Copd. pptx
- 2. DEFINITION: ? Copd is the progressive and partially reversible disease of the airway. ? Chronic obstruction of the flow of air through the airway and out of the lung permanent and progressive obstruction over time.
- 3. Causes ? SMOKING ? OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE ? AIR POLLUTION ? SUDDEN AIRWAY CONSTRICTION IN RESPONSE TO INHALED IRRITENT ? BRONCHIAL HUPERRESPONSIVENESS(IT IS A CHARACTERISTIC OF ASTHMA) ? GENETICS
- 4. COPD
- 5. Clinical Features ? Chronic cough ? Sputum production ? Wheezing ? Chest tightness ? Dyspnea on exertion ? Weight loss ? Respiratory insufficiency ? Respiratory infections
- 6. Physical Signs ? Barrel shaped chest ? Expiratory through pursed lips
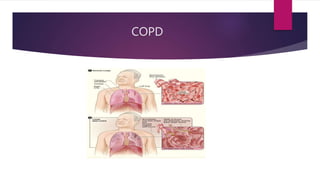
- 7. COPD Includes ? BRONCHITIS ? EMPHYSEMA
- 8. BRONCHITIS It is a inflammation of bronchi Leading to increase in mucus production , cough and eventual scaring Of the bronchial lining. It us defined as a Production of cough and sputum for 3 months.
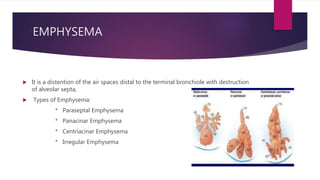
- 9. EMPHYSEMA ? It is a distention of the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchiole with destruction of alveolar septa, ? Types of Emphysema: * Paraseptal Emphysema * Panacinar Emphysema * Centriacinar Emphysema * Irregular Emphysema
- 10. RISK FACTORS
- 12. PATHOLOGY ? Chronic inflammation ? Increase in number of goblet cell ? Mucus gland hyperplasia ? Fibrosis ? Narrowing and reduction of small airways ? Airway collapse due to the Loss of tethering caused by alveolar wall destruction in Emphysema
- 13. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS ? Frequent productive cough during winter ? Chronic sputum production ? Dysnea ? Hemoptisis ? Hypercapnea ? Hypoximia
- 14. DIAGNOSIS ? Chest X Ray ? Sputum testing ? Lung functioning test ? ABG(Arterial Blood gas) ? CBC(Complete blood Count )
- 15. MANAGEMENT ? Medications ? Surgical management
- 16. MEDICATION ? Mild copd- Beta 2 Agonist { Formetrol ; Salmeterol;Terbutalin} ? Moderate copd- Along with beta 2 agonist {Ipratropium bromide;oxitropium bromide} and anticholinergics {Tiotropium} ? Severe copd- inhaled glucocorticosteroids {Beclomethosone;Budesonide;fluticasone}
- 17. MEDICATIONS ? Very severe copd *Long term o2 *Ventilatory assistance *Management of cardiac failure *Consider surgical management *All drugs are followed
- 18. Surgical management ? Bullectomy ? Lung volume reduction ? Lung transplantation
- 19. O2 therapy ? Goals of O2 therapy Its is used to treat hypoxia ? To refuse the work of breathing ? To maintain the PaO2 ? To reduse workload of the heart
- 20. COMPLICATIONS ? Pneumonia ? Respiratory failure ? Cor pulmonale
- 22. PREVENTION ? Stay away from infectious person
- 24. PREVENTION ? Eat regular balanced diet
- 25. PREVENTION ? DrInk plenty fresh water at least 1.5 L/day
- 26. PREVENTION ? Get plenty of sleep
- 27. ? THANK YOU
![COPD[CHRONIC
OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY
DISEASE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/copd-200705142359/85/Copd-pptx-1-320.jpg)