Ctc assignment
- 2. Different classification of buildings ´ü▒ Agricultural buildings ´éº Barn ´éº Chicken coop or chickenhouse ´éº Cow-shed ´éº Farmhouse ´éº Granary , H├│rreo ´éº Greenhouse ´éº Hayloft ´éº Pigpen or sty ´éº Root cellar ´éº Shed ´éº Silo ´éº Stable ´éº Storm cellar ´éº Well house ´éº underground Pit ´ü▒ Commercial buildings ´éº Automobile repair shop ´éº CarWash ´éº Convention center ´éº Forum ´éº Gas station ´éº Hotel ´éº Market ´éº Market house ´éº Skyscraper ´éº Shop ´éº Shopping mall ´éº Supermarket ´éº Warehouse ´éº Restaurant
- 3. ´ü▒ Educational buildings ´éº Archive ´éº College o Classroom Building o Gymnasium o Students' union ´éº School ´éº Library ´éº Museum o Art gallery ´éº Theater (building) o Amphitheater o Concert hall o Cinema o Opera house ´éº Boarding Schools ´ü▒ Government buildings ´éº Capitol ´éº City hall ´éº Consulate ´éº Courthouse ´éº Embassy ´éº Fire station ´éº Meeting house ´éº Moot hall ´éº Palace ´éº Parliament ´éº Police station ´éº Post office ´éº Prison
- 4. ´ü▒ Residential buildings ´éº Apartment block ´éº Asylum ´éº Condominium ´éº Dormitory ´éº Duplex ´éº House ´éº Nursing home ´éº Townhouse ´éº Villa ´éº Bungalow ´ü▒ Industrial buildings ´éº Brewery ´éº Factory ´éº Foundry ´éº Power plant ´éº Mill o Watermill o Wind mill o Horse mill o Tide mill ´ü▒ Military buildings ´éº Arsenal ´éº Barracks ´éº Bunker o Blockhouse ´éº Castle ´éº Citadel ´éº Fortification ´éº
- 5. Classification of Building Based on Occupancy General Classification All buildings, whether existing or hereafter erected shall be classified according to the use or the character of occupancy in one of the following groups: Group A Residential Group B Educational Group C Institutional Group D Assembly Group E Business Group F Mercantile Group G Industrial Group H Storage Group J Hazardous
- 6. A) Residential Buildings These shall include any building in which sleeping accommodation is provided for normal residential purposes with or without cooking or dining or both facilities, except any building classified under Group C. Buildings and structures under Group A shall be further sub-divided as follows: Sub-division A-1 Lodging or rooming houses Sub-division A-2 One or two-family private dwellings Sub-division A-3 Dormitories Sub-division A-4 Apartment houses (flats) Sub-division A-5 Hotels Sub-division A-6 Hotels (Starred) a) Sub-division A-1 Lodging or rooming houses ÔÇö These shall include any building or group of buildings under the same management, in which separate sleeping accommodation for a total of not more than 40 persons (beds), on transient or permanent basis, with or without dining facilities but without cooking facilities for individuals is provided. This includes ims, clubs, motels and guest houses. A lodging or rooming house shall be classified as a dwelling in sub-division A-2 if no room in any of its private dwelling units is rented to more than three persons.
- 7. b) Sub-division A-2 One or two-family private dwellings ÔÇö These shall include any private dwelling which is occupied by members of one or two families and has a total sleeping accommodation for not more than 20 persons. If rooms in a private dwelling are rented to outsiders, these shall be for accommodating not more than three persons per room. If sleeping accommodation for more than 20 persons is provided in any one residential building, it shall be classified as a building in sub-division A-1, A-3 or A-4 as the case may be. c) Sub-division A-3 Dormitories ÔÇö These shall include any building in which group sleeping accommodation is provided, with or without dining facilities for persons who are not members of the same family, in one room or a series of closely associated rooms under joint occupancy and single management, for example, school and college dormitories, students, and other hostels and military barracks.
- 8. c) Sub-division A-4 Apartment houses (flats) ÔÇö These shall include any building or structure in which living quarters are provided for three or more families, living independently of each other and with independent cooking facilities, for example, apartment houses, mansions and chawls. e) Sub-division A-5 Hotels ÔÇö These shall include any building or group of buildings under single management, in which sleeping accommodation is provided, with or without dining facilities for hotels classified up to4 Star Category. f) Sub-division A-6 Hotels (starred) ÔÇöThese shall include the hotels duly approved by the concerned authorities as Five Star and above Hotels.
- 9. B) Educational Buildings These shall include any building used for school, college, other training institutions for day-care purposes involving assembly for instruction, education or recreation for not less than 20 students. Buildings and structures under Group B shall be further sub-divided as follows: Sub-division B-1 Schools up to senior secondary level Sub-division B-2 All others/training institutions a) Sub-division B-1 Schools up to senior secondary level ÔÇö This sub- division shall include any building or a group of buildings under single management which is used for students not less than 20 in number. b) Sub-division B-2 All others/training institutions ÔÇö This sub-division shall include any building or a group of buildings under single management which is used for students not less than 100 in number. In the case of temporary buildings/structures which are utilized for educational purposes, the provisions of 3.2.5.3 shall apply. If residential accommodation is provided in the schools/institutions, that portion of occupancy shall be classified as a building in sub-division A-3.
- 10. C) Institutional Buildings These shall include any building or part thereof, which is used for purposes, such as medical or other treatment or care of persons suffering from physical or mental illness, disease or infirmity; care of infants, convalescents or aged persons and for penal or correctional detention in which the liberty of the inmates is restricted. Institutional buildings ordinarily provide sleeping accommodation for the occupants. Buildings and structures under Group C shall be further sub-divided as follows: Sub-division C-1 Hospitals and sanatoria Sub-division C-2 Custodial institutions Sub-division C-3 Penal and mental institutions a) Sub-division C-1 Hospitals and sanatoria ÔÇöThis sub-division shall include any building or a group of buildings under single management, which is used for housing persons suffering from physical limitations because of health or age, for example, hospitals, infirmaries, sanatoria and nursing homes.
- 11. b) Sub-division C-2 Custodial institutions ÔÇöThis sub-division shall include any building or a group of buildings under single management, which is used for the custody and care of persons, such as children, convalescents and the aged, for example, homes for the aged and infirm, convalescent homes and orphanages. c) Sub-division C-3 Penal and mental institutionsÔÇö This sub-division shall include any building or a group of buildings under single management, which !s used for housing persons under restraint, or who are detained for penal or corrective purposes, in which the liberty of the inmates is restricted, for example, jails, prisons, mental hospitals, mental sanatoria and reformatories.
- 12. D) Assembly Buildings These shall include any building or part of a building, where number of persons not less than 50 congregate or gather for amusement, recreation, social, religious, patriotic, civil, travel and similar purposes, for example, theatres, motion picture houses, assembly halls, auditoria, exhibition halls, museums, skating rinks, gymnasiums, restaurants, places of worship, dance halls, club rooms, passenger stations and terminals of air, surface and marine public transportation services, recreation piers and stadia, etc. Buildings under Group D shall be further sub-divided as follows: Sub-division D-1 Buildings having a theatrical or motion picture or any other stage and fixed seats for over 1000 persons Sub-division D-2 Buildings having a theatrical or motion picture or any other stage and fixed seats upto 1 000 persons Sub-division D-3 Buildings without a permanent stage having accommodation for 300 or more persons but no permanent seating arrangement. Sub-division D-4 Buildings without a permanent stage having accommodation for less than 300 persons with no permanent seating arrangement.
- 13. Sub-division D-5 All &her structures including temprory structures designed for assembly of people not covered by sub-divisions D-1 to D-4, at ground level. Sub-division D-6 Buildings having mixed occupancies providing facilities such as shopping, cinema theatres, and restaurants. Sub-division D-7 All other structures, elevated or underground, for assembly of people not covered by sub-divisions D-1 to D-6. a) Sub-division D-1 ÔÇö This sub-division shalllude any building primarily meant for theatrical or operatic performances and exhibitions and which has a raised stage, proscenium curtain, freed or portable scenery or scenery loft, lights, motion picture houses, mechanical appliances or other theatrical accessories and equipment and which is provided with fixed seats for over 1000 persons. b) Sub-division D-2 ÔÇö This sub-division shall include any building primarily meant for use as described for sub-division D-1, but with fixed seats up to 1000 persons. c) Sub-division D-3 ÔÇö This sub-division shall include any building, its lobbies, rooms and other spaces connected thereto, primarily intended for assembly of people, but which has no theatrical stage or permanent theatrical And for cinematographic accessories and has accommodation for 300 persons or more, for example, dance halls, night clubs, halls for
- 14. incidental picture shows, dramatic, theatrical or educational presentation, lectures or other similar purposes having no theatrical stage except a raised platform and used without permanent seating arrangement art galleries exhibition halls, community halls, marriage halls, places of worship, museums, lecture halls, passenger terminals and Heritage and Archeological Monuments. d) Sub-division D-4 ÔÇö This sub-division shall include any buiIding primarily intended for use as described in sub-division D-3, but with accommodation for less than 300 persons with no permanent seating arrangements. e) Sub-division D-5 ÔÇö This sub-division shall include any building or structure permanent or temporary meant for assembly of people not covered by sub-divisions D-1 to D-4, for example, grandstands, stadia, amusement park structures, reviewing stands and circus tents. f) Sub-division D-6 ÔÇö This sub-division shall include any building for assembly of people provided with multiple services/facilities like shopping, cinema theatres and restaurants, for example, multiplexes. e) Sub-division D-7 ÔÇö This sub-division shall include any building or structure permanent or temporary meant for assembly of people not covered by D-1 to D-6, for example, underground or elevated railways.
- 15. E) Business Buildings These shall include any building or part of a building which is used for transaction of business (other than that covered by Group F and part of buikhngs covered by , for keeping of accounts and records and similar purposes, professional establishments, service facilities, etc. City halls, town halls, court houses and libraries shall be classified in this group so far as the principal function of these is transaction of public business and keeping of books and records. Business buildings shall be further sub-divided as follows: Sub-division E-1 Offices, banks, professional establishments, like offices of architects, engineers, doctors, lawyers and police stations. Sub-division E-2 Laboratories, research establishments, libraries and test houses. Sub-division E-3 Computer installations. Sub-division E-4 Telephone exchanges. Sub-division E-5 Broadcasting stations and T.V. stations.
- 16. F) Mercantile Buildings These shall include any building or part of a building, which is used as shops, stores, market, for display and sale of merchandise, either wholesale or retail. Mercantile buildings shall be further sub-divided as follows: Sub-division F-1 : Shops, stores, departmental stores markets with area up to 500 mz. Sub-division F-2 : Shops, stores, departmental stores markets with area more than 500 mz . Sub-division F-3 : Underground shopping centres. Storage and service facilities incidental to the sale of merchandise and located in the same building shall be included under this group.
- 17. G Industrial Buildings These shall include any building or part of a building or structure, in which products or materials of all kinds and properties are fabricated, assembled, manufactured or processed, for example, assembly plants, industrial laboratories, dry cleaning plants, power plants, generating units, pumping stations, fumigation chambers, laundries, buildings or structures in gas plants, refineries, dairies a,d saw-mills, etc. Buildings under Group G shall be further sub-divided as follows: Sub-division G-1 Buildings used for low hazard industries. Sub-division G-2 Buildings used for moderate hazard industries. Sub-division G-3 Buildings used for high hazard industries. The hazard of occupancy, for the purpose of the Code, shall be the relative danger of the start and spread of
- 18. Floor Area Ratio
- 20. What is meant by carpet area, built-up area and super built-up area? ´â╝ Carpet area is the area enclosed within the walls, actual area to lay the carpet. This area does not include the thickness of the inner walls ´â╝ Built-up area is the carpet area plus the thickness of outer walls and the balcony. ´â╝ Super built-up area ÔÇÿSaleableÔÇÖ Area is the built up area plus proportionate area of common areas such as the lobby, lifts shaft, stairs, etc. The plinth area along with a share of all common areas proportionately divided amongst all unit owners makes up the super built-up area. ´â╝ Plinth Area = Carpet Area + Wall thickness
- 21. ´â╝ Canopy ÔÇö A projection over any entrance. ´â╝ Terrace ÔÇö Open area without roof, attached to the main unit that buyer gets exclusive rights to use and resell (with the main unit). Open areas with slab at least double the height of the floor are also considered terrace area. FSI is not applicable to terrace areas. ´â╝ Plinth ÔÇö The portion of a structure between the surface of the surrounding ground and surface of the floor, immediately above the ground. ´â╝ Plinth Area ÔÇö The built up covered area measured at the floor level of the basement or of any storey. ´â╝ Building Line ÔÇö The line upto which the plinth of a building adjoining a street or an extension of a street or on a future street may lawfully extend. It includes the lines prescribed, if any, in any scheme. The building line may change from time-to-time as decided by the Authority.
- 22. ´â╝ Habitable room ÔÇó Floor area of habitable room shall be less than 9.5 sq.m having the min. width of 2.4 m. ÔÇó In case of building having two room , one of this shall not be less than 9.5sq.m. and other not less than 7.5 sq.m. ÔÇó Height of habitable room shall be 2.75m(measured from floor to lowest point of ceiling. ÔÇó In case of air conditioned room a height of not less than 2.4 m. ÔÇó The min. head room under beam shall be 2.4m. ´â╝ Pressurization ÔÇö The establishment of a pressure difference across a barrier to protect a stairway, lobby, escape route or room of a building from smoke penetration. ´â╝ Pressurization Level ÔÇö The pressure difference between the pressurized space and the area served by the pressurized escape route, expressed in Pascal's (Pa).
- 23. ´â╝ Floor Space Index - This is ratio of land to carpet area. Generally it is 1 for residential plots (much less for agricultural land) For example, if FSI is 1, and land area is 3000 sq ft, then total carpet area on that land cannot exceed 3000 x 1 = 3000 sq ft. It should be noted that FSI is not applicable to terraces, balconies. Also, this definition is provided for your information, enforcement of FSI is taken care of by local authorities, and buyer should not worry about it (unless there are allegations against the builder of misusing FSI).
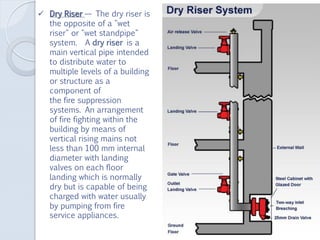
- 24. ´â╝ Dry Riser ÔÇö The dry riser is the opposite of a "wet riser" or "wet standpipe" system. A dry riser is a main vertical pipe intended to distribute water to multiple levels of a building or structure as a component of the fire suppression systems. An arrangement of fire fighting within the building by means of vertical rising mains not less than 100 mm internal diameter with landing valves on each floor landing which is normally dry but is capable of being charged with water usually by pumping from fire service appliances.
- 25. ´â╝ Wet Riser ÔÇö An arrangement for fire fighting within the building by means of vertical rising mains not less than 100 mm nominal diameter with landing valves on each floor landing for fire fighting purposes and permanently charged with water from a pressurized supply. ´â╝ Down-comer ÔÇö An arrangement of fire fighting within the building by means of down-comer pipe connected to terrace tank through terrace pump, gate valve and non-return valve and having mains not less than 100 mm internal diameter with landing valves on each floor/landing. It is also fitted with inlet connections at ground level for charging with water by pumping from fire service appliances and air release valve at roof level to release trapped air inside. ´â╝ Fire Separation ÔÇö The distance in metres measured from the external wall of the building concerned to the external wall of any other building on the site, or from other site, or from the opposite side of street or other public space for the purpose of preventing the spread of fire.
- 26. THANKYOU !