CT SCAN
3 likes171 views
A CT scan is a fast, easily accessible, cost efficient, non-invasive imaging technique used to detect fractures, bleeds, degenerative changes, abnormalities, and the extent of damage in the brain. A CT scan provides information about attenuation levels that can indicate hemorrhage, contrast, calcium, metal, ischemia, infection, or edema. When reading a CT scan, one examines the patient details, type of scan, purpose, cranial and extracranial structures, ventricles, cistern, sulci, and brain parenchyma for lesions characterized by their location, color, and margin.
1 of 18
















Recommended
Intra Vascular Ultrasound



Intra Vascular UltrasoundChetan Ganteppanavar
╠²
Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) uses a catheter-mounted ultrasound transducer to visualize the inside of blood vessels. The transducer emits high-frequency sound waves that bounce off vessel tissues and are converted into images. IVUS provides accurate measurements of vessel size and plaque buildup. It is used pre-and post-intervention to assess plaque and guide procedures like stenting. While it adds little risk, IVUS imaging may be limited in very narrow vessels. The detailed images aid clinical decisions regarding lesion assessment, stent selection and placement, and detection of complications.Ct head by sajid



Ct head by sajidSAJIDEJAZ1
╠²
This document discusses guidelines for performing CT scans of the head. It outlines positioning procedures such as aligning the orbitomeatal line parallel to the transverse plane. It recommends transaxial scan planes for routine exams and to view the posterior and middle cranial fossa. Coronal planes are preferred for examining the petrous bone. Examples of common indications are listed such as aneurysm, tumor, and trauma. Contrast administration parameters and slice widths are also provided.Cardiothoracic surgery Q&A 2019



Cardiothoracic surgery Q&A 2019Kareem Alnakeeb
╠²
Some notes in Cardiothoracic surgery. These notes were published in 2019.
You can download the file from:
- Mediafire: http://www.mediafire.com/file/zrxenwq4tjdnhsj/fileAlexandre Avran - Angiogram-how to record, analyseand prepare to the interven...



Alexandre Avran - Angiogram-how to record, analyseand prepare to the interven...Euro CTO Club
╠²
1) The angiogram must thoroughly define the characteristics of the CTO such as the proximal cap, length, calcification, bending, bifurcations, and presence of collaterals in order to determine the best initial strategy - antegrade, retrograde, or antegrade and retrograde.
2) Important aspects to analyze are the proximal cap using different projections, the full length of the occlusion, areas of calcification using fluoro without contrast, and the origin, size, tortuosity and entry angle of potential collateral channels.
3) By the end of the angiogram, the operator should be able to decide if the case is feasible for them or requires a proctor, the initial strategy, and backupcath conf 06-17-2010



cath conf 06-17-2010Imran Javed
╠²
This document discusses the development of a bespoke external aortic root support (EARS) for patients with Marfan syndrome using imaging and computer aided design. The EARS is placed around the ascending aorta during surgery to prevent dissection and rupture, reducing the risks associated with traditional aortic root replacement techniques. Initial results suggest the EARS provides effective support of the aorta without requiring open heart surgery or lifelong anticoagulation.Media presentation assignment tina knott



Media presentation assignment tina knotttinaknott
╠²
This document discusses laser angioplasty, a technological advancement in the medical field. It defines laser angioplasty as using a laser-tipped catheter to vaporize plaque blocking arteries. The procedure involves guiding a laser catheter to the blockage and pulsing laser light to remove the plaque. Risks include artery perforation while advantages are improved blood flow and reduced risk compared to surgery. While equipment costs are high, laser angioplasty is expected to become more common for fixing blockages.Philip Dingli. Javier Escaned - Intracoronary imaging in CTOs When to use, ho...



Philip Dingli. Javier Escaned - Intracoronary imaging in CTOs When to use, ho...Euro CTO Club
╠²
This document discusses the use of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) in percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) for chronic total occlusions (CTOs). It provides examples of how IVUS can aid in CTO procedures, including guiding wiring, assessing vessel size for balloon sizing, and optimizing stent placement. While IVUS use was associated with longer procedures, more contrast and radiation exposure, it did not negatively impact success rates or safety outcomes. IVUS may help with complex CTO cases and provide information on vessel remodeling and stent expansion to reduce risks of restenosis.How to learn the catheter skill techniques



How to learn the catheter skill techniquesdrmaisano
╠²
The document discusses the need for cross-training of surgeons and interventional cardiologists in percutaneous heart valve treatment. It states that the procedure requires skills independent of one's base discipline, and that specific training is required. Those undergoing the procedural training should be experienced interventionalists or surgeons. The document then outlines various pathways for acquiring the necessary skills through simulation, proctoring, visiting other centers, and industry-supported opportunities.Intracoronary Imaging ŌĆō when to use, how to use and how to interpret the images



Intracoronary Imaging ŌĆō when to use, how to use and how to interpret the imagesEuro CTO Club
╠²
This document discusses the use of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) in chronic total occlusion (CTO) percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI). IVUS can aid in CTO PCI in several ways, including guiding wiring of ostial lesions, sizing balloons for reverse controlled antegrade and retrograde subintimal tracking techniques, guiding re-entry maneuvers, assessing distal vessels, optimizing stent placement, and managing complications. Studies show IVUS guidance may improve outcomes after CTO PCI compared to angiography alone. IVUS provides valuable information on stent expansion and placement that can influence long-term results. While useful, IVUS requires contrast administration and cannot be used for real-time guidance in some techniques like controlled antegradeIntracoronary optical coherence tomography



Intracoronary optical coherence tomographyhttps://aiimsbhubaneswar.nic.in/
╠²
Optical coherence tomography-guided algorithm for percutaneous coronary intervention. Vessel diameter should be assessed using the external elastic lamina (EEL)-EEL diameter at the reference segments, and rounded down to select interventional devices (balloons, stents). If the EEL cannot be identified, luminal measures are used and rounded up to 0.5 mm larger for selection of the devices. Optical coherence tomography (OCT)-guided optimisation strategies post stent implantation per EEL-based diameter measurement and per lumen-based diameter measurement are shown. For instance, if the distal EEL-EEL diameter measures 3.2 mm├Ś3.1 mm (i.e., the mean EEL-based diameter is 3.15 mm), this number is rounded down to the next available stent size and post-dilation balloon to be used at the distal segment. Thus, a 3.0 mm stent and non-compliant balloon diameter is selected. If the proximal EEL cannot be visualised, the mean lumen diameter should be used for device sizing. For instance, if the mean proximal lumen diameter measures 3.4 mm, this number is rounded up to the next available balloon diameter (within up to 0.5 mm larger) for post-dilation. MLA: minimal lumen area; MSA: minimal stent area;NC: non-compliantISMRM Edition ŌĆō Issue 58



ISMRM Edition ŌĆō Issue 58Jhon Arriaga Cordova
╠²
The document discusses abdominal MRI on the new MAGNETOM Prisma 3T scanner. It notes the advantages of 3T MRI include higher signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio, allowing for improved spatial resolution and lesion detection. However, challenges at 3T include increased magnetic field inhomogeneities and susceptibility artifacts. The MAGNETOM Prisma addresses these challenges through technical advances, such as improved B0 and B1 field homogeneity which provide better image quality for liver imaging compared to standard 3T scanners. The article demonstrates examples of reduced distortion and improved diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver on MAGNETOM Prisma.Sirris materials day 2011 rapd manufacturing in medicine - prof poukens



Sirris materials day 2011 rapd manufacturing in medicine - prof poukensSirris
╠²
This document discusses rapid manufacturing techniques for customized implants used in craniofacial reconstructive surgery. It presents three case studies: 1) A skull defect reconstructed with a 3D printed titanium implant. 2) A customized temporomandibular joint implant to replace damaged bone. 3) A mandibular implant to replace an infected mandible. The document concludes that computer-aided engineering applied to medicine represents an important advancement, allowing customized implants to reconstruct complex craniofacial defects.EPUB Intracoronary Ultrasound 



EPUB Intracoronary Ultrasound gietvormen
╠²
Distilling more than ten years of experience with intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) Intracoronary Ultrasound summarizes Dr Mintz's own experiences as well as published and unpublished observations of others in the field. The text incorporates angiographic and uses pathologic observations to fill in the gaps in knowledge of coronary artery disease as assessed by IVUS alone. A major effort went into selecting and presenting figures for their illustrative value. In most cases each IVUS figure includes a linear sequence of equidistantlyspaced image slices that illustrates the full length morphology of the lesion andor the pullback of the transducer through the lesion. It provides the reader with an excellent guide for revision confirming diagnoses and teaching.FFR with St. Jude System



FFR with St. Jude SystemMuhammad Naveed Saeed
╠²
FFR is a technique used during coronary catheterization to measure pressure differences across a coronary artery stenosis to determine if it is restricting blood flow. FFR provides an invasive test to estimate the effects of a narrowed blood vessel in real-time without providing information on plaque morphology. Medications like adenosine are administered to increase the heart's workload and detect ischemia during FFR testing. Significant stenoses are considered less than 0.80 on the FFR scale while readings above 0.80 are not generally deemed significant obstructions.Principle of DSA



Principle of DSAMelwin Augustine
╠²
The document discusses digital subtraction angiography (DSA), a medical imaging technique used to visualize blood vessels. It provides an overview of the history and development of DSA, including key contributors and technological advances. Some of the main points covered include:
- DSA involves injecting contrast dye and digitally subtracting bone structures from images to clearly depict blood vessels
- It has been improved over time through the introduction of techniques like dual energy subtraction, temporal filtering, and more recently 3D and 4D DSA
- Advances like these have helped increase diagnostic accuracy for evaluating conditions like intracranial aneurysmsDIGITAL SUBTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY



DIGITAL SUBTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHYJoshua Mathew
╠²
A PROJECT REPORT ON THE ROLE OF " DIGITAL SUBTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY" IN CONVENTIONAL AND MORDERN RADIOLOGYNicolas Boudou - RetrogradeCTO PCI in leftdominant coronaryartery



Nicolas Boudou - RetrogradeCTO PCI in leftdominant coronaryarteryEuro CTO Club
╠²
The document discusses retrograde chronic total occlusion percutaneous coronary intervention in a left dominant coronary artery. It describes using a retrograde approach through a septal collateral into the left circumflex artery and placing a guide catheter extension in the left circumflex to protect the left main while performing a pure retrograde wire crossing and wiring in the guide catheter extension. This technique, known as the "ping pong technique", involves using two guide catheters in the same left coronary artery. The procedure was successfully performed in a patient with a chronic total occlusion of the ostial left anterior descending artery who previously failed intervention at another institution.Pitfalls of IVUS Imaging



Pitfalls of IVUS ImagingVein Global
╠²
By: Seshadri Raju, MD, FACS
Visit VeinGlobal at http://www.veinglobal.com/ for more presentations and videos on this topic, or for more information on venous disease news, education and research.Physiotherapy management of perceptual disorders



Physiotherapy management of perceptual disordersKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses various perceptual disorders including their definitions, types, causes, tests used for assessment, and treatment approaches. It covers disorders related to body scheme and image like unilateral neglect. It also discusses agnosia, spatial relation disorders involving figure ground discrimination, form discrimination, and position in space. Other topics include topographic disorientation, depth and distance perception, and vertical disorientation. The document also summarizes visual, auditory and tactile agnosia as well as different types of apraxia such as ideomotor, ideational, and buccofacial apraxia. Remedial, compensatory, sensory integration and neurofunctional approaches are discussed as treatment options.Physiotherapy management of Head Injury



Physiotherapy management of Head InjuryKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses head injuries and their classification, as well as scales used to measure head injuries. It describes physical therapy management for mild, moderate, and severe head injuries. For severe injuries, PT focuses on preventing secondary complications like contractures and bed sores through positioning, splinting, and early mobility. For moderate injuries, interventions include motor relearning programs and task-oriented approaches. PT for mild injuries includes vestibular rehabilitation and balance training.PT MANAGEMENT OF GBS



PT MANAGEMENT OF GBSKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses Guillain-Barr├® syndrome (GBS), including its definition, clinical features, assessment scales, and phases. It defines GBS as an acute/subacute symmetrical motor neuropathy involving more than one peripheral nerve. The phases of GBS are described as the acute, plateau, and recovery phases. For each phase, goals of physical therapy and examples of interventions are provided, such as chest physiotherapy, positioning, stretching, and strengthening exercises to address weaknesses and functional limitations during the different stages of GBS.PT MANAGEMENT OF INFECTIONS OF BRAIN



PT MANAGEMENT OF INFECTIONS OF BRAINKeerthi Priya
╠²
Inflammation of the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord (meninges) can cause meningitis. Common symptoms include vomiting, seizures, stiff neck, rash, and altered consciousness. Assessment involves evaluating neurological, vascular, musculoskeletal and other systems. Management aims to provide psychological support, prevent complications like chest issues and blood clots, correct deformities, improve strength and balance, and train gait. Techniques include stretching, positioning, exercises and assisted walking. Cerebellar Ataxia



Cerebellar AtaxiaKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses cerebellar ataxia, which is a lack of muscle coordination caused by dysfunction of the cerebellum. It classifies ataxia into hereditary, non-hereditary degenerative, and acquired types. Hereditary ataxia includes autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, and X-linked forms. Common symptoms are gait instability, limb incoordination, slurred speech, and eye movement abnormalities. Diagnosis involves testing for genetic mutations, imaging the brain, and checking for metabolic deficiencies. Treatment aims to reduce symptoms and improve coordination through medications, physical therapy, and assistive devices.Tabes dorsalis



Tabes dorsalisKeerthi Priya
╠²
Tabes dorsalis is a progressive degeneration of nerve cells and fibers in the spinal cord that carry sensory information to the brain, caused by untreated syphilis. It is characterized by sensory deficits, loss of coordination, and diminished reflexes. The disease progresses through preataxic, ataxic, and paralysis stages. Clinical features include loss of sensation, Argyll Robertson pupils, dementia, hypotonicity, loss of coordination, and trophic ulcers. Treatment involves antibiotics, steroids, pain medications, exercises, and splinting to manage symptoms.Neuro syphilis



Neuro syphilisKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses syphilis, a multi-system disease caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum that can involve the nervous system. It has various stages and presentations depending on whether it was acquired or congenital. Neurosyphilis can occur in early or late stages and manifest as asymptomatic neurosyphilis, meningitis, meningovascular symptoms, general paresis, or tabes dorsalis. Diagnosis involves serology and CSF tests. Treatment is with penicillin or other antibiotics. Complications can include hydrocephalus, myelitis, and Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction.Evoked potentials



Evoked potentialsKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses evoked potentials, which are electrical activities in the neural pathway generated in response to external stimuli. It focuses on three types of sensory evoked potentials: visual evoked potentials (VEP), somatosensory evoked potentials, and brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BEAP). VEP assess the visual pathway and look for abnormalities in P100 latency and amplitude. BEAP assess the auditory pathway by analyzing wave latencies and amplitudes, with abnormalities indicating lesions in the auditory nerve, brainstem, or cranial nerves. Evoked potentials are used to detect disturbances in the central nervous system.Craniotomy



CraniotomyKeerthi Priya
╠²
Craniotomy is a surgical procedure where a section of the skull is removed to access and expose the brain and intracranial structures. It is commonly used to clip aneurysms, remove tumors, abscesses or other lesions, decompress blood vessels, implant devices, biopsy tissue, or evacuate hematomas. Complications can include hemorrhage, seizures, cerebrospinal fluid leaks, infections, and neurological deficits. Craniotomies are classified based on location such as frontal, temporal, parietal or occipital, and may also be keyhole, stereotactic, or awake procedures. The case discussion involves an 11-year old girl who suffered head trauma in a car accident and showed signs ofSkull x ray



Skull x rayKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses an x-ray of the skull, including its anatomy, bones, sutures, fontanelles, and sinuses. It notes there are 22 total bones in the skull, with 8 in the cranium and 14 in the facial skeleton. It describes different views of skull x-rays and indications for skull x-rays such as shape, size, density, tumors, infections, and fractures. It outlines some abnormalities seen on skull x-rays related to density, contour, intracranial contents, and lytic or sclerotic lesions.CSF Analysis



CSF AnalysisKeerthi Priya
╠²
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a diagnostic procedure used to collect and analyze cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the spinal canal. It can help diagnose infectious and non-infectious neurological conditions. The document outlines the steps of a lumbar puncture procedure, including positioning the patient and inserting a needle between two vertebrae in the lower back to withdraw CSF. Complications are minor in most cases but can include back pain, headache, or nerve damage. Analysis of CSF properties and biochemical components can provide information about conditions affecting the central nervous system.TBI



TBIKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses traumatic brain injury (TBI). TBI is defined as damage to the brain caused by an external force and can be either open or closed injuries. It affects about 1.5-2 million people annually. Common causes include motor vehicle accidents (60%), falls (20-25%), and violence (15%). TBI can cause impairments in cognitive, physical, and behavioral/emotional functioning. Diagnosis involves imaging tests like CT scans and MRI to evaluate the severity and location of the brain damage. Management may include medications to reduce secondary brain damage, surgery to repair skull fractures or drain blood clots, and rehabilitation.More Related Content
What's hot (10)
Intracoronary Imaging ŌĆō when to use, how to use and how to interpret the images



Intracoronary Imaging ŌĆō when to use, how to use and how to interpret the imagesEuro CTO Club
╠²
This document discusses the use of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) in chronic total occlusion (CTO) percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI). IVUS can aid in CTO PCI in several ways, including guiding wiring of ostial lesions, sizing balloons for reverse controlled antegrade and retrograde subintimal tracking techniques, guiding re-entry maneuvers, assessing distal vessels, optimizing stent placement, and managing complications. Studies show IVUS guidance may improve outcomes after CTO PCI compared to angiography alone. IVUS provides valuable information on stent expansion and placement that can influence long-term results. While useful, IVUS requires contrast administration and cannot be used for real-time guidance in some techniques like controlled antegradeIntracoronary optical coherence tomography



Intracoronary optical coherence tomographyhttps://aiimsbhubaneswar.nic.in/
╠²
Optical coherence tomography-guided algorithm for percutaneous coronary intervention. Vessel diameter should be assessed using the external elastic lamina (EEL)-EEL diameter at the reference segments, and rounded down to select interventional devices (balloons, stents). If the EEL cannot be identified, luminal measures are used and rounded up to 0.5 mm larger for selection of the devices. Optical coherence tomography (OCT)-guided optimisation strategies post stent implantation per EEL-based diameter measurement and per lumen-based diameter measurement are shown. For instance, if the distal EEL-EEL diameter measures 3.2 mm├Ś3.1 mm (i.e., the mean EEL-based diameter is 3.15 mm), this number is rounded down to the next available stent size and post-dilation balloon to be used at the distal segment. Thus, a 3.0 mm stent and non-compliant balloon diameter is selected. If the proximal EEL cannot be visualised, the mean lumen diameter should be used for device sizing. For instance, if the mean proximal lumen diameter measures 3.4 mm, this number is rounded up to the next available balloon diameter (within up to 0.5 mm larger) for post-dilation. MLA: minimal lumen area; MSA: minimal stent area;NC: non-compliantISMRM Edition ŌĆō Issue 58



ISMRM Edition ŌĆō Issue 58Jhon Arriaga Cordova
╠²
The document discusses abdominal MRI on the new MAGNETOM Prisma 3T scanner. It notes the advantages of 3T MRI include higher signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio, allowing for improved spatial resolution and lesion detection. However, challenges at 3T include increased magnetic field inhomogeneities and susceptibility artifacts. The MAGNETOM Prisma addresses these challenges through technical advances, such as improved B0 and B1 field homogeneity which provide better image quality for liver imaging compared to standard 3T scanners. The article demonstrates examples of reduced distortion and improved diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver on MAGNETOM Prisma.Sirris materials day 2011 rapd manufacturing in medicine - prof poukens



Sirris materials day 2011 rapd manufacturing in medicine - prof poukensSirris
╠²
This document discusses rapid manufacturing techniques for customized implants used in craniofacial reconstructive surgery. It presents three case studies: 1) A skull defect reconstructed with a 3D printed titanium implant. 2) A customized temporomandibular joint implant to replace damaged bone. 3) A mandibular implant to replace an infected mandible. The document concludes that computer-aided engineering applied to medicine represents an important advancement, allowing customized implants to reconstruct complex craniofacial defects.EPUB Intracoronary Ultrasound 



EPUB Intracoronary Ultrasound gietvormen
╠²
Distilling more than ten years of experience with intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) Intracoronary Ultrasound summarizes Dr Mintz's own experiences as well as published and unpublished observations of others in the field. The text incorporates angiographic and uses pathologic observations to fill in the gaps in knowledge of coronary artery disease as assessed by IVUS alone. A major effort went into selecting and presenting figures for their illustrative value. In most cases each IVUS figure includes a linear sequence of equidistantlyspaced image slices that illustrates the full length morphology of the lesion andor the pullback of the transducer through the lesion. It provides the reader with an excellent guide for revision confirming diagnoses and teaching.FFR with St. Jude System



FFR with St. Jude SystemMuhammad Naveed Saeed
╠²
FFR is a technique used during coronary catheterization to measure pressure differences across a coronary artery stenosis to determine if it is restricting blood flow. FFR provides an invasive test to estimate the effects of a narrowed blood vessel in real-time without providing information on plaque morphology. Medications like adenosine are administered to increase the heart's workload and detect ischemia during FFR testing. Significant stenoses are considered less than 0.80 on the FFR scale while readings above 0.80 are not generally deemed significant obstructions.Principle of DSA



Principle of DSAMelwin Augustine
╠²
The document discusses digital subtraction angiography (DSA), a medical imaging technique used to visualize blood vessels. It provides an overview of the history and development of DSA, including key contributors and technological advances. Some of the main points covered include:
- DSA involves injecting contrast dye and digitally subtracting bone structures from images to clearly depict blood vessels
- It has been improved over time through the introduction of techniques like dual energy subtraction, temporal filtering, and more recently 3D and 4D DSA
- Advances like these have helped increase diagnostic accuracy for evaluating conditions like intracranial aneurysmsDIGITAL SUBTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY



DIGITAL SUBTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHYJoshua Mathew
╠²
A PROJECT REPORT ON THE ROLE OF " DIGITAL SUBTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY" IN CONVENTIONAL AND MORDERN RADIOLOGYNicolas Boudou - RetrogradeCTO PCI in leftdominant coronaryartery



Nicolas Boudou - RetrogradeCTO PCI in leftdominant coronaryarteryEuro CTO Club
╠²
The document discusses retrograde chronic total occlusion percutaneous coronary intervention in a left dominant coronary artery. It describes using a retrograde approach through a septal collateral into the left circumflex artery and placing a guide catheter extension in the left circumflex to protect the left main while performing a pure retrograde wire crossing and wiring in the guide catheter extension. This technique, known as the "ping pong technique", involves using two guide catheters in the same left coronary artery. The procedure was successfully performed in a patient with a chronic total occlusion of the ostial left anterior descending artery who previously failed intervention at another institution.Pitfalls of IVUS Imaging



Pitfalls of IVUS ImagingVein Global
╠²
By: Seshadri Raju, MD, FACS
Visit VeinGlobal at http://www.veinglobal.com/ for more presentations and videos on this topic, or for more information on venous disease news, education and research.More from Keerthi Priya (20)
Physiotherapy management of perceptual disorders



Physiotherapy management of perceptual disordersKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses various perceptual disorders including their definitions, types, causes, tests used for assessment, and treatment approaches. It covers disorders related to body scheme and image like unilateral neglect. It also discusses agnosia, spatial relation disorders involving figure ground discrimination, form discrimination, and position in space. Other topics include topographic disorientation, depth and distance perception, and vertical disorientation. The document also summarizes visual, auditory and tactile agnosia as well as different types of apraxia such as ideomotor, ideational, and buccofacial apraxia. Remedial, compensatory, sensory integration and neurofunctional approaches are discussed as treatment options.Physiotherapy management of Head Injury



Physiotherapy management of Head InjuryKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses head injuries and their classification, as well as scales used to measure head injuries. It describes physical therapy management for mild, moderate, and severe head injuries. For severe injuries, PT focuses on preventing secondary complications like contractures and bed sores through positioning, splinting, and early mobility. For moderate injuries, interventions include motor relearning programs and task-oriented approaches. PT for mild injuries includes vestibular rehabilitation and balance training.PT MANAGEMENT OF GBS



PT MANAGEMENT OF GBSKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses Guillain-Barr├® syndrome (GBS), including its definition, clinical features, assessment scales, and phases. It defines GBS as an acute/subacute symmetrical motor neuropathy involving more than one peripheral nerve. The phases of GBS are described as the acute, plateau, and recovery phases. For each phase, goals of physical therapy and examples of interventions are provided, such as chest physiotherapy, positioning, stretching, and strengthening exercises to address weaknesses and functional limitations during the different stages of GBS.PT MANAGEMENT OF INFECTIONS OF BRAIN



PT MANAGEMENT OF INFECTIONS OF BRAINKeerthi Priya
╠²
Inflammation of the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord (meninges) can cause meningitis. Common symptoms include vomiting, seizures, stiff neck, rash, and altered consciousness. Assessment involves evaluating neurological, vascular, musculoskeletal and other systems. Management aims to provide psychological support, prevent complications like chest issues and blood clots, correct deformities, improve strength and balance, and train gait. Techniques include stretching, positioning, exercises and assisted walking. Cerebellar Ataxia



Cerebellar AtaxiaKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses cerebellar ataxia, which is a lack of muscle coordination caused by dysfunction of the cerebellum. It classifies ataxia into hereditary, non-hereditary degenerative, and acquired types. Hereditary ataxia includes autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, and X-linked forms. Common symptoms are gait instability, limb incoordination, slurred speech, and eye movement abnormalities. Diagnosis involves testing for genetic mutations, imaging the brain, and checking for metabolic deficiencies. Treatment aims to reduce symptoms and improve coordination through medications, physical therapy, and assistive devices.Tabes dorsalis



Tabes dorsalisKeerthi Priya
╠²
Tabes dorsalis is a progressive degeneration of nerve cells and fibers in the spinal cord that carry sensory information to the brain, caused by untreated syphilis. It is characterized by sensory deficits, loss of coordination, and diminished reflexes. The disease progresses through preataxic, ataxic, and paralysis stages. Clinical features include loss of sensation, Argyll Robertson pupils, dementia, hypotonicity, loss of coordination, and trophic ulcers. Treatment involves antibiotics, steroids, pain medications, exercises, and splinting to manage symptoms.Neuro syphilis



Neuro syphilisKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses syphilis, a multi-system disease caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum that can involve the nervous system. It has various stages and presentations depending on whether it was acquired or congenital. Neurosyphilis can occur in early or late stages and manifest as asymptomatic neurosyphilis, meningitis, meningovascular symptoms, general paresis, or tabes dorsalis. Diagnosis involves serology and CSF tests. Treatment is with penicillin or other antibiotics. Complications can include hydrocephalus, myelitis, and Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction.Evoked potentials



Evoked potentialsKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses evoked potentials, which are electrical activities in the neural pathway generated in response to external stimuli. It focuses on three types of sensory evoked potentials: visual evoked potentials (VEP), somatosensory evoked potentials, and brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BEAP). VEP assess the visual pathway and look for abnormalities in P100 latency and amplitude. BEAP assess the auditory pathway by analyzing wave latencies and amplitudes, with abnormalities indicating lesions in the auditory nerve, brainstem, or cranial nerves. Evoked potentials are used to detect disturbances in the central nervous system.Craniotomy



CraniotomyKeerthi Priya
╠²
Craniotomy is a surgical procedure where a section of the skull is removed to access and expose the brain and intracranial structures. It is commonly used to clip aneurysms, remove tumors, abscesses or other lesions, decompress blood vessels, implant devices, biopsy tissue, or evacuate hematomas. Complications can include hemorrhage, seizures, cerebrospinal fluid leaks, infections, and neurological deficits. Craniotomies are classified based on location such as frontal, temporal, parietal or occipital, and may also be keyhole, stereotactic, or awake procedures. The case discussion involves an 11-year old girl who suffered head trauma in a car accident and showed signs ofSkull x ray



Skull x rayKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses an x-ray of the skull, including its anatomy, bones, sutures, fontanelles, and sinuses. It notes there are 22 total bones in the skull, with 8 in the cranium and 14 in the facial skeleton. It describes different views of skull x-rays and indications for skull x-rays such as shape, size, density, tumors, infections, and fractures. It outlines some abnormalities seen on skull x-rays related to density, contour, intracranial contents, and lytic or sclerotic lesions.CSF Analysis



CSF AnalysisKeerthi Priya
╠²
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a diagnostic procedure used to collect and analyze cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the spinal canal. It can help diagnose infectious and non-infectious neurological conditions. The document outlines the steps of a lumbar puncture procedure, including positioning the patient and inserting a needle between two vertebrae in the lower back to withdraw CSF. Complications are minor in most cases but can include back pain, headache, or nerve damage. Analysis of CSF properties and biochemical components can provide information about conditions affecting the central nervous system.TBI



TBIKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses traumatic brain injury (TBI). TBI is defined as damage to the brain caused by an external force and can be either open or closed injuries. It affects about 1.5-2 million people annually. Common causes include motor vehicle accidents (60%), falls (20-25%), and violence (15%). TBI can cause impairments in cognitive, physical, and behavioral/emotional functioning. Diagnosis involves imaging tests like CT scans and MRI to evaluate the severity and location of the brain damage. Management may include medications to reduce secondary brain damage, surgery to repair skull fractures or drain blood clots, and rehabilitation.SWD



SWDKeerthi Priya
╠²
Short wave diathermy uses electromagnetic waves between 107-108 Hz to induce heating in tissues. It has both thermal and non-thermal physiological effects and can be used to treat inflammatory conditions, infections, muscle injuries and more. The document describes the production of short wave diathermy through an oscillating circuit, and discusses methods of application including capacitor and cable techniques which create electric and magnetic fields. Precautions are outlined to avoid risks like burns. In summary, it provides an overview of short wave diathermy including its mechanisms, effects, indications and application methods.PEME



PEMEKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses pulsed electromagnetic energy (PEME) therapy. PEME uses non-thermal pulses of electromagnetic energy to stimulate tissues for therapeutic purposes. It can increase ATP production, alter cell membranes, decrease inflammation, and increase healing. PEME is used to treat neurological conditions like radiculopathies and neuropathies, musculoskeletal issues like fractures and strains, psychological disorders, and general wounds and sores. Contraindications include pregnancy, menstruation, metal implants and recent radiation therapy.LASER



LASERKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document discusses laser therapy, including its production, types, effects, applications, and techniques. It begins by defining laser as light amplified by stimulated emission of radiation. It then describes the key properties of lasers as monochromaticity, coherence, and collimation. It discusses the different types of lasers based on lasing medium (ruby, HeNe, diode) and intensity (high power, low power). The physiological and therapeutic effects of lasers are outlined, including effects on wound healing, pain relief, and inflammation. Applications such as wound healing and reducing pain and inflammation are indicated. The document concludes by describing techniques for laser application and important parameters like wavelength, energy density, and dosage.UVR



UVRKeerthi Priya
╠²
Ultraviolet radiation can be used therapeutically to treat various skin conditions. It has both immediate physiological effects like erythema, tanning, and long term effects like aging and cancer. There are different types of UV generators that produce UVA, UVB or UVC. Dosage is carefully determined based on skin type and response. PUVA treatment uses oral photosensitizing drugs before UVA exposure to treat conditions like psoriasis. Precautions must be taken with UV therapy due to risks of overexposure like burns, aging and skin cancer.Movemet disorders



Movemet disordersKeerthi Priya
╠²
This document provides an overview of various movement disorders including dystonia, chorea, ballismus, athetosis, tics, myoclonus, and Wilson's disease. It discusses the epidemiology, classification, etiology, clinical features, pathophysiology, investigations and treatment of each disorder. The classifications are based on factors like age of onset, distribution of symptoms, underlying etiology. Primary and secondary dystonias are described. Common types of chorea like Huntington's chorea are outlined. The document provides detailed information on different types of these movement disorders for healthcare professionals.Infra red rays



Infra red raysKeerthi Priya
╠²
Keerthi Priya MPT Neuro is an assistant professor discussing infrared rays. Infrared rays have wavelengths between 750 nm to 1 mm. They are produced through molecular vibration and can be generated through non-luminous electric wires or luminous generators. Infrared rays are absorbed by the skin where they cause vasodilation, sweating, and increased metabolism. Their therapeutic effects include relief of pain, reduction of muscle spasm, and acceleration of healing. Proper technique of application and precautions against dangers like burns are important.Electro magnetic spectrum



Electro magnetic spectrumKeerthi Priya
╠²
The document discusses the electromagnetic spectrum. It defines key terms like wavelength and frequency. The electromagnetic spectrum includes all types of electromagnetic radiation organized based on their wavelength and frequency. Radiation is produced through the interaction of electric and magnetic fields and can be classified as luminous or nonluminous. Laws governing radiation include reflection, refraction, absorption, transmission, penetration, and scattering. Specific laws of radiation discussed are the Arndt-Schultz principle, the law of Grotthus-Draper, the cosine law, and the inverse square law. The document also briefly mentions uses of electromagnetic radiation but does not provide details.Parkinsons disease



Parkinsons diseaseKeerthi Priya
╠²
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that results from the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the basal ganglia. The four primary symptoms are tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability. It typically presents after age 50 and treatment involves dopamine replacement therapy with levodopa/carbidopa or dopamine agonists to manage the motor symptoms. Deep brain stimulation may also be used in advanced cases that do not respond well to medication.Recently uploaded (20)
Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoy



Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoyEconomic and Social Research Institute
╠²
NAPD Annual Symposium
ŌĆ£Equity in our Schools: Does the system deliver for all young people?ŌĆØThe Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .



The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .saanidhyapatel09
╠²
This PowerPoint presentation provides an insightful overview of the Constitution, covering its key principles, features, and significance. It explains the fundamental rights, duties, structure of government, and the importance of constitutional law in governance. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the foundation of a nationŌĆÖs legal framework.
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH



BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHcoacharyasetiyaki
╠²
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHChapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdf



Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdfRommel Regala
╠²
This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdf



NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdfDolisha Warbi
╠²
NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION, Introduction, definition, types - macronutrient and micronutrient, food pyramid, meal planning, nutritional assessment of individual, family and community by using appropriate method, nutrition education, nutritional rehabilitation, nutritional deficiency disorder, law/policies regarding nutrition in India, food hygiene, food fortification, food handling and storage, food preservation, food preparation, food purchase, food consumption, food borne diseases, food poisoningHow to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok Sonawala



Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok SonawalaAssociation for Project Management
╠²
APM event hosted by the South Wales and West of England Network (SWWE Network)
Speaker: Aalok Sonawala
The SWWE Regional Network were very pleased to welcome Aalok Sonawala, Head of PMO, National Programmes, Rider Levett Bucknall on 26 February, to BAWA for our first face to face event of 2025. Aalok is a member of APMŌĆÖs Thames Valley Regional Network and also speaks to members of APMŌĆÖs PMO Interest Network, which aims to facilitate collaboration and learning, offer unbiased advice and guidance.
Tonight, Aalok planned to discuss the importance of a PMO within project-based organisations, the different types of PMO and their key elements, PMO governance and centres of excellence.
PMOŌĆÖs within an organisation can be centralised, hub and spoke with a central PMO with satellite PMOs globally, or embedded within projects. The appropriate structure will be determined by the specific business needs of the organisation. The PMO sits above PM delivery and the supply chain delivery teams.
For further information about the event please click here.Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatDot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatManaging expiration dates of products in odoo



Managing expiration dates of products in odooCeline George
╠²
Odoo allows users to set expiration dates at both the product and batch levels, providing flexibility and accuracy. By using Odoo's expiration date management, companies can minimize waste, optimize stock rotation, and maintain high standards of product quality. The system allows users to set expiration dates at both the product and batch levels, providing flexibility and accuracy.Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptx



Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptxRomaSmart1
╠²
Computers have revolutionized various sectors, including education, by enhancing learning experiences and making information more accessible. This presentation, "Computer Hardware for Educational Computing," introduces the fundamental aspects of computers, including their definition, characteristics, classification, and significance in the educational domain. Understanding these concepts helps educators and students leverage technology for more effective learning.Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatHow to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.CT SCAN
- 1. CT SCAN KEERTHI PRIYA MPT NEURO, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR
- 2. CT SCAN
- 3. WHAT IS CT SCAN?
- 4. ADVANTAGES ’ā╝ Fast ’ā╝Easily accessible ’ā╝Cost efficient ’ā╝Non invasive & painless ’ā╝Accurate
- 6. ATTENUATION
- 7. ATTENUATION HIGH ATTENUATION ’ā╝ Hemorrhage ’ā╝Contrast ’ā╝Calcium ’ā╝Metal LOW ATTENUATION ’ā╝ Ischemia ’ā╝Infection ’ā╝ Neoplasam ’ā╝Edema
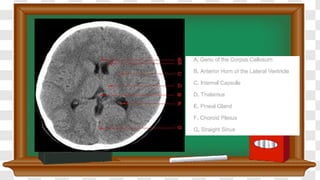
- 8. HOW TO READ ? ’ā╝Patient details ’ā╝Type of scan ’ā╝Purpose ’ā╝Cranial & extra cranial structures ’ā╝Ventricles, cistern & sulci ’ā╝Brain parenchyma
- 13. ISCHEMIA
- 14. HEMORRHAGE
- 15. TUMOUR
- 17. ANY QUERY ?






