COMPUTER AND ITS APPLICATION: PROCESS OF MEMORY
- 1. ALIGARH MUSLIM UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION PRESENTATION TOPIC:- COMPUTER AND ITS APPLICATION: PROCESS OF MEMORY PRESENTED BY: ABUL HASAN abulhasanranaamu2007@gmail.com
- 2. Computer and its application: Process of Memory SUBMITTED BY: ABUL HASAN SUBMITTED TO: NASRIN (MAAM)
- 3. COMPUTER ?The term computer is derived from the Latin term ¡®computare¡¯, this means to calculate or programmable machine. ?Computer is an electronic device that is designed to work with Information.
- 4. APPLICATION ? An application is any program, or group of programs, that is designed for the end user. ? Two types of application software's a) Systems software (File Manager tool, operating system, Dos). b) applications software (Games, Word processing).
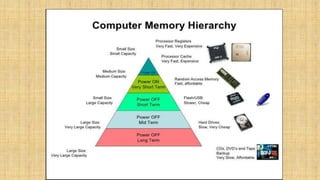
- 5. PROCESS OF MEMORY ?Computer memory is any physical device capable of storing information temporarily or permanently. For example, Random Access Memory (RAM), is a volatile memory that stores information on an integrated circuit used by the operating system, software, and hardware
- 6. The memory of the computer is divided into to categories: 1.Primary Memory 1.Secondary Memory
- 7. Primary Memory:- Main memory of the computer. CPU can directly read or write on this memory. It is fixed on the motherboard of the computer. 1. RAM (Random Access Memory):-is a temporary memory. Information lost if computer turn off.
- 8. 2. ROM(Read Only Memory):-Information stored permanent in nature, it holds data if the computer switch off. It cannot overwritten by the computer.
- 9. 2. Secondary memory:- This memory is permanent in nature.It holds the information till we erase it. Different types of secondary storage devices are: 1. Hard Disc capacity (Unlimited) 2. Compact Disc (upto 700 MB) 3. DVD (upto 4.7 GB) 4. Pen Drive (upto 2 TB) 5. Blue Ray disc upto 25 GB)
- 10. HARD DISC (UNLIMITED CAPACITY)
- 11. COMPACT DISC (700 MB)
- 12. DVD (DIGITAL VERSATILE DISC) (4.7 GB)
- 13. PEN DRIVE (2 TB)
- 14. BLUE RAY DISC (25 GB)
- 15. MEMORY UNIT 0 1 1 Kilobyte (KB) 1 KB = 1024 Bytes 2 Megabyte (MB) 1 MB = 1024 KB 3 GigaByte (GB) 1 GB = 1024 MB 4 TeraByte (TB) 1 TB = 1024 GB 5 PetaByte (PB) 1 PB = 1024 TB
- 17. USE OF COMPUTER MEMORY IN EDUCATION 1. To stored books. 2. Easily mobile in the form of pen drive, disc etc. 3. Stored lots of information regarding education. 4. Stored video lectures 5. Prepare dissertation 6. Easily accessible 7. Stored notes and write-up 8. Stored essential documents the form of .pdf, .docx, .ppt, .xlc etc 9. Stored soft copy of the documents. 10.Data base formation.