Critical_thinking.pptx
- 1. Musarrat ul Hasnain Critical Thinking
- 2. Why critical thinking? âĒ Seen as central to higher education âĒ Required in Masters level programmes âĒ Claimed as the cornerstone of science and development BUT âĒ Often implicit rather than explained in programmes
- 3. Outline âĒ Development â Stages model â Takes: time, practice, maturity, inclination âĒ Valuing â Teach, Practice, Assess (Curriculum) âĒ Understanding â Definitions â Bloomâs model âĒ Activities â Review, evaluate, apply
- 4. CT as stages of development âĒ Students (all of us) develop through stages â We may be at different stages in different contexts â Same for students e.g. in âreal lifeâ and in new academic situations 1 Absolute knowing 2 Transitional stage 3 Independent knowing 4 Contextual knowing Unreasonable to expect them to have fully reached contextual thinking âĒ Moon (2005) adapted from Baxter Magnolia & Perry
- 5. Stages of knowing 1 Absolute knowing Knowledge is certain â experts have the answers. Task is to absorb knowledge 2 Transitional stage There is some uncertainty â authorities differ. Need to understand in order to make judgements and apply 3 Independent knowing Learning is uncertain, everyone has own beliefs. Expected to have an opinion, peers can be valuable. Discriminating different perspectives overlooked 4 Contextual knowing Knowledge is constructed & often contextual, judgement requires evidence. Opinions must be evidenced
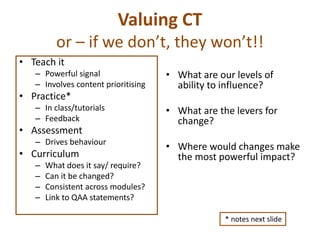
- 6. Valuing CT or â if we donât, they wonât!! âĒ Teach it â Powerful signal â Involves content prioritising âĒ Practice* â In class/tutorials â Feedback âĒ Assessment â Drives behaviour âĒ Curriculum â What does it say/ require? â Can it be changed? â Consistent across modules? â Link to QAA statements? âĒ What are our levels of ability to influence? âĒ What are the levers for change? âĒ Where would changes make the most powerful impact? * notes next slide
- 7. Deliberate Practice Research on achieving excellence reveals commonalities van Gelder 2005 p7 âĒ Focussed practice aimed to generate improvement âĒ Exercises to improve the skill (of CT) âĒ Graduated and with repetition âĒ Guidance, timely accurate feedback âĒ Ongoing â takes time
- 8. Fostering CT â in general âĒ Teach philosophy!! â Be explicit about epistemology and CT âĒ Challenge just beyond comfort zone â Vygotsky âĒ Recognise as a developmental process â Will be different stages in the class âĒ Encourage student interaction âĒ Set thinking activities â Reflection, PDP âĒ Give examples of CT âĒ Assessment â Remains a key issue Moon 2005 What do you do? What could you do?
- 9. Fostering CT â some more! âĒ Create risk-taking atmosphere in class â Exploring ideas OK (rather than knowledge transmission) âĒ Model CT â Think out loud âĒ Provide thinking time âĒ Assessment â There it is again! âĒ Use questions purposefully âĒ Support placements & out of class activities â Volunteering â International exchange âĒ Oral activities* âĒ Written*+ What do you do? What could you do? * see handout later Moon 2005 + see Thinking Writing project
- 10. Understanding CT âĒ Definitions âĒ Models â Bloomâs Taxonomy â Developmental (Baxter Magolda /Perry) âĒ Universal Standards
- 11. Critical thinking Is not: automatic response or intuition etc whatever their value or lack of value! Critical thinking is reasonable reflective thinking that is focused on deciding what to believe or do (R. Ennis) The significant problems we face cannot be solved at the same level of thinking we were at when we created them. A. Einstein
- 12. Critical & Critical thinking âĒ Critical position: personally derived evidenced based judgement Jude Carroll âĒ Critical thinking: thinking that helps you figure out whether you should believe some claim, and how strongly you should believe it â i.e. is it true or the art of being right! Tim van Gelder âĒ Critical thinking: capacity to work with complex ideasâĶ. Provide effective evidence to justify a reasonable judgementâĶ. Attending to context Jenny Moon
- 13. Each prisoner knows that there are 2 red hats and 2 blue hats, but no one knows the colour of his own hat
- 14. Six Levels of Thinking 1. Remembering 2. Understanding 3. Applying 4. Analysing 5. Evaluating 6. Synthesising â creating Researchers need the language of research Thinkers need the language of thinking! Bloom et al - a classic model
- 15. 1. Remembering Information list, name, identify, define, label, describe âĒ Mnemonic â system for improving memory âĒ Acronyms, Acrostics âĒ Use baroque music â Might not âlikeâ it â but it works! List: - ooops Liszt Music accesses memory
- 16. 2. Understanding Information âĒ Mind maps (webs) âĒ Key words âĒ Single word summarise, discuss, distinguish, predict, generalise, categorise Thinking is the hardest work there is â Thatâs why so few people do it â Henry Ford
- 17. âMind Mappingâ using Mind Genius Available on network
- 18. 3. Applying Information âĒ Problem solving âĒ Testing learning in the âreal worldâ or in class activities apply, demonstrate, examine, solve What we have to learn to do, we learn by doing - Aristotle (this includes CT!!)
- 19. 4. Analysing Information âĒ Breaking it down âĒ Fact v. opinion âĒ Reasoned judgement âĒ Logical thinking âĒ Activity - PMI analyse, explain, compare, classify See Alec Fisher Lots of activities to build arguments and reasoning
- 21. 5. Evaluating or criticising information âĒ Objective âĒ Open-minded, flexible âĒ Check assumptions âĒ Check bias assess, recommend, compare/contrast, conclude, justify, Questions are the active acts of intelligence - Frank Kingdom
- 22. 6. Synthesising or creating information âĒ New ideas-Creativity âĒ New applications of âoldâ ideas âĒ Lateral thinking design, invent, rewrite, rearrange Nothing can happen unless you first dream -Carl Sandburgh See de Bono Countless ideas: lateral thinking
- 23. Snake swallowing its own tail âCreative scientists are ones with access to their dreamsâ â Albert Einstein Let us learn to dream, gentlemen, and then perhaps we shall learn the truth. August KekulÃĐ
- 25. Creative brainstorming âSynecticsâ - very useful for problem solving 1. Remove negative stimuli (things that filter ideas out). 2. Separate âjudgmentâ from âidea gettingâ. a) Divergent mode. Create lots of ideas, irrespective of quality or relevance. There are no bad ideas! b) Convergent mode. Narrow down the ideas using various criteria. Task statement Final idea(s) a b
- 26. Universal Intellectual Standards âĒ Clarity âĒ Accuracy âĒ Precision âĒ Relevance âĒ Depth âĒ Breadth âĒ Logic Check thinking and writing against these universal standards http://set.lanl.gov/programs/cif/Resource/Han douts/intlStan.ht Critical thinking: involves improving the quality of thinkingâĶ by imposing intellectual standards - R. Paul
- 27. Knowledge dimension 1 Remem ber 2 Under stand 3 Apply 4 Analyse 5* Evaluate 6* Create A: Factual Terminology, details, facts B: Conceptual Theories, generalisations, classifications C: Procedural How to doâĶ Methods Subject skills D: Metacognitive Strategic Contextual Self- knowledge Krathwohl, D. (2002) A revision of Bloomâs taxonomy * Changed and reordered from original list Bloomâs taxonomy revised: analyse level of programme Locate learning outcomes in the grid; gives a âpictureâ of the programme
- 28. Argument Mapping âĒ Build reasoning skills âĒ Produce well organised arguments âĒ Communicate reasoning âĒ Evaluate reasoning âĒ Make better decisions www.austhink.org
- 29. Takeaways âĒ CT is developmental â Variety in class and over time âĒ Levels of thinking â a key model â Allows analysis of your teaching focus â Allows analysis of module/programme âĒ Lots of activities â Plenty on the web (subject centre, SNAS, Learn Higher, CT.org)
- 30. Summarising! âĒ Try some thinking skills activities â at any level âĒ Be explicit â think out loud âĒ Do it! Personal practical knowledge comes from putting ideas into practice A twit on the move may be worth ten seated philosophers - Unknown Harkat Main Barakat Hai
- 31. Sources Langreher J. (1992). Teach thinking strategies: Ideas for teachers Carr K. (2001) How can we teach critical thinking? Claxton G. (1997). Hare brain, tortoise mind Fisher A. (2001). Critical thinking: An introduction. Halpern, D. (1989). Thought and knowledge Krathwohl, D. (2002) A revision of Bloomâs taxonomy Paul, R. & Elder, L (2002). Critical thinking And more - including de Bono We think of the mind as a storehouse to be filled, when we should be thinking of it as an instrument to be used - Reed & Graeme
- 32. Useful Sites âĒ Articles by Tim Van Gelder â http://www.arts.unimelb.edu.au/~tgelder âĒ van Gelder, T. J. (2005). Teaching critical thinking: some lessons from cognitive science. College Teaching, 45, 1-6. âĒ Argument mapping â www.austhink.org âĒ Universal Intellectual Standards â http://set.lanl.gov/programs/cif/Resource/Handouts/Handouts.htm â http://criticalthinking.org/Posters.html âĒ Bloomâs Taxonomy â Skills and questions â http://www.coun.uvic.ca/learn/program/hndouts/bloom.html âĒ Thinking Writing â http://www.thinkingwriting.qmul.ac.uk/srb.htm â Jenny Moon (2005) We seek it here...a new perspective on the elusive activity of critical thinking. HEA Escalate â http://escalate.ac.uk/2041
- 33. Useful Sites âĒ Dan Kurland â http://www.criticalreading.com/ âĒ Pierce handbook of CT â http://academic.pgcc.edu/~wpeirce/MCCCTR/handbook.pdf âĒ Critical Thinking Community â http://www.criticalthinking.org/ABOUT/index.cfm âĒ SNAS (HEA) â http://www.heacademy.ac.uk/ourwork/professional/snas/snasdatabase âĒ Learn Higher â http://www.learnhigher.ac.uk/pages/critical_thinking_and_reflection. html