Cube rollup slides
- 1. Cube, Rollup and Materialized Views: Mining Oracle Gold John King King Training Resources 6341 South Williams Street Littleton, CO 80121-2627 USA www.kingtraining.com 800.252.0652 or 303.798.5727 Copyright @ 2000, John Jay King, All rights reserved
- 2. Objectives Become aware of Oracle8i Release 2 (8.1.6) Analytic Functions at a high level Learn about the Cube and Rollup enhancements to GROUP BY Be aware of Materialized Views and how they may be used to engineer more-useful and faster systems Know how to use the Cube, Rollup, and Materialized views to enhance systems
- 3. Oracle 8.1.6 Aggregates x AVG x REGR_R2 x CORR x REGR_SLOPE x COUNT x REGR_SXX x COVAR_POP x REGR_SYY x REGR_SXY x COVAR_SAMP x STDDEV x GROUPING x STDDEV_POP x MAX x STDDEV_SAMP x MIN x SUM x REGR_AVGX x VAR_POP x REGR_AVGY x REGR_COUNT x VAR_SAMP x REGR_INTERCEPT x VARIANCE
- 4. Oracle8i Version 2 (8.1.6) Analytic Functions x Oracle 8.1.6 includes a new set of functions designed to provide expanded support for data mining operations - (this topic is too rich to fully cover in the context of this paper) x The analytic functions are divided into four "families" x Lag/Lead Compares values of rows to other rows in same table: LAG, LEAD x Ranking Supports "top n" queries: CUME_DIST, DENSE_RANK, NTILE, PERCENT_RANK, RANK, ROW_NUMBER x Reporting Aggregate Compares aggregates to non-aggregates (pct of total): RATIO_TO_REPORT x Window Aggregate Moving average type queries: FIRST_VALUE, LAST_VALUE x The analytic functions allow users to divide query result sets into ordered groups of rows called partitions (not the same as database partitions)
- 5. Oracle8i Version 2 (8.1.6) Analytic Function Clauses x Along with the new functions came new clauses (again, too rich to cover completely here): analytic_function ( ) OVER (analytic clause) – Analytic clause Query_partition_clause-Order_by clause-Windowing clause – Query partition clause PARTITION BY list,of,cols – Windowing clause RANGE … or ROWS ... – Order by clause ORDER BY col,list
- 6. Analytic Function: RANK (8.1.6) x RANK provides rankings of values with gaps where sets of rows have equal values (DENSE_RANK removes gaps) SQL> run 1 select deptno,ename,sal, RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY DEPTNO ORDER BY SAL DESC) salrank 2 from emp where deptno in (10,30) DEPTNO ENAME SAL SALRANK ----------- ----------------- ---------- -------------- 10 KING 5000 1 10 CLARK 2450 2 10 MILLER 1300 3 30 BLAKE 2850 1 30 ALLEN 1600 2 30 TURNER 1500 3 30 MARTIN 1250 4 30 WARD 1250 4 30 JAMES 950 6
- 7. Old Aggregate, New Usage (8.1.6) x Analytic function clauses may be used with many existing aggregates SQL> run 1 select deptno, ename, sal, 2 ,round(avg(sal) OVER (PARTITION BY deptno) , 0) avg_sal 3 from emp 4* where deptno in (10,20) DEPTNO ENAME SAL AVG_SAL ----------- ---------------- ---------- ---------- 10 KING 5000 2917 10 CLARK 2450 2917 10 MILLER 1300 2917 20 JONES 2975 2175 20 FORD 3000 2175 20 SMITH 800 2175 20 SCOTT 3000 2175 20 ADAMS 1100 2175
- 8. ROW_NUMBER (8.1.6) x ROW_NUMBER allows ranking by criteria SQL> run 1 select deptno, ename, sal, 2 ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY deptno ORDER BY by sal desc) 3 sal_rank 4 from emp 5* where deptno in (10,20) DEPTNO ENAME SAL SAL_RANK ----------- ----------------- ---------- --------------- 10 KING 5000 1 10 CLARK 2450 2 10 MILLER 1300 3 20 FORD 3000 1 20 SCOTT 3000 2 20 JONES 2975 3 20 ADAMS 1100 4 20 SMITH 800 5
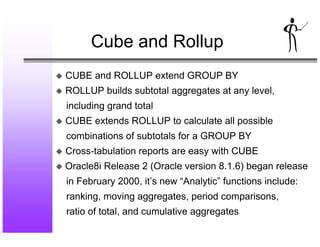
- 9. Cube and Rollup K CUBE and ROLLUP extend GROUP BY K ROLLUP builds subtotal aggregates at any level, including grand total K CUBE extends ROLLUP to calculate all possible combinations of subtotals for a GROUP BY K Cross-tabulation reports are easy with CUBE K Oracle8i Release 2 (Oracle version 8.1.6) began release in February 2000, it’s new “Analytic” functions include: ranking, moving aggregates, period comparisons, ratio of total, and cumulative aggregates
- 10. Normal GROUP BY Functionality x Normally, GROUP BY allows aggregates (sub-totals) by specific column or set of columns x Before Oracle8i SQL required JOIN or UNION to combine subtotal information and grand totals in a single SQL query x ROLLUP creates subtotals and grand totals in the same query along with intermediate subtotals x CUBE adds cross-tabulation information based upon the GROUP BY columns
- 11. GROUP BY (without CUBE or ROLLUP) x Normally GROUP BY sorts on GROUP BY columns, then calculates aggregates SQL> select deptno Department 2 ,job 3 ,sum(sal) "Total SAL" 4 from emp 5 group by deptno,job 6 / DEPARTMENT JOB Total SAL ---------- --------- --------- 10 CLERK 1300 10 MANAGER 2450 10 PRESIDENT 5000 20 ANALYST 6000 20 CLERK 1900 20 MANAGER 2975 30 CLERK 950 30 MANAGER 2850 30 SALESMAN 5600
- 12. GROUP BY ROLLUP K ROLLUP provides aggregates at each GROUP BY level SQL> col Department format a20 SQL> break on Department SQL> select nvl(to_char(deptno),'Whole Company') Department 2 ,nvl(job,'All Employees') job 3 ,sum(sal) "Total SAL" 4 from emp 5 group by rollup (deptno,job) 6 / DEPARTMENT JOB Total SAL -------------------- ------------- --------- 10 CLERK 1300 MANAGER 2450 PRESIDENT 5000 All Employees 8750 20 ANALYST 6000 CLERK 1900 MANAGER 2975 All Employees 10875 30 CLERK 950 MANAGER 2850 SALESMAN 5600 All Employees 9400 Whole Company All Employees 29025
- 13. NULL Values in CUBE/ROLLUP Rows x Subtotal and grand total lines generated by ROLLUP substitute NULL for column values not present in the manufactured output row x The example uses the NVL function to replace NULLS x Some columns might normally contain NULL values, thus, normally occurring NULLS would be grouped with rows manufactured by ROLLUP or CUBE
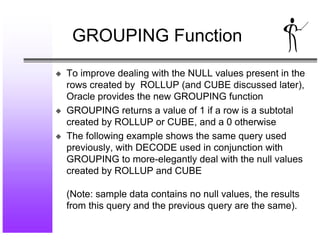
- 14. GROUPING Function x To improve dealing with the NULL values present in the rows created by ROLLUP (and CUBE discussed later), Oracle provides the new GROUPING function x GROUPING returns a value of 1 if a row is a subtotal created by ROLLUP or CUBE, and a 0 otherwise x The following example shows the same query used previously, with DECODE used in conjunction with GROUPING to more-elegantly deal with the null values created by ROLLUP and CUBE (Note: sample data contains no null values, the results from this query and the previous query are the same).
- 15. GROUPING Example SQL> col Department format a20 SQL> break on Department SQL> select decode(grouping(deptno),1,'Whole Company' 2 ,'Department ' || to_char(deptno)) Department 3 ,decode(grouping(job),1,'All Employees',job) job 4 ,sum(sal) "Total SAL" 5 from emp 6 GROUP BY ROLLUP (deptno,job) / DEPARTMENT JOB Total SAL -------------------- ------------- --------- Department 10 CLERK 1300 MANAGER 2450 PRESIDENT 5000 All Employees 8750 Department 20 ANALYST 6000 CLERK 1900 MANAGER 2975 All Employees 10875 Department 30 CLERK 950 MANAGER 2850 SALESMAN 5600 All Employees 9400 Whole Company All Employees 29025
- 16. GROUP BY CUBE x CUBE automatically calculates all possible combinations of subtotals SQL> select decode(grouping(deptno),1,'Whole Company','Department ' || to_char(deptno)) Department 2 ,decode(grouping(job),1,'All Employees',job) job 3 ,sum(sal) "Total SAL" 4 from emp GROUP BY CUBE(deptno,job) DEPARTMENT JOB Total SAL -------------------- ------------- --------- Department 10 CLERK 1300 MANAGER 2450 PRESIDENT 5000 All Employees 8750 Department 20 ANALYST 6000 CLERK 1900 MANAGER 2975 All Employees 10875 Department 30 CLERK 950 MANAGER 2850 All Employees 9400 Whole Company ANALYST 6000 CLERK 4150 MANAGER 8275 PRESIDENT 5000 SALESMAN 5600 All Employees 29025
- 17. GROUP BY/ROLLUP/CUBE x CUBE add subtotals for all combinations of categories (total salary for each job type was added in the example) x If there were three GROUP BY columns (i.e. country, customer_id, product): – GROUP BY would produce aggregates each unique combination of the three columns showing the aggregate for each product ordered by each customer within each country – ROLLUP would add aggregates showing the total products by country and customer_id, total products by country, and a grand total of all products sold – CUBE would add aggregates for each product regardless of country or customer id, aggregates for each customer_id regardless of country or products ordered, and aggregates of each product by country regardless of customer id
- 18. Materialized Views x Oracle's SNAPSHOT is a query result table created periodically to facilitate distribution or replication of data x Materialized Views in Oracle8i use similar technology to allow a view's results to be stored as materialized in the database for use by subsequent SQL statements x View materializations are refreshed periodically based upon time criteria (defined at creation) or upon demand x View data is "old" until the view is refreshed x Indexes may be defined for Materialized Views x Materialized views can improve performance of frequent requests for aggregate data or complex data
- 19. CUBE/ROLLUP & Analytic Functions (8.1.6) x Combine Analytic Functions and Clauses with CUBE and ROLLUP SQL> run 1 select decode(grouping(deptno),1,'Whole Company’ 2 ,'Department ' || to_char(deptno)) Department 3 ,decode(grouping(job),1,'All Employees',job) job 4 ,sum(sal) "Total SAL” 5 ,ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY deptno ORDER BY sum(sal)) rownbr 6* from emp where deptno in (10,20) group by rollup (deptno,job) DEPARTMENT JOB Total SAL ROWNBR -------------------- ------------- ---------- ------------ Department 10 CLERK 1300 1 MANAGER 2450 2 PRESIDENT 5000 3 All Employees 8750 4 Department 20 CLERK 1900 1 MANAGER 2975 2 ANALYST 6000 3 All Employees 10875 4 Whole Company All Employees 19625 1
- 20. CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW create materialized view dept_summary refresh start with sysdate next sysdate + 1 as select dept.deptno ,dname ,count(*) nbr_emps ,sum(nvl(sal,0)) tot_sal from scott.emp emp ,scott.dept dept where emp.deptno(+) = dept.deptno group by dept.deptno,dname;
- 21. Creation Caveats • ORACLE recommends names not exceed 19 characters, so that generated names are 30 characters or less • STORAGE, TABLESPACE, LOB, CACHE, LOGGING, CLUSTER, and partitioning are similar to CREATE TABLE • BUILD IMMEDIATE is default, can do BUILD DEFERRED • ON PREBUILT TABLE allows use of existing tables; the Materialized View name and the Table name must match • REFRESH controls reloading rate, START WITH specifies the first refresh, NEXT specifies subsequent refreshes (see the Oracle8i Replication manual for specifics) • AS describes the query for the materialized view, just about any query may be used with a few restrictions • Oracle8i Release 2 allows query to contain ORDER BY
- 22. Using Pre-built Tables x Basing a materialized view upon an existing table (ON PREBUILT TABLE) allows the use of existing tables and indexes x Using ON PREBUILT TABLE requires that the underlying table and the materialized view share the same name and schema x WITH REDUCED PRECISION allows a refresh to work properly even if some columns generate different precision than originally defined
- 23. Pre-Built Table: Example Table create table dept_summary_tab as select dept.deptno ,dname ,count(*) nbr_emps ,sum(nvl(sal,0)) tot_sal from scott.emp emp ,scott.dept dept where emp.deptno(+) = dept.deptno group by dept.deptno,dname;
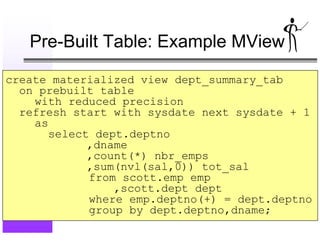
- 24. Pre-Built Table: Example MView create materialized view dept_summary_tab on prebuilt table with reduced precision refresh start with sysdate next sysdate + 1 as select dept.deptno ,dname ,count(*) nbr_emps ,sum(nvl(sal,0)) tot_sal from scott.emp emp ,scott.dept dept where emp.deptno(+) = dept.deptno group by dept.deptno,dname;
- 25. MView Refresh via PL/SQL x An Oracle-provided PL/SQL packaged procedure DBMS_MVIEW.REFRESH may be used to refresh upon demand x Careful! This procedure COMMITs changes in the active transaction begin dbms_mview.refresh('dept summary tab'); end; /
- 26. Conclusion x CUBE and ROLLUP reduce work necessary to code and create aggregates often requested by management to provide competitive or summary information x CUBE and ROLLUP provide mechanisms for using a single SQL statement to provide data that would have required multiple SQL statements, programming, or manual summarization in the past x Materialized Views reduce the impact of frequently executed queries by storing results and refreshing them on a periodic basis x These tools may be used to “mine” Oracle databases for the “golden” information frequently in demand today
- 27. To contact the author: John King King Training Resources 6341 South Williams Street Littleton, CO 80121-2627 USA 1.800.252.0652 - 1.303.798.5727 Email: john@kingtraining.com