Coping strategies in labour
Download as PPTX, PDF5 likes1,091 views
Coping strategies in labour, Helps to copp up with the pain in the labour, with the relaxation techniqiues mentioned, helps to prevent mother from psychological disorders.
1 of 18
Downloaded 11 times




’üĄ Imagery
’üĄ Hot water bath](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/copingstrategiesinlabour-191120163206/85/Coping-strategies-in-labour-4-320.jpg)













Recommended
Physiotherapy options for coping with labour (2)



Physiotherapy options for coping with labour (2)amrit kaur
╠²
Physiotherapists can help women cope with labor through various techniques including relaxation, breathing methods, positioning, massage, and other strategies. Relaxation is important for reducing pain and tension during labor. Breathing techniques aim to provide oxygen, reduce pain, induce relaxation, and act as a distraction. Different breathing patterns are recommended for the first, second, and third stages of labor to best assist the birthing process.Antenatal physiotherapy



Antenatal physiotherapyDr. Akshita Duha Juneja (PT)
╠²
This document provides information about antenatal physiotherapy including its aims, guidelines, exercises and common discomforts during pregnancy. The aims are to improve mother and baby's health and ensure they are prepared for labor, lactation and infant care. Guidelines include warming up, avoiding jerky movements, and stopping exercises if pain occurs. The exercise plan progresses from warm up to aerobic to strengthening and relaxation. Common discomforts like nausea, heartburn and backache are discussed with tips for management.Pelvic floor rehabilitation



Pelvic floor rehabilitationamrit kaur
╠²
The document discusses pelvic floor rehabilitation, including identifying the pelvic floor muscles, common pelvic floor exercises, proper technique, common errors to avoid, and functional retraining exercises like coughing and sneezing that require coordinated pelvic floor and abdominal muscle activation.Energy conservation techniques



Energy conservation techniquesyashpatel959
╠²
Physical therapists play a key role in identifying patients who have become too debilitated to independently perform daily living activities due to chronic diseases. They teach energy conservation and work simplification techniques to help patients pace themselves. These techniques include establishing routines with rest periods, sitting whenever possible, eliminating unnecessary tasks, avoiding strenuous activities, keeping cool, gradually increasing activity levels, organizing work areas, and using assisted devices.PHYSIOTHERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT POST RADICAL MASTECTOMY.pptx



PHYSIOTHERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT POST RADICAL MASTECTOMY.pptxDRNEHAINGALECHAUDHAR
╠²
radical mastectomy is a disabling condition, the side effects and post surgical complications of the conditions affect the patient both physically, psychologically and socially. in this presentation, an attempt to cover problem list, do's and don'ts, assessment, management is explained in detail. Positional release technique



Positional release techniqueVenus Pagare
╠²
This document discusses positional release technique (PRT), including:
1. PRT was developed by Dr. Lawrence Jones in 1964 as an osteopathic treatment technique using specific positions to reduce tender points and musculoskeletal dysfunction.
2. Assessment for PRT involves identifying areas of asymmetry, range of motion restrictions, texture changes, and tender points to determine dominant tender points and appropriate positions of treatment.
3. PRT is based on the theory that positions can help "arrest inappropriate proprioceptive activity" and allow tissues to return to a neutral length slowly for pain relief and release of somatic dysfunction.Myofascial Release Presentation 



Myofascial Release Presentation Katie Emmett ¤īÉ Myofascial Decompression Therapy
╠²
Presentation slides from our recent workshop on Myofascial Release. This workshop was delivered from our St John Street Clinic in Manchester on Saturday 17th March.MITCHELLŌĆÖS RELAXATION TECHNIQUE 



MITCHELLŌĆÖS RELAXATION TECHNIQUE ChristySopna
╠²
The document discusses Mitchell's relaxation technique, which uses diaphragmatic breathing and isotonic muscle contractions based on reciprocal inhibition. It can be used to treat respiratory, orthopedic, post-natal, and psychiatric conditions. The technique promotes relaxation and reduces muscle tension and pain perception. It is effective for pre-labor Braxton Hicks contractions and realigning stress-related postures by moving to a new position and increasing awareness of body position. Mitchell's relaxation technique can also help conditions involving a high tone pelvic floor like painful bladder syndrome.5 pelvic floor exercises for women



5 pelvic floor exercises for womenjagan _jaggi
╠²
To strengthen your pelvic floor muscles, sit comfortably and squeeze the muscles 10-15 times in a row. Don't hold your breath or tighten your stomach, buttock or thigh muscles at the same time. When you get used to doing pelvic floor exercises, you can try holding each squeeze for a few seconds.Musculoskeletal changes in pregnancy



Musculoskeletal changes in pregnancyamrit kaur
╠²
This document discusses the musculoskeletal changes that occur during pregnancy and the perinatal period. It notes that pregnancy results in weight gain, a shifting center of gravity, and ligamentous laxity that impacts posture. Hormonal changes like increased relaxin soften connective tissues. This leads to joint hypermobility and decreased proprioception. Back pain can result from these changes, weight gain, and repetitive motions. The document also examines muscle, ligament, spinal and uterine changes that impact biomechanics during pregnancy.Pnf respiratory



Pnf respiratoryApatel99094
╠²
Neurophysiological Facilitation of Respiration is a treatment technique used for respiratory care of patients with unconscious or non-alert, and ventilated, and also with a neurological condition
NPF is the use of external proprioceptive and tactile stimuli that produce reflex respiratory movement responses and that increase the rate and depth of breathingBiomechanics of throwing



Biomechanics of throwingAragyaKhadka
╠²
this involves the series of movements that occurs in the glenohumeral joints among the pitchers, like fast bowlers, baseball players. Women's health antenatal post natal



Women's health antenatal post natalThangamani Ramalingam
╠²
The document discusses women's health and exercise during pregnancy. It provides guidelines for exercise during each trimester, including frequency, intensity, time and type of exercise recommended. It also discusses potential complications during pregnancy, labor, and the postnatal period. Exercise is recommended to reduce health risks during pregnancy, but should avoid high impact activities and the supine position after the first trimester. Guidelines are given for safe exercise during and after pregnancy.WORK CONDITIONING AND WORK HARDENING



WORK CONDITIONING AND WORK HARDENINGDr. Nithin Nair (PT)
╠²
The document discusses work conditioning and work hardening programs. It defines each term and compares their key aspects. Work conditioning addresses physical and functional needs through exercises and job simulation to restore abilities. Work hardening is more intensive and also addresses psychosocial and vocational needs using real work activities. Both aim to increase strength, endurance and range of motion to safely return individuals to their prior level of work.PT IN OBSTETRICS



PT IN OBSTETRICSMuskan Qureshi
╠²
Its an elaborative slide explaining briefly the prestigious process of labour and mainly the physiotherapy required in it for ease of labourDiastasis recti



Diastasis rectiamrit kaur
╠²
This document discusses diastasis recti, which is a separation of the rectus abdominis muscles along the midline. Diastasis recti commonly occurs during pregnancy due to hormonal and biomechanical factors and can lead to back pain and hernias. Examination involves checking for a separation greater than 2 cm between the muscles. Treatment consists of exercises to gently bring the muscles back together, like pelvic tilts and modified crunches while avoiding twisting motions or heavy lifting that could worsen the separation. Proper form and gradual progression are important to rehabilitate the abdominal muscles.SI JOINT DYSFUNCTION.pptx



SI JOINT DYSFUNCTION.pptxkajal sansoya
╠²
SI joint dysfunction, causes,risk factors,muscles, ligaments affected the most, differentional diagnosis, x-findings, special test, muscles strengthening, ligament strengthening, daily physiotherapy protocal, electrotherapy treatment, strengthening and stretching protcol, precautions, postural correctionLecture 1: Pursed Lip and Diaphragmatic Breathing



Lecture 1: Pursed Lip and Diaphragmatic BreathingBabette Parthum
╠²
A presentation created for Pulmonary Rehab for breathing techniques. Overview of pursed lip breathing and diaphragmatic breathing.Normal labor and physical therapy role 



Normal labor and physical therapy role South Valley University, Egypt and Queen's University, Ontario
╠²
Labor is defined as the process of expelling the fetus from the uterus through contractions of the uterus and cervix. It has four stages: 1) cervical dilation and effacement, 2) delivery of the fetus, 3) delivery of the placenta, 4) observation of the mother and baby. The first stage involves regular contractions that thin and open the cervix. The second stage involves pushing the baby through the birth canal in two phases. The third stage involves delivering the placenta, and the fourth involves post-delivery monitoring.Mulligan mobilization (MWM)



Mulligan mobilization (MWM)Radhika Chintamani
╠²
A school of manual therapy, a therapy which provides Instant result with long lasting effect. treating almost all causes.Physical therapy for hysterectomy



Physical therapy for hysterectomySouth Valley University, Egypt and Queen's University, Ontario
╠²
Hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the uterus, and sometimes other female reproductive organs. It is one of the most common gynecological surgeries, with over 600,000 performed annually in the US. There are several types of hysterectomy that are performed depending on factors like the surgical approach and extent of organ removal. Physical therapy both before and after hysterectomy aims to improve patient strength, mobility, and recovery through exercises targeting the core, pelvic floor, breathing, and circulation. Complications can include infection, incontinence, and prolapse, so physical therapy also focuses on preventing and managing these issues.MET: Muscle Energy Technique



MET: Muscle Energy TechniqueRadhika Chintamani
╠²
Muscle energy technique, a manual therapy technique with a long term history and 8 variations which can be used in various condition to treat muscle as well as joints. This slide show consists of detailed history, variations/types and summary of MET in detail.Pre and post operative Physiotherapay 



Pre and post operative Physiotherapay Kaushik Patel
╠²
Physiotherapy plays an important role in the pre and postoperative care of patients undergoing abdominal surgery. In the preoperative stage, physiotherapy focuses on assessing respiratory and circulatory function, educating the patient on breathing and mobility exercises, and training the patient to prevent postoperative complications. Postoperatively, physiotherapy aims to prevent pulmonary and circulatory issues through techniques like breathing exercises, early ambulation, and limb movement. The overall goals are to enhance recovery and mobility and ensure patients regain independence.Myofacial Release Therapy(MFR).



Myofacial Release Therapy(MFR).Dr.Debanjan Mondal(PT)
╠²
Myofascial release refers to the manual
technique for stretching the fascia and
releasing bonds between fascia and
Lintegument, musles,and bones, with the goal of
eliminating pain, increasing range of motion
and balancing the body.Low back pain & ergonomics 



Low back pain & ergonomics Rajani Cartor
╠²
Low back pain is a common cause of disability that affects people of all cultures. It can be acute, lasting less than three months, or chronic, lasting over three months. Common causes include muscle strains, arthritis, herniated discs, and osteoporosis. Physical examination involves assessing range of motion, neurological function, and diagnostic tests like x-rays and MRIs. Physiotherapy management aims to reduce pain and inflammation, improve muscle strength and flexibility, and prevent recurrence through exercises and physical agents like ultrasound, TENS, and spinal traction.ROL METS.pptx



ROL METS.pptxPraneetha44
╠²
The document provides an overview of metabolic equivalents (METs), including:
- Definitions of METs and how they are used to quantify the intensity of physical activities.
- Clinical importance of METs in describing functional capacity and prescribing exercise intensities.
- Classification of activity intensities based on MET thresholds.
- How METs are calculated and converted and how they relate to functional capacity.
- Use of METs in cardiac rehabilitation to progress patients through levels of activity intensity.
- Limitations of MET measures including assumptions about energy expenditure.Principles of mulligan



Principles of mulliganDr.Debanjan Mondal(PT)
╠²
Brian Mulligan described novel concept of the simultaneous application of therapist applied accessory mobilizations and patient generated active movementsCongenital Dislocation of the Hip - PHYSIOTHERAPY



Congenital Dislocation of the Hip - PHYSIOTHERAPYUPASANA AGARWAL
╠²
Congenital dislocation of the hip (CDH), also known as developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), is a condition where the femoral head is displaced from the acetabulum. It can occur before, during or after birth. Girls are more commonly affected than boys. Causes may include hereditary joint laxity, breech birth position, or defective acetabulum development. Treatment involves splinting or bracing in infants to encourage reduction, and may require surgery in older children if reduction does not occur. Physiotherapy focuses on maintaining reduction, improving range of motion and strengthening muscles.Relaxation



RelaxationPoojaChaudhuri3
╠²
This document discusses relaxation techniques. It defines relaxation as a state where muscle tension and mental stress are reduced through conscious effort. Relaxation can be general, involving the whole body, or local, targeting specific muscle groups. Several factors like muscle tone, posture, movement, and mental state can affect relaxation. Techniques to achieve general relaxation include assuming supported, comfortable positions and creating a restful atmosphere. Specific techniques discussed are autogenic training, progressive muscle relaxation, and the contrast method, which involve sequentially contracting and relaxing different muscle groups.Relaxation 3.pptx



Relaxation 3.pptxDr. Nazish Rafique
╠²
Relaxation reduces muscle tension and mental stress through conscious effort. It can be classified as mental, physical, general, or local relaxation. Factors affecting relaxation include muscle tone, postural tone, voluntary movement, and mental attitudes. Relaxation training techniques aim to reduce tension through methods like progressive muscle relaxation, autogenic training, and awareness through movement. Relaxation can be tested and its level determined by indicators like decreased muscle tension, lowered vital signs, and a relaxed physical appearance and demeanor.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
5 pelvic floor exercises for women



5 pelvic floor exercises for womenjagan _jaggi
╠²
To strengthen your pelvic floor muscles, sit comfortably and squeeze the muscles 10-15 times in a row. Don't hold your breath or tighten your stomach, buttock or thigh muscles at the same time. When you get used to doing pelvic floor exercises, you can try holding each squeeze for a few seconds.Musculoskeletal changes in pregnancy



Musculoskeletal changes in pregnancyamrit kaur
╠²
This document discusses the musculoskeletal changes that occur during pregnancy and the perinatal period. It notes that pregnancy results in weight gain, a shifting center of gravity, and ligamentous laxity that impacts posture. Hormonal changes like increased relaxin soften connective tissues. This leads to joint hypermobility and decreased proprioception. Back pain can result from these changes, weight gain, and repetitive motions. The document also examines muscle, ligament, spinal and uterine changes that impact biomechanics during pregnancy.Pnf respiratory



Pnf respiratoryApatel99094
╠²
Neurophysiological Facilitation of Respiration is a treatment technique used for respiratory care of patients with unconscious or non-alert, and ventilated, and also with a neurological condition
NPF is the use of external proprioceptive and tactile stimuli that produce reflex respiratory movement responses and that increase the rate and depth of breathingBiomechanics of throwing



Biomechanics of throwingAragyaKhadka
╠²
this involves the series of movements that occurs in the glenohumeral joints among the pitchers, like fast bowlers, baseball players. Women's health antenatal post natal



Women's health antenatal post natalThangamani Ramalingam
╠²
The document discusses women's health and exercise during pregnancy. It provides guidelines for exercise during each trimester, including frequency, intensity, time and type of exercise recommended. It also discusses potential complications during pregnancy, labor, and the postnatal period. Exercise is recommended to reduce health risks during pregnancy, but should avoid high impact activities and the supine position after the first trimester. Guidelines are given for safe exercise during and after pregnancy.WORK CONDITIONING AND WORK HARDENING



WORK CONDITIONING AND WORK HARDENINGDr. Nithin Nair (PT)
╠²
The document discusses work conditioning and work hardening programs. It defines each term and compares their key aspects. Work conditioning addresses physical and functional needs through exercises and job simulation to restore abilities. Work hardening is more intensive and also addresses psychosocial and vocational needs using real work activities. Both aim to increase strength, endurance and range of motion to safely return individuals to their prior level of work.PT IN OBSTETRICS



PT IN OBSTETRICSMuskan Qureshi
╠²
Its an elaborative slide explaining briefly the prestigious process of labour and mainly the physiotherapy required in it for ease of labourDiastasis recti



Diastasis rectiamrit kaur
╠²
This document discusses diastasis recti, which is a separation of the rectus abdominis muscles along the midline. Diastasis recti commonly occurs during pregnancy due to hormonal and biomechanical factors and can lead to back pain and hernias. Examination involves checking for a separation greater than 2 cm between the muscles. Treatment consists of exercises to gently bring the muscles back together, like pelvic tilts and modified crunches while avoiding twisting motions or heavy lifting that could worsen the separation. Proper form and gradual progression are important to rehabilitate the abdominal muscles.SI JOINT DYSFUNCTION.pptx



SI JOINT DYSFUNCTION.pptxkajal sansoya
╠²
SI joint dysfunction, causes,risk factors,muscles, ligaments affected the most, differentional diagnosis, x-findings, special test, muscles strengthening, ligament strengthening, daily physiotherapy protocal, electrotherapy treatment, strengthening and stretching protcol, precautions, postural correctionLecture 1: Pursed Lip and Diaphragmatic Breathing



Lecture 1: Pursed Lip and Diaphragmatic BreathingBabette Parthum
╠²
A presentation created for Pulmonary Rehab for breathing techniques. Overview of pursed lip breathing and diaphragmatic breathing.Normal labor and physical therapy role 



Normal labor and physical therapy role South Valley University, Egypt and Queen's University, Ontario
╠²
Labor is defined as the process of expelling the fetus from the uterus through contractions of the uterus and cervix. It has four stages: 1) cervical dilation and effacement, 2) delivery of the fetus, 3) delivery of the placenta, 4) observation of the mother and baby. The first stage involves regular contractions that thin and open the cervix. The second stage involves pushing the baby through the birth canal in two phases. The third stage involves delivering the placenta, and the fourth involves post-delivery monitoring.Mulligan mobilization (MWM)



Mulligan mobilization (MWM)Radhika Chintamani
╠²
A school of manual therapy, a therapy which provides Instant result with long lasting effect. treating almost all causes.Physical therapy for hysterectomy



Physical therapy for hysterectomySouth Valley University, Egypt and Queen's University, Ontario
╠²
Hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the uterus, and sometimes other female reproductive organs. It is one of the most common gynecological surgeries, with over 600,000 performed annually in the US. There are several types of hysterectomy that are performed depending on factors like the surgical approach and extent of organ removal. Physical therapy both before and after hysterectomy aims to improve patient strength, mobility, and recovery through exercises targeting the core, pelvic floor, breathing, and circulation. Complications can include infection, incontinence, and prolapse, so physical therapy also focuses on preventing and managing these issues.MET: Muscle Energy Technique



MET: Muscle Energy TechniqueRadhika Chintamani
╠²
Muscle energy technique, a manual therapy technique with a long term history and 8 variations which can be used in various condition to treat muscle as well as joints. This slide show consists of detailed history, variations/types and summary of MET in detail.Pre and post operative Physiotherapay 



Pre and post operative Physiotherapay Kaushik Patel
╠²
Physiotherapy plays an important role in the pre and postoperative care of patients undergoing abdominal surgery. In the preoperative stage, physiotherapy focuses on assessing respiratory and circulatory function, educating the patient on breathing and mobility exercises, and training the patient to prevent postoperative complications. Postoperatively, physiotherapy aims to prevent pulmonary and circulatory issues through techniques like breathing exercises, early ambulation, and limb movement. The overall goals are to enhance recovery and mobility and ensure patients regain independence.Myofacial Release Therapy(MFR).



Myofacial Release Therapy(MFR).Dr.Debanjan Mondal(PT)
╠²
Myofascial release refers to the manual
technique for stretching the fascia and
releasing bonds between fascia and
Lintegument, musles,and bones, with the goal of
eliminating pain, increasing range of motion
and balancing the body.Low back pain & ergonomics 



Low back pain & ergonomics Rajani Cartor
╠²
Low back pain is a common cause of disability that affects people of all cultures. It can be acute, lasting less than three months, or chronic, lasting over three months. Common causes include muscle strains, arthritis, herniated discs, and osteoporosis. Physical examination involves assessing range of motion, neurological function, and diagnostic tests like x-rays and MRIs. Physiotherapy management aims to reduce pain and inflammation, improve muscle strength and flexibility, and prevent recurrence through exercises and physical agents like ultrasound, TENS, and spinal traction.ROL METS.pptx



ROL METS.pptxPraneetha44
╠²
The document provides an overview of metabolic equivalents (METs), including:
- Definitions of METs and how they are used to quantify the intensity of physical activities.
- Clinical importance of METs in describing functional capacity and prescribing exercise intensities.
- Classification of activity intensities based on MET thresholds.
- How METs are calculated and converted and how they relate to functional capacity.
- Use of METs in cardiac rehabilitation to progress patients through levels of activity intensity.
- Limitations of MET measures including assumptions about energy expenditure.Principles of mulligan



Principles of mulliganDr.Debanjan Mondal(PT)
╠²
Brian Mulligan described novel concept of the simultaneous application of therapist applied accessory mobilizations and patient generated active movementsCongenital Dislocation of the Hip - PHYSIOTHERAPY



Congenital Dislocation of the Hip - PHYSIOTHERAPYUPASANA AGARWAL
╠²
Congenital dislocation of the hip (CDH), also known as developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), is a condition where the femoral head is displaced from the acetabulum. It can occur before, during or after birth. Girls are more commonly affected than boys. Causes may include hereditary joint laxity, breech birth position, or defective acetabulum development. Treatment involves splinting or bracing in infants to encourage reduction, and may require surgery in older children if reduction does not occur. Physiotherapy focuses on maintaining reduction, improving range of motion and strengthening muscles.Similar to Coping strategies in labour (20)
Relaxation



RelaxationPoojaChaudhuri3
╠²
This document discusses relaxation techniques. It defines relaxation as a state where muscle tension and mental stress are reduced through conscious effort. Relaxation can be general, involving the whole body, or local, targeting specific muscle groups. Several factors like muscle tone, posture, movement, and mental state can affect relaxation. Techniques to achieve general relaxation include assuming supported, comfortable positions and creating a restful atmosphere. Specific techniques discussed are autogenic training, progressive muscle relaxation, and the contrast method, which involve sequentially contracting and relaxing different muscle groups.Relaxation 3.pptx



Relaxation 3.pptxDr. Nazish Rafique
╠²
Relaxation reduces muscle tension and mental stress through conscious effort. It can be classified as mental, physical, general, or local relaxation. Factors affecting relaxation include muscle tone, postural tone, voluntary movement, and mental attitudes. Relaxation training techniques aim to reduce tension through methods like progressive muscle relaxation, autogenic training, and awareness through movement. Relaxation can be tested and its level determined by indicators like decreased muscle tension, lowered vital signs, and a relaxed physical appearance and demeanor.Massage therapy



Massage therapyAndres Perez Zu├▒iga
╠²
Massage therapy has been practiced for millennia and involves manipulating the soft tissues of the body through techniques like effleurage, petrissage, and friction. It can provide physiological benefits like relaxation, reduced pain, and increased blood flow. The history of massage therapy is traced back to ancient civilizations but modern techniques were developed in the 19th century primarily in Europe and Sweden.Relaxation therapy



Relaxation therapyZahiruddin Othman
╠²
Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) and breathing exercises can help reduce tension and anxiety. PMR involves tensing then relaxing specific muscle groups to learn the difference between tension and relaxation. A full PMR schedule takes 10 minutes daily but can be shortened by focusing on muscle groups together. Deep muscle relaxation and cue-controlled relaxation allow inducing relaxation without tensing muscles. Abdominal breathing from the diaphragm and a calming breath exercise involving slow inhaling and exhaling can also help relax the body and mind. Regular practice of these techniques trains the body to maintain relaxation.Pain management of 1st stage of labour.pptx



Pain management of 1st stage of labour.pptxsimadas65117
╠²
Please do like and subscribe my channel for more details new upcoming updates for free version#pain#management@pain@management@first stage ~labour
follow me for more medical and nursing notes in detail
@nursing@medicine@public @all@health personal @medical students Chapter 6 relaxation.pptx



Chapter 6 relaxation.pptxFarwahAsad
╠²
This document discusses muscle relaxation and tone. It defines relaxation as muscles being free from tension at rest. Tension develops with muscle contraction and is reduced during relaxation. Muscles always maintain some tone or firmness even at rest due to muscle spindles. The document describes anatomy and function of muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs which help regulate muscle tone and relaxation. It provides techniques to achieve general relaxation through positioning, breathing, and progressive relaxation methods. Localized relaxation techniques are also discussed.Therapeutic Massage presentation, Massage ppt, 



Therapeutic Massage presentation, Massage ppt, MDSAMIMULLAH
╠²
Benefits of massage, Swedish massage, Massage presentation by samiullah, History of the Massage, Deep Tissue Massage, Hot Stone Massage, Purpose of Massage, Types of massage ppt, Purpose of the Massage, Physiological effects, Thai Massage, Contraindication of MassageRelaxation



RelaxationRAJESH MANI
╠²
The document discusses various techniques for relaxation in three parts. It first covers general relaxation methods like different lying positions, comfort, and creating a restful atmosphere. Second, it describes additional relaxation techniques like conscious breathing, progressive relaxation, and contrast methods. Finally, it discusses local relaxation techniques for specific purposes like preparing for massage, relieving spasms, and combating muscle imbalances. The overall document provides an in-depth overview of relaxation methods used in physiotherapy.Airway clearance techniques



Airway clearance techniquesBimal maurya
╠²
The document discusses various airway clearance techniques including active cycle of breathing techniques (ACBT), autogenic drainage, percussion, and vibration/shaking. ACBT uses breathing control, deep breathing exercises, and huffing to loosen and clear secretions from the lungs. Autogenic drainage uses different breathing patterns at low, middle, and high lung volumes to mobilize mucus. Percussion and vibration techniques involve manual chest compressions timed with breathing to enhance mucus clearance. These techniques aim to improve lung ventilation, cough effectiveness, and clear secretions from the airways.Massage Fusion: The Jing Method for the treatment of chronic pain - Massage W...



Massage Fusion: The Jing Method for the treatment of chronic pain - Massage W...Jing Massage
╠²
This document provides suggestions for a stress reduction protocol for massage clients suffering from chronic conditions like fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue. It outlines preparatory relaxation techniques, myofascial release methods like cross-hand stretches and leg/arm pulls, acupressure point treatment, breathing exercises, and concluding stretches. The protocol is designed to reduce stress and tension in the body through deep tissue work, fascial release, trigger point therapy, and integrating the client's breath.relaxation therapy.pptx



relaxation therapy.pptxKavitha Krishnan
╠²
A relaxation technique (also known as relaxation training) is any method, process, procedure, or activity that helps a person to relax; to attain a state of increased calmness; or otherwise reduce levels of pain, anxiety, stress or anger.
Relaxation therapy - Boo



Relaxation therapy - BooBoomi Nathan
╠²
This document provides an overview of relaxation therapy. It defines relaxation therapy as techniques that promote stress reduction and a calm state of mind. Some key techniques discussed include progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, yoga, biofeedback, physical exercise, and deep breathing. The goals of relaxation therapy are to calm the mind and induce a relaxation response. Benefits include reduced stress, anxiety, muscle tension, blood pressure, heart rate, and improved sleep, focus, and energy. The nurse's role is to help individuals identify sources of stress, coping methods, and evaluate the effectiveness of relaxation techniques.ALTERNATIVE AND COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES DURING INTRANATAL PERIOD



ALTERNATIVE AND COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES DURING INTRANATAL PERIODKanchan Mehra
╠²
Alternative and complementary therapies are increasingly popular during pregnancy and childbirth to help cope with symptoms and relieve pain. These include acupuncture, acupressure, herbal medicine, homeopathy, hypnotherapy, massage, aromatherapy, yoga, reflexology, therapeutic touch, osteopathy, and hydrotherapy. While many of these therapies can provide benefits, they must be used accurately and some carry risks, so it is important to consult medical professionals before trying any alternative or complementary therapies during pregnancy or labor.Progressive Relaxation Meditation.pdf



Progressive Relaxation Meditation.pdfKnowing Overt
╠²
Progressive relaxation meditation is a type of mindfulness meditation that involves focusing on the sensations of different parts of the body and deliberately relaxing them. The aim is to achieve a state of deep relaxation and increased awareness.Today, progressive relaxation meditation is widely practiced as a means of promoting relaxation, improving sleep, and reducing stress and anxiety. It is also sometimes used as a tool for managing chronic pain.
There is a growing body of scientific evidence to support the health benefits of progressive relaxation meditation. A recent study found that the practice can help to reduce blood pressure and heart rate, and improve sleep quality.
If you're interested in trying progressive relaxation meditation, there are a few things you can do to get started. First, find a comfortable place to sit or lie down. Then, begin to focus your attention on your breath.Progressive Relaxation Meditation.pdf



Progressive Relaxation Meditation.pdfKnowing Overt
╠²
Progressive relaxation meditation is a form of mindfulness meditation that involves focusing on each muscle group in the body, one at a time, and tensing and relaxing them. The goal is to achieve a state of complete muscle relaxation and to focus on the sensation of the breath.RELAXATION TECHNIQUES



RELAXATION TECHNIQUESKOMAL SAWANT
╠²
The document discusses various relaxation techniques. It begins by defining relaxation as a conscious effort to relieve muscle tension. It then lists several benefits of relaxation, such as lowering blood pressure and improving mood. The document goes on to describe different relaxation techniques including general relaxation, local relaxation, progressive relaxation, contrast methods, and physiological relaxation. It provides details on creating a restful atmosphere and promoting relaxation through positioning, breathing exercises, and passive movement. The overall purpose is to outline strategies for reducing tension and anxiety through therapeutic relaxation methods.ALTERNATIVE THERAPIES DURING LABOUR.pptx



ALTERNATIVE THERAPIES DURING LABOUR.pptxBhagyashreeDash6
╠²
LABOR IS DIFFICULT PROCESS WHICH NEED ALTERNATIES MODALITIES.Yoga in chronic pulmonary diseases



Yoga in chronic pulmonary diseasesMaher AlQuaimi
╠²
This document discusses various yoga breathing techniques (pranayama) and their effects on the respiratory system. It provides definitions and origins of yoga, describes different types of yoga including Hatha and Iyengar, and outlines several pranayama techniques including Bhastrika, Kapalabhati, Ujjayi, Bhramari, and Anuloma Viloma. Studies are summarized that show pranayama can improve parameters like peak expiratory flow rate, lung function, and respiratory muscle strength while also providing benefits like stress reduction. Precautions and contraindications for certain techniques are also mentioned.More from KariPhysio (6)
Assessment of obesity



Assessment of obesityKariPhysio
╠²
The document discusses several methods for assessing obesity: BMI uses height and weight; waist circumference measures abdominal fat risk; and skinfold thickness measures subcutaneous fat. Additional methods include hydrostatic weighing, bioelectrical impedance analysis, dual energy X-ray absorptiometry, and air displacement plethysmography. Each method has advantages and limitations in accurately determining body fat percentage and distribution.DESCENDING PERINEUM SYNDROME



DESCENDING PERINEUM SYNDROMEKariPhysio
╠²
Descending perineum syndrome (DPS) is characterized by the ballooning of the perineum below the pelvis during straining. It is caused by excessive straining during bowel movements which impairs pelvic floor muscle tone over time. This leads to a descent of the pelvic floor and symptoms like obstructed defecation and eventually fecal incontinence. DPS involves the anterior, middle, and posterior pelvic areas in women. Accurate diagnosis requires examination, imaging, and functional tests to evaluate DPS stage and severity. Treatment may involve biofeedback, pelvic floor exercises or surgery depending on symptoms, stage and response to conservative therapies.Pelvic inflammatory disease



Pelvic inflammatory diseaseKariPhysio
╠²
Pelvic inflammatory disease, describing about the PID causes, investigations, physiotherapy management in acute and chronic stage of PID Neuroanatomy and neurophysiology of pelvic floor



Neuroanatomy and neurophysiology of pelvic floorKariPhysio
╠²
Neuroanatomy and neurophysiology of pelvic floor, described about the neuroanatomy and neurophysiology of pelvic floor, Exercises in high risk pregnancy



Exercises in high risk pregnancyKariPhysio
╠²
Exercises in high risk pregnancy, DESCRIBED about the physical activity during high risk pregnancy according to the levels of high risk pregancy.Menstural cycle 1



Menstural cycle 1KariPhysio
╠²
catamenia is also other name for menstural cycle.
phases of menstural cycle with simple detail about harmones responsible.
Recently uploaded (20)
HER2-Targeting Therapy in HER2+ MBC With and Without CNS Metastases: Selectio...



HER2-Targeting Therapy in HER2+ MBC With and Without CNS Metastases: Selectio...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair and Presenters Sara A. Hurvitz, MD, FACP, Carey K. Anders, MD, FASCO, and Vyshak Venur, MD, discuss metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer in this CME/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE activity titled ŌĆ£Fine-Tuning the Selection and Sequencing of HER2-Targeting Therapies in HER2-Positive MBC With and Without CNS Metastases: Expert Guidance on How to Individualize Therapy Based on Latest Evidence, Disease Features, Treatment Characteristics, and Patient Needs and Preferences.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/4f8sUs7. CME/NCPD/CPE/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until March 2, 2026.BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptx



BIOMECHANICS OF THE MOVEMENT OF THE SHOULDER COMPLEX.pptxdrnidhimnd
╠²
The shoulder complex acts as in coordinated fashion to provide the smoothest and greatest range of motion possible of the upper limb.
Combined motion of GH and ST joint of shoulder complex helps in:
Distribution of motion between other two joints.
Maintenance of glenoid fossa in optimal position.
Maintenance of good length tension
Although some amount of glenohumeral motion may occur while the other shoulder articulations remain stabilized, movement of the humerus more commonly involves some movement at all three shoulder joints.
Description of Beta thalassemia its cause and management.



Description of Beta thalassemia its cause and management.KIMS
╠²
All about Beta Thalassemia etiology , pathology , manifestation and treatment & prevention..Sudurpaschim logsewa aayog Medical Officer 8th Level Curriculum



Sudurpaschim logsewa aayog Medical Officer 8th Level CurriculumDr Ovels
╠²
Sudurpaschim province psc ( lok sewa aayog) medical officer 8th level syllabusBiography of Dr. Vincenzo Giordano



Biography of Dr. Vincenzo GiordanoDr. Vincenzo Giordano
╠²
Dr. Vincenzo Giordano began his medical career 2011 at Aberdeen Royal Infirmary in the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery. Here, he performed complex adult cardiothoracic surgical procedures, significantly enhancing his proficiency in patient critical care, as evidenced by his FCCS certification.MALE REPRODUCTIVE PHYSIOLOGY up load.pptx



MALE REPRODUCTIVE PHYSIOLOGY up load.pptxYIHENEW CHALLIE LIYEW
╠²
Male animal reproductive physiology including sexual maturity ,reproductive hormone ,sperm production Best Sampling Practices Webinar ŌĆō USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monito...



Best Sampling Practices Webinar ŌĆō USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monito...NuAire
╠²
Best Sampling Practices Webinar ŌĆō USP <797> Compliance & Environmental Monitoring
Are your cleanroom sampling practices USP <797> compliant? This webinar, hosted by Pharmacy Purchasing & Products (PP&P Magazine) and sponsored by NuAire, features microbiology expert Abby Roth discussing best practices for surface & air sampling, data analysis, and compliance.
¤ÆĪ Key Topics Covered:
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Viable air & surface sampling best practices
Ō£ö’ĖÅ USP <797> requirements & compliance strategies
Ō£ö’ĖÅ How to analyze & trend viable sample data
Ō£ö’ĖÅ Improving environmental monitoring in cleanrooms
¤Äź Watch Now: https://www.nuaire.com/resources/best-sampling-practices-cleanroom-usp-797
¤ōó Stay informedŌĆöfollow Abby Roth on LinkedIn for more cleanroom insights!reproductive disorder, etiology ,pathobiology ,clinical sign, treatment and p...



reproductive disorder, etiology ,pathobiology ,clinical sign, treatment and p...YIHENEW CHALLIE LIYEW
╠²
animal reproductive problemsOp-eds and commentaries 101: U-M IHPI Elevating Impact series



Op-eds and commentaries 101: U-M IHPI Elevating Impact seriesKara Gavin
╠²
A slide set about writing opinion and commentary pieces, created for the University of Michigan Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation in Jan. 2025physiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation ž│žżž¦┘ä.pptx



physiology 1 T3T4 & Jaundice & capillary circulation ž│žżž¦┘ä.pptxamralmohammady27
╠²
┘ä┘ł ž╣┘åž»┘ā ┘䞦ž© ž¬┘łž© žŻ┘ł ž¬ž¦ž©┘䞬 ┘üž¦┘ä
power point show
┘ć┘Ŗ┘å┘üž╣┘ā ž¼ž»ž¦ ┘ü┘Ŗ ┘ģž▒ž¦ž¼ž╣ž® ž│ž▒┘Ŗž╣ž® ┘ä┘Ŗ┘äž® ž¦┘䞦┘ģž¬žŁž¦┘å
┘łž¦┘ä┘ä┘Ŗ ┘Ŗ┘éž»ž▒ ┘Ŗž╣┘ģ┘ä žŁž¦ž¼ž® ┘Ŗž╣┘ģ┘ä┘枦
┘łž┤┘āž▒ž¦ ┘ä┘äž»┘āž¬┘łž▒ž® ┘å┘łž¦┘ä ž╣┘ä┘ē ž¬ž¼┘ģ┘Ŗž╣ž® žŻž│ž”┘äž® ž¦┘äž©┘Ŗ┘łPARIS SYSTEM FOR URINE CYTOLOGY paris system of reporting urine slidespptx



PARIS SYSTEM FOR URINE CYTOLOGY paris system of reporting urine slidespptxDrDivitasaxena1
╠²
Paris system for reporting urine cytologyOptimization in Pharmaceutical Formulations: Concepts, Methods & Applications



Optimization in Pharmaceutical Formulations: Concepts, Methods & ApplicationsKHUSHAL CHAVAN
╠²
This presentation provides a comprehensive overview of optimization in pharmaceutical formulations. It explains the concept of optimization, different types of optimization problems (constrained and unconstrained), and the mathematical principles behind formulation development. Key topics include:
Methods for optimization (Sequential Simplex Method, Classical Mathematical Methods)
Statistical analysis in optimization (Mean, Standard Deviation, Regression, Hypothesis Testing)
Factorial Design & Quality by Design (QbD) for process improvement
Applications of optimization in drug formulation
This resource is beneficial for pharmaceutical scientists, R&D professionals, regulatory experts, and students looking to understand pharmaceutical process optimization and quality by design approaches.HUMAN SEXUALITY AND SEXUAL RESPONCE CYCLE



HUMAN SEXUALITY AND SEXUAL RESPONCE CYCLEdaminipatel37
╠²
It is all about topic of obg for new semester students Cardiac Arrhythmias for paramedical students.



Cardiac Arrhythmias for paramedical students.helanmariaarockkiasa
╠²
Cardiac Arrhythmia definition, classification, normal sinus rhythm, characteristics , types and management with medical ,surgical & nursing, health education and nursing diagnosis for paramedical students. HER2-Targeting Therapy in HER2+ MBC With and Without CNS Metastases: Selectio...



HER2-Targeting Therapy in HER2+ MBC With and Without CNS Metastases: Selectio...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
reproductive disorder, etiology ,pathobiology ,clinical sign, treatment and p...



reproductive disorder, etiology ,pathobiology ,clinical sign, treatment and p...YIHENEW CHALLIE LIYEW
╠²
Coping strategies in labour
- 1. COPING STRATEGIES IN LABOUR KARISHMA MOHAMMAD MPT(OBGYN)
- 2. Coping strategies include:- ’üĄ Pharmacological ’üĄ Entonox ’üĄ Pethidine ’üĄ Epidural ’üĄ Paracetamol ’üĄ Meptid ’üĄ Non pharmacological ’üĄ Relaxation ’üĄ Breathing techniques ’üĄ Positioning ’üĄ Pain relief ’üĄ Tens ’üĄ Massage ’üĄ Acupuncture ’üĄ Acupressure ’üĄ Water birth ’üĄ Hypnobirthing ’üĄ Aromatherapy ’üĄ Hydrotherapy
- 3. Role of physiotherapist during labor ’üĄ Relaxation ’üĄ Breathing techniques ’üĄ Positioning ’üĄ Pain relief ’üĄ Massage ’üĄ Other coping strategies (hypnosis, warm water Bath, acupuncture)
- 4. RELAXATION ’üĄ Breathing - Essential to most methods of relaxation; taught concurrently ’üĄ Physiological- Laura Mitchell Method (1963),Jacobson's ’üĄ Touch/massage- Kitzinger (1987) ’üĄ Dissociation and unblocking -Noble (1996) Passive relaxation practiced within pregnancy is replaced by an alert but ŌĆ£non-strivingŌĆØ state of relaxation in labor [selective dissociation](releasing excess tension) ’üĄ Imagery ’üĄ Hot water bath
- 5. ’üĄ Jacobson used a tenseŌĆōrelease approach that activates both antagonists and agonists maximally. ’üĄ The Mitchell method-MitchellŌĆÖs method activates only antagonists, and moderately. ’üĄ Dissociation and unblocking-Noble says that relaxation is more than rest or stillness; it involves recognizing and releasing excess tension ŌĆō whatever the cause. ’üĄ Touch relaxation-Kitzinger discusses the concept of ŌĆśtouch relaxationŌĆÖ, where a woman relaxes towards the touch of her partner.
- 6. BREATHING TECHNIQUES ’üĄ Benefits/Purpose of Breathing Techniques ’üĄ Provides Oxygen- to mother, baby, and hard working uterus. Well oxygenated muscles function more effectively and efficiently. ’üĄ Reduces Pain. ’üĄ Relaxation- Rhythmic breathing promotes physical relaxation by reducing muscle tension, and promotes emotional relaxation by reducing anxiety. ’üĄ Distraction- by helping the mother concentrate and focus on breathing instead of her contractions.
- 7. First Stage Labor ’üĄ Slow Breathing (Relaxed Chest Breathing, Abdominal Breathing) Begin by doing one cleansing breath. ’üĄ Light Breathing (Hee Hee Breathing) Begin by doing one cleansing breath. Start your breathing like slow breathing and as the contraction intensifies your breathing becomes quicker and shallower. ’üĄ Patterned Breathing (Hee-Blow Breathing, Lamaze Breathing) Begin by doing one cleansing breath. Breath in quick and shallow breathes. For three exhales make a quick ŌĆśheeŌĆÖ noise, one exhale make a slow ŌĆ£hooŌĆÖ noise. ’üĄ Variable Breathing ( Transitional Breathing, Take Charge Routine) Begin by doing a cleansing breath. This is just like patterned breathing except that you vary anywhere from one to four ŌĆśheeŌĆÖ exhales with one ŌĆśhooŌĆÖ exhale
- 8. Second stage labour ’üĄ Breathing awareness can be used to facilitate pushing. ’üĄ The woman can be trained to breathe in, then slowly out on exertion (e.g. during defecation) so that it will become instinctive to ŌĆśbreatheŌĆÖ out as she pushes, and to maintain the push at the same time as she breathes in. ’üĄ Each push should last about 5 to 10 seconds, and each contraction may demand three to four pushes. ’üĄ Labor Pant-Blow. This breathing technique is used when it is necessary to keep from pushing.
- 9. ’üĄ Spontaneous Bearing Down (Expulsion Breathing) ŌĆó Breath comfortably until the urge to push becomes irresistible. Next take a deep breath and hold it or slowly release it while bearing down for 5-7 seconds. After bearing down, release any remaining oxygen and breath comfortably the next strong urge- then repeat.
- 10. POSITIONING
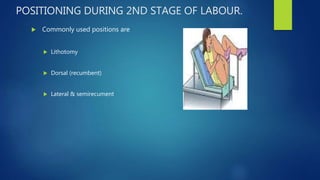
- 12. POSITIONING DURING 2ND STAGE OF LABOUR. ’üĄ Commonly used positions are ’üĄ Lithotomy ’üĄ Dorsal (recumbent) ’üĄ Lateral & semirecument
- 13. Massage in labor ’üĄ It is probable that the soothing sensory inputs from stroking, effleurage and kneading activates the gate closing mechanism at spinal level. ’üĄ Area of massage back ’üĄ deep kneading over painful area, ’üĄ double handed kneeding over SI joint., ’üĄ effleurage from sacro coccygeal area, up and over the iliac crest, ’üĄ slow, rhythmical longitudinal stroking, from occiput to coccyx can relieve tension. ’üĄ Abdominal stroking ’üĄ Perineal massage
- 15. Tens in labour:- ’üĄ TENS is a form of non-invasive pain relief ’üĄ TENS has no harmful effects on either the mother or baby ’üĄ TENS does not restrict your ability to move about in labour ’üĄ TENS can be applied at home during early labour ’üĄ Other pain relief options can still be used if TENS does not provide you with adequate pain relief
- 16. Modes of stimulation ’üĄ Two of the TENS parameters are used for labor. ’üĄ These are burst train TENS and brief intense TENS. ’üĄ Burst Train TENS-This is characterized by low- frequency bursts (4 Hz) of higher-frequency stimulation. This type of stimulation has the properties of both conventional TENS and acupuncture-like TENS. ’üĄ Brief Intense TENS This is characterized by a high frequency (100 Hz),a long pulse duration (150s) and the highest intensity that can be tolerated by the patient. It is best used for short periods of time
- 17. Placement of the electrodes ’üĄ During the first stage, labor pain information, when pain is at its most intense, will be entering segments T10ŌĆōL1. The information from the parasympathetic nerves and the pudendal nerve arrives at the spinal segments S2ŌĆōS4. ’üĄ As your labor progresses or if you are experiencing lower back or pelvic pain you can start using the Channel 1 electrodes which are placed either side of the lower spine below the waist
- 18. THANK YOU







