Constitutive modelling of soil (Duncan-chang Model)
- 1. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi ŌĆ½ž▒žŁ█ī┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█īž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒žŁ┘ģž¦┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½█īž¦ŌĆ¼ 1
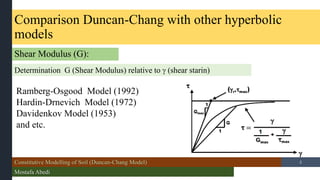
- 2. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 Comparison Duncan-Chang with other hyperbolic models Shear Modulus (G): Determination G (Shear Modulus) relative to ’ü¦ (shear starin) 2 Ramberg-Osgood Model (1992) Hardin-Drnevich Model (1972) Davidenkov Model (1953) and etc.
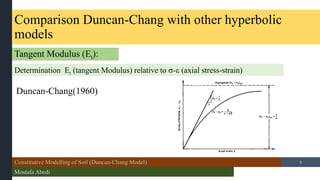
- 3. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 Comparison Duncan-Chang with other hyperbolic models Tangent Modulus (Et): Determination Et (tangent Modulus) relative to ’ü│-’üź (axial stress-strain) 3 Duncan-Chang(1960)
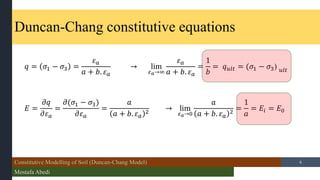
- 4. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 Duncan-Chang constitutive equations Kondner and et al. (1963) have shown that the nonlinear stress-strain curves of both clay and sand may be approximated by hyperbolae with a high degrss of accuracy. The hyperbolic equation propose by Kondner was: Ø£Ä1 ŌłÆ Ø£Ä3 = Ø£Ć ØæÄ + ØæÅ. Ø£Ć 4
- 5. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 Duncan-Chang constitutive equations 5 E0 or Ei Et Esec
- 6. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 Duncan-Chang constitutive equations Øæ× = Ø£Ä1 ŌłÆ Ø£Ä3 = Ø£ĆØæÄ ØæÄ + ØæÅ. Ø£ĆØæÄ ŌåÆ lim Ø£ĆØæÄŌåÆŌł× Ø£ĆØæÄ ØæÄ + ØæÅ. Ø£ĆØæÄ = 1 ØæÅ = Øæ×ØæóØæÖØæĪ = (Ø£Ä1 ŌłÆ Ø£Ä3) ØæóØæÖØæĪ ØÉĖ = Ø£ĢØæ× Ø£ĢØ£ĆØæÄ = Ø£Ģ(Ø£Ä1 ŌłÆ Ø£Ä3) Ø£ĢØ£ĆØæÄ = ØæÄ ØæÄ + ØæÅ. Ø£ĆØæÄ 2 ŌåÆ lim Ø£ĆØæÄŌåÆ0 ØæÄ ØæÄ + ØæÅ. Ø£ĆØæÄ 2 = 1 ØæÄ = ØÉĖØæ¢ = ØÉĖ0 6
- 7. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 Duncan-Chang constitutive equations 7
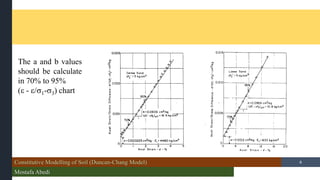
- 8. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 8 The a and b values should be calculate in 70% to 95% (’üź - ’üź/’ü│1-’ü│3) chart
- 9. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 Duncan-Chang constitutive equations Failure ratio (Rf): ØæģØæō = Ø£Ä1 ŌłÆ Ø£Ä3 Øæō Ø£Ä1 ŌłÆ Ø£Ä3 ØæóØæÖØæĪ Ōēż 1.0 independent of confining pressure Rf = 0.75 ’üŠ 1.0 9
- 10. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 Duncan-Chang constitutive equations If the parameters a and b are expressed in terms of E0, Rf, and (’ü│1-’ü│3): Ø£Ä1 ŌłÆ Ø£Ä3 = Ø£Ć 1 ØÉĖ0 + Ø£Ć. ØæģØæō Ø£Ä1 ŌłÆ Ø£Ä3 Øæō 10
- 11. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 Duncan-Chang constitutive equations Janbu (1963): ØÉĖ0 = Øæś. ØæØØæÄ Ø£Ä3 ØæØØæÄ Øæø 11
- 12. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 Duncan-Chang constitutive equations Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion: Ø£Ä1 ŌłÆ Ø£Ä3 Øæō = 2ØæÉ. ØæÉØæ£ØæĀØ£æ + 2Ø£Ä3. ØæĀØæ¢ØæøØ£æ 1 ŌłÆ ØæĀØæ¢ØæøØ£æ 12
- 13. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 Duncan-Chang constitutive equations ŌĆó Tangent modulus values (Et): ØÉĖØæĪ = 1 ŌłÆ ØæģØæō (1 ŌłÆ ØæĀØæ¢ØæøØ£æ)(Ø£Ä1 ŌłÆ Ø£Ä3) 2(ØæÉ. ØæÉØæ£ØæĀØ£æ + Ø£Ä3. ØæĀØæ¢ØæøØ£æ) 2 Øæś. Ø£Ä3 ØæØØæÄ Øæø 13
- 14. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 Duncan-Chang constitutive equations ŌĆó Tangent modulus values (Et): ØÉĖØæĪ = 1 ŌłÆ ØæģØæō (1 ŌłÆ ØæĀØæ¢ØæøØ£æ)(Ø£Ä1 ŌłÆ Ø£Ä3) 2(ØæÉ. ØæÉØæ£ØæĀØ£æ + Ø£Ä3. ØæĀØæ¢ØæøØ£æ) 2 Øæś. Ø£Ä3 ØæØØæÄ Øæø 14
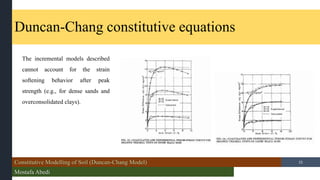
- 15. Constitutive Modelling of Soil (Duncan-Chang Model) Mostafa Abedi /15 Duncan-Chang constitutive equations 15 The incremental models described cannot account for the strain softening behavior after peak strength (e.g., for dense sands and overconsolidated clays).