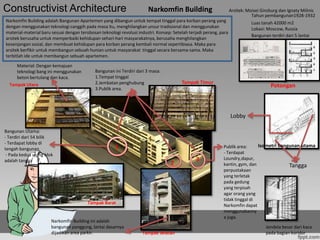
Constructivist architecture
- 1. Constructivist Architecture Narkomfin Building Arsitek: Moisei Ginzburg dan Ignaty Milinis Tahun pembangunan1928-1932 Narkomfin Building adalah Bangunan Apartemen yang dibangun untuk tempat tinggal para korban perang yang Luas tanah 42000 m2 dengan menggunakan teknologi canggih pada masa itu, menghilangkan unsur tradisional dan menggunakan Lokasi: Moscow, Russia material-material baru sesuai dengan terobosan teknologi revolusi industri. Konsep: Setelah terjadi perang, para Bangunan terdiri dari 5 lantai arsitek berusaha untuk memperbaiki kehidupan sehari-hari masyarakatnya, berusaha menghilangkan kesenjangan sosial, dan membuat kehidupan para korban perang kembali normal sepertibiasa. Maka para arsitek berfikir untuk membangun sebuah hunian untuk masyarakat tinggal secara bersama-sama. Maka terbitlah ide untuk membangun sebuah apartemen. Material: Dengan kemajuan teknologi bang ini menggunakan Bangunan ini Terdiri dari 3 masa: beton bertulang dan kaca. 1.Tempat tinggal Tampak Utara 2.Jembatan penghubung Tampak Timur 3.Publik area. Potongan Lobby Bangunan Utama: - Terdiri dari 54 bilik - Terdapat lobby di 1 Publik area: Isometri bangunan utama tengah bangunan - Pada kedua ujung blok - Terdapat adalah tangga 3 Loundry,dapur, 2 kantin, gym, dan Tangga perpustakaan yang terletak pada gedung yang terpisah agar orang yang tidak tinggal di Tampak Barat Narkomfin dapat menggunakanny a juga. Narkomfin Building ini adalah bangunan panggung, lantai dasarnya Jendela besar dari kaca dijadikan area parkir. Tampak Selatan pada bagian koridor
- 2. Bakhmetevsky Bus Garage Arsitek: Konstantin Melnikov dan Vladimir Shukhov Tahun pembangunan1926-1927 Luas tanah 8500 m2 Lokasi: Moscow, Russia Jumlah tampung: 104 Bus Interior
- 3. Penyusun: Merisa kadrina Yuni Triana Safrizal 0903110559 0903110572 0903110570 M.Nazli Rinaldi Iswandi 0803110429 0903110582 0803110414