Context-Aware Computing
- 1. Context-Aware Computing Concepts & Architecture
- 2. â Identification of place lies as a generative core of architecture. Place is to architecture as meaning is to languageâ Prof. Sharad Atre College of Architecture & Environmental Design
- 3. Agenda Concepts Technology & Design Architecture Conclusions Questions
- 4. Concepts
- 5. Ubiquitous/Pervasive Computing The general trend of computing is to have devices seamlessly integrated into the life of users and having services readily available to everywhere users go It is an emerging paradigm to free everyday users from manually configuring and instructing computer systems Allow us âto do more, by doing lessâ
- 6. Proactive/Autonomic Computing Is about building systems that can self-monitor, self-heal and self-configure (zero maintenance). Human attention devoted to interaction can be reduced so that users can focus on high-level tasks Both relate to ubiquitous computing and could use context information from environment and users to make decisions
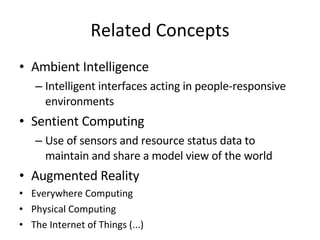
- 7. Related Concepts Ambient Intelligence Intelligent interfaces acting in people-responsive environments Sentient Computing Use of sensors and resource status data to maintain and share a model view of the world Augmented Reality Everywhere Computing Physical Computing The Internet of Things (...)
- 9. What is Context? Context is that which surrounds, and gives meaning, to something else Context is any information that can be used to characterize the situation of an entity Typically the location, identity and state of people, groups, computational and physical objects May come from disparate sources and has a relatively transient lifetime But historic data about context is important, anyway
- 10. â An example of a piece of relevant context information is the most common question posed when communicating on mobile phones: âWhere are you?ââ Louise Barhuus Department of Design and Use of Information Technology The IT University of Copenhagen
- 11. Context-Aware Computing Not just âdeliver any service at any time, anywhereâ, but rather âdelivering the right service at the right momentâ Mobile computing is introducing the possibility that the physical and logical context of a user might influence the behavior of services called for Mobile computing decouples function from location User location is transparent to function Recent trends are extending this concept of context to include many other facets of the userâs physical environment Many sensors are being added to characterize context
- 12. Context-Aware Applications Must acquire context information and use it in an intelligent manner (beneficial to either the service, the user or both) In the mobile systems of today this would most likely be expressed as calls for service from either local or remote service providers The mobile user and his device becomes the âservice consumerâ Meaning arises in the course of action, is not inherent in the technology, but arises from how that technology is used This means the designer does not have absolute control, only influence Users feel less in control when using context-aware applications than when personalizing their own applications Despite this, context-aware applications are preferred over the personalization oriented ones
- 13. Context Domains The situation of any entity is characterized by using several informations surrounding the service consumer Historical information about any of these might also be considered Can also be deduced from interactions the user has made with services over time
- 14. Contextual Information Samples User identity Spatial information (location, orientation, speed, acceleration) Temporal information (time of the day, date, season of the year) Environmental information (temperature, air quality, light or noise level) Social situation (who you are with, people that are nearby) Resources that are nearby (accessible devices, networks, hosts) Availability of resources (battery, display, network, bandwidth) Physiological measurements (blood pressure, heart rate, respiration rate, muscle activity, tone of voice) Activity (talking, reading, walking, running, sleeping) Schedules and agendas
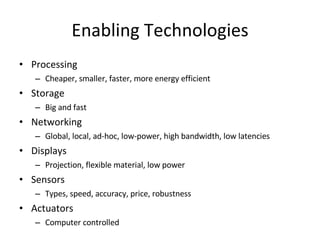
- 16. Enabling Technologies Processing Cheaper, smaller, faster, more energy efficient Storage Big and fast Networking Global, local, ad-hoc, low-power, high bandwidth, low latencies Displays Projection, flexible material, low power Sensors Types, speed, accuracy, price, robustness Actuators Computer controlled
- 17. Design Provide Services System design: which embedded system? Web server? Sensors and actuators? Naming, registration, discovery Physical/virtual mapping Mobility management, energy management Service composition, I/O matching, adaptation, environment monitoring
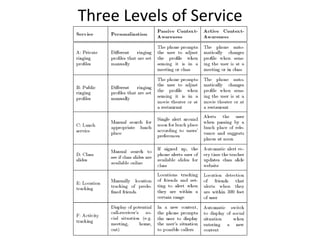
- 18. Three Levels of Service
- 19. Some More Examples... Wearable Computer A t-shirt that automatically adjust the ambient temperature of the room by sensing body temperature Ambient Intelligence User presence is detected to show email in a nearby computer. This feature can be coupled with a coffee machine that senses the user to make coffee according to preferences, etc. Context-Aware Phone Only accepts calls that are important, according to user context
- 20. Architecture
- 21. â The most profound technologies are those that disappear. They weave themselves into the fabric of everyday life until they are undistinguishable from it.â Mark Weiser Chief Scientist at Xerox PARC
- 22. Principles of Ubiquitous Computing The purpose of a computer is to help you do something else The best computer is a quiet, invisible servant The more you can do by intuition the smarter you are. The computer should extend your unconscious Technology should create calm Calm technology is that which informs but doesnât demand our focus or attention A road to Peace through global conscience
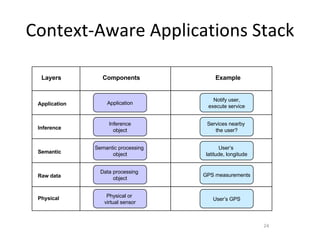
- 24. Context-Aware Applications Stack Physical Raw data Semantic Inference Application Physical or virtual sensor Data processing object Semantic processing object Inference object Application Userâs GPS GPS measurements Userâs latitude, longitude Services nearby the user? Notify user, execute service Components Layers Example
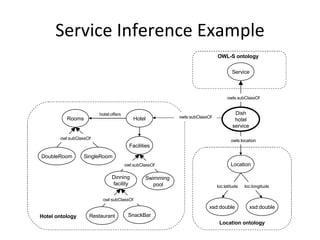
- 25. Service Inference Example Service Hotel Dish hotel service xsd:double Location xsd:double Rooms Facilities Dinning facility SnackBar Swimming pool DoubleRoom SingleRoom hotel:offers loc:latitude loc:longitude Restaurant owls:subClassOf Hotel ontology Location ontology OWL-S ontology owls:location owls:subClassOf owl:subClassOf owl:subClassOf owl:subClassOf
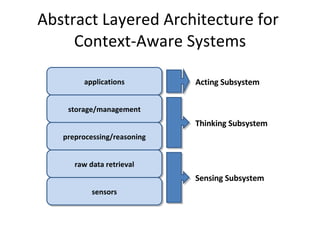
- 26. Abstract Layered Architecture for Context-Aware Systems applications storage/management preprocessing/reasoning raw data retrieval sensors Acting Subsystem Thinking Subsystem Sensing Subsystem
- 27. Research Issues Context Modeling & Reasoning How to build representations of context that can be processed and reasoned about by the computers Knowledge Maintenance & Sharing How to maintain consistent knowledge about the context and share that information with other systems User Privacy Protection How to give users the control of their situational information that is acquired from the hidden sensors
- 28. Some Ideas A repository of context knowledge can help resource-limited devices to become context aware Ontologies can help to share context knowledge, reducing the redundancy in sensing Policies can give users the control of their context information, protecting their privacy in an open environment People are willing to give up partial control if the reward in usefulness is great enough
- 30. Conclusions (I) Context-Aware Computing demands for lots of different knowledge fields to follow: System infrastructures, networking, security, user interfaces, embedded systems, AI, perception, speech recognition, etc. Systems integration is the key Many new and fascinating research problems are emerging
- 31. Conclusions (II) There is no common way to acquire and handle context Unlike regular user input, context information is distributed and arrives from heterogeneous sources The infrastructure must support the aggregation of context about entities in the environment Performance is vital Actions need to be taken in time for it to be of use to the users Very difficult to achieve near real-time User should retain control Should be able to cancel, stop and undo actions Not always possible Privacy and Security must be guaranteed The users should decide how, where, to whom and for how long their personal information is accessible
- 32. Context-Aware Computing Concepts & Architecture