Comprehensive Hematology Overview: Blood Physiology, Disorders, and Diagnostics
- 1. HEMA TOLOG Y
- 2. INTRODUCTIO N Hematology Aids in the diagnosis and management of numerous health conditions in animals. Useful for evaluating anemia, helping to determine its type and severity, whether caused by blood loss, hemolysis, or bone marrow issues. Assists in identifying infections and assessing inflammatory responses by analyzing changes in white blood cell counts.
- 3. Hematology Essential for detecting cancers like leukemia and lymphoma, as well as diagnosing bleeding disorders by examining platelet function and clotting factors. Valuable for pre-surgical assessments to confirm an animal's fitness for surgery and for monitoring chronic conditions such as kidney disease or diabetes. INTRODUCTIO N
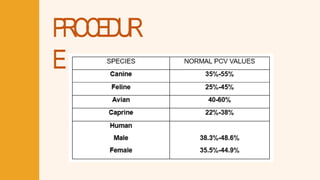
- 4. BACKGROUND & HISTORY Sample 1: GOA T Name: Allan Sex: Male Breed: Native Age: 8 months History: Recently castrated
- 5. BACKGROUND & HISTORY Sample 2: CA T Name: Pearl Sex: Female Breed: Puspin Age: 3 years old History: No disease history
- 6. BACKGROUND & HISTORY Sample 3: D O G Name: Brownie Sex: Male Breed: Aspin Age: 7 years old History: No disease history/ Stress and uncomfortable during blood collection
- 7. BACKGROUND & HISTORY Sample 4: HUMAN Name: Joshua Noble Sex: Male Age: 23 History: Has an allergy (hives)
- 8. BACKGROUND & HISTORY Sample 5: CA T Name: Nathan Sex: Male Breed: Puspin Age: 4 years old History: No disease history
- 9. BACKGROUND & HISTORY Sample 6: TURKEY Name: Turkey Sex: Male Breed: Beltsville Small White Age: 5 months old History: No disease history
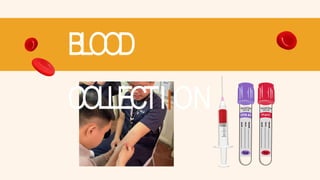
- 11. BLOOD COLLECTIION Materials: Sterile syringes EDTA & Red top Alcohol Cotton balls or gauze Assistant for restraining (if necessary) Protective gloves
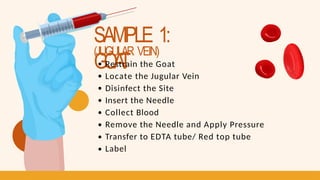
- 12. SAMPLE 1: GOA T (JUGULAR VEIN) Restrain the Goat Locate the Jugular Vein Disinfect the Site Insert the Needle Collect Blood Remove the Needle and Apply Pressure Transfer to EDTA tube/ Red top tube Label
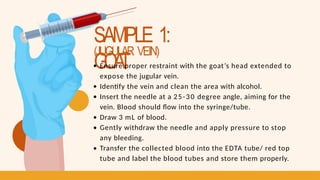
- 13. SAMPLE 1: GOA T (JUGULAR VEIN) Ensure proper restraint with the goat’s head extended to expose the jugular vein. Identify the vein and clean the area with alcohol. Insert the needle at a 25-30 degree angle, aiming for the vein. Blood should flow into the syringe/tube. Draw 3 mL of blood. Gently withdraw the needle and apply pressure to stop any bleeding. Transfer the collected blood into the EDTA tube/ red top tube and label the blood tubes and store them properly.
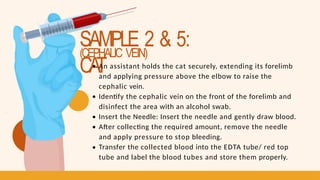
- 15. SAMPLE 2, 3, & 5: CA T & D O G (CEPHALIC VEIN) Restrain the Cat/Dog Locate and Clean the Vein Insert the Needle Remove Needle and Apply Pressure Transfer to EDTA tube/ Red top tube Label
- 16. SAMPLE 2 & 5: CA T (CEPHALIC VEIN) An assistant holds the cat securely, extending its forelimb and applying pressure above the elbow to raise the cephalic vein. Identify the cephalic vein on the front of the forelimb and disinfect the area with an alcohol swab. Insert the Needle: Insert the needle and gently draw blood. After collecting the required amount, remove the needle and apply pressure to stop bleeding. Transfer the collected blood into the EDTA tube/ red top tube and label the blood tubes and store them properly.
- 17. SAMPLE 3: D O G (CEPHALIC VEIN) An assistant holds the dog securely and extends the forelimb, applying pressure above the elbow to raise the cephalic vein. Identify the cephalic vein along the front of the forelimb and disinfect the area with an alcohol swab. Insert the needle and slowly draw the desired amount of blood. After collecting the sample, remove the needle and apply pressure to stop any bleeding. Transfer the collected blood into the EDTA tube/ red top tube and label the blood tubes and store them properly.
- 19. SAMPLE 4: HUMAN (CEPHALIC VEIN) Patient Positioning Apply Tourniquet Locate and Clean the Vein Insert the Needle Remove Needle and Apply Pressure Transfer to EDTA tube/ Red top tube Label
- 20. SAMPLE 4: HUMAN (CEPHALIC VEIN) The patient should sit or lie comfortably with the arm extended. Place the tourniquet above the elbow to help distend the cephalic vein, located on the outer side of the forearm. Identify the cephalic vein and clean the area with an alcohol swab. Insert the needle into the vein and collect the desired amount of blood. After collecting the blood, remove the needle and apply pressure to the puncture site to stop bleeding. Transfer the collected blood into the EDTA tube/ red top tube and label the blood tubes and store them properly.
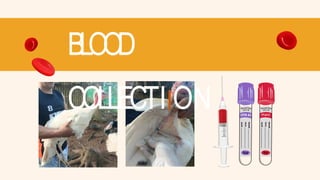
- 22. SAMPLE 6: TURKEY (CEPHALIC VEIN) Restrain the Turkey Locate and Clean the Vein Insert the Needle Remove Needle and Apply Pressure Transfer to EDTA tube/ Red top tube Label
- 23. SAMPLE 6: TURKEY (CEPHALIC VEIN) Secure the turkey in a comfortable position, such as wrapping it in a towel to limit movement, ensuring the wing is extended gently but firmly. Identify the cephalic vein along the ventral (underside) surface of the wing, near the elbow joint and disinfect the area with an alcohol swab. Insert the needle and slowly draw the desired amount of blood. After collecting the sample, remove the needle and apply pressure to stop any bleeding. Transfer the collected blood into the EDTA tube/ red top tube and label the blood tubes and store them properly.
- 26. MATERIIA LS ((BLLOOD SMEAR STTAIINIING)) Blood sample Clean microscope slides Hemaquick stain Distilled water Dropper/pipette Microscope Tissue
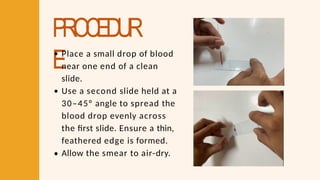
- 27. PROCEDUR EPlace a small drop of blood near one end of a clean slide. Use a second slide held at a 30–45° angle to spread the blood drop evenly across the first slide. Ensure a thin, feathered edge is formed. Allow the smear to air-dry.
- 28. PROCEDUR E Place the dry blood smear into the jar filled with stain. Gently agitate the slide for 10 seconds interval by dipping the slide in and out of the stain starting with fixative solution, then Eosin stain and the Methylene blue. Allow the excess methylene blue dye to drain onto a tissue.
- 29. PROCEDUR E Rinse the slide gently with the buffer solution to remove excess stain and balance pH. Rinse the slide in distilled water for about 10 seconds Place the slide in a drying rack to air dry thoroughly. Once thoroughly dried, evaluate the slide using a light microscope.
- 30. DETERMIINATIION OF P ACKED CELL VOLUME USIING HEMA TOCRIIT METHOD
- 31. MATERIIA LS (( DDEETTEERRMIINNAATTIIOONN OOFF PPAACCKKEEDD CCEELLLL VVOOLLUUMEE UUSSIINNGG HHEEMAATTOOCCRRIITT MEETTHHOODD )) Blood sample Microhematocrit tube (capillary tube) Microhematocrit centrifuge Clay seal Microhematocrit reader
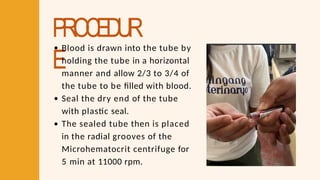
- 32. PROCEDUR E Blood is drawn into the tube by holding the tube in a horizontal manner and allow 2/3 to 3/4 of the tube to be filled with blood. Seal the dry end of the tube with plastic seal. The sealed tube then is placed in the radial grooves of the Microhematocrit centrifuge for 5 min at 11000 rpm.
- 33. PROCEDUR E Balance the tubes in the centrifuge with the clay ends facing the outside away from the center (place the tubes opposite each other in the centrifuge). Looking at a centrifuged hematoerit tube, you will see three distinct layers. Using the hematocrit reader, read the PCV value.
- 34. PROCEDUR E
- 36. MATERIIA LS ((NEUBAUER TTECHNIIQUE)) Blood sample Counting chamber (Neubaeur chamber) WBC pipette/ RBC pipette
- 37. MATERIIA LS ((NEUBAUER TTECHNIIQUE)) Diluting fluid (3% glacial acetic acid) Hayem’s solution Microscope Alcohol Cotton Glass cover Syringe
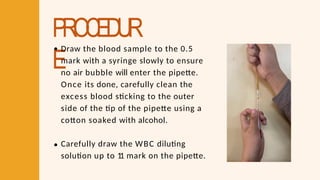
- 38. PROCEDUR E Draw the blood sample to the 0.5 mark with a syringe slowly to ensure no air bubble will enter the pipette. Once its done, carefully clean the excess blood sticking to the outer side of the tip of the pipette using a cotton soaked with alcohol. Carefully draw the WBC diluting solution up to 1 1 mark on the pipette.
- 39. PROCEDUR E Hold the pipette in a horizontal position and rotate the pipette several times to allow mixing of blood and diluting solution thoroughly. Prepare the counting chamber for sample loading. Carefully position the cover glass on top of the support platform of the chamber.
- 40. PROCEDUR E Carefully position the tip of the pipette on one edge of the cover glass and allow the contents of the pipette to gradually flow into the narrow space between the cover glass and the counting chamber via capillary force. Load the other counting chamber as well in a similar manner.
- 41. PROCEDUR EKeep aside the counting chamber for a few minutes to allow WBCs to settle. The slide is now ready for microscopic observation.
- 42. RULE FO R C O U N T I N G WBC White blood cells are counted in the 4 corner squares of the counting chamber. Counted using the LPO Cells touching the top and left boundaries are counted. Cells touching the right and bottom boundaries are not included. Difference between average cells in each chamber should not be greater than 10%.
- 43. RULE FO R C O U N T I N G RBC Red blood cells are counted in the central large square, specifically in 5 smaller squares (4 corners and 1 center). Counted using the HPO. Cells touching the top and left boundaries are counted. Cells touching the right and bottom boundaries are not included. The difference between counts in both chambers should not exceed 10%.
- 45. MA TERIIA LS ((CLLOTTTTI ING TTIIME)) Blood sample Capillary tube Clay Stop watch
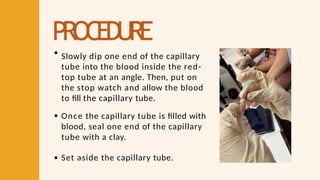
- 46. PROCEDURE Slowly dip one end of the capillary tube into the blood inside the red- top tube at an angle. Then, put on the stop watch and allow the blood to fill the capillary tube. Once the capillary tube is filled with blood, seal one end of the capillary tube with a clay. Set aside the capillary tube.
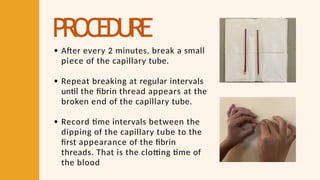
- 47. PROCEDURE After every 2 minutes, break a small piece of the capillary tube. Repeat breaking at regular intervals until the fibrin thread appears at the broken end of the capillary tube. Record time intervals between the dipping of the capillary tube to the first appearance of the fibrin threads. That is the clotting time of the blood
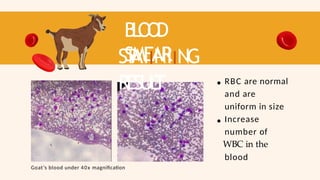
- 50. B L O O D SMEAR ST AIINIING RESUL T Goat’s blood under 40x magnification RBC are normal and are uniform in size Increase number of WBC in the blood
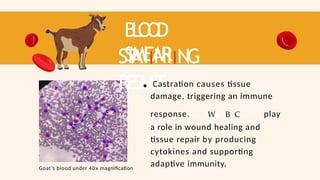
- 51. B L O O D SMEAR ST AIINIING RESUL T Goat’s blood under 40x magnification Castration causes tissue damage, triggering an immune response. LymWphBoCcytes play a role in wound healing and tissue repair by producing cytokines and supporting adaptive immunity.
- 52. TREA TMEN T Clean the Wound: Use antiseptic solutions (e.g., iodine or chlorhexidine) to prevent infection. Inspect Regularly: Check for signs of infection, such as swelling, redness, heat, or discharge Prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics like oxytetracycline or amoxicillin.
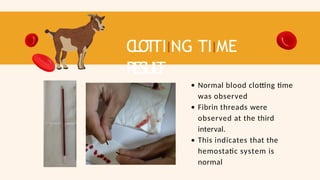
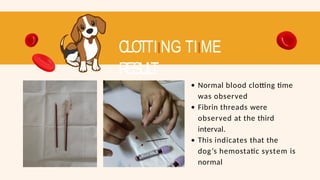
- 53. C L OT TIING TIIME RESUL T Normal blood clotting time was observed Fibrin threads were observed at the third interval. This indicates that the hemostatic system is normal
- 55. B L O O D SMEAR ST AIINIING RESUL T RBC are normal and are uniform in size No visible WBC is seen in the field of view Cat’s blood under 40x magnification
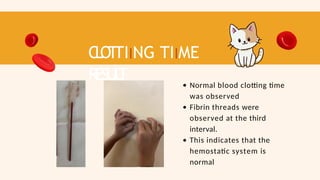
- 56. C L O T TIING TIIME RESUL T Normal blood clotting time was observed Fibrin threads were observed at the third interval. This indicates that the hemostatic system is normal
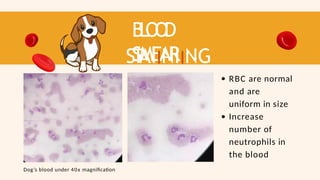
- 58. B L O O D SMEAR ST AIINIING RESUL T RBC are normal and are uniform in size Increase number of neutrophils in the blood Dog’s blood under 40x magnification
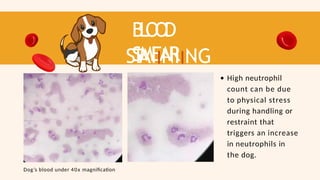
- 59. B L O O D SMEAR ST AIINIING RESUL T High neutrophil count can be due to physical stress during handling or restraint that triggers an increase in neutrophils in the dog. Dog’s blood under 40x magnification
- 60. TREA TMEN T Neutrophilia No treatment is needed; monitor and reduce stressors.
- 61. CLOTTIING TIIME RESUL T Normal blood clotting time was observed Fibrin threads were observed at the third interval. This indicates that the dog’s hemostatic system is normal
- 63. BLOOD SMEAR STAIINIING RESUL T RBC are normal and are uniform in size Only one WBC (monocyte) was seen in the field of view Human’s blood under 40x magnification
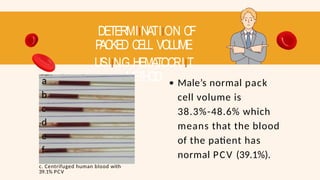
- 64. DETERMIINATIION OF P ACKED CELL VOLUME USIING HEMATOCRIIT METHOD - a - b - c c) Erythrocytes a) Plasma, b) Buffy coat; Heamatocrit reader. a b c d e f c. Centrifuged human blood with 39% PCV
- 65. DETERMIINATIION OF P ACKED CELL VOLUME USIING HEMATOCRIIT METHOD a b c d e f c. Centrifuged human blood with 39.1% PCV Male’s normal pack cell volume is 38.3%-48.6% which means that the blood of the patient has normal PCV (39.1%).
- 66. CLOTTIING TIIME RESUL T Normal blood clotting time was observed Fibrin threads were observed at the third interval. This indicates that the Joshua’s hemostatic system is normal
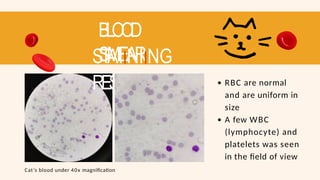
- 68. BLOOD SMEAR STAIINIING RESUL T RBC are normal and are uniform in size A few WBC (lymphocyte) and platelets was seen in the field of view Cat’s blood under 40x magnification
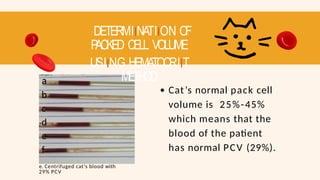
- 69. DETERMIINATIION OF P ACKED CELL VOLUME USIING HEMATOCRIIT METHOD a b c d e f e. Centrifuged cat’s blood with 29% PCV Cat’s normal pack cell volume is 25%-45% which means that the blood of the patient has normal PCV (29%).
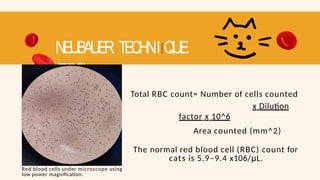
- 70. NEUBAUER TECHNIIQUE (RBC) Red blood cells under microscope using low power magnification. Total RBC count= Number of cells counted x Dilution factor x 10^6 Area counted (mm^2) The normal red blood cell (RBC) count for cats is 5.9–9.4 x106/μL.
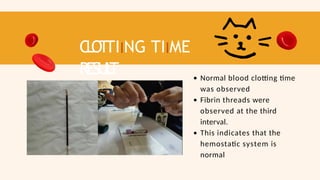
- 71. C L OT TIING TIIME RESUL T Normal blood clotting time was observed Fibrin threads were observed at the third interval. This indicates that the hemostatic system is normal
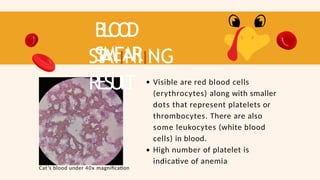
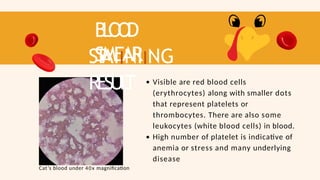
- 73. B L O O D SMEAR ST AIINIING RESUL T Visible are red blood cells (erythrocytes) along with smaller dots that represent platelets or thrombocytes. There are also some leukocytes (white blood cells) in blood. High number of platelet is indicative of anemia Cat’s blood under 40x magnification
- 74. B L O O D SMEAR ST AIINIING RESUL T Visible are red blood cells (erythrocytes) along with smaller dots that represent platelets or thrombocytes. There are also some leukocytes (white blood cells) in blood. High number of platelet is indicative of anemia or stress and many underlying disease Cat’s blood under 40x magnification
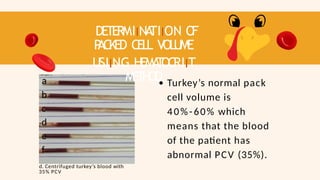
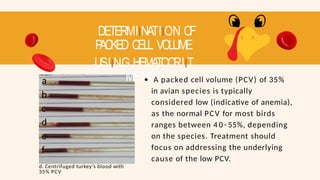
- 75. DETERMIINA TIION O F P ACKED CELL VOLUME USIING HEMA T OCRIIT METHOD a b c d e f d. Centrifuged turkey’s blood with 35% PCV Turkey’s normal pack cell volume is 40%-60% which means that the blood of the patient has abnormal PCV (35%).
- 76. DETERMIINATIION OF P ACKED CELL VOLUME USIING HEMATOCRIIT METHOD a b c d e f d. Centrifuged turkey’s blood with 35% PCV A packed cell volume (PCV) of 35% in avian species is typically considered low (indicative of anemia), as the normal PCV for most birds ranges between 4 0 - 55%, depending on the species. Treatment should focus on addressing the underlying cause of the low PCV.
- 77. TREA TMEN T Treatment should focus on addressing the underlying cause of the low PCV. Nutritional Deficiency Parasites (Internal or External) Chronic Disease or Infection Blood Loss (Acute or Chronic) Toxins or Heavy Metals
- 78. The volume of fluid is 1 mm2 (area of one square) x 4 (no. of squares counted) x 1/10 (depth) or 0.4 mm3. WBC (cells/mm3) = Cells counted x 20 (=dilution factor) / Volume (=0.4 mm) = Number of cells counted x 50. 89 x 50 = 4,450 µL Normal range of WBC in Turkeys: 5,000 and 20,000 µL NEUBAUER TECHNIIQUE (WBC) White blood cells under microscope using high power
- 79. CLOTTIING TIIME RESUL T Normal blood clotting time was observed Fibrin threads were observed at the third interval. This indicates that the hemostatic system is normal
- 80. REFERENCE S Abnormal Blood Counts Treatment (n.d.). Froedtert & the Medical College of Wisconsin. Retrieved from https://www.froedtert.com/benign- hematology/conditions/abnormal-blood- counts Duncan, J. R., & Latimer, K. S. (2011). Duncan & Prasse's Veterinary Laboratory Medicine: Clinical Pathology. Wiley-Blackwell. Hematology (Advia 2021). Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine. (2021, February 9). Retrieved https://www.vet.cornell.edu/animal-health- diagnosticcenter/laboratories/clinical- pathology/referenceintervals/hematology Jones, M. (2011). Interpreting of blood work in small ruminants (Proceedings). MJH Life Sciences™ and dvm360. Retrieved from https://www.dvm360.com/view/interpreting- blood-work-small-ruminants- proceedings Kendall, A. & Marks, S. (2019). Anemia in Animals. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. Retrieved from https://www.msdvetmanual.com/circulatory- system/anemia/anemia-in-animals#v4487143
- 81. THANK YOU!