Controlling and organization of international business
- 1. WELCOME
- 2. International Business Marketing Strategy Planning Finance The important question is how to manage them
- 3. Management control and organization You can’t manage what you can’t measure
- 4. Controlling and Organization of International Business By Arpit amar International marketing-2011
- 5. Contents •Organization of business •Architecture and structure of organization •Principles of controlling •Importance of controlling •Levels of controlling •Factors affecting controlling •Steps in controlling •How to control international marketing •How control and organization relates to marketing IM@ 2011
- 6. Principles of organization “The organization of international business refers to the integrated function of formal organization structure, coordination, control system, processes, culture and people. -Charles W.L. Hill” Three factors in organization •Division of the organization into subunits •Decision-making responsibilities (centralized vs. decentralized) •The establishment of integrating mechanisms to coordinate the activities. IM@ 2011
- 7. Architecture of organization People Internal body parts of organization Example process structure Siemens culture system IM@ 2011
- 8. Structure of organization External body adjustments Vertical of differentiation organization Horizontal differentiation Integrating mechanism IM@ 2011
- 9. Vertical differentiation The location of Centralization decision making responsibilities with in the structure of organization Decentralization IM@ 2011
- 10. Horizontal differentiation Function How the organization decides to divide Types of business its various departments or activities into sub units Geographical area IM@ 2011
- 11. Integrating mechanism •Direct contacts How the •Teams Formal organization •Matrix structures develops various mechanism to coordinate and integrate between •Knowledge network Informal different sub units •Information transmission IM@ 2011
- 12. Principles of controlling “Control refers to the task of ensuring that activities are producing the desired results and is limited to monitoring the outcome of activities, reviewing feedback information about this outcome, and if necessary, taking corrective actions". - Reeves and Woodward Features of Controlling •One can control future happenings but not what has happened. •Every manager in an organization has to perform the control function. •Control is a continuous process IM@ 2011
- 13. Why is it important? Helps in Performance Efficiency in decision evaluation operation making Establish Monitoring of superior- process and subordinate planning relation IM@ 2011
- 14. Levels of controlling • Strategic control • Organization • Operations control control • How the international • How the • How the business international international formulates and business design business focus achieves its acts in response on operating strategic goals to changes in systems in an organization organization and environment its subsidiaries IM@ 2011
- 15. Strategic Organization Operation control control control examples examples examples •Market entry •Finance and cost regulation •Production analysis •Environment •Credit rating checks •Cost factors •Profitability analysis •Consulting and •Supply and logistics •Innovation and communication regulation development •Promotion and advertising •Auditing and inspection •Product mix •legal regulations •Time management •Competitor analysis •Uniformity to standards •Storage and transport IM@ 2011
- 16. Factors affecting controlling Domestic values and practices Communication systems Distance Environmental differences Environmental stability Subsidiary performance Quality of international operations IM@ 2011
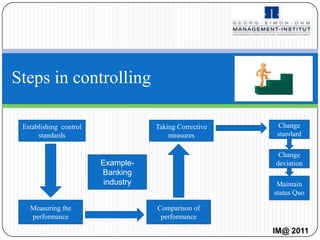
- 17. Steps in controlling Establishing control Taking Corrective Change standards measures standard Change Example- deviation Banking industry Maintain status Quo Measuring the Comparison of performance performance IM@ 2011
- 18. “How to control international marketing operations” Break even analysis- total revenue and total cost Financial analysis - cash flow analysis, ratio analysis, monitoring capital expenditure Return on investment(ROI)- on fixed asset, working capital ,analyzing risk taking Management audit- efficiency evaluation by experts of plans, policies, systems and procedures Management information system- data collection and processing to manager, delegation and control Performance evaluation techniques- benchmarking for processes and competitor, balance score card IM@ 2011
- 19. How controlling and organization affects international marketing Strategic If organization is Apple marketing centralized control Luxemburg If organization is Operations level based De decentralized marketing control beers If marketing Organizational Amazon strategies control changes fast IM@ 2011
- 20. Summary •Organization of international business •Controlling of international business •Marketing control techniques •Relation of controlling and organization to marketing References: Handbook marketing – controlling by Christopher zerres, Michael p. zerres Marketing management by Philip kotler Global marketing management by W. keegen, M.green IM@ 2011
- 21. Questions Thanks IM@ 2011