Coordinate geometry
- 2. âĒADITYA PRASAD SAHU â AUM PRASAD SAHU â SUNIL â BISWAJIT SABAR â PAWAN
- 3. âĒ Western Europe. Analytic geometry was independently invented by RenÃĐ Descartes and Pierre de Fermat, although Descartes is sometimes given sole credit. Cartesian geometry, the alternative term used for analytic geometry, is named after Descartes. ... Pierre de Fermat also pioneered the development of analytic geometry.
- 4. âĒ The definition of coordinate geometry is the study of algebraic equations on graphs. An example of coordinate geometry is plotting points, lines and curves on an x and y axis. Introduction
- 5. âĒA Cartesian plane consist of two mutually perpendicular number lines intersecting each other at their zero.
- 6. âĒAs shown in the adjoining diagram, the coordinate axes divide a coordinate plane into four parts which are known as Quadrants.
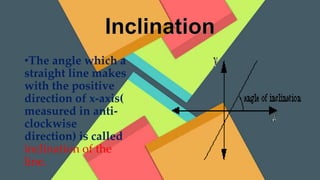
- 7. âĒThe angle which a straight line makes with the positive direction of x-axis( measured in anti- clockwise direction) is called inclination of the line.
- 8. âĒIf à is the inclination of a line; the slope of the line is tan à and is usually denoted by letter m,
- 9. âĒIf a straight line meets y axis at a point ,the distance of point from the origin is called Y-intercept .
- 10. Horizontal and Vertical lines âĒThe gradient of horizontal line is zero. (horizontal line is flat â No slope) The gradient of a vertical line is infinity. (Vertical line â gradient is maximum.)
- 11. âĒThe positive of any point in the Cartesian Plane can be determined by its distance from each axes.
- 12. Collinear point *Point are collinear if they al lie on the same line *You need to establish that they have -a common direction -a common point
- 13. Median âĒA median is the line that joins a vertex of a triangle to the midpoints of the opposite side.
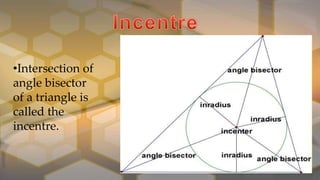
- 14. âĒIntersection of angle bisector of a triangle is called the incentre.
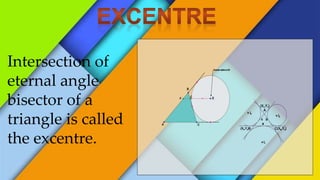
- 15. Intersection of eternal angle bisector of a triangle is called the excentre.
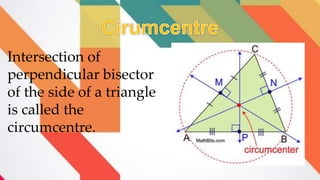
- 16. Intersection of perpendicular bisector of the side of a triangle is called the circumcentre.
- 17. âĒIntersection of altitudes of a triangle is called the orthocentre.
- 18. Thanks!