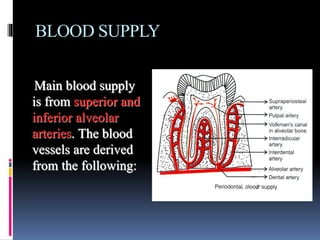
- 33. BLOOD SUPPLY Main blood supply is from superior and inferior alveolar arteries. The blood vessels are derived from the following:
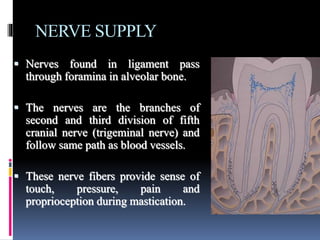
- 34. NERVE SUPPLY ’é¦ Nerves found in ligament pass through foramina in alveolar bone. ’é¦ The nerves are the branches of second and third division of fifth cranial nerve (trigeminal nerve) and follow same path as blood vessels. ’é¦ These nerve fibers provide sense of touch, pressure, pain and proprioception during mastication.
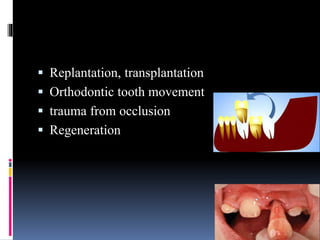
- 36. ’é¦ Replantation, transplantation ’é¦ Orthodontic tooth movement ’é¦ trauma from occlusion ’é¦ Regeneration
- 37. PICK UP THE ODD ONE OUT ’é¦ Cementum, bone, gingiva, pulp, periodontal ligament ’é¦ Apical fibers, horizontal fibers, circular fibers,oblique fi ’é¦ Fibroblast, osteoblast, osteoclast, ameloblast ’é¦ Physical, chemical, nutritive, sensory,
- 38. WHO AM I ’é¦ I am the largest group of fibers ’é¦ I resist extrusion of tooth ’é¦ I have 19 family members ’é¦ I connect cell and cell, cell and matrix ’é¦ I am present between mid third & apical third of root
