Concept learning
- 1. MUSA AL HAWAMDAH / 128129001011 15-10-2012
- 2. Concept Learning as Search: ? Concept learning can be viewed as the task of searching through a large space of hypothesis implicitly defined by the hypothesis representation. ? The goal of the concept learning search is to find the hypothesis that best fits the training examples.
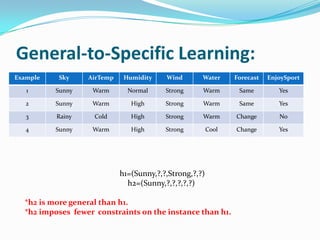
- 4. General-to-Specific Learning: Example Sky AirTemp Humidity Wind Water Forecast EnjoySport 1 Sunny Warm Normal Strong Warm Same Yes 2 Sunny Warm High Strong Warm Same Yes 3 Rainy Cold High Strong Warm Change No 4 Sunny Warm High Strong Cool Change Yes h1=(Sunny,?,?,Strong,?,?) h2=(Sunny,?,?,?,?,?) *h2 is more general than h1. *h2 imposes fewer constraints on the instance than h1.
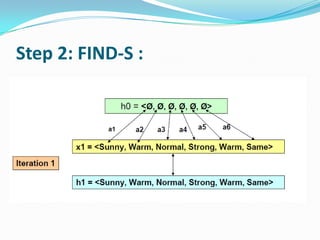
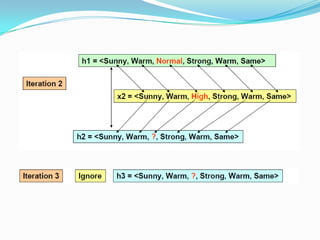
- 5. FIND-S: Finding a Maximally Specific Hypothesis: 1-Initialize h to the most specific hypotesis in h 2-for each positive training instance x - For each attribute constraint aj in h if the constraint aj is satisfied by x then do nothing else replace aj in h by the next more general constraint that is satisfied by x 3- output hypothesis h.
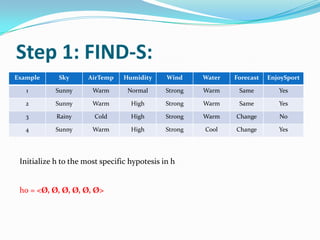
- 6. Step 1: FIND-S: Example Sky AirTemp Humidity Wind Water Forecast EnjoySport 1 Sunny Warm Normal Strong Warm Same Yes 2 Sunny Warm High Strong Warm Same Yes 3 Rainy Cold High Strong Warm Change No 4 Sunny Warm High Strong Cool Change Yes Initialize h to the most specific hypotesis in h h0 = <?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?>
- 7. Step 2: FIND-S :
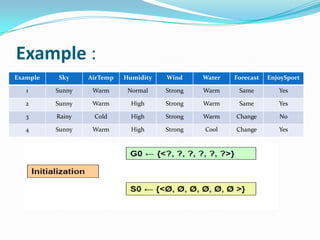
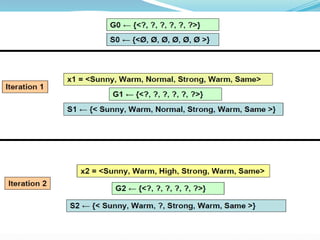
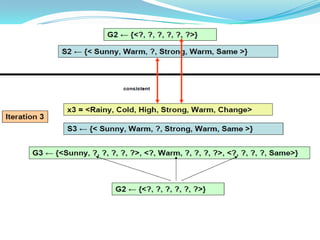
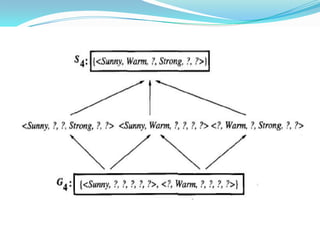
- 10. ? Version Space: The set of all valid hypotheses provided by an algorithm is called version space (VS)with respect to the hypothesis space Hand the given example set D. ? Candidate-Elimination Algorithm: * The Candidate-Eliminationalgorithm finds all describable hypotheses that are consistent with the observed training examples. * Hypothesis is derived from examples regardless of whether x is positive or negative example
- 11. LIST-THEN-ELIMINATE Algorithm to Obtain Version Space:
- 12. ? In principle, the LIST-THEN-ELIMINATE algorithm can be applied whenever the hypothesis space H is finite. ? It is guaranteed to output all hypotheses consistent with the training data. ? Unfortunately, it requires exhaustively enumerating all hypotheses in H-an unrealistic requirement for all but the most trivial hypothesis spaces.
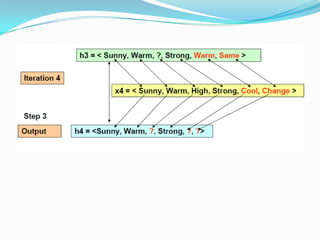
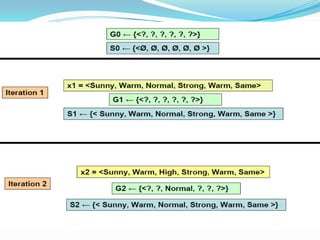
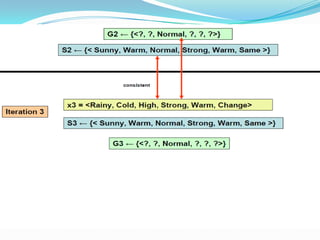
- 13. Candidate-Elimination Algorithm: ?The CANDIDATE-ELIMINATION algorithm works on the same principleas the above LIST-THEN- ELIMINATE algorithm. ?It employs a much more compact representation of the version space. ?In this the version spaceis represented by its most general and least general members (Specific). ?These members form general and specific boundary sets that delimit the version space within the partially ordered hypothesis space.
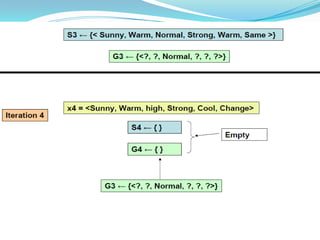
- 15. Example : Example Sky AirTemp Humidity Wind Water Forecast EnjoySport 1 Sunny Warm Normal Strong Warm Same Yes 2 Sunny Warm High Strong Warm Same Yes 3 Rainy Cold High Strong Warm Change No 4 Sunny Warm High Strong Cool Change Yes
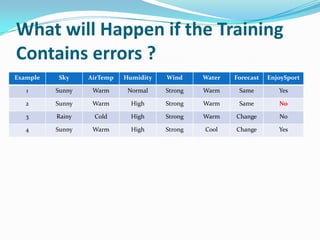
- 20. What will Happen if the Training Contains errors ? Example Sky AirTemp Humidity Wind Water Forecast EnjoySport 1 Sunny Warm Normal Strong Warm Same Yes 2 Sunny Warm High Strong Warm Same No 3 Rainy Cold High Strong Warm Change No 4 Sunny Warm High Strong Cool Change Yes