Connective Tissue Fibers Histology
- 1. 1
- 2. CONNECTIVE TISSUE Connective tissue fibers 1.Collagen fibers 2.Reticular fibers 3.Elastic fibers 2Dr.M.Attia
- 3. CONNECTIVE TISSUE Collagen fibers ’āśMost abundant in the body ’āśInsoluble fibrous protein, forms the major component of the extracellular matrix. 3Dr.M.Attia
- 4. Collagen fibers CONNECTIVE TISSUE ’āśColorless in fresh state ’āśVery strong, flexible, inelastic with great resistance to tension ’āśAffected by weak acids and alkalies. 4Dr.M.Attia
- 5. Collagen fibers LM: Stains: ’āśH&E: ACIDOPHILIC ’āśMalloryŌĆÖs trichrome: blue ’āśVan giesson trichrome: green SHAPE Long, wavy , unbranched fibers and present in bundles CONNECTIVE TISSUE 5Dr.M.Attia
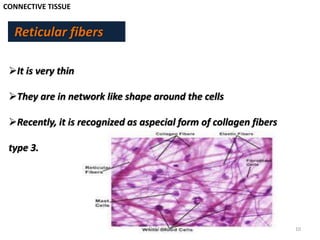
- 10. CONNECTIVE TISSUE Reticular fibers ’āśIt is very thin ’āśThey are in network like shape around the cells ’āśRecently, it is recognized as aspecial form of collagen fibers type 3. 10Dr.M.Attia
- 12. CONNECTIVE TISSUE Reticular fibers Site ’āśStroma of the organs ’āśSmooth muscles ’āśEndoneurium 12Dr.M.Attia
- 13. CONNECTIVE TISSUE ’āśHighly elastic and stretchable in response to tension ’āśColorless in fresh state ’āśAppear yellow in colour ’āśThey are stronge but less than collagen fibers ’āśThey are not affected by acids, alkalies, boiling ’āśDestroy by elastase enzyme. 13Dr.M.Attia
- 15. CONNECTIVE TISSUE Site ’ü▒ Lung, skin, Urinary bladder ’ü▒ Wall of the large arteries like Aorta ’ü▒ Elastic ligaments like : ligamentum flavum, ligamntum nuchae 15Dr.M.Attia
- 16. 16Dr.M.Attia