Cs 361 2015 lec 1-2
- 3. WHAT IS AI? ÔÉíAI is the study of how to make computers make things which at the moment people do better.
- 4. DEFINING THE PROBLEM ÔÉí Defining the problem as State Space Search ÔÉí Initial state ÔÉí Goal state ÔÉí Rules: Matching ----- forward ----> Action
- 5. EXAMPLE (1): WATER JUG PROBLEM ÔÉí If you have 2 jugs (4 gallon - 3 gallon), how can you get exactly 2 gallons into the 4 gallon jug? ÔÉí The state space for this problem can be described as the set of ordered pairs of integers (x,y) such that x = 0, 1,2, 3 or 4 and y = 0,1,2 or 3; x represents the number of gallons of water in the 4-gallon jug and y represents the quantity of water in 3-gallon jug ÔÉí The start state is (0,0) The goal state is (2,n)
- 6. PRODUCTION RULES FOR WATER JUG PROBLEM No Current state Next State Description 1 (x,y) if x < 4 (4,y) Fill the 4 gallon jug 2 (x,y) if y <3 (x,3) Fill the 3 gallon jug 3 (x,y) if x > 0 (x-d, y) Pour some water out of the 4 gallon jug 4 (x,y) if y > 0 (x, y-d) Pour some water out of the 3-gallon jug 5 (x,y) if x>0 (0, y) Empty the 4 gallon jug 6 (x,y) if y >0 (x,0) Empty the 3 gallon jug on the ground 7 (x,y) if x+y >= 4 and y >0 (4, y-(4-x)) Pour water from the 3 –gallon jug into the 4 –gallon jug until the 4-gallon jug is full 8 (x, y) if x+y >= 3 and x>0 (x-(3-y), 3) Pour water from the 4-gallon jug into the 3-gallon jug until the 3-gallon jug is full 9 (x, y) if x+y <=4 and y>0 (x+y, 0) Pour all the water from the 3-gallon jug into the 4- gallon jug 10 (x, y) if x+y <= 3 and x>0 (0, x+y) Pour all the water from the 4-gallon jug into the 3- gallon jug
- 7. TO SOLVE THE WATER JUG PROBLEM Gallons in the 4-gallon jug Gallons in the 3-gallon jug Rule applied 0 0 2 0 3 9 3 0 2 3 3 7 4 2 5 0 2 9 2 0
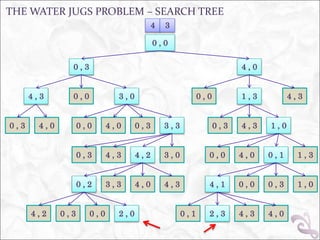
- 8. THE WATER JUGS PROBLEM – SEARCH TREE 0 , 0 4 3 0 , 3 4 , 0 0 , 0 3 , 04 , 3 1 , 3 4 , 30 , 0 0 , 3 4 , 0 0 , 0 4 , 0 0 , 3 3 , 3 0 , 3 4 , 3 1 , 0 3 , 04 , 24 , 30 , 3 0 , 14 , 00 , 0 1 , 3 4 , 03 , 3 4 , 30 , 2 0 , 0 0 , 34 , 1 1 , 0 0 , 34 , 2 0 , 0 2 , 0 2 , 30 , 1 4 , 3 4 , 0
- 9. PROBLEM SEARCH  Blind Search … Blind Search – Breadth First … Blind Search – Depth First  Heuristic Search
- 10. THE WATER JUGS PROBLEM – SEARCH TREE 0 , 0 4 3 0 , 3 4 , 0 0 , 0 3 , 04 , 3 1 , 3 4 , 30 , 0 0 , 3 4 , 0 0 , 0 4 , 0 0 , 3 3 , 3 0 , 3 4 , 3 1 , 0 3 , 04 , 24 , 30 , 3 0 , 14 , 00 , 0 1 , 3 4 , 03 , 3 4 , 30 , 2 0 , 0 0 , 34 , 1 1 , 0 0 , 34 , 2 0 , 0 2 , 0 2 , 30 , 1 4 , 3 4 , 0
- 11. BLIND SEARCH – BREADTH FIRST 0 , 0 4 3 0 , 3 4 , 0 3 , 04 , 3 1 , 3 3 , 3 1 , 0 4 , 2 0 , 1 0 , 2 4 , 1 2 , 0
- 12. THE WATER JUGS PROBLEM – SEARCH TREE 0 , 0 4 3 0 , 3 4 , 0 0 , 0 3 , 04 , 3 1 , 3 4 , 30 , 0 0 , 3 4 , 0 0 , 0 4 , 0 0 , 3 3 , 3 0 , 3 4 , 3 1 , 0 3 , 04 , 24 , 30 , 3 0 , 14 , 00 , 0 1 , 3 4 , 03 , 3 4 , 30 , 2 0 , 0 0 , 34 , 1 1 , 0 0 , 34 , 2 0 , 0 2 , 0 2 , 30 , 1 4 , 3 4 , 0
- 13. BLIND SEARCH – DEPTH FIRST 0 , 0 4 3 0 , 3 3 , 04 , 3 3 , 3 4 , 2 0 , 2 2 , 0
- 14. EXAMPLE (2): WATER JUG PROBLEM ÔÉí You are given three jugs, a 10-gallon one, 7-gallon one, and 3-gallon one. ÔÉí Neither have any measuring markers on it. ÔÉí There is a pump that can used to fill the jugs with water. ÔÉí Use Breadth First and Depth First search to get exactly 5-gallons of water into 7-gallon jug. ÔÉí The start state is (0,0,0) The goal state is (n,5,n)
- 15. EXAMPLE (3): TRAVERSING A MAZE ÔÉí The wall follower, the best-known rule for traversing mazes, is also known as either the left-hand rule or the right-hand rule.
- 16. TRAVERSING A MAZE PROBLEM – SEARCH TREE A CB D FE HG I KJ NML
- 17. TRAVERSING A MAZE PROBLEM – BREADTH FIRST A B D I K M
- 18. TRAVERSING A MAZE PROBLEM – SEARCH TREE A CB D FE HG I KJ NML
- 19. TRAVERSING A MAZE PROBLEM – DEPTH FIRST A B D I K M
- 20. EXAMPLE (4): TRAVERSING A MAZE
- 21. END