CP oppurtunities in Pulp & Paper sector.ppt
- 1. Pulp and paper industry Case study Presentation by: Dalia Jankunaite www.forestproducts.sca.com
- 2. Introduction ? The pulp and paper industry converts wood or recycled fibre into pulp and primary forms of paper. ? In the 1800s, there was a shift away from using cotton rags for paper production. Wood became the most important source of fiber. ? First mechanical and then chemical methods have been developed to produce pulp from wood.
- 3. Pulp and paper mills ? Pulp mills separate the fibres of wood or from other materials, such as rags, wastepaper or straw in order to create pulp. ? Paper mills primarily are engaged in manufacturing paper from wood pulp and other fibre pulp, and may also manufacture converted paper products.
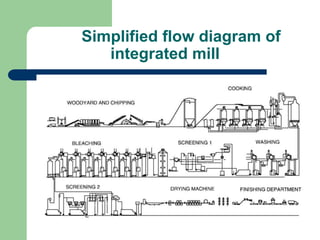
- 4. Production process The production process can be divided into 7 sub-processes: ? raw materials processes; ? wood-yard; ? fibre line; ? chemical recovery; ? bleaching; ? paper production; ? products and recycling.
- 5. Simplified flow diagram of integrated mill
- 6. Pulping processes Pulping aims to separate cellulose fibers from the wood structure. Possible types of pulp production are: ? Kraft (68%) ? mechanical (22%) ? semi-chemical (4%) ? sulphite (4%) ? dissolving (2%). www.handprint.com
- 7. Kraft Pulping Sulfate or Kraft pulping was invented in Germany in 1884 and remains the dominating technology today. Advantages: ¨C higher pulp strength ¨C wider variety of wood species may be used ¨C more effective at removing impurities like resins. Disadvantage: ¨C the pulp yield is low, less than 50%.
- 8. Environmental problems (1) Regulated wastes and emissions from the pulp and paper industry include liquid and solid wastes, air emissions, and wastewater. ? Air emissions related with this process are: sulphur dioxide, nitrous oxides, particulate matter, methanol, polycyclic organic matter, hydrogen chloride, formaldehyde, chloroform, phenol and chlorinated phenolics, dioxins, furans and other chlorinated compounds.
- 9. Environmental problems (2) ? Wastewater releases include chlorinated phenolics, dioxins, furans and other chlorinated compounds, phosphates and suspended sediments. ? Paper mills also produce non-hazardous solid waste such as sludge derived from their pulping and bleaching operations.
- 10. Raw water use ? Pulp mills are big water users. The total requirement of raw water has through cleaner production measures been reduced from about 200-300 m3 per ton of pulp in 1970 to well below 50 m3/ton, in some mills even below 10 m3/ton. ? Consumption of fresh water can seriously harm habitats near mills, reduce water levels necessary for fish, and change water temperature, a critical environmental factor for fish.
- 11. Pollutants in effluents ? The most common organic pollutants are suspended solids (SS): ¨C lost cellulose fibre, ¨C dissolved organic compounds such as dissolved lignin compounds, carbohydrates, starch and hemi-cellulose ? Acidic compounds are predominantly natural resin acids. ? Chlorinated organics (AOX) are found if elemental chlorine is used in the process.
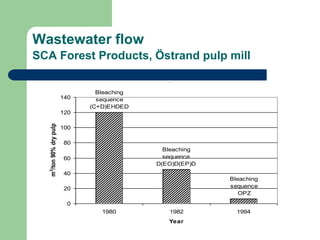
- 12. Wastewater flow SCA Forest Products, ?strand pulp mill Waste water flow from SCA Forest Products, ?strand plant Bleaching sequence OPZ Bleaching sequence D(EO)D(EP)D Bleaching sequence (C+D)EHDED 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 1980 1982 1994 Year m 3 /ton 90% dry pulp
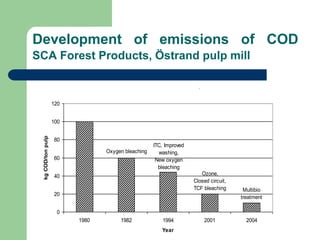
- 13. Development of emissions of COD SCA Forest Products, ?strand pulp mill COD levels after technical improvements at SCA Forest Products, ?strand plant Multibio treatment Ozone, Closed circuit, TCF bleaching ITC, Improved washing, New oxygen bleaching Oxygen bleaching 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 1980 1982 1994 2001 2004 Year kg COD/ton pulp
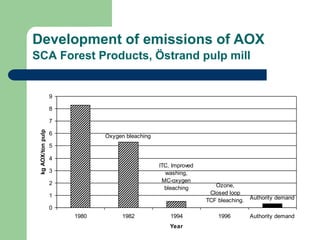
- 14. Development of emissions of AOX SCA Forest Products, ?strand pulp mill AOX levels after technical improvements at SCA Forest Products, ?strand plant Authority demand Ozone, Closed loop TCF bleaching. ITC, Improved washing, MC-oxygen bleaching Oxygen bleaching 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1980 1982 1994 1996 Authority demand Year kg AOX/ton pulp
- 15. Solid wastes ? Dirty wood chips or fibers as well as bark. ? The broken, low-quality fibres are separated out to become waste sludge. ? All the inks, dyes, coatings, pigments, staples and "stickies" (tape, plastic films, etc.) washed off the recycled fibres.
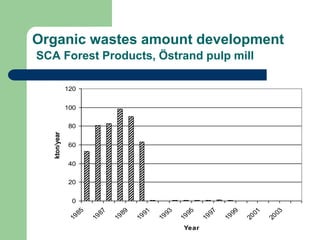
- 16. Organic wastes amount development SCA Forest Products, ?strand pulp mill Organic waste to landfill 1985-2005, SCA Forest products, ?strand mill 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 1 9 8 5 1 9 8 7 1 9 8 9 1 9 9 1 1 9 9 3 1 9 9 5 1 9 9 7 1 9 9 9 2 0 0 1 2 0 0 3 Year kton/year
- 17. Energy use (1) ? The pulp and paper industry uses 84% of the fuel energy consumed by the forest products industry as a whole. ? It is one of the largest producers of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. ? Over the past few years, the pulp and paper industry has considerably reduced its GHG emissions by introducing energy conservation projects and by increasing its use of biomass as an energy source.
- 18. Energy use (2) ? A modern kraft pulp mill is essentially self- sufficient in energy. The only oil consumer is the causticing oven, which however can be replaced with bio-fuel. ? A paper mill requires between 400 and 1000 kWh electricity/ton paper and 4 ¨C 8 GJ heat/ton for drying in the paper machine. ? In an integrated pulp and paper mill this energy is provided from the recovery boiler.
- 19. Cleaner production measures Raw materials ? Maintaining moisture content of the raw materials constant all year around. ? Keeping chemical inventory to a minimum and buying small containers of infrequently used materials. ? Labelling storage area for hazardous substances. ? Providing spill containment and collection systems during storage. ? Genetically modifying forest trees.
- 20. Genetically modified trees ? Lignin is the main wood component that must be effectively removed from the pulp. ? It has been possible to use genetic engineering to modify lignin content and/or composition in poplars. courses.washington.edu
- 21. Advantages of genetic modifications ? Genetic modifications improved characteristics, allowing easier delignification, using smaller amount of chemicals, while yielding more high- quality pulp. ? Owing to the genetic modification savings in energy and pollutant chemicals are achieved, thus leading to an environmentally more sustainable process.
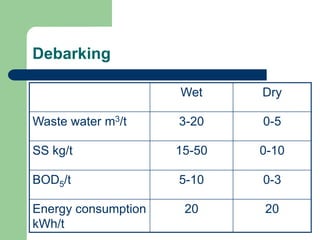
- 22. Debarking Wet Dry Waste water m3/t 3-20 0-5 SS kg/t 15-50 0-10 BOD5/t 5-10 0-3 Energy consumption kWh/t 20 20
- 23. Cleaner production measures Wood-yard (1) ? Pulp mills integrated with lumbering facilities: acceptable lumber wood is removed during debarking; residual or waste wood from lumber processing is returned to the chipping process; in-house lumbering rejects can be a significant source of wood furnish. ? Avoiding hydraulic debarking ¨C saving energy and water consumption, reducing wastewater amount.
- 24. Cleaner production measures Wood-yard (2) ? Reusing leachate water. ? Co-production from bark: mulch, ground cover, charcoal. ? Burning bark from debarking and small chips from chipping for energy production (depends on the moisture content).
- 25. Cleaner production measures Pulp production (1) ? Increasing brown stock washing efficiency. Any remaining cooking liquor will increase the chemical consumption in subsequent stages. ? Water reuse from evaporators. The evaporation plant is always one of the largest steam consumers in the mill. Condensate might be used instead of fresh water in the mill. ? Repulping the rejects from screening rather than putting them into the landfill.
- 26. Cleaner production measures Pulp production (2) ? Using pulp centrifuging to remove any remaining impurities. ? Sludge utilization by means of land- spreading. This method of sludge disposal is an area of concern, as sludge constituents are not well identified. ? Air emissions control devices. ? Providing spill containment and collection system.
- 27. Cleaner production measures Chemicals recovery (1) ? Using of new technologies (CHP, BLG, heat transfer, heat exchanger). ? Improvements technical parameters of recovery boiler or furnace (geometrical shape etc.). ? Using light gas strippers and gas collection systems which will remove hazardous and foul smelling pollution from the air and increase workplace safety.
- 28. Cleaner production measures Chemicals recovery (2) ? Deaerator tanks ahead of the boilers to help reduce the intake of freshwater. ? Air emissions control devices. ? Providing spill containment and collection system.
- 29. Cleaner production measures Bleaching ? Avoiding chlorine bleaching. ? Continuing research on biotechnological bleaching and electrochemical bleaching. ? Air emissions control devices. ? Providing spill containment and collection systems.
- 30. Cleaner production measures Paper production (1) ? Cleaning the roll in the paper machines to avoid broken paper line. ? Adjustment of edge cutter to reduce side trimming loss. ? Use of soft water as a boiler feed water. ? Recycling water evaporated from drying process by condensing.
- 31. Cleaner production measures Paper production (2) ? Optimizing the thermal effects on water used in the paper machine and stock preparation area. ? Providing disk save-all for paper machine. ? Repulping rejected paper in a closed loop manner.
- 32. Cleaner production measures Products processes and recycling ? Increasing recycling rates. Recycling reduces energy consumption, decreases combustion and landfill emissions, and decreases the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. This process also saves money. ? Possibility for easy packaging recycling. ? Using ¡°green¡± fuel for transportation.
- 33. Recycling In Europe an average of 56% of used paper is recovered. The recycling process includes following stages: ¨C Sorting ¨C Dissolving ¨C De ¨C inking ¨C Mixing ¨C Papermaking process
- 34. Ideal paper mill (1) ? From cleaner production point of view is a chlorine-free and zero-discharge one, with minimized quantity and toxicity of air pollution and solid wastes. ? It is seen that closed loops represent the most effective approach to save both energy and resource consumption and at the same way to decrease all kind of wastes production.
- 35. Ideal paper mill (2) ? Such an approach is developed in the form of paper recycling, different types of substances re-use during production processes, co- production and chemicals recovery. ? Future research can develop more sustainable reuse options for kraft pulping solid wastes, as well as pulping methods that result in purified by-products that can serve as feedstock for other manufacturing processes.