computer-virus-and-anti-virus-160219142022 (1).pdf
0 likes1,302 views
Brief description of computer viruses and antiviruses
1 of 25
Download to read offline
























Ad
Recommended
Computer viruses
Computer virusesAnnies Minu
╠²
This document provides an overview of computer viruses, including their history, concepts, symptoms, types, and preventive measures. It discusses how the first computer virus was created in 1981 and that viruses now number in the millions. Various types of viruses are defined, such as boot sector viruses, browser hijackers, file infectors, and polymorphic viruses. Symptoms of a virus include slow performance, crashes, and file loss. The document concludes with recommendations to use reputable download sources, firewalls, avoid suspicious emails, and install antivirus software to prevent virus infections.presentation on computer virus
presentation on computer virusYogesh Singh Rawat
╠²
This document discusses computer viruses including their similarities to biological viruses, how they work and spread, types of viruses, virus detection methods, and prevention. It notes that computer viruses can replicate and spread like biological viruses, infecting host systems and slowing them down. The main types discussed are macro, boot sector, worm, Trojan horse, and logic bomb viruses. Virus detection methods covered include signature-based, behavior-based, and heuristic-based detection. Prevention methods recommended are using antivirus software, not sharing drives without passwords, deleting email attachments, backing up files, and using secure operating systems.computer viruses power point presentation
computer viruses power point presentationRohit Kashyap
╠²
The document discusses computer viruses, how they spread, types of viruses, and how to prevent and cure virus infections. Computer viruses are software programs that replicate like biological viruses and can spread by attaching to other files. When files are exchanged between computers, the virus can spread. Viruses can slow down systems, use memory, and even crash computers. Antivirus software can be installed to prevent and remove viruses, and files should only be downloaded from trusted sources.Computer virus
Computer virusAnkita Shirke
╠²
This document defines and describes various types of computer viruses and malware. It explains that viruses are malicious programs that spread from device to device and can damage systems or steal data. Common types of viruses mentioned include boot sector viruses, file-infecting viruses, and macro viruses. The document also discusses malware, worms, Trojans, spyware, ransomware, rootkits, and backdoors. It provides tips for protecting systems with antivirus software, firewalls, and safe computing practices.Cyber ppt
Cyber pptMandar Pathrikar
╠²
This document discusses cyber security issues and solutions in the modern world. It outlines growing cyber crimes like computer viruses, password cracking, and unauthorized network access. It then describes brute force attacks and software available to detect them. It discusses strong authentication and Snort centers used in US cyber security. The Radar Page and Nessus vulnerability scanner are presented as tools to monitor cyber crimes. Preventions like intrusion alerts, encryption, and network scanning are recommended.Computer virus
Computer virusPriti Singh
╠²
A computer virus is a program that installs itself and runs without permission on an infected computer. There are different types of viruses like email viruses, trojan horses, and worms. Viruses can spread through email attachments, websites, networks, software, and removable drives. Symptoms of a virus include slow performance, unexpected program/file changes, browser issues, and unauthorized emails sent from the infected device. People are advised to use antivirus software, practice safe browsing/email habits, keep systems updated, and use firewalls to protect against viruses. Popular antivirus programs are listed that can help keep computers secure.Cyber Security PPT.pptx
Cyber Security PPT.pptx56ushodayareddy
╠²
Cyber security is important to protect computers, networks, programs, and data from threats such as theft, damage, and unauthorized access or disclosure. As technology has advanced and more devices are connected, the threats have also increased and become more sophisticated. Cyber security involves various elements like data security, network security, cloud security, and disaster recovery plans. Common cyber threats include phishing, malware, SQL injection, and denial of service attacks. It is important for individuals and organizations to implement cyber security best practices such as strong passwords, updates, backups, access control, and employee training to protect against cybercrime and attacks.Parts of motherboard and its function
Parts of motherboard and its functionmyebautista01031980
╠²
The document discusses the main components of a motherboard and their functions. It describes the CPU as the brain that executes instructions and performs calculations. RAM temporarily stores dynamic data to enhance performance. The BIOS controls hardware and interfaces with the operating system. Expansion buses allow adding features through adapter cards. The Northbridge controls transfers between the CPU and RAM, while the Southbridge handles communication with peripheral devices. It also discusses common computer cable types like VGA, HDMI, USB, IDE, SATA, FireWire, and Ethernet.Computer virus
Computer virusAarya Khanal
╠²
The document discusses computer viruses, including what they are, common symptoms, types, and methods of prevention. It defines viruses as malicious programs that replicate by modifying other programs and spread from computer to computer. The document outlines types like boot viruses, program viruses, and macro viruses. It also provides recommendations for prevention such as installing antivirus software, keeping systems updated, using strong passwords, and backing up files. The role of antivirus programs in detecting and removing malware through signature-based scanning is also covered.Computer Virus
Computer VirusOECLIB Odisha Electronics Control Library
╠²
Computer viruses are malicious programs that can damage systems and erase data. There are different types like viruses, worms, and Trojan horses. Viruses piggyback on other programs to replicate, worms use networks to spread, while Trojans masquerade as useful programs but have hidden harms. Signs of infection include slow performance, crashes, and missing files. Regular antivirus updates, secure practices like avoiding untrusted sources can help prevent damage from viruses.What is computer
What is computerChandnisinghkhushwaha
╠²
Supercomputers are the most powerful and expensive computers, used to solve complex science and engineering problems through parallel processing of up to ten trillion calculations per second. Mainframes are similar but perform many concurrent operations for large organizations, while servers store data and applications to solve smaller problems for many users simultaneously. Workstations are high-end computers for one user for complex science, math, and engineering tasks. Personal computers are smaller computers designed for individual use in homes and small offices. Microcontrollers are embedded processors that control machinery. Smartphones perform computer-like functions with touchscreens and apps.Taking care of your computers
Taking care of your computersJean Ulpindo
╠²
The document provides tips for caring for and maintaining a laptop computer. It recommends keeping liquids, food, and other debris away from the laptop. Important maintenance steps include using antivirus software, cleaning the laptop regularly by removing dust and debris, protecting the screen, and avoiding rapid temperature changes or heavy objects on top of the laptop. Proper handling and use of a laptop case can help prevent damage.Computer virus
Computer virusWalden University
╠²
Computer viruses can spread easily over the internet. A true virus is capable of self-replication and can spread between files, disks, or hosts. There are over 30,000 computer viruses in existence with over 300 new ones created each month. Common symptoms of a virus attack include computers running slower, files disappearing, and systems crashing. The most common way viruses spread today is through the internet. Viruses are classified into categories like stealth, polymorphic, and armored and types like worms, trojan horses, and macros. Protection methods include having proper anti-virus software, configurations, and only running necessary programs.Types of software
Types of softwarelatifah2001
╠²
There are two main types of software: system software and application software. System software includes operating systems and disk operating systems, which allow hardware and applications to communicate. Application software accomplishes specific tasks and is divided into user-designed and ready-made categories. User-designed software is tailored for a specific organization, while ready-made software like word processors and spreadsheets are off-the-shelf packages that may not fully suit an organization's needs but are cheaper and easier to use.What is computer hardware and software
What is computer hardware and softwareparag dhok
╠²
The document explains the distinction between computer hardware, which refers to the physical components of a computer system, and software, which consists of the programs and instructions that enable hardware functionality. It categorizes software into system software, which controls hardware operations, and application software, which allows users to perform specific tasks. Additionally, it outlines various hardware components such as the motherboard, CPU, RAM, and hard disk, and describes their respective roles within a computer system.Virus and Anti Virus - Types of Virus and Anti Virus
Virus and Anti Virus - Types of Virus and Anti VirusAdeel Rasheed
╠²
The document provides an overview of computer viruses, including their definitions, types, and sources of infection, as well as explaining how antivirus software functions to detect and eliminate these threats. It details various types of viruses like macro, memory resident, and email viruses, and describes the mechanisms of antivirus software in scanning and quarantining infected files. Additionally, it lists popular antivirus software options available on the market, highlighting features and subscription costs for products like Bit Defender, Norton Antivirus, McAfee, Kaspersky, and Avast.Computer software
Computer softwarejuna luna
╠²
The document provides an overview of computer software, dividing it into system software, which manages hardware and provides a platform for application software, and application software, which helps users perform specific tasks. Examples of system software include operating systems like Microsoft Windows and MS-DOS, while application software examples include Microsoft Office, Google Chrome, and inventory management software. Additionally, it discusses the roles of linkers and boot sectors in the software ecosystem.CS6004 Cyber Forensics
CS6004 Cyber ForensicsKathirvel Ayyaswamy
╠²
The document provides an extensive overview of computer forensics, including its definition, goals, and various techniques for investigating computer-related crimes such as identity theft and cybercrime. It discusses the importance of digital evidence, its admissibility in court, and specific case studies illustrating failures in electronic records authentication. Additionally, it covers the roles of various stakeholders in computer forensics, including law enforcement and private corporations, and outlines the types and categories of cybercrime.Computer security
Computer securityfiza1975
╠²
The document discusses computer security threats and measures. It describes types of security like hardware security, software security and network security. It then discusses various malicious codes like viruses, trojans, worms and logic bombs. It also discusses hacking, natural threats like fires and floods, and theft. It concludes by describing various security measures that can be taken like using antivirus software, firewalls, encryption, backups and focusing on the human aspect of security.Computer Viruses
Computer VirusesAnnies Minu
╠²
1. Computer viruses are programs that can copy themselves and infect computers without permission by attaching to other files or programs.
2. Viruses have existed since the early 1970s and have caused issues like slow performance, crashes, missing files, and unexpected pop-ups.
3. There are many types of viruses including file infectors, macro viruses, and polymorphic viruses that disguise their code, and each can impact computers in different ways such as corrupting files or redirecting web browsers.Computer security and
Computer security andRana Usman Sattar
╠²
This document discusses various topics related to computer security including risks, attacks, safeguards, and ethics. It describes common security threats like viruses, hacking, denial of service attacks, and information theft. It also outlines methods to identify users, protect against threats, and investigate security incidents through digital forensics. Safeguards include firewalls, antivirus software, encryption, and physical access controls.Threats to a computer
Threats to a computer FCA - Future Chartered Accountants
╠²
This document is a project report submitted by Deeptika Soni on threats to computers. It discusses various types of threats like viruses, worms, hackers and their symptoms. It outlines system requirements and provides an index with sections on virus components, how threats are noticed, suggestions to prevent threats, and conclusions. The report references hardware and software vulnerabilities that can be exploited by interceptions, interruptions, modifications and fabrications. It notes threats involve theft, destruction or unauthorized access and tampering with computer assets.System software vs application software
System software vs application softwarebaabtra.com - No. 1 supplier of quality freshers
╠²
The document discusses the differences between system software and application software. It defines system software as programs that enable application software to interact with hardware and control computer hardware. Application software is defined as end-user software that can be general purpose, meant for common tasks, or special purpose, meant for specific tasks. Examples are provided of operating systems, device drivers, and servers as system software and office suites, media players, ERP software and games as application software.Virus and malware presentation
Virus and malware presentationAmjad Bhutto
╠²
Viruses and malware can damage computers. Viruses spread by copying themselves, while malware is designed to access or harm devices without owner knowledge. Common malware includes adware, bugs, rootkits, Trojans, and ransomware. It is important to use updated antivirus software, strong passwords, firewalls, and be cautious of suspicious links and downloads to protect devices from viruses and malware.Computer maintenance
Computer maintenanceCelia Bandelier
╠²
This document provides guidance on performing preventative maintenance on a computer to improve performance and extend its lifespan. It recommends cleaning the external components like the monitor, keyboard, and mouse regularly, as dust can accumulate quickly. Internally, it suggests using the Disk Cleanup and Disk Defragmenter tools periodically to free up hard drive space and optimize file placement. It also stresses the importance of installing operating system and software updates, scanning for viruses regularly, and backing up files in case of hardware failure or malware infection. Regular maintenance through cleaning, optimization, and backup is presented as an effective way to care for a computer over time.Computer Malware
Computer Malwareaztechtchr
╠²
Malware refers to unwanted software that can damage computers, including viruses, trojans, worms, spyware, and more. Viruses attach to files and programs to spread without permission and can damage systems. Trojans also spread unwittingly but allow hackers to access and control infected devices. Worms multiply to use up memory and resources. Spyware collects personal information without consent. Users can protect against malware through antivirus software, firewalls, safe computing habits like avoiding suspicious downloads and emails, and using strong passwords.Information Processing Cycle
Information Processing Cycle MudAssar IQbal
╠²
This document discusses the key components of computer systems: input, processing, storage, and output. It lists common input devices like keyboards and mice that send data to computers. It describes processing as passing data through stages and the CPU as the component that performs operations. It defines output as any information sent from the computer via monitors, printers, or other devices. It also discusses storage devices like hard drives that hold processed data for future use.Virus, Worms And Antivirus
Virus, Worms And AntivirusLokesh Kumar N
╠²
The document discusses computer viruses and antivirus technologies. It begins with defining computer viruses and outlining their history. It then analyzes three common types of viruses: file infectors, macro viruses, and the "I LOVE YOU" virus. The document also describes how antivirus software detects and removes viruses and outlines best practices for preventing virus infections like regular backups and keeping antivirus definitions up to date.cambios_emocionales en los traumas presentes en adolescentes
cambios_emocionales en los traumas presentes en adolescentesvivianyarenivallecil
╠²
cambios emocionalesMore Related Content
What's hot (20)
Computer virus
Computer virusAarya Khanal
╠²
The document discusses computer viruses, including what they are, common symptoms, types, and methods of prevention. It defines viruses as malicious programs that replicate by modifying other programs and spread from computer to computer. The document outlines types like boot viruses, program viruses, and macro viruses. It also provides recommendations for prevention such as installing antivirus software, keeping systems updated, using strong passwords, and backing up files. The role of antivirus programs in detecting and removing malware through signature-based scanning is also covered.Computer Virus
Computer VirusOECLIB Odisha Electronics Control Library
╠²
Computer viruses are malicious programs that can damage systems and erase data. There are different types like viruses, worms, and Trojan horses. Viruses piggyback on other programs to replicate, worms use networks to spread, while Trojans masquerade as useful programs but have hidden harms. Signs of infection include slow performance, crashes, and missing files. Regular antivirus updates, secure practices like avoiding untrusted sources can help prevent damage from viruses.What is computer
What is computerChandnisinghkhushwaha
╠²
Supercomputers are the most powerful and expensive computers, used to solve complex science and engineering problems through parallel processing of up to ten trillion calculations per second. Mainframes are similar but perform many concurrent operations for large organizations, while servers store data and applications to solve smaller problems for many users simultaneously. Workstations are high-end computers for one user for complex science, math, and engineering tasks. Personal computers are smaller computers designed for individual use in homes and small offices. Microcontrollers are embedded processors that control machinery. Smartphones perform computer-like functions with touchscreens and apps.Taking care of your computers
Taking care of your computersJean Ulpindo
╠²
The document provides tips for caring for and maintaining a laptop computer. It recommends keeping liquids, food, and other debris away from the laptop. Important maintenance steps include using antivirus software, cleaning the laptop regularly by removing dust and debris, protecting the screen, and avoiding rapid temperature changes or heavy objects on top of the laptop. Proper handling and use of a laptop case can help prevent damage.Computer virus
Computer virusWalden University
╠²
Computer viruses can spread easily over the internet. A true virus is capable of self-replication and can spread between files, disks, or hosts. There are over 30,000 computer viruses in existence with over 300 new ones created each month. Common symptoms of a virus attack include computers running slower, files disappearing, and systems crashing. The most common way viruses spread today is through the internet. Viruses are classified into categories like stealth, polymorphic, and armored and types like worms, trojan horses, and macros. Protection methods include having proper anti-virus software, configurations, and only running necessary programs.Types of software
Types of softwarelatifah2001
╠²
There are two main types of software: system software and application software. System software includes operating systems and disk operating systems, which allow hardware and applications to communicate. Application software accomplishes specific tasks and is divided into user-designed and ready-made categories. User-designed software is tailored for a specific organization, while ready-made software like word processors and spreadsheets are off-the-shelf packages that may not fully suit an organization's needs but are cheaper and easier to use.What is computer hardware and software
What is computer hardware and softwareparag dhok
╠²
The document explains the distinction between computer hardware, which refers to the physical components of a computer system, and software, which consists of the programs and instructions that enable hardware functionality. It categorizes software into system software, which controls hardware operations, and application software, which allows users to perform specific tasks. Additionally, it outlines various hardware components such as the motherboard, CPU, RAM, and hard disk, and describes their respective roles within a computer system.Virus and Anti Virus - Types of Virus and Anti Virus
Virus and Anti Virus - Types of Virus and Anti VirusAdeel Rasheed
╠²
The document provides an overview of computer viruses, including their definitions, types, and sources of infection, as well as explaining how antivirus software functions to detect and eliminate these threats. It details various types of viruses like macro, memory resident, and email viruses, and describes the mechanisms of antivirus software in scanning and quarantining infected files. Additionally, it lists popular antivirus software options available on the market, highlighting features and subscription costs for products like Bit Defender, Norton Antivirus, McAfee, Kaspersky, and Avast.Computer software
Computer softwarejuna luna
╠²
The document provides an overview of computer software, dividing it into system software, which manages hardware and provides a platform for application software, and application software, which helps users perform specific tasks. Examples of system software include operating systems like Microsoft Windows and MS-DOS, while application software examples include Microsoft Office, Google Chrome, and inventory management software. Additionally, it discusses the roles of linkers and boot sectors in the software ecosystem.CS6004 Cyber Forensics
CS6004 Cyber ForensicsKathirvel Ayyaswamy
╠²
The document provides an extensive overview of computer forensics, including its definition, goals, and various techniques for investigating computer-related crimes such as identity theft and cybercrime. It discusses the importance of digital evidence, its admissibility in court, and specific case studies illustrating failures in electronic records authentication. Additionally, it covers the roles of various stakeholders in computer forensics, including law enforcement and private corporations, and outlines the types and categories of cybercrime.Computer security
Computer securityfiza1975
╠²
The document discusses computer security threats and measures. It describes types of security like hardware security, software security and network security. It then discusses various malicious codes like viruses, trojans, worms and logic bombs. It also discusses hacking, natural threats like fires and floods, and theft. It concludes by describing various security measures that can be taken like using antivirus software, firewalls, encryption, backups and focusing on the human aspect of security.Computer Viruses
Computer VirusesAnnies Minu
╠²
1. Computer viruses are programs that can copy themselves and infect computers without permission by attaching to other files or programs.
2. Viruses have existed since the early 1970s and have caused issues like slow performance, crashes, missing files, and unexpected pop-ups.
3. There are many types of viruses including file infectors, macro viruses, and polymorphic viruses that disguise their code, and each can impact computers in different ways such as corrupting files or redirecting web browsers.Computer security and
Computer security andRana Usman Sattar
╠²
This document discusses various topics related to computer security including risks, attacks, safeguards, and ethics. It describes common security threats like viruses, hacking, denial of service attacks, and information theft. It also outlines methods to identify users, protect against threats, and investigate security incidents through digital forensics. Safeguards include firewalls, antivirus software, encryption, and physical access controls.Threats to a computer
Threats to a computer FCA - Future Chartered Accountants
╠²
This document is a project report submitted by Deeptika Soni on threats to computers. It discusses various types of threats like viruses, worms, hackers and their symptoms. It outlines system requirements and provides an index with sections on virus components, how threats are noticed, suggestions to prevent threats, and conclusions. The report references hardware and software vulnerabilities that can be exploited by interceptions, interruptions, modifications and fabrications. It notes threats involve theft, destruction or unauthorized access and tampering with computer assets.System software vs application software
System software vs application softwarebaabtra.com - No. 1 supplier of quality freshers
╠²
The document discusses the differences between system software and application software. It defines system software as programs that enable application software to interact with hardware and control computer hardware. Application software is defined as end-user software that can be general purpose, meant for common tasks, or special purpose, meant for specific tasks. Examples are provided of operating systems, device drivers, and servers as system software and office suites, media players, ERP software and games as application software.Virus and malware presentation
Virus and malware presentationAmjad Bhutto
╠²
Viruses and malware can damage computers. Viruses spread by copying themselves, while malware is designed to access or harm devices without owner knowledge. Common malware includes adware, bugs, rootkits, Trojans, and ransomware. It is important to use updated antivirus software, strong passwords, firewalls, and be cautious of suspicious links and downloads to protect devices from viruses and malware.Computer maintenance
Computer maintenanceCelia Bandelier
╠²
This document provides guidance on performing preventative maintenance on a computer to improve performance and extend its lifespan. It recommends cleaning the external components like the monitor, keyboard, and mouse regularly, as dust can accumulate quickly. Internally, it suggests using the Disk Cleanup and Disk Defragmenter tools periodically to free up hard drive space and optimize file placement. It also stresses the importance of installing operating system and software updates, scanning for viruses regularly, and backing up files in case of hardware failure or malware infection. Regular maintenance through cleaning, optimization, and backup is presented as an effective way to care for a computer over time.Computer Malware
Computer Malwareaztechtchr
╠²
Malware refers to unwanted software that can damage computers, including viruses, trojans, worms, spyware, and more. Viruses attach to files and programs to spread without permission and can damage systems. Trojans also spread unwittingly but allow hackers to access and control infected devices. Worms multiply to use up memory and resources. Spyware collects personal information without consent. Users can protect against malware through antivirus software, firewalls, safe computing habits like avoiding suspicious downloads and emails, and using strong passwords.Information Processing Cycle
Information Processing Cycle MudAssar IQbal
╠²
This document discusses the key components of computer systems: input, processing, storage, and output. It lists common input devices like keyboards and mice that send data to computers. It describes processing as passing data through stages and the CPU as the component that performs operations. It defines output as any information sent from the computer via monitors, printers, or other devices. It also discusses storage devices like hard drives that hold processed data for future use.Virus, Worms And Antivirus
Virus, Worms And AntivirusLokesh Kumar N
╠²
The document discusses computer viruses and antivirus technologies. It begins with defining computer viruses and outlining their history. It then analyzes three common types of viruses: file infectors, macro viruses, and the "I LOVE YOU" virus. The document also describes how antivirus software detects and removes viruses and outlines best practices for preventing virus infections like regular backups and keeping antivirus definitions up to date.Recently uploaded (10)
cambios_emocionales en los traumas presentes en adolescentes
cambios_emocionales en los traumas presentes en adolescentesvivianyarenivallecil
╠²
cambios emocionalesGazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places G-Krasno.pdf
Gazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places G-Krasno.pdfpeivhau
╠²
Detailed gazetteer of cities, towns and villages of Russia. Census results. Name changes. Incorporations. Latitudes and longitudes.Gazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places A-F.pdf
Gazetteer of Russia. Part: Populated places A-F.pdfpeivhau
╠²
Detailed gazetteer of cities, towns and villages of Russia. Census results. Name changes. Incorporations. Latitudes and longitudes. Aylanmadan olinadigan soliq.2025 yil.pdf
Aylanmadan olinadigan soliq.2025 yil.pdfilxomislomov2020
╠²
soliqlar. Aylanmadan olinadigan soliq.soliq 2025.Qarshi davlat texnika universiteti.soliq stavkalari 2025 y. O'zR soliq kodeksi.Prezentatsiya 2025. yFlashcards Animais brasileiros Ilustrado Verde.pdf
Flashcards Animais brasileiros Ilustrado Verde.pdfPriscilaRibeiro803210
╠²
Jogo com animais brasileirospdf-p-classtruncatedtext-module-lineclamped-85ulhh-style-max-lines5topik-tema...
pdf-p-classtruncatedtext-module-lineclamped-85ulhh-style-max-lines5topik-tema...Ifa Nofalia
╠²
bjbij jknkj knlk ml ko k lk lkmk k kmpom kmp kl pk km op lk ok p m k k ,l pom l pmfpoasfmasmfp om k kmp kla fpmpaf pkokmp pmppmpa fkmpo l pmo l pamfomaf afpomopafa pompo kmapofma poąĮą░ą║ą░ąĘ ą┐čĆąŠ ąĘą░čĆą░čģčāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅą┤ąŠ 1 ą║ą╗ą░čüčā kg72 2025
ąĮą░ą║ą░ąĘ ą┐čĆąŠ ąĘą░čĆą░čģčāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅą┤ąŠ 1 ą║ą╗ą░čüčā kg72 2025AleksSaf
╠²
ąĮą░ą║ą░ąĘ ą┐čĆąŠ ąĘą░čĆą░čģčāą▓ą░ąĮąĮčÅą┤ąŠ 1 ą║ą╗ą░čüčā 2025Ad
computer-virus-and-anti-virus-160219142022 (1).pdf
- 2. ’āśWhat is a computer virus? ’āśWhat a computer virus do? ’āśHistory of virus. ’āśWhy do people create viruses? ’āśHow do viruses spread? ’āśSigns of a viruses in computer. ’āśTypes of computer viruses. ’āśAnti virus software. ’āśHow an Anti virus works. ’āśHow to Protect your System Against Virus? CONTENTS
- 4. ’āśComputer viruses are small software or code that can cause damage to your data and software on a computer. What is a computer virus ?
- 5. ’āśA virus tries to take control of computer system at the first opportunity available. ’āśAlso it makes copies of it self and try to carry harmful task written in its program. ’āś This process can happen so quickly that the user is not even aware of the presence of a virus in computer. What a computer virus do?
- 6. Like any other field in computer science viruses have evolved over the years. ’āśThe first computer virus was called ŌĆśCreeperŌĆÖ. ’āśIt was invented in the early 1971 by Bob Thomas. ’āśThis program has been designed not to damage the computer, but only to display a messages. ’āśSince then, millions of viruses have been invented. History of Virus
- 7. ’āśTo take control of a computer and use it for specific tasks. ’āśTo steal sensitive information (credit card numbers, passwords, personal details, data etc.) Why do People Create Computer Viruses? Any programmer can make a virus to:
- 8. ’āśTo take money. ’āśTo prove ones skill or for revenge purposes. ’āśTo disable a computer or network. Any programmer can make a virus to: Why do People Create Computer Viruses?
- 9. ’āśFrom removable media. How do viruses spread?
- 10. How do viruses spread? ’āśFrom downloads off the Internet.
- 11. ’āśAnd from e-mail attachments. How do viruses spread?
- 12. ’āśYour computer functions slower than normal. ’āśYour computer responds slowly and freezes often. ’āśYour computer restarts itself often. How to detect a Virus Some signs that may indicate that your computer is infected include:
- 13. How to detect a Virus ’āśYou see uncommon error messages. ’āśApplications won't start. ’āśYour antivirus has disappeared, and firewall is disabled Some signs that may indicate that your computer is infected include:
- 14. Types of computer viruses 1. Macro virus 2. File Infector virus 3. Boot sector virus 4. E-mail virus 5. Trojan virus 6. Resident virus 7. Multipartite virus 8. Worm virus There are so many types of computer viruses some of them are :
- 16. ’āśAn antivirus software is a computer program that identify and remove computer viruses, and other malicious software like Worms and Trojans from an infected computer. ’āśAlso an antivirus software protects the computer from further virus attacks. Anti virus software
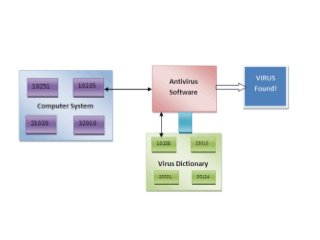
- 17. ’āśThe antivirus software examines each and every file in a computer and examines its content with the virus definitions stored in its virus dictionary. ’āśA virus dictionary is an inbuilt file belonging to an antivirus software that contains code identified as a virus by the antivirus authors. How an anti virus works?
- 19. How to Protect your System Against Virus? To Protect your system against Viruses you have to follow these steps :
- 20. How to Protect your System Against Virus? ’āśInstall a good Anti-Virus software on your computer. ’āśUpdate Anti-Virus regularly. To Protect your system against Viruses you have to follow these steps :
- 21. How to Protect your System Against Virus? ’āśBe careful while Downloading files or programs from the internet. ’āśAlways scan your floppies, CDs, flash drives before using them. To Protect your system against Viruses you have to follow these steps :
- 22. ’āśDo not use pirated software. ’āśTurn on firewall of your computer operating system. How to Protect your System Against Virus? To Protect your system against Viruses you have to follow these steps :
- 24. Q ?