Conditional probability
Download as PPTX, PDF22 likes25,034 views
This document discusses conditional probability and independence. It defines conditional probability as P(B|A), the probability of event B given that event A has occurred. To calculate this, one considers only the outcomes where A occurred and calculates the fraction where B also occurred. Two events A and B are independent if P(B|A) = P(B), meaning the probability of B is unaffected by the occurrence of A. The general multiplication rule for any events A and B is P(A and B) = P(A) ├Ś P(B|A) or P(A) ├Ś P(B|A). Disjoint events cannot be independent as the occurrence of one rules out the other. Conditional probabilities are best understood
1 of 9
Downloaded 696 times








Recommended
Conditional Probability



Conditional ProbabilityMaria Romina Angustia
╠²
Conditional probability is the probability of an event occurring given that another event has occurred. It is calculated as the probability of both events occurring divided by the probability of the first event. An example is given of calculating the probability of drawing two white balls in succession from an urn without replacement. The formula for conditional probability is derived as the probability of events A and B occurring divided by the probability of A. This is demonstrated using an example of finding the percentage of friends who like chocolate that also like strawberry.Bayes Theorem



Bayes Theoremsabareeshbabu
╠²
Bayes' Theorem relates prior probabilities, conditional probabilities, and posterior probabilities. It provides a mathematical rule for updating estimates based on new evidence or observations. The theorem states that the posterior probability of an event is equal to the conditional probability of the event given the evidence multiplied by the prior probability, divided by the probability of the evidence. Bayes' Theorem can be used to calculate conditional probabilities, like the probability of a woman having breast cancer given a positive mammogram result, or the probability that a part came from a specific supplier given that it is non-defective. It is widely applicable in science, medicine, and other fields for revising hypotheses based on new data.Bayes' theorem



Bayes' theoremDr. C.V. Suresh Babu
╠²
This presentation gives a brief introduction about Bayes' Theorem and its applications in Artificial intelligencePROBABILITY AND IT'S TYPES WITH RULES



PROBABILITY AND IT'S TYPES WITH RULESBhargavi Bhanu
╠²
This document discusses types of probability and provides definitions and examples of key probability concepts. It begins with an introduction to probability theory and its applications. The document then defines terms like random experiments, sample spaces, events, favorable events, mutually exclusive events, and independent events. It describes three approaches to measuring probability: classical, frequency, and axiomatic. It concludes with theorems of probability and references.Geometric Distribution



Geometric DistributionRatul Basak
╠²
The document discusses the geometric distribution, a discrete probability distribution that models the number of Bernoulli trials needed to get one success. It defines the geometric distribution and gives its probability mass function. Some key properties and applications are discussed, including: the mean is 1/p, the variance is q/p^2, where q is 1-p. It is used in situations like modeling the probability of events occurring after repeated independent trials with a constant probability of success each trial. Examples given include analyzing success rates in sports and deciding when to stop research trials.Bayes rule (Bayes Law)



Bayes rule (Bayes Law)Tish997
╠²
This document discusses probability and Bayes' theorem. It provides examples of basic probability concepts like the probability of a coin toss. It then defines conditional probability as the probability of an event given another event. Bayes' theorem is introduced as a way to revise a probability based on new information. An example problem demonstrates how to calculate the probability of rain given a weather forecast using Bayes' theorem.Probability Distributions



Probability DistributionsBirinder Singh Gulati
╠²
It includes various cases and practice problems related to Binomial, Poisson & Normal Distributions. Detailed information on where tp use which probability.Conditional Probability



Conditional ProbabilityArijitDhali
╠²
These slides represent a brief idea about conditional probability along with illustrative examples and discussions. It also consists the use of sets to develop a better understanding for the students having the following theorem in their course.Basic concepts of probability



Basic concepts of probabilityAvjinder (Avi) Kaler
╠²
This document discusses basic concepts of probability, including:
- The addition rule and multiplication rule for calculating probabilities of compound events.
- Events can be disjoint (mutually exclusive) or not disjoint.
- The probability of an event occurring or its complement must equal 1.
- How to calculate the probability of at least one occurrence of an event using the complement.
- When applying the multiplication rule, you must consider whether events are independent or dependent.Sample Space and Event,Probability,The Axioms of Probability,Bayes Theorem



Sample Space and Event,Probability,The Axioms of Probability,Bayes TheoremBharath kumar Karanam
╠²
The document discusses key concepts in statistics including:
- A sample space contains all possible outcomes of an experiment and events are subsets of the sample space.
- Probability is a branch of mathematics that quantifies the likelihood of events based on the sample space.
- The axioms of probability establish rules like probabilities being between 0 and 1 and the probability of the entire sample space being 1.
- Bayes' theorem calculates conditional probabilities and allows updating probabilities as new evidence becomes available.Probability Theory



Probability TheoryParul Singh
╠²
The document discusses probability theory and provides definitions and examples of key concepts like conditional probability and Bayes' theorem. It defines probability as the ratio of favorable events to total possible events. Conditional probability is the probability of an event given that another event has occurred. Bayes' theorem provides a way to update or revise beliefs based on new evidence and relates conditional probabilities. Examples are provided to illustrate concepts like conditional probability calculations.Conditional-Probability-Powerpoint.pptx



Conditional-Probability-Powerpoint.pptxVilDom
╠²
The document defines conditional probability as the probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred. It provides the formula for conditional probability as P(B|A) = P(A and B) / P(A). Several examples are worked through applying this formula to calculate conditional probabilities in different contexts like selecting chips from a box, survey responses, exam scores, and dice rolls. Exercises at the end provide additional practice problems for calculating conditional probabilities.Probability basics and bayes' theorem



Probability basics and bayes' theoremBalaji P
╠²
It gives detail description about probability, types of probability, difference between mutually exclusive events and independent events, difference between conditional and unconditional probability and Bayes' theoremprobability



probabilityUnsa Shakir
╠²
This document provides an overview of probability concepts including:
- Probability is a numerical measure of the likelihood of an event occurring, ranging from 0 (impossible) to 1 (certain).
- An experiment generates outcomes that make up the sample space. Events are collections of outcomes.
- Simple events have a defined probability based on being equally likely. The probability of an event is the sum of probabilities of the simple events it contains.
- Rules like the multiplication rule for independent events and additive rule for unions allow calculating probabilities of composite events.
- Complement and conditional probabilities relate the probabilities of events. Independent events do not influence each other's probabilities.Linear regression



Linear regressionKarishma Chaudhary
╠²
- Simple linear regression is used to predict values of one variable (dependent variable) given known values of another variable (independent variable).
- A regression line is fitted through the data points to minimize the deviations between the observed and predicted dependent variable values. The equation of this line allows predicting dependent variable values for given independent variable values.
- The coefficient of determination (R2) indicates how much of the total variation in the dependent variable is explained by the regression line. The standard error of estimate provides a measure of how far the observed data points deviate from the regression line on average.
- Prediction intervals can be constructed around predicted dependent variable values to indicate the uncertainty in predictions for a given confidence level, based on theDiscreet and continuous probability



Discreet and continuous probabilitynj1992
╠²
The document discusses discrete and continuous probability distributions, explaining that a discrete distribution applies to variables that can take on countable values while a continuous distribution is used for variables that can take any value within a range. It provides examples of discrete variables like coin flips and continuous variables like weights. The document also outlines the differences between discrete and continuous probability distributions in how they are represented and calculated.Probability Density Function (PDF)



Probability Density Function (PDF)AakankshaR
╠²
This document outlines probability density functions (PDFs) including:
- The definition of a PDF as describing the relative likelihood of a random variable taking a value.
- Properties of PDFs such as being nonnegative and integrating to 1.
- Joint PDFs describing the probability of multiple random variables taking values simultaneously.
- Marginal PDFs describing probabilities of single variables without reference to others.
- An example calculating a joint PDF and its marginals.Basic probability concept



Basic probability conceptMmedsc Hahm
╠²
This document outlines basic probability concepts, including definitions of probability, views of probability (objective and subjective), and elementary properties. It discusses calculating probabilities of events from data in tables, including unconditional/marginal probabilities, conditional probabilities, and joint probabilities. Rules of probability are presented, including the multiplicative rule that the joint probability of two events is equal to the product of the marginal probability of one event and the conditional probability of the other event given the first event. Examples are provided to illustrate key concepts.Basic concept of probability



Basic concept of probabilityIkhlas Rahman
╠²
This presentation provides an introduction to basic probability concepts. It defines probability as the study of randomness and uncertainty, and describes how probability was originally associated with games of chance. Key concepts discussed include random experiments, sample spaces, events, unions and intersections of events, and Venn diagrams. The presentation establishes the axioms of probability, including that a probability must be between 0 and 1, the probability of the sample space is 1, and probabilities of mutually exclusive events sum to the total probability. Formulas for computing probabilities of unions, intersections, and complements of events are also presented.Binomial distribution



Binomial distributionyatin bhardwaj
╠²
A binomial random variable is the number of successes x in n repeated trials of a binomial experiment. The probability distribution of a binomial random variable is called a binomial distribution. Suppose we flip a coin two times and count the number of heads (successes).Generalized linear model



Generalized linear modelRahul Rockers
╠²
This Presentation course will help you in understanding the Machine Learning model i.e. Generalized Linear Models for classification and regression with an intuitive approach of presenting the core conceptsProbability



ProbabilityRushina Singhi
╠²
The document provides an overview of key probability concepts including:
1. Random experiments, sample spaces, events, and the classification of events as simple, mutually exclusive, independent, and exhaustive.
2. The three main approaches to defining probability: classical, relative frequency, and subjective.
3. Important probability theorems like the addition rule, multiplication rule, and Bayes' theorem.
4. How to calculate probabilities of events using these theorems, including examples of finding probabilities of independent, dependent, mutually exclusive, and conditional events.Probability concept and Probability distribution



Probability concept and Probability distributionSouthern Range, Berhampur, Odisha
╠²
The document summarizes key concepts in probability and statistics as they relate to biostatistics and medical research. It discusses basic probability concepts like classical probability, relative frequency probability, and subjective probability. It also covers probability distributions, screening tests, and key metrics like sensitivity and specificity. Specific topics covered include the binomial, Poisson, and normal distributions, conditional probability, joint probability, independence of events, and marginal probability. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating probabilities from data using concepts like the multiplication rule.Introduction to Maximum Likelihood Estimator



Introduction to Maximum Likelihood EstimatorAmir Al-Ansary
╠²
This document provides an overview of maximum likelihood estimation (MLE). It discusses key concepts like probability models, parameters, and the likelihood function. MLE aims to find the parameter values that make the observed data most likely. This can be done analytically by taking derivatives or numerically using optimization algorithms. Practical considerations like removing constants and using the log-likelihood are also covered. The document concludes by introducing the likelihood ratio test for comparing nested models.Lecture: Joint, Conditional and Marginal Probabilities 



Lecture: Joint, Conditional and Marginal Probabilities Marina Santini
╠²
The document discusses joint, conditional, and marginal probabilities. It begins with an introduction to joint and conditional probabilities, defining conditional probability as the probability of event A given event B. It then presents the multiplication rule for calculating joint probabilities from conditional probabilities and marginal probabilities. The document provides examples and calculations to illustrate these probability concepts. It concludes with short quizzes to test understanding of applying the multiplication rule.Probability



Probabilityvar93
╠²
This document discusses key concepts in probability. It defines basic terms like experiment, sample space, event, and probability. It provides examples of calculating probability for coin tosses and dice rolls using the classical method of dividing the number of ways an event can occur by the total number of possible outcomes. The document also discusses limitations of the classical method and introduces the empirical and subjective methods of determining probability based on observed frequencies and personal judgment respectively.Maximum likelihood estimation



Maximum likelihood estimationzihad164
╠²
This document provides an overview of maximum likelihood estimation. It explains that maximum likelihood estimation finds the parameters of a probability distribution that make the observed data most probable. It gives the example of using maximum likelihood estimation to find the values of ╬╝ and Žā that result in a normal distribution that best fits a data set. The goal of maximum likelihood is to find the parameter values that give the distribution with the highest probability of observing the actual data. It also discusses the concept of likelihood and compares it to probability, as well as considerations for removing constants and using the log-likelihood.Geometric probability distribution



Geometric probability distributionNadeem Uddin
╠²
1. A geometric experiment involves independent trials with two possible outcomes (success/failure), where the probability of success (p) is constant across trials.
2. The geometric random variable (X) represents the number of trials until the first success. It has a geometric distribution where P(X=x) = p(1-p)^(x-1).
3. Examples are provided to illustrate calculating the probability of success on a given trial (x), as well as the mean and standard deviation, for geometric distributions with different probabilities of success (p).Basics of probability



Basics of probabilitysuncil0071
╠²
The document discusses key concepts in probability, including:
1) Random phenomena involve outcomes that are unknown but have possible values. Trials produce outcomes that make up events within a sample space.
2) The Law of Large Numbers states that independent repeated events will have a relative frequency that approaches a single probability value.
3) Theoretical probability is calculated by dividing the number of favorable outcomes by the total number of possible outcomes, assuming all outcomes are equally likely.bbs14e_ppt_ch04.pptx



bbs14e_ppt_ch04.pptxkajalthakkar16
╠²
This document contains slides from a Pearson education presentation on basic probability concepts for a business statistics and research methods course. The slides cover topics such as sample spaces, events, probability definitions and calculations including simple, joint, conditional and marginal probabilities. Examples are provided using contingency tables to demonstrate calculating probabilities for planned and actual purchase scenarios. The document aims to help students understand fundamental probability terms and computations.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Basic concepts of probability



Basic concepts of probabilityAvjinder (Avi) Kaler
╠²
This document discusses basic concepts of probability, including:
- The addition rule and multiplication rule for calculating probabilities of compound events.
- Events can be disjoint (mutually exclusive) or not disjoint.
- The probability of an event occurring or its complement must equal 1.
- How to calculate the probability of at least one occurrence of an event using the complement.
- When applying the multiplication rule, you must consider whether events are independent or dependent.Sample Space and Event,Probability,The Axioms of Probability,Bayes Theorem



Sample Space and Event,Probability,The Axioms of Probability,Bayes TheoremBharath kumar Karanam
╠²
The document discusses key concepts in statistics including:
- A sample space contains all possible outcomes of an experiment and events are subsets of the sample space.
- Probability is a branch of mathematics that quantifies the likelihood of events based on the sample space.
- The axioms of probability establish rules like probabilities being between 0 and 1 and the probability of the entire sample space being 1.
- Bayes' theorem calculates conditional probabilities and allows updating probabilities as new evidence becomes available.Probability Theory



Probability TheoryParul Singh
╠²
The document discusses probability theory and provides definitions and examples of key concepts like conditional probability and Bayes' theorem. It defines probability as the ratio of favorable events to total possible events. Conditional probability is the probability of an event given that another event has occurred. Bayes' theorem provides a way to update or revise beliefs based on new evidence and relates conditional probabilities. Examples are provided to illustrate concepts like conditional probability calculations.Conditional-Probability-Powerpoint.pptx



Conditional-Probability-Powerpoint.pptxVilDom
╠²
The document defines conditional probability as the probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred. It provides the formula for conditional probability as P(B|A) = P(A and B) / P(A). Several examples are worked through applying this formula to calculate conditional probabilities in different contexts like selecting chips from a box, survey responses, exam scores, and dice rolls. Exercises at the end provide additional practice problems for calculating conditional probabilities.Probability basics and bayes' theorem



Probability basics and bayes' theoremBalaji P
╠²
It gives detail description about probability, types of probability, difference between mutually exclusive events and independent events, difference between conditional and unconditional probability and Bayes' theoremprobability



probabilityUnsa Shakir
╠²
This document provides an overview of probability concepts including:
- Probability is a numerical measure of the likelihood of an event occurring, ranging from 0 (impossible) to 1 (certain).
- An experiment generates outcomes that make up the sample space. Events are collections of outcomes.
- Simple events have a defined probability based on being equally likely. The probability of an event is the sum of probabilities of the simple events it contains.
- Rules like the multiplication rule for independent events and additive rule for unions allow calculating probabilities of composite events.
- Complement and conditional probabilities relate the probabilities of events. Independent events do not influence each other's probabilities.Linear regression



Linear regressionKarishma Chaudhary
╠²
- Simple linear regression is used to predict values of one variable (dependent variable) given known values of another variable (independent variable).
- A regression line is fitted through the data points to minimize the deviations between the observed and predicted dependent variable values. The equation of this line allows predicting dependent variable values for given independent variable values.
- The coefficient of determination (R2) indicates how much of the total variation in the dependent variable is explained by the regression line. The standard error of estimate provides a measure of how far the observed data points deviate from the regression line on average.
- Prediction intervals can be constructed around predicted dependent variable values to indicate the uncertainty in predictions for a given confidence level, based on theDiscreet and continuous probability



Discreet and continuous probabilitynj1992
╠²
The document discusses discrete and continuous probability distributions, explaining that a discrete distribution applies to variables that can take on countable values while a continuous distribution is used for variables that can take any value within a range. It provides examples of discrete variables like coin flips and continuous variables like weights. The document also outlines the differences between discrete and continuous probability distributions in how they are represented and calculated.Probability Density Function (PDF)



Probability Density Function (PDF)AakankshaR
╠²
This document outlines probability density functions (PDFs) including:
- The definition of a PDF as describing the relative likelihood of a random variable taking a value.
- Properties of PDFs such as being nonnegative and integrating to 1.
- Joint PDFs describing the probability of multiple random variables taking values simultaneously.
- Marginal PDFs describing probabilities of single variables without reference to others.
- An example calculating a joint PDF and its marginals.Basic probability concept



Basic probability conceptMmedsc Hahm
╠²
This document outlines basic probability concepts, including definitions of probability, views of probability (objective and subjective), and elementary properties. It discusses calculating probabilities of events from data in tables, including unconditional/marginal probabilities, conditional probabilities, and joint probabilities. Rules of probability are presented, including the multiplicative rule that the joint probability of two events is equal to the product of the marginal probability of one event and the conditional probability of the other event given the first event. Examples are provided to illustrate key concepts.Basic concept of probability



Basic concept of probabilityIkhlas Rahman
╠²
This presentation provides an introduction to basic probability concepts. It defines probability as the study of randomness and uncertainty, and describes how probability was originally associated with games of chance. Key concepts discussed include random experiments, sample spaces, events, unions and intersections of events, and Venn diagrams. The presentation establishes the axioms of probability, including that a probability must be between 0 and 1, the probability of the sample space is 1, and probabilities of mutually exclusive events sum to the total probability. Formulas for computing probabilities of unions, intersections, and complements of events are also presented.Binomial distribution



Binomial distributionyatin bhardwaj
╠²
A binomial random variable is the number of successes x in n repeated trials of a binomial experiment. The probability distribution of a binomial random variable is called a binomial distribution. Suppose we flip a coin two times and count the number of heads (successes).Generalized linear model



Generalized linear modelRahul Rockers
╠²
This Presentation course will help you in understanding the Machine Learning model i.e. Generalized Linear Models for classification and regression with an intuitive approach of presenting the core conceptsProbability



ProbabilityRushina Singhi
╠²
The document provides an overview of key probability concepts including:
1. Random experiments, sample spaces, events, and the classification of events as simple, mutually exclusive, independent, and exhaustive.
2. The three main approaches to defining probability: classical, relative frequency, and subjective.
3. Important probability theorems like the addition rule, multiplication rule, and Bayes' theorem.
4. How to calculate probabilities of events using these theorems, including examples of finding probabilities of independent, dependent, mutually exclusive, and conditional events.Probability concept and Probability distribution



Probability concept and Probability distributionSouthern Range, Berhampur, Odisha
╠²
The document summarizes key concepts in probability and statistics as they relate to biostatistics and medical research. It discusses basic probability concepts like classical probability, relative frequency probability, and subjective probability. It also covers probability distributions, screening tests, and key metrics like sensitivity and specificity. Specific topics covered include the binomial, Poisson, and normal distributions, conditional probability, joint probability, independence of events, and marginal probability. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating probabilities from data using concepts like the multiplication rule.Introduction to Maximum Likelihood Estimator



Introduction to Maximum Likelihood EstimatorAmir Al-Ansary
╠²
This document provides an overview of maximum likelihood estimation (MLE). It discusses key concepts like probability models, parameters, and the likelihood function. MLE aims to find the parameter values that make the observed data most likely. This can be done analytically by taking derivatives or numerically using optimization algorithms. Practical considerations like removing constants and using the log-likelihood are also covered. The document concludes by introducing the likelihood ratio test for comparing nested models.Lecture: Joint, Conditional and Marginal Probabilities 



Lecture: Joint, Conditional and Marginal Probabilities Marina Santini
╠²
The document discusses joint, conditional, and marginal probabilities. It begins with an introduction to joint and conditional probabilities, defining conditional probability as the probability of event A given event B. It then presents the multiplication rule for calculating joint probabilities from conditional probabilities and marginal probabilities. The document provides examples and calculations to illustrate these probability concepts. It concludes with short quizzes to test understanding of applying the multiplication rule.Probability



Probabilityvar93
╠²
This document discusses key concepts in probability. It defines basic terms like experiment, sample space, event, and probability. It provides examples of calculating probability for coin tosses and dice rolls using the classical method of dividing the number of ways an event can occur by the total number of possible outcomes. The document also discusses limitations of the classical method and introduces the empirical and subjective methods of determining probability based on observed frequencies and personal judgment respectively.Maximum likelihood estimation



Maximum likelihood estimationzihad164
╠²
This document provides an overview of maximum likelihood estimation. It explains that maximum likelihood estimation finds the parameters of a probability distribution that make the observed data most probable. It gives the example of using maximum likelihood estimation to find the values of ╬╝ and Žā that result in a normal distribution that best fits a data set. The goal of maximum likelihood is to find the parameter values that give the distribution with the highest probability of observing the actual data. It also discusses the concept of likelihood and compares it to probability, as well as considerations for removing constants and using the log-likelihood.Geometric probability distribution



Geometric probability distributionNadeem Uddin
╠²
1. A geometric experiment involves independent trials with two possible outcomes (success/failure), where the probability of success (p) is constant across trials.
2. The geometric random variable (X) represents the number of trials until the first success. It has a geometric distribution where P(X=x) = p(1-p)^(x-1).
3. Examples are provided to illustrate calculating the probability of success on a given trial (x), as well as the mean and standard deviation, for geometric distributions with different probabilities of success (p).Similar to Conditional probability (8)
Basics of probability



Basics of probabilitysuncil0071
╠²
The document discusses key concepts in probability, including:
1) Random phenomena involve outcomes that are unknown but have possible values. Trials produce outcomes that make up events within a sample space.
2) The Law of Large Numbers states that independent repeated events will have a relative frequency that approaches a single probability value.
3) Theoretical probability is calculated by dividing the number of favorable outcomes by the total number of possible outcomes, assuming all outcomes are equally likely.bbs14e_ppt_ch04.pptx



bbs14e_ppt_ch04.pptxkajalthakkar16
╠²
This document contains slides from a Pearson education presentation on basic probability concepts for a business statistics and research methods course. The slides cover topics such as sample spaces, events, probability definitions and calculations including simple, joint, conditional and marginal probabilities. Examples are provided using contingency tables to demonstrate calculating probabilities for planned and actual purchase scenarios. The document aims to help students understand fundamental probability terms and computations.Chapter 4 Section 2.ppt



Chapter 4 Section 2.pptManoloTaquire
╠²
This document contains sections from a textbook on elementary statistics and probability. It covers key concepts in probability, including defining events, sample spaces, notation for probabilities, and three approaches to computing probabilities: relative frequency, classical, and subjective. It also discusses simulations, probability limits, rounding probabilities, complementary events, odds, and provides examples to illustrate these concepts.Stat11t chapter4



Stat11t chapter4raylenepotter
╠²
This document provides a summary of key concepts from Chapter 4 of the textbook "Elementary Statistics". It covers probability, including basic concepts like events, sample spaces, and rules for computing probability. It discusses addition and multiplication rules, conditional probability, counting methods using factorials and permutations, and using simulations to estimate probabilities. The key ideas are calculating probabilities of compound events using rules of addition and multiplication, and adjusting probabilities when events are dependent rather than independent.Triola t11 chapter4



Triola t11 chapter4babygirl5810
╠²
This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 4 on probability, including the addition rule, multiplication rule, conditional probability, dependent and independent events, and applying these concepts to calculate probabilities. The chapter covers basic probability concepts like sample spaces, events, and computing probabilities using relative frequency, classical, and subjective approaches. It also discusses odds, complementary events, and using simulations and counting to calculate probabilities.Basic Business Statistics 12-th edition,Chapter 4,Basic Probability



Basic Business Statistics 12-th edition,Chapter 4,Basic Probabilitymuradsuleymanzade5
╠²
Basic Business Statistics 12-th edition,Chapter 4,Basic Probabilitychapter_4_modified_slides_0.ppt



chapter_4_modified_slides_0.pptShubhamChauhan562815
╠²
This document outlines key concepts from Chapter 4 on basic probability. It discusses probability concepts like simple, joint, conditional, and subjective probabilities. It introduces topics like sample spaces, events, mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive events, and how to calculate probabilities using formulas and counting rules. The objectives are to understand basic and conditional probabilities, Bayes' theorem, and various counting rules for computing probabilities.Lecture3 Applied Econometrics and Economic Modeling



Lecture3 Applied Econometrics and Economic Modelingstone55
╠²
The document discusses probability concepts including conditional probability, independence, and distributions of single and joint random variables. It provides an example where an investor analyzes the probability distributions of returns from investing in GM stock and gold under different economic scenarios. Summary measures like mean, variance, and correlation are calculated to characterize the distributions and relationship between the random variables. Simulation is used to help explain the covariance and correlation between the returns.More from suncil0071 (13)
WhoŌĆÖs who



WhoŌĆÖs whosuncil0071
╠²
The document discusses potential issues that can arise when conducting surveys, including ambiguity around defining the target population and sampling frame. It notes that the sample obtained may not adequately represent these intended groups due to constraints introduced and biases from nonresponse, response biases, and inappropriate sampling methods. The document advocates specifying sampling methods clearly and evaluating potential biases in order to obtain meaningful, representative survey results.Cluster and multistage sampling



Cluster and multistage samplingsuncil0071
╠²
The document discusses cluster sampling and multistage sampling methods. Cluster sampling involves splitting the population into clusters, randomly selecting some clusters, and sampling every unit within those clusters. Multistage sampling combines multiple sampling methods, such as stratified and cluster sampling. It is commonly used in surveys conducted by polling organizations. Some advantages of cluster and multistage sampling are that they are simpler and less costly than simple random sampling, while still allowing estimates of population characteristics.Stratified sampling



Stratified samplingsuncil0071
╠²
The document discusses stratified random sampling, which is a statistical sampling technique where the population is first divided into homogeneous subgroups or strata, then a random sample is drawn from each stratum. The key steps are to 1) identify and define the population, 2) determine sample size, 3) identify variables and subgroups for representation, 4) classify population members into subgroups, and 5) randomly select an appropriate number of individuals from each subgroup. Stratified random sampling can reduce bias and variability compared to simple random sampling. However, it requires knowing the names of all population members and may be difficult if some selected cannot be reached.Simple random sampling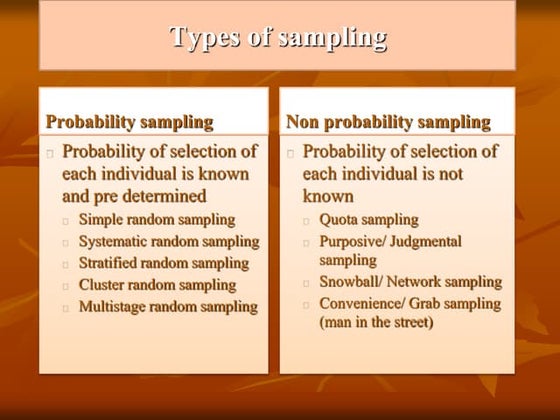



Simple random samplingsuncil0071
╠²
There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling involves methods where the probability of selection of each individual is known, such as simple random sampling, systematic random sampling, stratified random sampling, and cluster random sampling. Simple random sampling involves selecting a sample that gives each individual an equal chance of being selected by identifying the population, determining sample size, listing all population members, assigning them numbers, selecting numbers at random from a table, and including individuals in the sample if their number is selected. The advantages are it is easy to conduct and requires minimum population knowledge, while disadvantages include needing all population member names and potential over or under-representation.Simple random sampling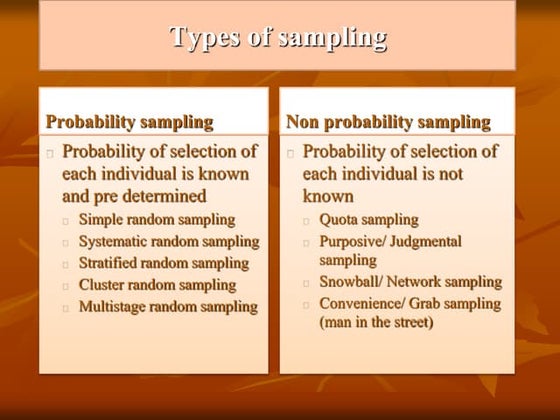



Simple random samplingsuncil0071
╠²
There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling involves methods where the probability of selection of each individual is known, such as simple random sampling, systematic random sampling, stratified random sampling, and cluster random sampling. Simple random sampling involves selecting a sample that gives each individual an equal chance of being selected by identifying the population, determining sample size, listing all population members, assigning them numbers, selecting numbers at random from a table, and including individuals in the sample if their number is selected. The advantages are it is easy to conduct and requires minimum population knowledge, while disadvantages include needing all population member names and potential over or under representation.Ideas to understand



Ideas to understandsuncil0071
╠²
This document discusses three key ideas for making inferences about populations based on samples:
1) Examining a sample of a population rather than the entire population, since examining everything is impractical. Samples should be representative.
2) Randomizing the sample selection to avoid bias and allow inferences about the population. Randomization protects against known and unknown factors.
3) The size of the sample is important, not the size of the population. Large enough sample sizes allow samples to reasonably represent populations. Censuses are problematic due to difficulties in measuring entire populations.Understanding randomness



Understanding randomnesssuncil0071
╠²
While computers are often used to generate random numbers, they are not truly random and instead produce pseudorandom values following a program. There are better ways to generate random data that is equally likely and truly random. Simulations are used to model and investigate random processes, events, and questions when collecting real data is difficult. A successful simulation involves identifying components, modeling outcomes, defining response variables, running multiple trials, analyzing results, and drawing conclusions. Care must be taken to avoid overstating findings or confusing simulation results with reality.Linear regression



Linear regressionsuncil0071
╠²
The document discusses linear regression models, which provide a linear equation to model the relationship between two quantitative variables. A linear regression finds the line of best fit that minimizes the sum of squared residuals between observed and predicted values. The regression outputs include the slope, intercept, and R2 value, which indicates the proportion of variance in the dependent variable that is explained by the model. Key assumptions are that the variables have a linear relationship, there are no outliers, and the residuals are randomly distributed with no discernible pattern.Linear regression



Linear regressionsuncil0071
╠²
The document discusses linear regression models. It explains that a linear regression model finds the straight line that best fits a set of data points and can be used to understand the relationship between two quantitative variables. The linear model is an equation of a straight line that may not fit all data points perfectly but can summarize the overall pattern. The difference between observed and predicted values (residuals) indicates how well the model fits the data. The model with the least sum of squared residuals is considered the best fit. The document provides an example of modeling the relationship between fat and protein content in Burger King menu items.Linear regression



Linear regressionsuncil0071
╠²
The document discusses linear regression analysis. It explains that linear regression finds the best fitting straight line through data points in order to model the relationship between two quantitative variables. The regression line minimizes the sum of squared residuals. The R-squared value indicates how much of the variability in the data is explained by the linear model. Residual plots are examined to check if the linear model is appropriate.Correlation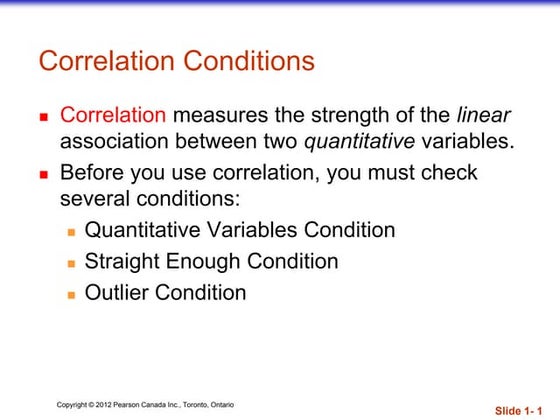



Correlationsuncil0071
╠²
The document discusses correlation and the conditions that must be checked before calculating correlation between two quantitative variables. It explains that correlation measures the strength of the linear association between variables and can only be applied to quantitative, not categorical, variables. Additionally, the relationship must be sufficiently linear for correlation to be valid and outliers can distort results. The document also defines positive and negative correlation and different types of correlation based on the number of variables.Measures of central tendency mean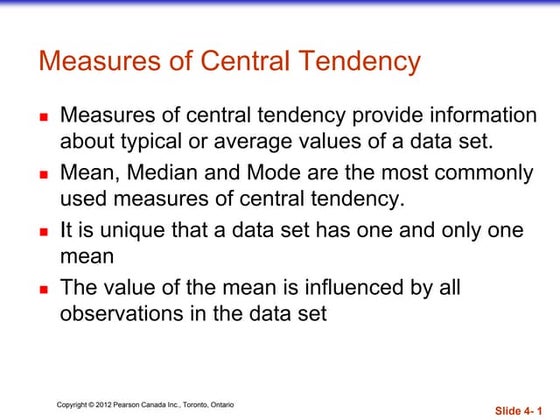



Measures of central tendency meansuncil0071
╠²
The document discusses measures of central tendency, specifically the mean. It defines the mean as the average of all values in a data set, found by adding all values and dividing by the total number of data points. The mean represents the balance point of a distribution and feels like the center because it is the value where the data balances on either side when represented visually in a histogram. The mean is unique in that a data set only has one mean, and it is influenced by all observations in the data set.Histograms & stem plots



Histograms & stem plotssuncil0071
╠²
The document discusses different methods for visualizing data distributions, including histograms and stem-and-leaf displays. It provides examples of histograms of earthquake magnitudes, including a regular histogram showing counts in bins and a relative frequency histogram showing percentages. It also explains that stem-and-leaf displays show the distribution of a quantitative variable while preserving individual values.Recently uploaded (20)
Key Benefits of Implementing Contify's M&CI Platform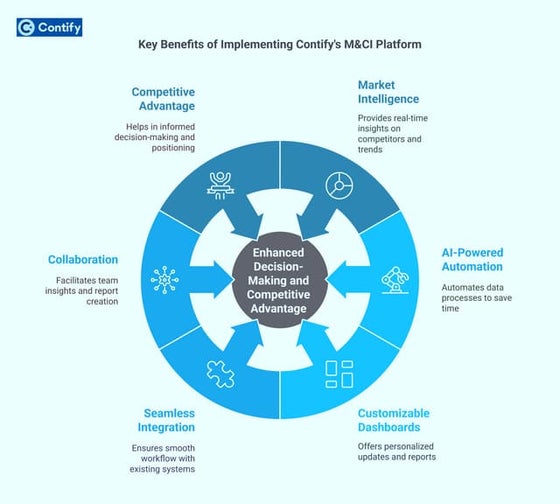



Key Benefits of Implementing Contify's M&CI PlatformContify
╠²
Contify's Market & Competitive Intelligence platform empowers businesses with real-time insights, automated intelligence gathering, and AI-driven analytics. It enhances decision-making, streamlines competitor tracking, and delivers personalized intelligence reports. With Contify, organizations gain a strategic edge by identifying trends, mitigating risks, and seizing growth opportunities in dynamic market landscapes.
For more information please visit here https://www.contify.com/platform/How the Best News APIs Work: A Visual Guide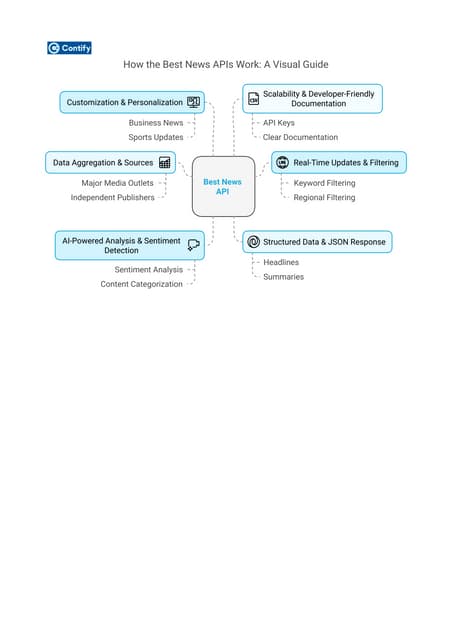



How the Best News APIs Work: A Visual GuideContify
╠²
Discover how the best news APIs function with this visual guide. Learn how they fetch real-time news, filter content, and integrate seamlessly with apps. Understand key features like authentication, endpoints, and data formats, making it easier to choose the right API for your needs. Perfect for developers and businesses!
For more information please visit here https://www.contify.com/news-api/Elevate Your Space with Premium Design Services from NInterior Design



Elevate Your Space with Premium Design Services from NInterior DesignNinterior Design
╠²
ItŌĆÖs our mission at Ninteriordesign to provide client-focused service through the responsible practice of architecture.Large Language Models (LLMs) part one.pptx



Large Language Models (LLMs) part one.pptxharmardir
╠²
**The Rise and Impact of Large Language Models (LLMs)**
**Introduction**
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI), one of the most groundbreaking advancements has been the development of Large Language Models (LLMs). These AI systems, trained on massive amounts of text data, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in understanding, generating, and manipulating human language. LLMs have transformed industries, reshaped the way people interact with technology, and raised ethical concerns regarding their usage. This essay delves into the history, development, applications, challenges, and future of LLMs, providing a comprehensive understanding of their significance.
**Historical Background and Development**
The foundation of LLMs is built on decades of research in natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML). Early language models were relatively simple and rule-based, relying on statistical methods to predict word sequences. However, the emergence of deep learning, particularly the introduction of neural networks, revolutionized NLP. The introduction of recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks in the late 1990s and early 2000s allowed for better sequential data processing.
The breakthrough moment for LLMs came with the development of Transformer architectures, introduced in the seminal 2017 paper "Attention Is All You Need" by Vaswani et al. The Transformer model enabled more efficient parallel processing and improved context understanding. This led to the creation of models like BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) and OpenAIŌĆÖs GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) series, which have since set new benchmarks in AI-driven text generation and comprehension.
**Core Mechanisms of LLMs**
LLMs rely on deep neural networks trained on extensive datasets comprising books, articles, websites, and other textual resources. The training process involves:
1. **Tokenization:** Breaking down text into smaller units (words, subwords, or characters) to be processed by the model.
2. **Pretraining:** The model learns general language patterns through unsupervised learning, predicting missing words or the next sequence in a text.
3. **Fine-tuning:** Adjusting the model for specific tasks, such as summarization, translation, or question-answering, using supervised learning.
4. **Inference:** The trained model generates text based on user input, leveraging probabilistic predictions to produce coherent responses.
Through these mechanisms, LLMs can perform a wide range of linguistic tasks with human-like proficiency.
**Applications of LLMs**
LLMs have found applications across various domains, including but not limited to:
1. **Content Generation:** LLMs assist in writing articles, blogs, poetry, and even code, helping content creators enhance productivity.
2. **Customer Support:** Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by LLMs provide automated yet contPlant Disease Prediction with Image Classification using CNN.pdf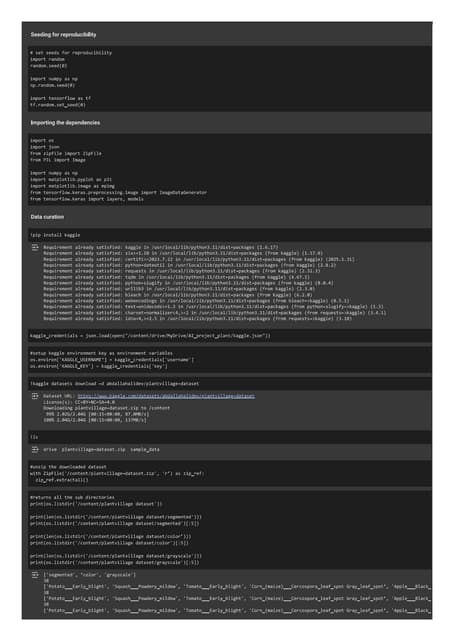



Plant Disease Prediction with Image Classification using CNN.pdfTheekshana Wanniarachchi
╠²
Plant diseases pose a significant threat to agricultural productivity. Early detection and classification of plant diseases can help mitigate losses. This project focuses on building a Plant Disease Prediction system using Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). The system leverages NumPy, TensorFlow, and Streamlit to develop a model and deploy a web-based application. The final model is also containerized using Docker for efficient deployment.Updated Willow 2025 Media Deck_280225 Updated.pdf



Updated Willow 2025 Media Deck_280225 Updated.pdftangramcommunication
╠²
Updated with the edits we last spoke Bhavanaev3-software-tutorial-dc terminologia en ibgles.ppt



ev3-software-tutorial-dc terminologia en ibgles.ppthectormartinez817322
╠²
en ingles esta prressetnacion es muy buena lasdla lkaskl siempreew aaslkd llasaslas as asasd lk aslk al kjal kj allks50-Database Efficiency 101 Understanding and Implementing PostgreSQL Indexes....



50-Database Efficiency 101 Understanding and Implementing PostgreSQL Indexes....Doug Ortiz
╠²
Understanding and Implementing PostgreSQL Indexes
Certificado Business Intelligence - Alber Florentin.pdf



Certificado Business Intelligence - Alber Florentin.pdfalberalen
╠²
Operador de Excel Empresarial - Business Intelligence.Conditional probability
- 1. Copyright ┬® 2012 Pearson Canada Inc., Toronto, Ontario Probability Conditional Probability
- 2. Copyright ┬® 2012 Pearson Canada Inc., Toronto, Ontario ║▌║▌▀Ż 15- 2 Conditional Probability ’ü« When we want the probability of an event from a conditional distribution, we write P(B|A) and pronounce it ŌĆ£the probability of B given A.ŌĆØ ’ü« A probability that takes into account a given condition is called a conditional probability.
- 3. Copyright ┬® 2012 Pearson Canada Inc., Toronto, Ontario ║▌║▌▀Ż 15- 3 Conditional Probability (cont.) ’ü« To find the probability of the event B given the event A, we restrict our attention to the outcomes in A. We then find in what fraction of those outcomes B also occurred. ’ü« Note: P(A) cannot equal 0, since we know that A has occurred. (A and B)( | ) ( ) PP P ’ĆĮB A A
- 4. Copyright ┬® 2012 Pearson Canada Inc., Toronto, Ontario ║▌║▌▀Ż 15- 4 Independence ’ü« Independence of two events means that the outcome of one event does not influence the probability of the other. ’ü« With our new notation for conditional probabilities, we can now formalize this definition: ’ü« Events A and B are independent whenever P(B|A) = P(B). (Equivalently, events A and B are independent whenever P(A|B) = P(A).)
- 5. Copyright ┬® 2012 Pearson Canada Inc., Toronto, Ontario ║▌║▌▀Ż 15- 5 The General Multiplication Rule ’ü« When two events A and B are independent, we can use the multiplication rule for independent events : P(A and B) = P(A) x P(B) ’ü« However, when our events are not independent, this earlier multiplication rule does not work. Thus, we need the General Multiplication Rule.
- 6. Copyright ┬® 2012 Pearson Canada Inc., Toronto, Ontario ║▌║▌▀Ż 15- 6 The General Multiplication Rule (cont.) ’ü« We encountered the general multiplication rule in the form of conditional probability. ’ü« Rearranging the equation in the definition for conditional probability, we get the General Multiplication Rule: ’ü« For any two events A and B, P(A and B) = P(A) x P(B|A) or P(A and B) = P(B) x P(A|B)
- 7. Copyright ┬® 2012 Pearson Canada Inc., Toronto, Ontario ║▌║▌▀Ż 15- 7 Independent ŌēĀ Disjoint ’ü« Disjoint events cannot be independent! Well, why not? ’ü« Since we know that disjoint events have no outcomes in common, knowing that one occurred means the other didnŌĆÖt. ’ü« Thus, the probability of the second occurring changed based on our knowledge that the first occurred. ’ü« It follows, then, that the two events are not independent. ’ü« A common error is to treat disjoint events as if they were independent, and apply the Multiplication Rule for independent eventsŌĆödonŌĆÖt make that mistake.
- 8. Copyright ┬® 2012 Pearson Canada Inc., Toronto, Ontario ║▌║▌▀Ż 15- 8 Depending on Independence ’ü« ItŌĆÖs much easier to think about independent events than to deal with conditional probabilities. ’ü« It seems that most peopleŌĆÖs natural intuition for probabilities breaks down when it comes to conditional probabilities. ’ü« DonŌĆÖt fall into this trap: whenever you see probabilities multiplied together, stop and ask whether you think they are really independent.
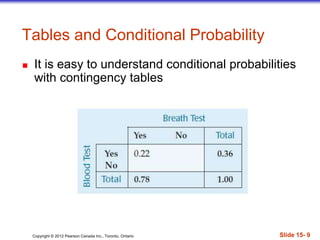
- 9. Copyright ┬® 2012 Pearson Canada Inc., Toronto, Ontario ║▌║▌▀Ż 15- 9 Tables and Conditional Probability ’ü« It is easy to understand conditional probabilities with contingency tables










