ConcurrentHashMap Code Reading
- 1. ConcurrentHashMap Code Reading Ω«ÃÔ ÷±–– <kakuda@gmail.com>
- 2. Agenda ? ú ±∏ ? Overview ? ’i§‡ ? §fi§»§·
- 3. ú ±∏
- 4. ú ±∏§π§Î§‚§Œ ? Eclipse ? •Ω©`•π ? ConcurrentHashMap.java ? •∆•π•»•±©`•π ? JSR166TestCase.java ? ConcurrentHashMapTest.java ? ConcurrentHashMap§ÀÈv§π§Î≤Œ’’ŸY¡œ ? ö›∫œ§§
- 5. •Ω©`•π§Œ»°µ√àˆÀ˘ ? ConcurrentHashMap.java§œJDK§Ë§Í ? •∆•π•»•±©`•π§œDoug Lea§µ§Û§Œ•µ•§•»§Ë§Í http://gee.cs.oswego.edu/dl/concurrency-interest/
- 6. ≤Œ’’§∑§øŸY¡œ ? JavaDoc http://java.sun.com/javase/ja/6/docs/ja/api/java/util/concurrent/ ConcurrentHashMap.html ? IBM developerWorks:Éû§Ï§øHashMap§Œòã∫B http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/jp/java/library/j-jtp08223/ ? IT•¢©`•≠•∆•Ø•» J2SE 5.0§Œ–¬ôCƒ‹ http://www.itarchitect.jp/technology_and_programming/-/24161-3.html ? Servlet Gardern@§œ§∆§ http://d.hatena.ne.jp/yokolet/20071005
- 7. Overview
- 8. Overview ? Constants: 6§ƒ ? Field: 6§ƒ ? •Ê©`•∆•£•Í•∆•£: 2§ƒ(hash(), segmentFor()) ? •§•Û• ©`•Ø•È•π: 2§ƒ(HashEntry, Segment) ? Public •·•Ω•√•…: 24•≥(Constructor§œ5§ƒ) ? Iterator•µ•›©`•»: 8§ƒ ? Serialization•µ•›©`•»: 2§ƒ(writeObject(), readObject())
- 9. ∂‡∑÷÷ÿ“™§ •»•≥ ? Constants: 6§ƒ ? Field: 6§ƒ ? •Ê©`•∆•£•Í•∆•£: 2§ƒ(hash(), segmentFor()) ? •§•Û• ©`•Ø•È•π: 2§ƒ(HashEntry, Segment) ? Public •·•Ω•√•…: 24•≥(Constructor§œ5§ƒ) ? Iterator•µ•›©`•»: 8§ƒ ? Serialization•µ•›©`•»: 2§ƒ(writeObject(), readObject())
- 10. ΩÒªÿ§œ∏Óꀧπ§Î•»•≥ ? Constants: 6§ƒ ? Field: 6§ƒ ? •Ê©`•∆•£•Í•∆•£: 2§ƒ(hash(), segmentFor()) ? •§•Û• ©`•Ø•È•π: 2§ƒ(HashEntry, Segment) ? Public •·•Ω•√•…: 24•≥(Constructor§œ5§ƒ) ? Iterator•µ•›©`•»: 8§ƒ ? Serialization•µ•›©`•»: 2§ƒ(writeObject(), readObject())
- 11. ’i§‡
- 12. •≥•Û•π•»•È•Ø•ø public ConcurrentHashMap() { this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL); } public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL); } public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL); }
- 13. •≥•Û•π•»•È•Ø•ø /** •«•’•©•Î•»§Œ≥ı∆⁄»›¡ø */ static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; /** •«•’•©•Î•»§Œÿì∫…ÇS ˝ */ static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; /** •«•’•©•Î•»§ŒÅK––ÑI¿Ì•Ï•Ÿ•Î */ static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
- 14. •≥•Û•π•»•È•Ø•ø /** ◊Ó¥ÛSegment ˝?1§Ú16•”•√•»∑÷◊Û§À•∑•’•»§∑§∆§Î§Œ§«65536 */ static final int MAX_SEGMENTS = 1 << 16; ... public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) { if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); // ÅK––ÑI¿Ì•Ï•Ÿ•Î§¨◊Ó¥Û•ª•∞•·•Û•» ˝§Ú≥¨§®§∆§œ§ §È§ §§ if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS) concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS; ...
- 15. Segment ˝§ŒõQ∂® /** §…§ŒSegment§À§¢§Î§´§ÚÃÿ∂®§π§Î§ø§·§Œ•fi•π•ØÇé */ final int segmentMask; /** §…§ŒSegment§À§¢§Î§´§ÚÃÿ∂®§π§Î§ø§·§Œ•∑•’•»Çé */ final int segmentShift; // Segment§»Hash•®•Û•»•Í§Œ◊Óflm§ “˝ ˝§Ú“䧃§±§Î int sshift = 0; int ssize = 1; while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) { ++sshift; ssize <<= 1; } // currencyLevel§¨16(•«•’•©•Î•»)§Œïr°¢sshift§œ4°¢ssize§œ16§À§ §Î segmentShift = 32 - sshift; // 28(32§œ32bit§Œ§≥§»?) segmentMask = ssize - 1; // 15(0b0111) this.segments = Segment.newArray(ssize);
- 16. Segment§Œ…˙≥… /** ◊Ó¥Û»›¡ø?1§Ú30•”•√•»∑÷◊Û§À•∑•’•»§∑§∆§Î§Œ§«1073741824 */ static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; // Segment§Œ≥ı∆⁄»›¡ø§ŒÀ„≥ˆ if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; int c = initialCapacity / ssize; if (c * ssize < initialCapacity) ++c; int cap = 1; while (cap < c) cap <<= 1; for (int i = 0; i < this.segments.length; ++i) this.segments[i] = new Segment<K,V>(cap, loadFactor); }
- 17. Segment§»§œ ? ConcurrentHashMap.java§À§∆∂®¡x§µ§Ï§∆ §§§Î•§•Û• ©`•Ø•È•π ? 1§ƒ§ŒConcurrentHashMap•§•Û•π•ø•Û•π §À—} ˝(•«•’•©•Î•»16)§ŒSegment§Ú≥÷§ƒ ? •œ•√•∑•Â•∆©`•÷•Î§ŒÃÿÑe•–©`•∏•Á•Û ? ReentrantLock§Œ•µ•÷•Ø•È•π
- 18. Segment§Œ•≥•Û•π•»•È•Ø•ø static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable { ... transient int threshold; // ∏˜Segment§ÀHashEntry§Œ≈‰¡–§Ú±£≥÷ transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table; ... Segment(int initialCapacity, float lf) { loadFactor = lf; setTable(HashEntry.<K,V>newArray(initialCapacity)); } ... void setTable(HashEntry<K,V>[] newTable) { threshold = (int)(newTable.length * loadFactor); table = newTable; }
- 19. HashEntry§»§œ ? ConcurrentHashMap.java§À§∆∂®¡x§µ§Ï§∆ §§§Î•§•Û• ©`•Ø•È•π ? 1§ƒ§ŒSegment•§•Û•π•ø•Û•π§À1§ƒ“‘…œ§Œ HashEntry§Ú≥÷§ƒ ? •’•£©`•Î•…§Àkey, hashÇé, value, next(¥Œ§Œ HashEntry)§Ú≥÷§ƒ ? key, hash, next§œ?nal
- 20. HashEntry static final class HashEntry<K,V> { final K key; final int hash; volatile V value; final HashEntry<K,V> next; HashEntry(K key, int hash, HashEntry<K,V> next, V value) { this.key = key; this.hash = hash; this.next = next; this.value = value; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") static final <K,V> HashEntry<K,V>[] newArray(int i) { return new HashEntry[i]; } }
- 22. ≥ß±≤µ≥æ±≤‘≥Ÿ°¢±·≤π≤ı≥Û∑°≤‘≥Ÿ∞˘≤‚§Œππ‘Ï ConcurrentHashMap
- 23. ≥ß±≤µ≥æ±≤‘≥Ÿ°¢±·≤π≤ı≥Û∑°≤‘≥Ÿ∞˘≤‚§Œππ‘Ï Segment Segment ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 24. ≥ß±≤µ≥æ±≤‘≥Ÿ°¢±·≤π≤ı≥Û∑°≤‘≥Ÿ∞˘≤‚§Œππ‘Ï Hash Entry Segment Segment ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 25. ≥ß±≤µ≥æ±≤‘≥Ÿ°¢±·≤π≤ı≥Û∑°≤‘≥Ÿ∞˘≤‚§Œππ‘Ï Hash Entry Segment Hash Entry Segment ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 26. ≥ß±≤µ≥æ±≤‘≥Ÿ°¢±·≤π≤ı≥Û∑°≤‘≥Ÿ∞˘≤‚§Œππ‘Ï Hash Hash Entry Segment Entry Hash Entry Segment ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 27. ≥ß±≤µ≥æ±≤‘≥Ÿ°¢±·≤π≤ı≥Û∑°≤‘≥Ÿ∞˘≤‚§Œππ‘Ï Hash Hash Entry Segment Entry Hash Hash Entry Segment Entry ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 28. ≥ß±≤µ≥æ±≤‘≥Ÿ°¢±·≤π≤ı≥Û∑°≤‘≥Ÿ∞˘≤‚§Œππ‘Ï Hash Hash Hash Entry Segment Entry Entry Hash Hash Entry Segment Entry ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 29. ≥ß±≤µ≥æ±≤‘≥Ÿ°¢±·≤π≤ı≥Û∑°≤‘≥Ÿ∞˘≤‚§Œππ‘Ï Hash Hash Hash Entry Segment Entry Entry ågÎH§Œ•¡•ß©`•Û ˝§œ 1°´2Çħاȧ§ Hash Hash Entry Segment Entry ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 30. ≥ß±≤µ≥æ±≤‘≥Ÿ°¢±·≤π≤ı≥Û∑°≤‘≥Ÿ∞˘≤‚§Œππ‘Ï Hash Hash Hash Entry Segment Entry Entry ågÎH§Œ•¡•ß©`•Û ˝§œ 1°´2Çħاȧ§ Hash Hash Entry Segment Entry ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Hash Entry Segment
- 31. ≥ß±≤µ≥æ±≤‘≥Ÿ°¢±·≤π≤ı≥Û∑°≤‘≥Ÿ∞˘≤‚§Œππ‘Ï Hash Hash Hash Entry Segment Entry Entry ågÎH§Œ•¡•ß©`•Û ˝§œ 1°´2Çħاȧ§ Hash Hash Entry Segment Entry ConcurrentHashMap ? ? »´Segment§¨¬Ò§fi§√§ø§ÈSegment ? §Œ•µ•§•∫§œ2±∂§Àíàè৵§Ï§Î Hash Entry Segment
- 32. ConcurrentHashMap#get public V get(Object key) { // ”Χ®§È§Ï§ø•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú‘™§À§¡§„§Û§»§∑§ø•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú«Û§·§Î int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); // •œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§À‘ìµ±§π§Î•ª•∞•·•Û•»§Ú“䧃§±Segment#get§Úcall return segmentFor(hash).get(key, hash); }
- 33. À˚§Œ÷˜“™•·•Ω•√•…§‚ À∆§ø§Ë§¶§ ÑI¿Ì public boolean remove(Object key, Object value) { int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); public boolean containsKey(Object key) { if (value == null) int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); return false; return segmentFor(hash).containsKey(key, hash); return segmentFor(hash).remove(key, hash, value) != } null; public V put(K key, V value) { } if (value == null) public boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) { throw new NullPointerException(); if (oldValue == null || newValue == null) int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); throw new NullPointerException(); return segmentFor(hash).put(key, hash, value, false); int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); } return segmentFor(hash).replace(key, hash, oldValue, public V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) { newValue); if (value == null) } throw new NullPointerException(); public V replace(K key, V value) { int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); if (value == null) return segmentFor(hash).put(key, hash, value, true); throw new NullPointerException(); } int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); return segmentFor(hash).replace(key, hash, value); }
- 34. À˚§Œ÷˜“™•·•Ω•√•…§‚ À∆§ø§Ë§¶§ ÑI¿Ì public boolean remove(Object key, Object value) { int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); public boolean containsKey(Object key) { if (value == null) int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); return false; return segmentFor(hash).containsKey(key, hash); return segmentFor(hash).remove(key, hash, value) != } null; public V put(K key, V value) { } if (value == null) public boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) { throw new NullPointerException(); if (oldValue == null || newValue == null) int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); throw new NullPointerException(); return segmentFor(hash).put(key, hash, value, false); int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); } return segmentFor(hash).replace(key, hash, oldValue, public V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) { newValue); if (value == null) } throw new NullPointerException(); public V replace(K key, V value) { int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); if (value == null) return segmentFor(hash).put(key, hash, value, true); throw new NullPointerException(); } int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); return segmentFor(hash).replace(key, hash, value); }
- 35. ConcurrentHashMap#hash ∫Œ§‰§√§∆§§§Î§´§Ô§´§Í§fi§ª§Û???orz private static int hash(int h) { // Spread bits to regularize both segment and index locations, // using variant of single-word Wang/Jenkins hash. h += (h << 15) ^ 0xffffcd7d; h ^= (h >>> 10); h += (h << 3); h ^= (h >>> 6); h += (h << 2) + (h << 14); return h ^ (h >>> 16); } HashMap#hash§Ë§ÍBetter§ åg◊∞§À÷√§≠ìQ§®§∆§Î http://www.concentric.net/ Ttwang/tech/inthash.htm §¨≤Œøº•Ω©`•π£ø
- 36. §§§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? Segment Segment ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 37. §§§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? Segment (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) Segment PUT ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 38. §§§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) Segment Segment ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 39. §§§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) Segment (°∞2°±, °∞b°±) Segment PUT ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 40. §§§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) Segment (°∞2°±, °∞b°±) Segment ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 41. §§§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) Segment (°∞3°±, °∞c°±) (°∞2°±, °∞b°±) Segment PUT ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 42. §§§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) Segment (°∞2°±, °∞b°±) Segment ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? (°∞3°±, °∞c°±) Segment
- 43. §§§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) Segment (°∞2°±, °∞b°±) Segment §¡§„§Û§»•–•È§±§∆§Ø§Ï§Î£° ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? (°∞3°±, °∞c°±) Segment
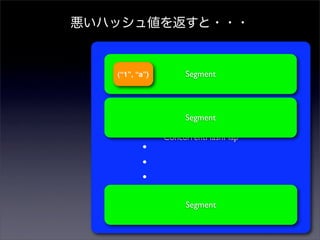
- 44. êô§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? Segment Segment ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 45. êô§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? Segment (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) Segment PUT ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 46. êô§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) Segment Segment ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 47. êô§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) Segment (°∞2°±, °∞b°±) Segment PUT ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 48. êô§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) (°∞2°±, Segment °∞b°±) Segment ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 49. êô§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) (°∞2°±, Segment °∞b°±) (°∞3°±, °∞c°±) Segment PUT ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 50. êô§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) (°∞2°±, Segment °∞b°±) (°∞3°±, °∞c°±) Segment ConcurrentHashMap ? ? ? Segment
- 51. êô§§•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú∑µ§π§»??? (°∞1°±, °∞a°±) (°∞2°±, Segment °∞b°±) (°∞3°±, °∞c°±) Segment ∆´§√§∆§∑§fi§§°¢ ConcurrentHashMap ? §π§¥§ØÑø¬ §¨êô§Ø§ §Î£° ? ? Segment
- 52. Segment#get V get(Object key, int hash) { if (count != 0) { // read-volatile // hash§Àœ‡µ±§π§ÎHashEntry§Œ“™Àÿ§Ú»°§Í≥ˆ§π HashEntry<K,V> e = getFirst(hash); while (e != null) { if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) { // HashEntry§Œ•œ•√•∑•ÂÇ駻•≠©`§¨ÅI∑Ω§»§‚∫œ§®§– V v = e.value; if (v != null) return v; return readValueUnderLock(e); // recheck } e = e.next; } } return null; }
- 53. Segment#containsKey ª˘±æSegment#get§»Õ¨§∏ boolean containsKey(Object key, int hash) { if (count != 0) { // read-volatile HashEntry<K,V> e = getFirst(hash); while (e != null) { if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) return true; e = e.next; } } return false; }
- 54. Segment#containsValue boolean containsValue(Object value) { if (count != 0) { // read-volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; // ≪اπ§Îø÷§Ï§¨§¢§Î§Œ§«◊˜òI”√§À÷√§§§∆§Î£ø int len = tab.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { for (HashEntry<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { V v = e.value; if (v == null) // recheck v = readValueUnderLock(e); // ¿Ì«¸…œ§≥§¶§§§¶§≥§»§¨§¢§Í§¶§Î§È§∑§§ if (value.equals(v)) return true; } } } return false; }
- 55. Segment#put V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { lock(); // HashEntry§Œ∏¸–¬œµ(put, remove, replace...)§œ•Ì•√•Ø§¨±ÿ“™ try { int c = count; if (c++ > threshold) // ensure capacity rehash(); // •µ•§•∫§¨§∑§≠§§Çé§Ú≥¨§®§ø§È∏˜“™Àÿ§Œ•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú‘Ÿ”ãÀ„ HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; int index = hash & (tab.length - 1); HashEntry<K,V> first = tab[index]; HashEntry<K,V> e = first; while (e != null && (e.hash != hash || !key.equals(e.key))) // §…§¶§§§¶•±©`•π? e = e.next; ...
- 56. Segment#put V oldValue; if (e != null) { oldValue = e.value; if (! onlyIfAbsent) e.value = value; } else { // ª˘±æ§œ§≥§≥§ÚÕ®§Î oldValue = null; ++modCount; // HashEntry§Œòã‘ϧ¨â‰∏¸§µ§Ï§øªÿ ˝§Úâ৉§π tab[index] = new HashEntry<K,V>(key, hash, first, value); count = c; // write-volatile } return oldValue; } finally { unlock(); } }
- 57. Segment#remove «∞∞Î≤ø∑÷§œSegment#put§»¥ÛÃÂÕ¨§∏ V remove(Object key, int hash, Object value) { lock(); try { int c = count - 1; // •µ•§•∫§Ú1§ƒúp§È§π HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; int index = hash & (tab.length - 1); HashEntry<K,V> first = tab[index]; HashEntry<K,V> e = first; while (e != null && (e.hash != hash || !key.equals(e.key))) e = e.next; V oldValue = null; ...
- 58. Segment#remove if (e != null) { V v = e.value; if (value == null || value.equals(v)) { oldValue = v; ++modCount; HashEntry<K,V> newFirst = e.next; for (HashEntry<K,V> p = first; p != e; p = p.next) newFirst = new HashEntry<K,V>(p.key, p.hash, newFirst, p.value); tab[index] = newFirst; count = c; // write-volatile } } return oldValue; } finally { unlock(); } }
- 59. Segment#remove if (e != null) { V v = e.value; if (value == null || value.equals(v)) { oldValue = v; ++modCount; HashEntry<K,V> newFirst = e.next; for (HashEntry<K,V> p = first; p != e; p = p.next) newFirst = new HashEntry<K,V>(p.key, p.hash, newFirst, p.value); tab[index] = newFirst; count = c; // write-volatile } } return oldValue; } finally { unlock(); } }
- 60. Segment#remove ? HashEntry§À§œnext§»§§§¶¥Œ§Œ“™Àÿ§Ú±Ì§π •’•£©`•Î•…§¨§¢§Î ? remove§¨––§Ô§Ï§Î§»next§Œ∏∂§±Ãʧ®§¨∞k…˙ §π§Î ? next•’•£©`•Î•…§œ?nal§ §Œ§«œ˜≥˝§∑§ø“™Àÿ§Ë §Í«∞§Ú◊˜§Í÷±§µ§ §±§Ï§–§ §È§ §§
- 61. A B C D E Segment Next = B Next = C Next = D Next = E Next = null
- 62. A B C D E Segment Next = B Next = C Next = D Next = E Next = null remove(°∞C°±)
- 63. A B D E Segment Next = B Next = C Next = E Next = null
- 64. Next§¨?nal§ §Œ§« A B D§Àâ‰∏¸§«§≠§ §§£°D E Segment Next = B Next = C Next = E Next = null
- 65. Next§¨?nal§ §Œ§« A B D§Àâ‰∏¸§«§≠§ §§£°D E Segment Next = B Next = C Next = E Next = null A§»B§œ◊˜§Í÷±§∑
- 66. Segment#rehash putïr§À•µ•§•∫§¨capacity§Ú≥¨§®§øïr§À∞k…˙ void rehash() { HashEntry<K,V>[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; if (oldCapacity >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) return; /* * Reclassify nodes in each list to new Map. Because we are * using power-of-two expansion, the elements from each bin * must either stay at same index, or move with a power of two * offset. We eliminate unnecessary node creation by catching ...
- 67. •≥•·•Û•»§Œ≥¨“‚‘U ? ∏˜•Í•π•»§Œ•Œ©`•…§Ú–¬§∑§§Map§À‘Ÿ∑÷Óê§π§Î°£2§ƒ§Œè䡶 § íàèà(Segment§»HashEntry)§Ú π§√§∆§§§Î§ø§·°¢Õ¨§∏ index§Ú±£§ƒ§´2§ƒ§Œo?set§ÚÕ¨ïr§À“∆Ñ”§µ§ª§ §±§Ï§–§ §È § §§°£next•’•£©`•Î•…§œâ‰§Ô§È§ §§§Œ§«°¢π≈§§•Œ©`•…§œ‘Ÿ ¿˚”√§«§≠≤ª±ÿ“™§ •Œ©`•…§Ú◊˜§È§ §Ø§∆§π§‡°£Ωy”㵃§À°¢•« •’•©•Î•»§Œthreshold§¿§»•∆©`•÷•Î§Ú2±∂§À§π§Îïr§À•Ø•Ì©` •Û§π§Î±ÿ“™§¨§¢§Î§Œ§œºs1/6°£÷√§≠ìQ§Ô§Îπ≈§§•Œ©`•…§œ reader•π•Ï•√•…§¨§π§∞§À•∆©`•÷•Î§Ú◊flñÀ§π§Î§≥§»§«≤Œ’’§µ §Ï§ §Ø§ §ÍGCåùœÛ§»§ §Î°£
- 68. Segment#clear void clear() { if (count != 0) { lock(); try { HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; for (int i = 0; i < tab.length ; i++) tab[i] = null; ++modCount; count = 0; // write-volatile } finally { unlock(); } } }
- 69. Segment#replace V replace(K key, int hash, V newValue) { lock(); try { HashEntry<K,V> e = getFirst(hash); while (e != null && (e.hash != hash || !key.equals(e.key))) e = e.next; V oldValue = null; if (e != null) { oldValue = e.value; e.value = newValue; } return oldValue; } finally { unlock(); } }
- 70. Segment#replace §Ω§Œ2 boolean replace(K key, int hash, V oldValue, V newValue) { lock(); try { HashEntry<K,V> e = getFirst(hash); while (e != null && (e.hash != hash || !key.equals(e.key))) e = e.next; boolean replaced = false; if (e != null && oldValue.equals(e.value)) { replaced = true; e.value = newValue; } return replaced; } finally { unlock(); } }
- 71. ConcurrentHashMap#isEmpty public boolean isEmpty() { final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments; int[] mc = new int[segments.length]; int mcsum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) { if (segments[i].count != 0) return false; else // »´segment§Œ•µ•§•∫§¨0§Œïr°¢§Ω§Ï§æ§Ï§Œâ‰∏¸ªÿ ˝§Œ∫Õ§Ú”ãÀ„§π§Î mcsum += mc[i] = segments[i].modCount; } ...
- 72. ConcurrentHashMap#isEmpty if (mcsum != 0) { // ∫Œ§´§∑§È§Œâ‰∏¸ (ABAÜñÓ}) §¨§¢§√§øàˆ∫œ for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) { if (segments[i].count != 0 || mc[i] != segments[i].modCount) return false; } } return true; }
- 73. isEmpty§Œ•≥•·•Û•»≥¨“‚‘U ? §§§ƒ§Œïrµ„§«§‚•∆©`•÷•Î§¨ø’§À§ §È§ §´§√§øàˆ∫œ°¢§¢§Î segment§Œ“ª“™Àÿ§¨◊∑º”§µ§ÏÑe§«◊flñÀ÷–§Àœ˜≥˝§µ§Ï§Î§»§§ §¶ABAÜñÓ}(°∏JavaÅK––ÑI¿Ì•◊•Ì•∞•È•fl•Û•∞°π15’¬≤Œ’’)§Ú ±‹§±§Î§ø§·§À∏˜segment§ŒmodCount§Ú◊∑€E§π§Î°£À˚§À ABAÜñÓ}§Œ”∞Ìë§Ú ‹§±§Îø…ƒ‹–‘§¨§¢§Îsize()§‰ containsValue()•·•Ω•√•…§«§‚Õ¨òî§ÀmodCount§Ú π§√§∆§§ §Î°£
- 74. ConcurrentHashMap#size ? §fi§∫§œ•Ì•√•Øüo§∑§«2ªÿ§fi§«•»•È•§§π§Î ? ˝§®§∆§§§ÎÈg§À°¢Ñe§«â‰∏¸ÑI¿Ì§¨––§Ô§Ï§ø §È§‰§Í÷±§π ? 2ªÿ§»§‚–∞ƒß§µ§Ï§∆§∑§fi§√§ø§È»´Segment§À •Ì•√•Ø§Ú§´§±§∆ ˝§®§Î
- 75. ConcurrentHashMap#size /** size()§»containsValue()§« π§Ô§Ï§Î */ static final int RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK = 2; public int size() { final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments; long sum = 0; long check = 0; int[] mc = new int[segments.length]; // Try a few times to get accurate count. On failure due to // continuous async changes in table, resort to locking. for (int k = 0; k < RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK; ++k) { check = 0; sum = 0; int mcsum = 0; ...
- 76. ConcurrentHashMap#size for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) { sum += segments[i].count; mcsum += mc[i] = segments[i].modCount; } if (mcsum != 0) { // ≥ı∆⁄◊¥ëB§´§Èâ‰∏¸§¨––§Ô§Ï§ø for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) { check += segments[i].count; if (mc[i] != segments[i].modCount) { // â‰∏¸§µ§Ï§ø check = -1; // force retry(°∏JavaÅK––ÑI¿Ì•◊•Ì•∞•È•fl•Û•∞°πP269) break; } } } if (check == sum) break; }
- 77. ConcurrentHashMap#size if (check != sum) { // Resort to locking all segments sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) //»´Segment§Ú•Ì•√•Ø segments[i].lock(); for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) sum += segments[i].count; for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) segments[i].unlock(); } if (sum > Integer.MAX_VALUE) return Integer.MAX_VALUE; else return (int)sum; }
- 78. ConcurrentHashMap#containsValue ConcurrentHashMap#size§»¥ÛÃÂÕ¨§∏ public boolean containsValue(Object value) { if (value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); // See explanation of modCount use above final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments; int[] mc = new int[segments.length]; // Try a few times without locking for (int k = 0; k < RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK; ++k) { int sum = 0; int mcsum = 0; ...
- 79. ConcurrentHashMap#containsValue for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) { int c = segments[i].count; // •·•‚•Í§ÚÕ¨∆⁄ªØ mcsum += mc[i] = segments[i].modCount; if (segments[i].containsValue(value)) return true; } boolean cleanSweep = true; if (mcsum != 0) { // ≥ı∆⁄◊¥ëB§´§Èâ‰∏¸§µ§Ï§ø for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) { int c = segments[i].count; // •·•‚•Í§ÚÕ¨∆⁄ªØ if (mc[i] != segments[i].modCount) { // â‰∏¸§µ§Ï§ø§Œ§«§‰§Í÷±§∑ cleanSweep = false; break; } } } if (cleanSweep) return false; }
- 80. ConcurrentHashMap#containsValue // Resort to locking all segments for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) segments[i].lock(); boolean found = false; try { for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) { if (segments[i].containsValue(value)) { // Segment#containsValue found = true; break; } } } finally { for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) segments[i].unlock(); } return found; }
- 81. §fi§»§·
- 82. §fi§»§· ? ConcurrentHashMap§œ°¢Segment§» HashEntry§»§§§¶•«©`•øòã‘ϧ¨∏Œ ? ∏flÀŸªØ§Œ§ø§·§À…´§Û§ §≥§»§Ú§‰§√§∆§Î ? ?nal§«readïr§œ•Ì•√•Ø§∑§ §§§Ë§¶§À ? hashÇé”ãÀ„§«§¡§„§Û§»§–§È§±§µ§ª§Î ? •Ì•√•ØÑI¿Ì§Ú◊Ó–°œfi§À“÷§®§Î
- 83. §¡§ §fl§À ? ConcurrentHashMap§Ë§ÍÀŸ§§ NonBlockingHashMap§»§§§¶§Œ§¨§¢§Î ? Azul Systems§ŒCli? Click œ◊˜ (DN$&6;OK)$P$&$QA/R$5F*. :L$@8M+0 :D$@8M+0 77768)*+.-./01.6591 !' !' &< HIE"" &< JKDE"" &' &' DE9F.G.05 DE9F.G.05 HIE>< :< :< :' JKDE>< :' < < HI ' ' JKD : & ! ; < = > ? : & ! ; < = > ? @AB08C. @AB08C. $ #$$$$%&''!$()*+$,-./01.2$3456 !"
- 84. ‘î§∑§Ø÷™§Í§ø§§»À§œ ? JavaOneŸY¡œ°∏A Lock-Free Hash Table°π http://www.azulsystems.com/events/javaone_2007/2007_LockFreeHash.pdf ? Blog”õ ¬°∏A Non-Blocking HashTable°π http://blogs.azulsystems.com/cli?/2007/03/a_nonblocking_h.html ? Highly Scalable Java http://sourceforge.net/projects/high-scale-lib
















![Segment§Œ…˙≥…
/** ◊Ó¥Û»›¡ø?1§Ú30•”•√•»∑÷◊Û§À•∑•’•»§∑§∆§Î§Œ§«1073741824 */
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// Segment§Œ≥ı∆⁄»›¡ø§ŒÀ„≥ˆ
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
int c = initialCapacity / ssize;
if (c * ssize < initialCapacity)
++c;
int cap = 1;
while (cap < c)
cap <<= 1;
for (int i = 0; i < this.segments.length; ++i)
this.segments[i] = new Segment<K,V>(cap, loadFactor);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-16-320.jpg)

![Segment§Œ•≥•Û•π•»•È•Ø•ø
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
...
transient int threshold;
// ∏˜Segment§ÀHashEntry§Œ≈‰¡–§Ú±£≥÷
transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table;
...
Segment(int initialCapacity, float lf) {
loadFactor = lf;
setTable(HashEntry.<K,V>newArray(initialCapacity));
}
...
void setTable(HashEntry<K,V>[] newTable) {
threshold = (int)(newTable.length * loadFactor);
table = newTable;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-18-320.jpg)

![HashEntry
static final class HashEntry<K,V> {
final K key;
final int hash;
volatile V value;
final HashEntry<K,V> next;
HashEntry(K key, int hash, HashEntry<K,V> next, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.hash = hash;
this.next = next;
this.value = value;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static final <K,V> HashEntry<K,V>[] newArray(int i) {
return new HashEntry[i];
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-20-320.jpg)
































![Segment#containsValue
boolean containsValue(Object value) {
if (count != 0) { // read-volatile
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; // ≪اπ§Îø÷§Ï§¨§¢§Î§Œ§«◊˜òI”√§À÷√§§§∆§Î£ø
int len = tab.length;
for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) {
for (HashEntry<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
V v = e.value;
if (v == null) // recheck
v = readValueUnderLock(e); // ¿Ì«¸…œ§≥§¶§§§¶§≥§»§¨§¢§Í§¶§Î§È§∑§§
if (value.equals(v))
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-54-320.jpg)
![Segment#put
V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
lock(); // HashEntry§Œ∏¸–¬œµ(put, remove, replace...)§œ•Ì•√•Ø§¨±ÿ“™
try {
int c = count;
if (c++ > threshold) // ensure capacity
rehash(); // •µ•§•∫§¨§∑§≠§§Çé§Ú≥¨§®§ø§È∏˜“™Àÿ§Œ•œ•√•∑•ÂÇé§Ú‘Ÿ”ãÀ„
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
HashEntry<K,V> first = tab[index];
HashEntry<K,V> e = first;
while (e != null && (e.hash != hash || !key.equals(e.key))) // §…§¶§§§¶•±©`•π?
e = e.next;
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-55-320.jpg)
![Segment#put
V oldValue;
if (e != null) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (! onlyIfAbsent) e.value = value;
}
else { // ª˘±æ§œ§≥§≥§ÚÕ®§Î
oldValue = null;
++modCount; // HashEntry§Œòã‘ϧ¨â‰∏¸§µ§Ï§øªÿ ˝§Úâ৉§π
tab[index] = new HashEntry<K,V>(key, hash, first, value);
count = c; // write-volatile
}
return oldValue;
} finally {
unlock();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-56-320.jpg)
![Segment#remove
«∞∞Î≤ø∑÷§œSegment#put§»¥ÛÃÂÕ¨§∏
V remove(Object key, int hash, Object value) {
lock();
try {
int c = count - 1; // •µ•§•∫§Ú1§ƒúp§È§π
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
HashEntry<K,V> first = tab[index];
HashEntry<K,V> e = first;
while (e != null && (e.hash != hash || !key.equals(e.key)))
e = e.next;
V oldValue = null;
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-57-320.jpg)
![Segment#remove
if (e != null) {
V v = e.value;
if (value == null || value.equals(v)) {
oldValue = v;
++modCount;
HashEntry<K,V> newFirst = e.next;
for (HashEntry<K,V> p = first; p != e; p = p.next)
newFirst = new HashEntry<K,V>(p.key, p.hash, newFirst, p.value);
tab[index] = newFirst;
count = c; // write-volatile
}
}
return oldValue;
} finally {
unlock();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-58-320.jpg)
![Segment#remove
if (e != null) {
V v = e.value;
if (value == null || value.equals(v)) {
oldValue = v;
++modCount;
HashEntry<K,V> newFirst = e.next;
for (HashEntry<K,V> p = first; p != e; p = p.next)
newFirst = new HashEntry<K,V>(p.key, p.hash, newFirst, p.value);
tab[index] = newFirst;
count = c; // write-volatile
}
}
return oldValue;
} finally {
unlock();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-59-320.jpg)






![Segment#rehash
putïr§À•µ•§•∫§¨capacity§Ú≥¨§®§øïr§À∞k…˙
void rehash() {
HashEntry<K,V>[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
return;
/*
* Reclassify nodes in each list to new Map. Because we are
* using power-of-two expansion, the elements from each bin
* must either stay at same index, or move with a power of two
* offset. We eliminate unnecessary node creation by catching
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-66-320.jpg)

![Segment#clear
void clear() {
if (count != 0) {
lock();
try {
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length ; i++)
tab[i] = null;
++modCount;
count = 0; // write-volatile
} finally {
unlock();
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-68-320.jpg)


![ConcurrentHashMap#isEmpty
public boolean isEmpty() {
final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments;
int[] mc = new int[segments.length];
int mcsum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) {
if (segments[i].count != 0)
return false;
else
// »´segment§Œ•µ•§•∫§¨0§Œïr°¢§Ω§Ï§æ§Ï§Œâ‰∏¸ªÿ ˝§Œ∫Õ§Ú”ãÀ„§π§Î
mcsum += mc[i] = segments[i].modCount;
}
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-71-320.jpg)
![ConcurrentHashMap#isEmpty
if (mcsum != 0) {
// ∫Œ§´§∑§È§Œâ‰∏¸ (ABAÜñÓ}) §¨§¢§√§øàˆ∫œ
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) {
if (segments[i].count != 0 || mc[i] != segments[i].modCount)
return false;
}
}
return true;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-72-320.jpg)


![ConcurrentHashMap#size
/** size()§»containsValue()§« π§Ô§Ï§Î */
static final int RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK = 2;
public int size() {
final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments;
long sum = 0;
long check = 0;
int[] mc = new int[segments.length];
// Try a few times to get accurate count. On failure due to
// continuous async changes in table, resort to locking.
for (int k = 0; k < RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK; ++k) {
check = 0;
sum = 0;
int mcsum = 0;
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-75-320.jpg)
![ConcurrentHashMap#size
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) {
sum += segments[i].count;
mcsum += mc[i] = segments[i].modCount;
}
if (mcsum != 0) { // ≥ı∆⁄◊¥ëB§´§Èâ‰∏¸§¨––§Ô§Ï§ø
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) {
check += segments[i].count;
if (mc[i] != segments[i].modCount) { // â‰∏¸§µ§Ï§ø
check = -1; // force retry(°∏JavaÅK––ÑI¿Ì•◊•Ì•∞•È•fl•Û•∞°πP269)
break;
}
}
}
if (check == sum) break;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-76-320.jpg)
![ConcurrentHashMap#size
if (check != sum) { // Resort to locking all segments
sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) //»´Segment§Ú•Ì•√•Ø
segments[i].lock();
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i)
sum += segments[i].count;
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i)
segments[i].unlock();
}
if (sum > Integer.MAX_VALUE)
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
else
return (int)sum;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-77-320.jpg)
![ConcurrentHashMap#containsValue
ConcurrentHashMap#size§»¥ÛÃÂÕ¨§∏
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// See explanation of modCount use above
final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments;
int[] mc = new int[segments.length];
// Try a few times without locking
for (int k = 0; k < RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK; ++k) {
int sum = 0;
int mcsum = 0;
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-78-320.jpg)
![ConcurrentHashMap#containsValue
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) {
int c = segments[i].count; // •·•‚•Í§ÚÕ¨∆⁄ªØ
mcsum += mc[i] = segments[i].modCount;
if (segments[i].containsValue(value)) return true;
}
boolean cleanSweep = true;
if (mcsum != 0) { // ≥ı∆⁄◊¥ëB§´§Èâ‰∏¸§µ§Ï§ø
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) {
int c = segments[i].count; // •·•‚•Í§ÚÕ¨∆⁄ªØ
if (mc[i] != segments[i].modCount) { // â‰∏¸§µ§Ï§ø§Œ§«§‰§Í÷±§∑
cleanSweep = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (cleanSweep) return false;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-79-320.jpg)
![ConcurrentHashMap#containsValue
// Resort to locking all segments
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i)
segments[i].lock();
boolean found = false;
try {
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i) {
if (segments[i].containsValue(value)) { // Segment#containsValue
found = true;
break;
}
}
} finally {
for (int i = 0; i < segments.length; ++i)
segments[i].unlock();
}
return found;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/concurrenthashmap-code-reading-1206295774186779-2/85/ConcurrentHashMap-Code-Reading-80-320.jpg)




