Creating the Future with Firefox OS
- 1. @ Firefox Developer Conference 2014 in Kyoto by Tomoya Asai (dynamis) Creating the Future with Firefox OS
- 2. about:me
- 3. Tomoya ASAI (dynamis) Mozilla Japan Mobile & Ecosystem Manager Technical Marketing (Evangelist) dynamis mozilla-japan.org Community dynamis.jp @dynamitter facebook.com/dynamis Ü▌▌Xż╦ż╔ż”żŠŻĪ @
- 6. Cisco ż╦żĶżļ 2020 ─Ļż╬ IoT ╩ął÷ėĶ£y
- 7. Intel ż╦żĶżļ 2020 ─Ļż╬ IoT ╩ął÷ėĶ£y
- 8. Internet of Things żóżķżµżļźŌź╬ż¼┐Äż¼żļ╬┤└┤ 2020 ─Ļż╦żŽ 260 ā| by Gartner 2020 ─Ļż╦żŽ 500 ā| by cisco 2020 ─Ļż╦żŽ 2000 ā| by Intel ę╗╚╦żŪ 4 26 éĆż╬źŪźąźżź╣ Internet of Things żŽ 1991 ─Ļż╦żŽ╠ß│¬żĄżņżŲżżż┐
- 9. ź╣ź▐®`ź╚źšź®ź¾ ╩└Įńż╬│÷║╔╠©╩²żŽ╝▒│╔ķLųą 2012 ─Ļż╦╩└ĮńżŪ 7 ā|╠© 2013 ─Ļż╦╩└ĮńżŪ 10 ā|╠© ą┬┼d╣·żŽż▐ż└ż▐ż└│╔ķLż╣żļ ╣·─┌ż╬│÷║╔╠©╩²żŽŅ^┤“ż┴ż½ 2012 ─Ļż╦╣·─┌żŪ 2848 ═“╠© 2013 ─Ļż╦╣·─┌żŪ 3031 ═“╠©
- 11. Web of Things Web of Things żóżķżµżļżŌż╬ż¼ Web ż╦┐Äż¼żļ żóżķżµżļźŪźąźżź╣ż¼ Web ╝╝ągż╦īØÅĻ Web ╝╝ągż¼żĶżĻųžę¬ż╦ HTML5, JavaScript ż╩ż╔ż╬ Web ╝╝ąg API ż╬ś╦£╩╗»ż╚īgū░ż¼╝▒äš Web of Things ż╚żżż”čį╚~żŌ 2008 ─Ļż½żķ
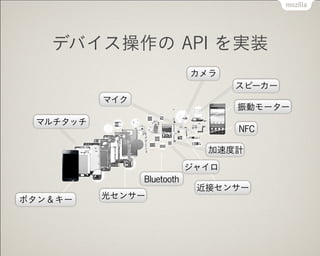
- 13. Web źūźķź├ź╚źšź®®`źÓż╬▀M╗» Web API ż╬Æł┤¾ żóżķżµżļźŪźąźżź╣ż╦īØÅĻ ź═źżźŲźŻźųüKż╬Ė▀╦┘╗» ╩┬Ū░ź│ź¾źčźżźļżõ GPU ż╬źšźļ╗Ņė├ źóźūźĻ┼õą┼ż╦īØÅĻ źóźūźĻ╣▄└ĒżõšnĮ API ż¼ī¦╚ļ
- 14. Firefox OS Web źĄźżź╚ ŻĮ źóźūźĻ Web ż╚źóźūźĻż“źĘ®`źÓźņź╣ż╦╚┌║Ž Web ╝╝ąg ŻĮ ź═źżźŲźŻźų╝╝ąg Web ╝╝ągż└ż▒żŪ║╬żŪżŌ┐╔─▄ż╦ ▓╗ūŃÖC─▄żŽ API ż“Č©┴x?ś╦£╩╗» Web ? ź▐®`ź▒ź├ź╚ Web ╚½╠Õż¼źóźūźĻ┼õą┼ŁhŠ│ ź▐®`ź▒ź├ź╚żŽ Web ż╬ę╗▓┐ż╦▀^ż«ż╩żż
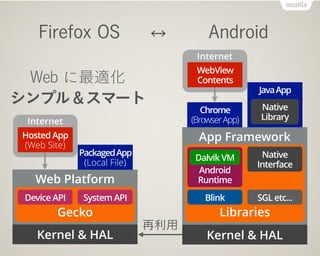
- 15. Internet Firefox OS Android Kernel & HAL Kernel & HAL Web Platform Gecko Device API Web ż╦ūŅ▀m╗» źĘź¾źūźļŻ”ź╣ź▐®`ź╚ System API PackagedApp? (Local File) Hosted App? (Web Site) App Framework Libraries Blink SGL etc... Android? Runtime Native Interface Dalvik VM JavaApp Native Library Chrome (BrowserApp) Internet WebView Contents į┘└¹ė├
- 16. Demo...
- 17. Web API ż╬Æł┤¾ ź╣ź▐ź█Ž“ż▒ API żŽżĶżĻ│õīg źŌźąźżźļŽ“ż▒ż╬╗∙▒ŠĄ─ API żŽīgū░£gż▀ čuŲĘż╬┤Ņ▌dźŽ®`ź╔ż╦ÅĻżĖżŲĒś┤╬Æł┤¾ żóżķżµżļźŪźąźżź╣ż╦īØÅĻ TV Ž“ż▒ż╬īgū░żŽ Panasonic ż╚╣▓ż╦ ūŅ┴╝ĪóūŅ▌X┴┐ż╬ Web OS
- 19. ═©ų¬ (Push) ! ź½źßźķ ! Marketplace ! FM źķźĖź¬ OS ŁhŠ│įOČ© ? ź█®`źÓŻ”▒┌╝ł? ? ļŖįÆĪóSMS ź═ź├ź╚ĪóļŖ│ž ! ▀BĮjÄż ! äė╗ŁŻ”궜S ! ═©ą┼┴┐╣▄└Ē ! źóźūźĻż╬╣▄└Ē? źóźūźĻķg▀Bą»? ? źųźķź”źČ ż╣ż┘żŲ Web ╝╝ągżŪ
- 20. Web API (źŌźąźżźļ OS Ž“ż▒) ═©ą┼ż╚ź═ź├ź╚ź’®`ź» Network Information, MMS, Mobile Connection, Network Stats, Serial, Simple Push, SMS, SystemXHR, TCP Socket, Telephony, UDB Diagram Socket, Voicemail, WiFi Information źŪźąźżź╣żõź╗ź¾źĄ®`ųŲė∙ Ambient Light Sensor, Battery Status, Bluetooth, Camera, Device Orientation, FM Radio, Geolocation, NFC, Pointer Lock, Power Management, Print, Proximity Sensor, Screen Orientation, USB, Vibration, WebCL, WebGL, WebGL2 Ž┬ŠĆ := ūó─┐Īóźżź┐źĻź├ź» := ╬┤īgū░ or ╠ß░ĖĪóhttps://wiki.mozilla.org/WebAPI
- 21. Web API (źŌźąźżźļ OS Ž“ż▒) źŪ®`ź┐ż╬╣▄└Ēż╚╣▓ėą Archive, DeviceIndexedDB, FileHandle, IndexedDB, Contacts, Data Store, Device Storage, USB File Reading źóźūźĻ╣▄└Ēż╚źóźūźĻķg═©ą┼ Apps, Inter App Communication, Permissions, Web Activities, WebSocket Over Apps źĘź╣źŲźÓ Alarm, Background Services, Browser, Idle, Keyboard/IME, Log, Noti?cations, Payment, Resource Lock, Settings, Time/Clock Ž┬ŠĆ := ūó─┐Īóźżź┐źĻź├ź» := ╬┤īgū░ or ╠ß░ĖĪóhttps://wiki.mozilla.org/WebAPI
- 22. NFC ż╬īØÅĻū┤ør ż▐ż║ NDEF ż╦īØÅĻ NFC Data Exchange Format Android źė®`źÓż╦żŌīØÅĻ Android Beam ŻĮ NDEF Push with NFC żĮż╬╦¹żŌĒś┤╬īØÅĻ Tap2Pay ż╩ż╔īØÅĻż“Ś╩ėæųą
- 24. ź═źżźŲźŻźųüKż╬Ė▀╦┘╗» C čįšZż╦Į³żż╦┘Č╚ż“īg¼F ź▐źżź»źĒź┘ź¾ź┴źņź┘źļż╩żķä┘ż─ż│ż╚żŌ ┤¾ęÄ─Żź▓®`źÓżŪżŌ 67% ż╬╦┘Č╚ż“▀_│╔ ūŅą┬ź▓®`źÓź©ź¾źĖź¾żŌīØÅĻ WebGL + JavaScript (asm.js) ż╦īØÅĻ Unity 5, Unreal Engine 4, PlayCanvas, CreateJS, Goo Engine, Flambe, Esenthel Engine ... and more ...
- 25. Unreal Engine 4 (Epic Soul) ūŅą┬ź▓®`źÓź©ź¾źĖź¾żŌ╦┘żõż½ż╦ Firefox ż╦īØÅĻ ź═źżźŲźŻźųź▓®`źÓżŌūŅ│§ż╬ź┐źżź╚źļż¼│÷ż┐żąż½żĻ http://www.mozilla.jp/blog/entry/10388/
- 26. Unity 5 żŌ WebGL+asm.js īØÅĻ 250 ═“╚╦ż╬ Unity ķ_░kš▀żŌ Web źóźūźĻż╬╠ß╣®š▀ż╦ http://www.mozilla.jp/blog/entry/10387/
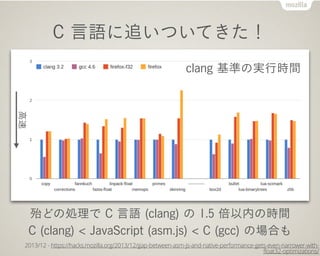
- 27. C čįšZż╦ūĘżżż─żżżŲżŁż┐ŻĪ ┤∙ż╔ż╬äI└ĒżŪ C čįšZ (clang) ż╬ 1.5 ▒Čęį─┌ż╬Ģrķg C (clang) < JavaScript (asm.js) < C (gcc) ż╬ł÷║ŽżŌ 2013/12 - https://hacks.mozilla.org/2013/12/gap-between-asm-js-and-native-performance-gets-even-narrower-with- float32-optimizations/ clang ╗∙£╩ż╬īgąąĢrķg Ė▀╦┘
- 28. źóźūźĻ┼õą┼ż╦īØÅĻ Hosted & Packaged źóźūźĻ źĄźżź╚ż“źóźūźĻż╚żĘżŲźżź¾ź╣ź╚®`źļ ź└ź”ź¾źĒ®`ź╔ą═ż╬ Web źóźūźĻż╦żŌīØÅĻ Firefox Marketplace ╦¹ż╬ OS ═¼śöż╦ź▐®`ź▒ź├ź╚żŌ╠ß╣® šnĮøQ£gė├ż╬ API ╦¹ż╬ OS ═¼śöż╦šnĮ API żŌ╠ß╣®
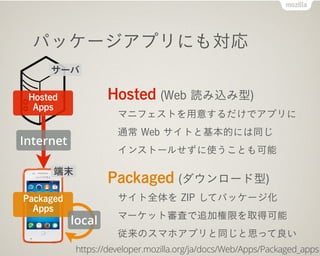
- 29. źčź├ź▒®`źĖźóźūźĻż╦żŌīØÅĻ Hosted (Web šiż▀▐zż▀ą═) ź▐ź╦źšź¦ź╣ź╚ż“ė├ęŌż╣żļż└ż▒żŪźóźūźĻż╦ ═©│Ż Web źĄźżź╚ż╚╗∙▒ŠĄ─ż╦żŽ═¼żĖ źżź¾ź╣ź╚®`źļż╗ż║ż╦╩╣ż”ż│ż╚żŌ┐╔─▄ Packaged (ź└ź”ź¾źĒ®`ź╔ą═) źĄźżź╚╚½╠Õż“ ZIP żĘżŲźčź├ź▒®`źĖ╗» ź▐®`ź▒ź├ź╚īÅ¢╦żŪūĘ╝ėśžŽ▐ż“╚ĪĄ├┐╔─▄ ÅŠ└┤ż╬ź╣ź▐ź█źóźūźĻż╚═¼żĖż╚╦╝ż├żŲ┴╝żż https://developer.mozilla.org/ja/docs/Web/Apps/Packaged_apps Packaged Apps Hosted? Apps Internet źĄ®`źą Č╦─® local
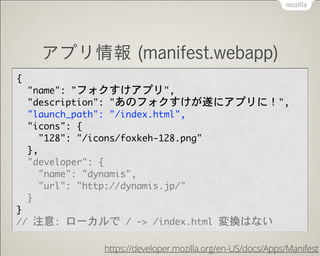
- 30. źóźūźĻŪķł¾źšźĪźżźļĢ°ż»ż└ż▒ Hosted (Web šiż▀▐zż▀ą═) źĄźżź╚ + manifest.webapp 1. manifest.webapp ū„│╔ źóźūźĻŪķł¾Ģ°ż»ż└ż▒żŪĮK┴╦
- 32. ZIP żĘżŲ Packaged App ż╦ Packaged (ź└ź”ź¾źĒ®`ź╔ą═) ZIP + package.manifest 1. manifest.webapp ū„│╔ Hosted Apps ż╬Ģrż╚═¼żĖ 2. źĄźżź╚╚½╠Õż“ ZIP ż╣żļ 3. package.manifest ż“ū„│╔
- 33. Firefox Marketplace ź▐źļź┴źŪźąźżź╣īØÅĻ Web Platform ż╬ż┐żßż╬ź╣ź╚źó Android Firefox żõ PC Firefox żŌīØÅĻ ź¬®`źūź¾ż╩ź▐®`ź▒ź├ź╚ Č└ūįż╬ź╣ź╚źóĪóšnĮĪóšJį^ż“╩╣ż”ż╬żŌūįė╔ źĮ®`ź╣żŌ╣½ķ_ĪóźņźėźÕ®`ż╦żŌ▓╬╝ė┐╔─▄
- 34. Marketplace ż╬źņźėźÕ®` └¹ė├ API ż╦ÅĻżĖż┐┤_šJ ▌Xż»äėū„┤_šJż╚╣½ą“┴╝╦ū┤_šJż╩ż╔ż¼╗∙▒Š ź╗ź¾źĘźŲźŻźųż╩ API żŽź│®`ź╔źņźėźÕ®` żóż╩ż┐żŌźņźėźÕźó®`ż╦ŻĪ źņźėźÕ®`źó®`żŌ╦µĢr─╝╝»żĘżŲżżż▐ż╣ Firefox ż╬źóź╔ź¬ź¾ż╚═¼żĖ╩ųĘ© źņźėźÕ®`żŌź¬®`źūź¾żŪ╣½ŲĮż╩ź▐®`ź▒ź├ź╚ https://developer.mozilla.org/ja/docs/Web/Apps/Marketplace_review_criteria
- 35. Web źóźūźĻż╬šnĮ API ╚╬ęŌż╬ Web šnĮ API WebPay, FastPay, Paypal, ? Google In-App Payment, etc... Firefox ż╬šnĮ API navigator.mozPay ėą┴ŽźóźūźĻĪóźóźūźĻ─┌šnĮż╩ż╔īØÅĻ Android żõ Desktop ż╬ Firefox ż╦żŌ mozPay żŽ Google In-App Payment ═¼śöż╬ API
- 37. Firefox OS ż╬„╚┴” ū„żĻż┐żżčuŲĘż¼ū„żņżļ ź¬®`źūź¾ż½ż─ģf┴”Ą─ż╩ķ_░kźūźĒź╗ź╣ ūŅą┬ż╬čuŲĘė├źĮ®`ź╣ź│®`ź╔ż╚ēõĖ³┬─Üs ╩└Įńųąż╬źč®`ź╚ź╩®`Ų¾śIż╚ż╬╣▓═¼ķ_░k Web źŪźąźżź╣ż╦ūŅ▀mż╩ OS Ę∙Ä┌żżūŅą┬ Web ╝╝ągż╦īØÅĻ ūŅżŌ▌X┴┐żŪĖ▀╦┘ż╩ Web OS
- 38. Mozilla ż╬„╚┴” ĘŪåė└¹ųą┴óĮM┐Ś Web ╝╝ągż“īgū░ż╣żļųą┴óĮM┐Ś Č╦─®ž£ēėżõźµ®`źČŽ“ż▒źėźĖź═ź╣żŽūįė╔ż╦ ź╗źŁźÕźĻźŲźŻż╚źūźķźżźąźĘ®`ż“ūŅā׎╚ Web ╝╝ągż╬ūŅŽ╚Č╦ ╩└Įńź╚ź├źūż╬ Web ╝╝ągš▀ż¼╝»ĮY ś╦£╩╗»ż╚īgū░ż“źĻ®`ź╔żĘŠAż▒żļĮM┐Ś
- 43. Line
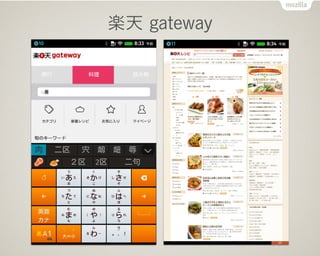
- 45. śS╠ņ gateway
- 46. iWnn IME for Firefox OS ź¬źÓźĒź¾źĮźšź╚ź”ź¦źó Mozilla ż╚ģf┴”żĘżŲķ_░kųą Firefox OS é╚ż╬▓╗ūŃÖC─▄żŽ▀mŪąż╦īgū░ ╗∙▒ŠÖC─▄ż╦żŽ╝╚ż╦īØÅĻ źšźĻź├ź»╚ļ┴”Īóź╚ź░źļ╚ļ┴”ĪóėĶ£y╚ļ┴”Īó Į}╬─ūų╚ļ┴”Īó▀B╬─╣Ø╚ļ┴”Īóźµ®`źČ┤ŪĢ° Č╦─®ż╦┤Ņ▌dżĄżņż┐żżĘĮżŽź¬źÓźĒź¾źĮźšź╚ź”ź¦źóżĄż▐ż╦ż┤ŽÓšäż»ż└żĄżż
- 48. Future of Mobile Privacy Deutsche Telekom Ī┴ Mozilla źūźķźżźąźĘ®`ųžęĢż╬┼Ęų▌żķżĘżż Find My Fox (Č╦─®╠ĮżĘ) Privacy Panel (ę╗į¬╣▄└Ē╗Ł├µ) Location Blur (╬╗ų├Ūķł¾Š½Č╚╣▄└Ē) Guest Mode (ųŲŽ▐źŌ®`ź╔żŪ┘Jż╣) etc...
- 49. Firefox OS żŪĮŌżŁĘ┼żŲŻĪ╬┤└┤ ą┬żĘżżżŌż╬ż┼ż»żĻż“ ź¬®`źūź¾źūźĒź╗ź╣żŪ Web OS ╣▓═¼ķ_░k Mozilla żŽźūźķź├ź╚źšź®®`źÓū„żĻż“ų¦į« ┤╬żŽ┘FĘĮż¼ę╗Šwż╦ŻĪ ź╣ź▐®`ź╚źšź®ź¾Īóź╣ź▐®`ź╚źŲźņźėż╦ŠAż▒ źß®`ź½®`ż└ż▒żŪż╩ż»źóźūźĻķ_░kš▀żŌ ż▀ż¾ż╩żŪę╗Šwż╦╠ž╔½čuŲĘū„żĻż“
- 51. For More Info
- 52. Firefox OS ź│ź▀źÕź╦źŲźŻŻĪ http://FxOS.org źżź┘ź¾ź╚żõź╔źŁźÕźßź¾ź╚ż“ż┤░Ė─┌ http://FxOS.org/ml (Google Group ż╬źĻź¾ź»: https:// groups.google.com/group/?refoxos)