CSSD
- 1. MR. PRATIK TRIVEDI OT MANAGER CSSD Central Sterile Supply Department
- 2. THE CENTRAL STERILIZATION & SUPPLY DEPARTMENT (CSSD) ï§Mission of CSSD ïąTimely delivery of sterile goods ïąQuality (according to European Standards â EN) ïąEfficiency (line process) ï§Activities of the CSSD ïąCleaning ïąDisinfection of semi- / non critical items ïąSterilization of critical items (high risk for infection) ïąSupply of sterile materials
- 3. DEFINITION Service, with in the hospital, catering for the sterile supplies to all departments , both to specialized units as well as general wards and OPDs.
- 4. AIM Centralizing the activities of receipt, cleaning, assembly, sterilization, storage and distribution of sterilized materials from a central department where safe sterilization is done under controlled conditions with adequate managerial and technical supervision at an optimum cost. To provide an efficient, economic, continuous and quality supply of sterilized material to various areas of the hospital to deliver quality and infection free patient care. Contributes to reduction in hospital infection rate To reduce the burden of work of the nursing personnel, there by enabling them to devote more of their time to patient care .
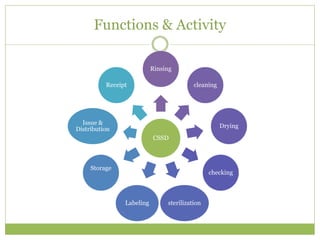
- 5. Functions & Activity CSSD Rinsing cleaning Drying checking sterilizationLabeling Storage Issue & Distribution Receipt
- 6. FUNCTIONS OF CSSD âĒ Receiving and sorting soiled materials used in the hospital. âĒ Determining whether the item should be reused or discarded. âĒ Carry out the process of decontamination or disinfection prior to sterilization. âĒ Carry out specialized cleaning of equipments and supplies. âĒ Inspecting and testing instruments, equipments and linen. âĒ Assembling treatments trays, instrument sets, linen packs, etc. âĒ Packing all materials for sterilization. âĒ Sterilizing. âĒ Labeling and dating materials. âĒ Storing and controlling inventory. âĒ Issuing and distributing.
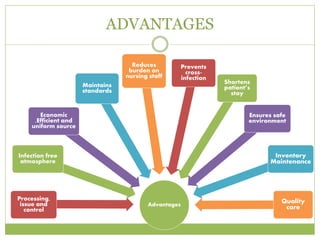
- 7. ADVANTAGES Advantages Processing, issue and control Infection free atmosphere Economic ,Efficient and uniform source Maintains standards Reduces burden on nursing staff Prevents cross- infection Shortens patientâs stay Ensures safe environment Inventory Maintenance Quality care
- 8. ADVANTAGES 1. Bacteriological safe sterilization. 2. Less expensive. 3. Elimination of unsound practices & establishment of standard procedures. 4. Assurance of adequate supply of sterile products immediately and constantly available for sometime as well as emergency use. 5. Conservation of trained staff. 6. Better quality control 7. Better good of material flow 8. Prolonged life by proper care of equipment
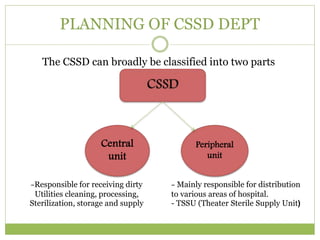
- 9. PLANNING OF CSSD DEPT The CSSD can broadly be classified into two parts Central unit Peripheral unit -Responsible for receiving dirty Utilities cleaning, processing, Sterilization, storage and supply - Mainly responsible for distribution to various areas of hospital. - TSSU (Theater Sterile Supply Unit)
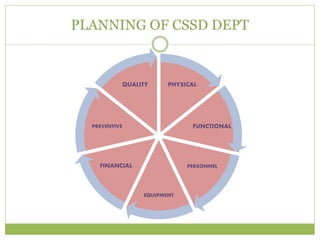
- 10. PLANNING OF CSSD DEPT PHYSICAL FUNCTIONAL PERSONNEL EQUIPMENT FINANCIAL PREVENTIVE QUALITY
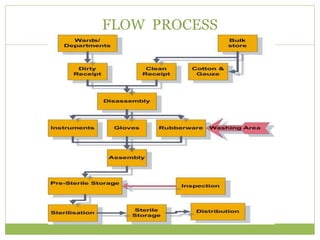
- 11. FLOW PROCESS
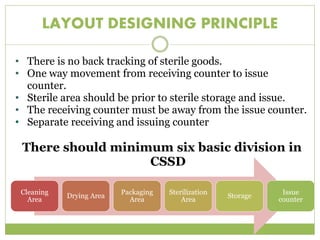
- 12. LAYOUT DESIGNING PRINCIPLE âĒ There is no back tracking of sterile goods. âĒ One way movement from receiving counter to issue counter. âĒ Sterile area should be prior to sterile storage and issue. âĒ The receiving counter must be away from the issue counter. âĒ Separate receiving and issuing counter There should minimum six basic division in CSSD Cleaning Area Drying Area Packaging Area Sterilization Area Storage Issue counter
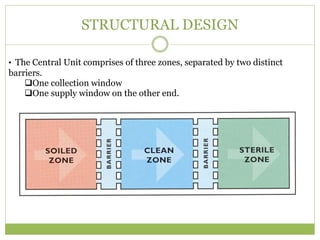
- 13. STRUCTURAL DESIGN âĒ The Central Unit comprises of three zones, separated by two distinct barriers. ïąOne collection window ïąOne supply window on the other end.
- 14. EQUIPMENT IN CSSD âĒ Cleaning and decontamination devices âĒHot air Oven for drying & heat sterilization âĒGlove processing unit for surgical gloves âĒInstrument sharper e.g.. Needle sharper âĒTesting apparatus for emergency sterilization âĒOthers :- trolleys, work surface, telephones âĒMaintenance and repair of equipments âĒMaterial : chemicals for washing and cleaning âĒSteam Boiler âĒHot air ovens for drying instruments âĒAutoclaves using dry heat, moist heat. âĒEthylene oxide sterilizers. âĒTesting material to check effectiveness of sterilization. âĒSealing machine âĒUltrasonic Washer
- 15. STERILIZATION âĒIt is a process of freeing an article from all living organisms including bacteria ,fungal spores and viruses. âĒA material is pronounced sterile if it achieves 99.99% kill of bacterial spores.
- 16. TYPES OF STERILIZATION âĒ Dry Heat âĒ Steam High Pressure-Autoclaves operated by Gas, K.oil or Electricity ( Flash, Pulse) âĒ Ethylene Oxide Sterilization. âĒ Chemical Sterilization. âĒ Radiation Sterilization. âĒ Infra Red Radiation â Syringes âĒ Ultra Violet Radiation â Decontamination of Air âĒ Ionizing Radiation / Gamma Radiation
- 17. CHEMICAL STERILIZATION CIDEX âĒA Glutaraldehyde derivative is most effective as it destroys spores too. âĒIt is high level disinfectant. It kills spores within 12 hrs and viruses within 10 min. âĒWidely used because of their excellent biocidal properties, activity in the presence of organic matter, non corrosiveness and noncoagulation of proteinaceous material Hydrogen peroxide âĒIt is an effective bactericidal, fungicidal, viricidal and sporicidal. âĒIt is commercially available as 3% solution but can be used upto 25% concentration. âĒIt is non corrosive and not inactivated by organic matter but irritant to skin and eyes lutaraldehyde derivative is most effective as it destroys spores too.
- 18. STEAM STERILATION The equipments are first cleaned & the packaged in muslin, linen or paper which are easily penetrated by steam & then placed on shelf in the chamber. Water ï Saturated ï Wet vapor ï Dry saturated Vapor ï Super Heated Vapor / Steam - Steam with <0.95 Dryness Factor is not useful for Sterilization. - Superheated Steam acts like Dry Hot Air only . ( Strength Of Steam is its Latent Heat) Total time Required ïąAutoclave â 45 to 50 min ïąETO(Ethylene Oxide) sterilizer â 11 to 12 hours
- 19. STERILIZATION INDICATORS Mechanical Monitors: ïą Devices that record time, temperature & pressure. Biological Indicators: ïą They are standardized preparation of spores. ïą A positive biological indicator is indicative of possible sterilization process failure. ïą They should be used atleast once a week but ïą Time needed for incubation is long. E.g. spores of Bacillus Sterothermophilus.
- 20. STERILIZATION INDICATORS Chemical Indicators: ïąThese are more practical means & detect problems immediately. ïąThe CDC & all major U.S organizations standards & guidelines advocate that a chemical indicator be attached to every package that goes through a sterilization cycle & within each package to be sterilized in what is expected to be the most difficult-to-sterilize location. These are divided into 6 classes, higher the class, more sensitive the indicator Class 1- These are Internal & External Process Indicator These inform that item has been exposed to sterilization process. E.g. External Process Indicator â Autoclave Tape.
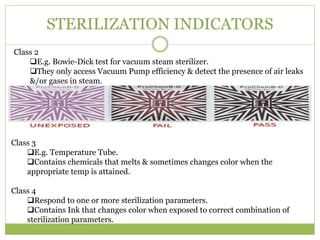
- 21. STERILIZATION INDICATORS Class 2 ïąE.g. Bowie-Dick test for vacuum steam sterilizer. ïąThey only access Vacuum Pump efficiency & detect the presence of air leaks &/or gases in steam. Class 3 ïąE.g. Temperature Tube. ïąContains chemicals that melts & sometimes changes color when the appropriate temp is attained. Class 4 ïąRespond to one or more sterilization parameters. ïąContains Ink that changes color when exposed to correct combination of sterilization parameters.
- 22. STERILIZATION INDICATORS Class 5 ïąKnown as Integrating Indicators or Integrators ïąRespond to all parameters of sterilization over a specified range of temperatures. Class 6 ïąThese are emulating indicators. ïąThese are designed to react to all critical parameters over a specified range of sterilization cycles for which the stated values are based on the settings of the selected sterilization cycles
- 23. STORAGE âĒ After sterilization the sterilized items are kept in different racks as per labeling. âĒ Supplied as per the demand of different area. âĒ To ensure continuous availability of sterile supply five times of daily requirement should be available in storage.
- 24. ROLE OF MANAGER âĒ Maintenance and repair of equipment âĒ Inventory management of supplies and consumable âĒ Ensure quality of sterilization âĒ Ensure proper distribution and transport âĒ Cost control measure, to analyze and reduce the number of cycle âĒ Record keeping and data analysis âĒ Optimal utilization of manpower and equipment âĒ Motivation of staff and training âĒ Inter departmental coordination