Conditionals Bach
- 2. TYPE ZERO / UNIVERSAL ïķ FORM IF + Present, Present / Imperative ïķ USE ïž True / scientific facts ïž Instructions
- 3. ïķ EXAMPLES ï If you put paper on a fire, it burns ï If the phone rings, answer it
- 4. FIRST CONDITIONAL (TYPE 1) ïķ FORM IF + Present, WILL (Must / can / may) ïķ USE ïž Likely / probable results ïž Promises, warnings, threats
- 5. ïķ EXAMPLES ï If we donât leave now, weâll miss the train ï If you pass your exam, Iâll give you a job
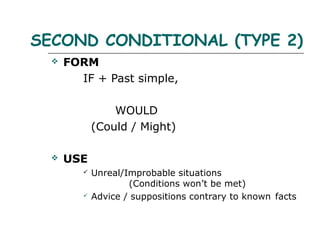
- 6. SECOND CONDITIONAL (TYPE 2) ïķ FORM IF + Past simple, WOULD (Could / Might) ïķ USE ïž Unreal/Improbable situations (Conditions wonât be met) ïž Advice / suppositions contrary to known facts
- 7. ïķ EXAMPLES ï If you did more exercise, youâd feel better ï If I were you, I wouldnât drive so fast ï If she was / were taller, she would play basketball ïķ NOTES ïž If I were you (Written / formal language) ïž If I were / was you (spoken language) ïž If he / she / it were (more usual) ïž If he / she / it was (more colloquial)
- 8. THIRD CONDITIONAL (TYPE 3) ïķ FORM IF + Past perfect, WOULD HAVE + Past Participle (Could / Might) ïķ USE ïž Impossible situations (Speculation about the past)
- 9. ïķ EXAMPLES ï If I had had your address, (Iâd had) I would have sent you a postcard (Iâd have)
- 10. MIXED CONDITIONALS To talk about past events or actions that have a result in the present, we can mix the second and the third conditional: If I had passed all my exams, I would be on the beach now.
- 11. ïķ GENERAL FACTS ïķ We can exchange the order of the clauses ï If you go, Iâll go ï Iâll go if you go
- 12. ïķ Connectors ï UNLESS = IF âĶ NOT âA menos que / a no ser queâ âYou wonât pass if you donât studyâ âYou wonât pass unless you studyâ ï PROVIDED / PROVIDING (THAT) âCon tal de queâ ï ON CONDITION (THAT) âA condiciÃģn de queâ ï IN CASE âPor siâ ï ASSUMING / SUPPOSING (THAT) âSuponiendo queâ ï AS LONG AS / SO LONG AS âSiempre queâ ï EVEN IF ï WHETHER
- 13. THETHE ENDEND