concept of different bodies
- 1. Name: I.Patel vaibhav II.Patel devang III.Parmar hiren IV.Himanshu olkiya V.Bhalodiya jenish Subject : Heat transfer
- 2. Concept Of Different Bodies
- 3. Black Body: a black body is an object that absorbs all the radiant energy reaching its surface from all the direction with all the with all the wavelengths. it is perfect absorbing body.
- 4. Blackbody Radiation i. The characteristics of a blackbody are : ii. It is a perfect emitter. iii. At any prescribed temperature it has the highest monochromatic emissive power at all wave lengths. iv. A blackbody absorbs all the incident energy and there fore A = al = 1. v. It is non reflective body (t=0). vi. It is opaque (t = 0). vii. It is a diffuse emitter
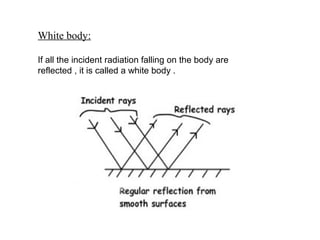
- 5. White body: If all the incident radiation falling on the body are reflected , it is called a white body .
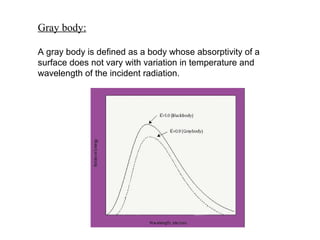
- 6. Gray body: A gray body is defined as a body whose absorptivity of a surface does not vary with variation in temperature and wavelength of the incident radiation.
- 8. Opaque body: When no irradiation is transmitted through the body, it is called ‘opaque body’ . Examples : all the thick metallic and non- metalic surface , all liquids, etc.
- 9. Transparent body: When all the irradiation is transmitted through the body, it is called transparent body. For transparent body : a = 0 , p = 0 , t = 1 For example : dry air
- 10. Regular and diffuse reflection Regular reflection: If the angle between the reflected beam and normal to the surface equals the angle made by the irradiation with the same normal then it is called regular or specular or highly polished one.
- 11. Diffused reflection : In this case, the incident radiation beam is reflected in all the directions. The reflection from real surface is neither diffused nor regular but combination of above two and its specular behaviour is shown in figure.
- 12. Thank you