Cryptography
- 1. Cryptography Subodh B. Pawar Ruksar I. Shaikh
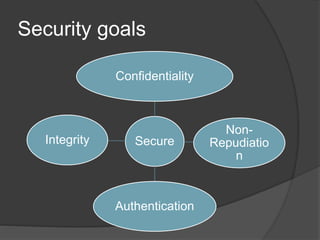
- 2. What is Cryptography?  Cryptography is a method of storing and transmitting data in a particular form so that only those for whom it is intended can read and process it.  Cryptography derived its name from a Greek word called “Kryptos” which means “Hidden Secrets”.
- 3. History of Cryptography ÔÇû The earliest forms of cryptography were found in the cradle of civilization, including the regions currently encompassed by Greece and Rome.
- 4. Greece: Wrap a tape around a stick and write the message on the wound tape. Rome: Caesar Shift Cipher was used. It utilized the idea of shifting letters by an agreed upon number (three was a common historical choice), and thus writing the message using the letter-shift.
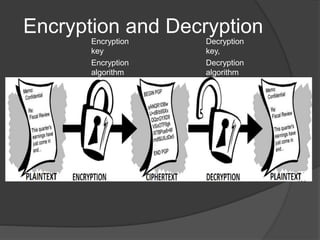
- 6. Encryption and Decryption Decryption key, Decryption algorithm Encryption key Encryption algorithm
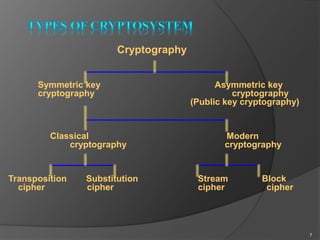
- 7. Cryptography Symmetric key Asymmetric key cryptography cryptography (Public key cryptography) Classical Modern cryptography cryptography Transposition Substitution Stream Block cipher cipher cipher cipher 7
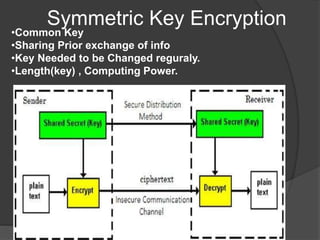
- 8. Symmetric Key Encryption •Common Key •Sharing Prior exchange of info •Key Needed to be Changed reguraly. •Length(key) , Computing Power.
- 9. Challenges: 1.Key Establishment: Secure Key Establishment. 2.Trust Issue: Receiver Lost key to attacker & no informed. Solution: Why did asymmetric key came into picture? ÔÇó People needs to exchange information with non- familier & non-trusted parties. ÔÇó Regular Change Of keys->Complex & Cumbersome. ÔÇó Pre-sharing of Secret Keys
- 10. Asymmetric EncryptionÔÇû Different Keys. ÔÇó But Mathematically Related. ÔÇó Computationally Not Feasible for attacker. ÔÇû Each User ÔÇó Pair of Key ÔÇó Public Key Encryption Public key Repository & Private Key Guarded.
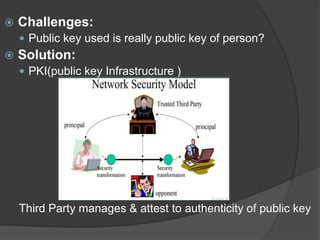
- 11. ÔÇû Challenges: ÔÇó Public key used is really public key of person? ÔÇû Solution: ÔÇó PKI(public key Infrastructure ) Third Party manages & attest to authenticity of public key
- 12. Classical Cryptography 1. Transposition: -In the transposition technique the positions of in plaintext is changed with one another. e.g Plain text: MEET ME AFTER PARTY ÔÇû Cipher text: TEMEEMEFAPTRYRAT ÔÇû KEY USED: 421635 1 2 3 4 5 6 M E E T M E A F T E R P A R T Y 4 2 1 6 3 5 T E M E E M E F A P T R Y R A T
- 13. 13 ÔÇßEvery alphabet is shifted with fixed number. ÔÇßKey: Shift number. ÔÇßProblem: Only 26 keys to find out.
- 14. Modern Cryptography 1.Block Ciphers -encryption of one block of text at a time -e.g. : Plain text: four and five Four and five Key Key Key wvfa ast wvfa :cipher text
- 15. 2.Steam Ciphers: -plaintext is processed one bit at a time - e.g. : Plain text: Pay 100 Binary of plain text: 010111101 (hypothetical) Key: 100101011 ----- Perform XOR ____________________ Cipher text 110010110 ----- ZTU9^%D
- 16. Encryption and Decryption algorithms • Data Encryption Standard(DES) • Advanced Encryption Standard(AES)
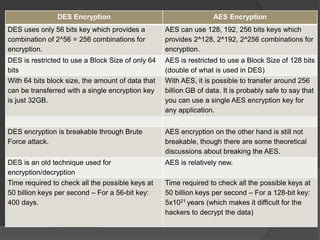
- 17. DES Encryption AES Encryption DES uses only 56 bits key which provides a combination of 2^56 = 256 combinations for encryption. AES can use 128, 192, 256 bits keys which provides 2^128, 2^192, 2^256 combinations for encryption. DES is restricted to use a Block Size of only 64 bits AES is restricted to use a Block Size of 128 bits (double of what is used in DES) With 64 bits block size, the amount of data that can be transferred with a single encryption key is just 32GB. With AES, it is possible to transfer around 256 billion GB of data. It is probably safe to say that you can use a single AES encryption key for any application. DES encryption is breakable through Brute Force attack. AES encryption on the other hand is still not breakable, though there are some theoretical discussions about breaking the AES. DES is an old technique used for encryption/decryption AES is relatively new. Time required to check all the possible keys at 50 billion keys per second – For a 56-bit key: 400 days. Time required to check all the possible keys at 50 billion keys per second – For a 128-bit key: 5x1021 years (which makes it difficult for the hackers to decrypt the data)
- 18. APPLICATIONS  Defense services  Secure data manipulation  E –commerce  Business transactions  Internet payment systems  User identification systems  Access control  Data security
- 19. CONCLUSION ÔÇû By using Cryptography techniques confidentiality, authentication, integrity, access control and availability of data is maintained ÔÇû Secure Communication is obtained.
- 20. THANK YOU!