COMPUTER MEMORY : TYPES & FUNCTIONS
- 1. ANGELA MARY G MBA (EVENING) 2ND SEMESTER IMK, KARYAVATTOM
- 2. ’é© Memory is the most essential part of a computer. ’é© Without memory there would be no computer, as we know it today. ’é© It is used for storing both instructions to be executed and data. ’é© This presentation has been developed after an intensive research on Memory Devices. ’é© The CPU accesses each location in memory by using a unique number, called a memory address
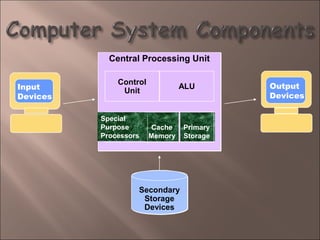
- 3. Central Processing UnitCentral Processing Unit Output Devices Cache Memory Primary Storage Secondary Storage Devices Control Unit ALU Special Purpose Processors Output Devices Input Devices
- 4. I.PRIMARY MEMORY OR MAIN MEMORY ’āśRandom Access Memory (RAM) ’āśRead Only Memory (ROM) II.CACHE MEMORY ’āśLevel 1 (L1) cache ’āśLevel 2 (L2) cache III. SECONDARY MEMORY ’āśOptical Media Devices ’āśMagnetic Media Devices
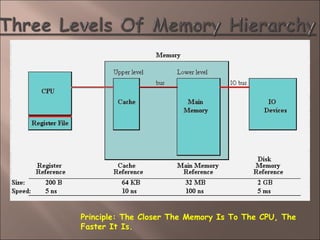
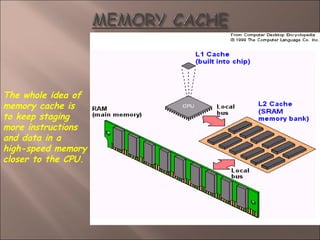
- 5. Principle: The Closer The Memory Is To The CPU, The Faster It Is.
- 7. ’āśDirectly or indirectly connected to the CPU via a╠²memory bus. ’āśComprises of two buses: an address bus╠²and a data bus . ’āśThe CPU firstly sends a number through an address bus, a number called memory address, that indicates the desired location of data. Then it reads or writes the data itself using the data bus. ’āśAdditionally, A Memory Management Unit (MMU) is a small device between CPU and RAM recalculating the actual memory address, for example to provide an abstraction of virtual memory╠²or other task. ’āśBroadly, the main memory is of two types- i. Random Access Memory (RAM) ii. Read Only Memory (ROM).
- 9. ’é© A RAM memory chip is an integrated circuit (IC) made of millions of transistors and capacitors.
- 10. ’é© This is a type of memory serves as╠²Main Memory Of A Computer. ’é© It temporarily stores copy of information and files loaded from a computer hard drive ╠²that are required by a processor. ’é© It is volatile in nature, which means that data will be erased once supply to the storage device is turned off. ’é© RAM stores data randomly and the processor accesses these data randomly from the RAM storage.
- 11. ’é© The RAM chips are of two types- I. Dynamic RAM(DRAM) A form of volatile memory which also requires the stored information to be periodically re-read and re-written, or╠²refreshed, otherwise it would vanish. II. Static RAM (SRAM) A╠²form of volatile memory similar to DRAM with the exception that it never needs to be refreshed.
- 12. ’é© A type of╠²RAM╠²that stores each╠²bit╠²of data in a separate╠²capacitor╠²within an integrated circuit.
- 13. ’é© Its advantage is its structural simplicity: only one transistor and a capacitor are required per bit, compared to four transistors in SRAM. This allows DRAM to reach very high density.
- 14. ’é© DRAM chips are available in various designs: i. EDODRAM (Extended Data Out DRAM) ii. SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM) iii. RDRAM (Rambus DRAM) iv. DDRDRAM (Double Data Rate DRAM)
- 15. ’é© Its cells keep the data valid until it receives an additional signal. ’é© It has a dual-pipeline architecture that allows the memory controller to simultaneously read new data while discharging the old. A pair of 32 MB╠²EDO DRAM modules
- 16. ’éŚ SDRAM has a synchronous interface, meaning that it waits for a╠²signal╠²before responding to control inputs and is therefore synchronized with the computer's system bus.
- 17. ’éŚ This allows the chip to have a more complex pattern of operation than asynchronous DRAM╠²which does not have a synchronized interface. ’éŚ Pipelining ╠²means that the chip can accept a new instruction before it has finished processing the previous
- 18. ’é© It is a type of synchronous DRAM, designed by the╠²Rambus╠²Corporation ’é© It is fairly fast and has tried to address some of the complex electrical and physical problems involved with memory.
- 19. ’é© Unlike SDRAM, it can do two operations per cycle thereby doubling the memory bandwidth over the corresponding single-data-rate SDRAM
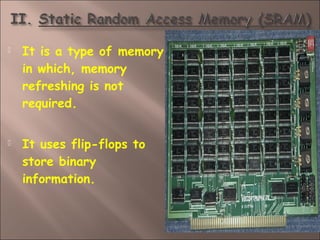
- 20. ’é© It is a type of╠²memory in which, memory refreshing is not required. ’é© It uses flip-flops to store binary information.
- 21. ’é© As it takes up more space than DRAM, it is used for specialized applications. ’é© It is much easier to use and has shorter read-write cycles compared to DRAM.
- 22. ’é© It performs only read function not write function. So the data stored in ROM cannot be modified. ’é© It comes with special internal electronic fuses that can be programmed for a specific configuration. ’é© Once this pattern is established it stays in the unit. Thus, ROM is non-
- 23. 1. PROGRAMMABLE READ-ONLY MEMORY╠²(PROM) ŌĆóThis device uses high voltages to permanently destroy or create internal links (fuses╠²or╠²antifuses) within the chip. ŌĆóConsequently, a PROM can only be programmed once.
- 24. 2. ELECTRICALLY ERASABLE PROGRAMMABLE READ-ONLY MEMORY╠²(EEPROM) It allows its entire contents (or selected╠²banks) to be electrically erased, then rewritten electrically, so that they need not be removed from the computer (or camera, MP3 player, etc.)
- 25. 3.ERASABLE PROGRAMMABLE READ-ONLY MEMORY╠²(EPROM) It can be erased by exposure to strong╠²ultraviolet╠²light (typically for 10 minutes or longer), then rewritten with a process that again requires application of higher than usual voltage. A 32╠²KB (256╠²Kbit) EPROM
- 27. ’é© It is a high speed storage mechanism. ’é© It Can be either a reserved section of main memory or an independent storage device. ’é© It speeds up access to data and instructions stored in RAM. ’é© MEMORY CACHE- ’éĪ It is a portion of memory of SRAM instead of the slower DRAM. By keeping as much of the information as possible in high speed SRAM, it avoids accessing the slower DRAM ’é© DISK CACHE- ’éĪ It works under the same principle, but uses conventional main memory (DRAM) instead of high speed SRAM. It improves the computers performance a lot as accessing data from RAM is much faster than from hard-disk.
- 28. ’é© Level 1 (L1) cache ’ā║ Built inside the CPU. ’ā║ It works at half CPU clock speed. ’é© Level 2 (L2) cache ’ā║ Built external to CPU, in the motherboard. ’ā║ It works at the motherboard bus speed. ’é© Nowadays both L1 and L2 are integrated in the CPU to reduce access time and further improve system performance.
- 29. The whole idea of memory cache is to keep staging more instructions and data in a high-speed memory closer to the CPU.
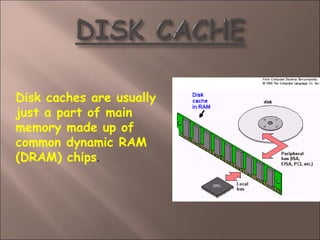
- 30. Disk caches are usually just a part of main memory made up of common dynamic RAM (DRAM) chips.
- 32. ’é© These devices are used to store large amount of data permanently. ’é© It differs from primary storage in that it is not directly accessible by the CPU. So they need more access time and thus are much slower. ’é© Per unit, it is typically also an order of magnitude less expensive than primary storage. Consequently, modern computer systems have an order of magnitude more secondary storage than primary storage and data is kept for a longer time there (such as in hard disk). ’é© It is broadly of two types- ’é© 1) MAGNETIC MEDIA ’é© 2) OPTIC MEDIA.
- 33. ’é© Magnetic storage uses different patterns of╠²magnetization╠²in a magnetizable material to store data ’é© It is a form of╠²non-volatile memory. ’é© The information is accessed using one or more╠²read/write heads. ’é© HARD DISKS and FLOPPY DISKS are such devices
- 34. ’é© It stores information on one or more continuously spinning disks which are coated with magnetic material. ’é© Information is recorded by magnetic heads called access arms. ’é© These days, hard disks have storage capacity between 80 to 300 GB. ACCESS ARM
- 35. ’é© It is made of a flexible substance called Mylar. ’é© It has a magnetic surface for recording data. ’é© It stores up to 1.44 MB of data. ’é© It cannot include graphics or pictures within it. ’é© All floppy disks must be formatted before data can be written on it.
- 36. ’é© Optic devices are generally circular disc which can contain╠²data╠²encoded in bumps on a special material on one of its flat surfaces. ’é© The encoding pattern follows a continuous, spiral path covering the entire disc surface and extending from the innermost track to the outermost track.
- 37. ’é© The data is stored on the disc with a╠²laser╠²or stamping machine, and can be accessed when the data path is illuminated with a╠²laser diode╠²in an╠²optical disc drive ’é© These are broadly of two types- ’é© 1) CDs and 2) DVDs
- 38. ’é© CDs are very cheap and store up to 700 MB of data. ’é© They are of three types- 1. CD-ROM (CD Read Only Memory) 2. CD-R (CD Recordable) 3. CD-RW (CD Rewritable
- 39. ’é© It is of the same size as a CD but stores 15 times as much information, is 20 times faster than it. ’é© It can hold 17 GB of data. ’é© It comes in three varieties- 1. DVD-ROM (DVD Read Only Memory) 2. DVD-R (DVD Recordable) 3. DVD-RW (DVD Rewritable)
- 40. FLASH MEMORY BLU-RAY DISK ’ā╝ Is a╠²non- volatile╠²memory ’ā╝ It is a specific type of╠²EEPROM╠² ’ā╝ Primarily used in╠²memory cards╠²and╠²USB flash drives ’āś Supersedes DVDs ’āś Uses blue-violet laser╠²to read the disc ’āś stores almost six times more data than on a DVD
- 41. Memory plays great role in computer systems. As we have discussed, there are three╠²computer memory types╠²available in standard computer based on their function and physical makeup. However, only the main memory that can be upgraded and changed, the others comes with the system whether it is a processor, ROM or graphics card.╠²