Computer modelling and simulations
- 1. Computer Modeling and Simulations
- 2. Computer Simulations and Models A simulation is basically an attempt to imitate reality. Simulation is used in many contexts, including the modeling of natural systems or human systems in order to gain insight into their functioning. A computer model is the mathematical representation of the functioning of a process, concept or system, presented in the form of a computer program.
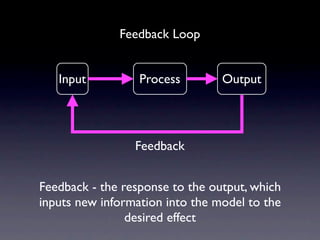
- 3. Feedback Loops Good computer models are dependent of feedback loops. Essentially, feedback loops are the part of the system model that, based on the current output, allows for response and / or self-correction to achieve the desired output.
- 4. Feedback Loop Input Process Output Feedback Feedback - the response to the output, which inputs new information into the model to the desired effect
- 5. Steps involved in creating simulations ŌĆó Gather and prepare accurate data to re’¼éect the real world. ŌĆó Create mathematical formulas (algorithms) to generate output data from that which is input. ŌĆó Create animations, graphs or other output displays for the information. ŌĆó Verify and validate the data by re-testing the scenarios to ensure that the same result occurs.
- 6. Advantages of modeling and simulations ŌĆó Safety - able to test or experiment without harming the person or environment. ŌĆó Economic savings from the use of models to design and test new products before prototypes or the ’¼ünal product is made. ŌĆó Projection - can look into the future and highlight potential impacts and address them before they occur. ŌĆó Visualisation - can see and understand relationships. Can speed up or slow down time. ŌĆó Replication - able to look at things under a variety of different scenarios
- 7. Disadvantages of modeling and simulations ŌĆó The mathematical (computational) calculations are very complex, maybe too complex, to simulate 'real life' situations or activities. Therefore, simulations really identify possible trends. ŌĆó Faulty or hidden assumptions ŌĆó Extent and effect of the simpli’¼ücation of reality ŌĆó Processing power needed to create complex models ŌĆó Can be costly to purchase the processing power and labour
- 8. Complexity and Assumptions ŌĆó Mathematical models are built on assumptions, many of which are dif’¼ücult to verify. ŌĆó Possibility for the assumptions to be faulty, the creators of the model to overlook things (hidden assumptions) and also clerical errors can be made with the programming. ŌĆó Daily weather report - to be 100% accurate is too dif’¼ücult. Usually, the report is 55-65% accurate. ŌĆó Errors with computer models can have disastrous results.
- 9. Weather Forecasting and Climate Models ŌĆó The importance of the weather and the need to predict it accurately is illustrated by the fact that every local news show includes weather forecasts. ŌĆó People need to know what the weather will be likeŌĆōeither where they are or where they are goingŌĆōso that they can plan their activities accordingly.
- 10. A brief history Weather forecasting is no new trend. As far back as 650 BC, there is evidence of early humans attempting to read the weather. ŌĆó Observing cloud patterns ŌĆó Colour of the sunset e.g. red These forecasting methods proved to be primitive and unreliable.
- 11. A brief history 1837 did real weather forecasting truly begin. With the creation of the telegraph, people could now begin to draw more or less accurate reports of weather conditions. In the 1840s, the telegraph allowed people to record weather conditions over a much larger area.
- 12. A brief history 1922 when Lewis Fry Richardson proposed his idea of using numerical weather prediction to forecast the weather. ŌĆ£Numerical weather prediction used mathematical models of the atmosphere to predict the weather.ŌĆØ This new idea was not used until 1955.
- 13. Five basic steps of weather forecasting ŌĆó Data collection (observations from surface, stratosphere or satellite) ŌĆó Data assimilation - production of a model ŌĆó Numerical weather prediction ŌĆó Model processing - adds human observations ŌĆó Presentation of a forecast
- 14. Stakeholders ŌĆó General public ŌĆó Air traf’¼üc ŌĆó Military / Navy ŌĆó Farmers ŌĆó Utility companies e.g. Origin Energy ŌĆó Private companies
- 15. Issues - Reliability ŌĆó Not always accurate; extent of situation could be overestimated ŌĆó Better safe than sorry or donŌĆÖt provide warnings
- 16. Issues - Integrity ŌĆó Accuracy of the data and the instruments collecting the data
- 17. Equality of Access ŌĆó Quite easy to translate forecasts because of visual information ŌĆó Not everyone has access to radio, TV, Internet for emergency warnings
- 18. Issues - Control ŌĆó The weather forecast may control our day ŌĆó Companies respond to forecasts - potential economic cost
- 19. Issues - People and Machines ŌĆó Requires people to interpret the information produced by the models ŌĆó Need for human observation to be added to the forecast ŌĆó Future weather forecasts may be able to be delivered without the aid of humans.
- 20. Digital Experimentation ŌĆó Digital Experimentation is the act of conducting experiments on a computer without ever physically touching the test subject. ŌĆó For example, engineers can create digital models to crash-test a car to observe how the crash-test dummies would react to the impact. ŌĆó Another way to digitally experiment is by using image- enhancing programs like Photoshop. LetŌĆÖs say youŌĆÖre wondering what you would look like with purple hair but you donŌĆÖt actually want to dye it: by using certain tools and techniques on Photoshop, you can!
- 21. Car Crash Simulators Car Crash simulations offer a way to gain information about the causes of the accidents and how to improve the safety of the car bodies.
- 22. How car crash test simulators work They use the ’¼ünite element method - grid superimposed on the object and numerical data is entered to each corresponding square of the to provide information on density, strength and elasticity.
- 23. Calculating the effect of a head-on collision ŌĆó Data can be initialised to represent a crash into a wall at a speci’¼üed speed. ŌĆó The program computes the force, acceleration and displacement of each grid square, plus the stress and strain of each element of the model. ŌĆó Program relies on intense computation and highly dependent of graphics programs.
- 24. Bene’¼üts ŌĆó Can look at a variety of designs before building the prototype. ŌĆó Saves several design being built and having to be crash-tested. Each crash test costs between A$ 100,000 to 1.6 million. ŌĆó Saves on material waste.
- 25. Issues - Reliability ŌĆó Good understanding of the physics involved, especially force and acceleration. ŌĆó Material properties are relatively well known. ŌĆó Behaviour of the materials under abrupt acceleration e.g. high speed impact and at near breaking point are less understood
- 26. Issues - Reliability ŌĆó Simpli’¼ücation involved in the model. Cars are smooth and a grid does not replicate this.You can produce smaller grids but such a model requires far more processing power and cost. ŌĆó Comparison with real-life situation is, arguably, good. Use of video cameras on actual crash tests with data, such as displacement points, fed back into the computer model.
- 27. Issues - Integrity ŌĆó Incorrect entry of data ŌĆó Hackers changing data
- 28. Issues - Equality of Access ŌĆó Small companies looking to break into the car market would need a lot of money to compete with big corporations such as GM.
- 29. Issues - Policy and Standards ŌĆó Saves on environment in terms of materials used ŌĆó Economic savings ŌĆó Saves time
- 30. Traf’¼üc Simulation Models De’¼ünition: A computer program that uses mathematical models to conduct experiments with traf’¼üc events on a transportation facility or system over extended periods of time.
- 31. Complex Networks Network traf’¼üc simulation is a process used in telecommunications engineering to measure the ef’¼üciency of a communications network. Telecommunications systems are complex real-world systems, containing many different components, which interact, in complex interrelationships.
- 32. Determining the ef’¼üciency of a road netwrok ŌĆó Most obvious ef’¼üciency factor - the pattern of roads that currently exist In addition, consider ’¼ürst the travel behaviour - ŌĆó Number of trips (data loggers) ŌĆó Origin and destination of trips ŌĆó Transport mode ŌĆó Route taken
- 33. Use of zones ŌĆó Models incorporates zoning e.g. some 542 zones across the Greater Dublin area. ŌĆó Zones de’¼üne the demand for travel in terms of origins and destinations. ŌĆó Need to consider external zones for trips into and out of the area.
- 34. Increasing ef’¼üciency Once the ŌĆśgeneralŌĆÖ ef’¼üciency is found, control measures that may assist improve the ef’¼üciency of the model may be incorporated:- ŌĆó Speed limits ŌĆó Overtaking bans for trucks, especially at uphill or downhill sections ŌĆó Restrictions for lane changing, especially before or at merging regions ŌĆó Traf’¼üc ’¼éow control at on on-off ramps at intersections
- 35. Improving Ef’¼üciency Traf’¼üc simulation models can also be used to look at future scenarios:- ŌĆó To simulate the effect of new infrastructure before it has been build. ŌĆó To simulate the in’¼éuence of vehicles with adaptive cruise-control systems. If an increasing percentage of vehicles has such systems, does traf’¼üc become more stable? Can the traf’¼üc ’¼éow per lane be increased? ŌĆó Finally one can even simulate different or new traf’¼üc rules. For example, allowing overtaking on freeways at either side combined with a speed limit.
- 36. Advantages of traf’¼üc simulation models ŌĆó It is possible to easily compare alternative designs so as to select the optimal system ŌĆó The actual process of developing the simulation can itself provide valuable insights into the inner workings of the network which can in turn be used at a later stage ŌĆó Time and money saving ŌĆó Possible to test new traf’¼üc rules without putting humans into dangerous situations and comparing the results of different types of traf’¼üc rules
- 37. Disadvantages of traf’¼üc simulations ŌĆó Data can be incorrectly input ŌĆó Accurate simulation model development requires extensive resources ŌĆó The simulation results are only as good as the model and as such are still only estimates ŌĆó It is very costly to develop a good, reliable and realistic simulation
- 38. Issues - Reliability and Integrity ŌĆó Data can be incorrectly input ŌĆó Data becomes out of date quickly ŌĆó Vast networks dif’¼ücult to survey ŌĆó Need for accurate for casting e.g. number trips determined by population projections and level of car ownership or even environmental consciousness
- 39. Issues - Security ŌĆó Need to protect the simulation from those who may wish to tamper with it.
- 40. Issues - Equality of Access ŌĆó Costly and extremely dif’¼ücult to do in developing countries
- 41. Demographic Models Demographics refers to certain population characteristics such as race, age, gender, income, disabilities, literacy rate, home ownership, employment status, and location. It is useful for the government of a country, coming up with marketing strategies, and for economic research.












































![System simulation & modeling notes[sjbit]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/systemsimulationmodelingnotessjbit-110929031610-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)


















































