Cryptography
- 2. âĒCryptography is the science and art of transforming messages to make them secure and immune to attack.
- 3. Origin of Cryptography: âĒ The first known evidence of cryptography can be traced to the use of âhieroglyphâ. Some 4000 years ago, the Egyptians used to communicate by messages written in hieroglyph. âĒ The most widely known rotor cipher device is the German Enigma machine used during World War II, of which there were a number of variants. âĒ the Zimmermann Telegram triggered the United States' entry into World War I.
- 4. âĒ A Purpose of cryptography: The main purpose of cryptography is to defend the transmitted information and it plays an important role in the following: âĒ Authentication âĒ Data confidentiality âĒ Data integrity âĒ Non-repudiation
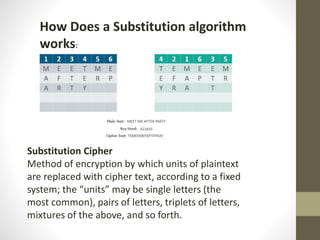
- 6. How Does a Substitution algorithm works: Substitution Cipher Method of encryption by which units of plaintext are replaced with cipher text, according to a fixed system; the âunitsâ may be single letters (the most common), pairs of letters, triplets of letters, mixtures of the above, and so forth.
- 7. âĒ Cryptography is an actively developed library that provides cryptographic recipes and primitives. It supports Python 2.6-2.7 and Python 3.3+. âĒ cryptography is divided into two layers of recipes and hazardous materials (hazmat). The recipes layer provides a simple API for proper symmetric encryption and the hazmat layer provides low- level cryptographic primitives. Lib:
- 8. Types: âĒ Secret Key Cryptography (SKC): Uses a single key for both encryption and decryption; also called symmetric encryption. Primarily used for privacy and confidentiality. âĒ Public Key Cryptography (PKC): Uses one key for encryption and another for decryption; also called asymmetric encryption. Primarily used for authentication, non-repudiation, and key exchange. âĒ Hash Functions: Uses a mathematical transformation to irreversibly "encrypt" information, providing a digital fingerprint. Primarily used for message integrity.
- 10. Applications: âĒ Authentication/Digital Signatures âĒ Time Stamping âĒ Electronic Money âĒ Disk Encryption âĒ Secure Network Communications
- 11. References: âĒ https://www.garykessler.net/library/crypto.html âĒ https://intellipaat.com/blog/tutorial/ethical-hacking-cyber- security-tutorial/encryption-techniques/ âĒ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9-Yw434IbVM âĒ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryptography