Customer Journey Mapping - An Introduction
- 2. Why User/ Customer Experience Journeys? The Journey Mapping Framework Key Decisions and How to¡¯s? Our Journey Today¡
- 3. 1) Based on key Assumptions that there is no alternative to the Product/ Service being used 2) There are no distractions to usage 3) User is on-boarded successfully in a single attempt Realistic 1) Experience Journeys should emulate user¡¯s/ customer¡¯s real-life behavioral patterns 2) They should consider the scenarios, Encounters in the real-life of the user/ customer 3) Frame-work should Learn, adapt & evolve based on real-world validation and domain best-practices Realistic Conventional Task Flows/ User Flows Experience Journeys Understanding Experience Journeys
- 4. Six Components of Human Beings
- 5. Customer Thoughts/ Emotional Response Journey Phases Journey Steps Estimated Impact (KPIs) Customer Expectations Root Cause of Pain Experience Opportunities Persona Scenario The Journey Mapping Framework Channels & Touch-points
- 6. Customer Thoughts/ Emotional Response Journey Phases Journey Steps Estimated Impact (KPIs) Customer Expectations Root Cause of Pain Experience Opportunities Persona Scenario The Journey Mapping Framework Channels & Touch-points
- 8. Product Push (First time Use) Back to default Lured to come back Adoption Journey Phases Create a ¡®Hook¡¯ Back to default (With Interest Generated) Fresh Stimulus to Pull back Pull back for the ¡®Hook¡¯ Create a habit based on the ¡®Hook¡¯ Replace to be the new Default
- 10. Customer Thoughts/ Emotional Response Journey Phases Journey Steps Estimated Impact (KPIs) Customer Expectations Root Cause of Pain Experience Opportunities Persona Scenario The Journey Mapping Framework Channels & Touch-points
- 11. Discovery phase Step 1 (Identify Initial Consideration set of brands) Step 2 (Identify available Touch-points to research upon) Step 3 (Identify available Touch-points to research upon) Step 4 (Research Offerings/ Value Props of Brand 1) Step 5 (Research Offerings/ Value Props of competing Brand 2 Transaction phase Step 1 (Identify Value to Receive) Step 2 (Modify the Value to suit personal need) Step 3 (Aggregate Value all-together) Step 4 (Receive Value) Step-wise break-down of each Journey Phase
- 12. Customer Thoughts/ Emotional Response Journey Phases Journey Steps Estimated Impact (KPIs) Customer Expectations Root Cause of Pain Experience Opportunities Persona Scenario The Journey Mapping Framework Channels & Touch-points
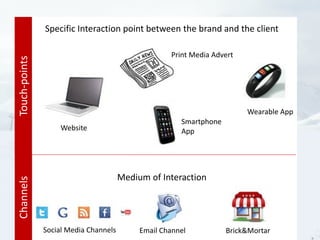
- 13. Touch-pointsChannels Specific Interaction point between the brand and the client Medium of Interaction Website Smartphone App Wearable App Print Media Advert Social Media Channels Email Channel Brick&Mortar
- 14. Customer Thoughts/ Emotional Response Journey Phases Journey Steps Estimated Impact (KPIs) Customer Expectations Root Cause of Pain Experience Opportunities Persona Scenario The Journey Mapping Framework Channels & Touch-points
- 15. Example - ¡°Buying a TV¡± Emotion Graph Empathy Map
- 17. Customer Thoughts/ Emotional Response Journey Phases Journey Steps Estimated Impact (KPIs) Customer Expectations Root Cause of Pain Experience Opportunities Persona Scenario The Journey Mapping Framework Channels & Touch-points
- 18. Frustrations Emotional Discomfort Un-met Needs Irritation Hassle Pains = Friction Points in the Journey
- 19. Customer Thoughts/ Emotional Response Journey Phases Journey Steps Estimated Impact (KPIs) Customer Expectations Root Cause of Pain Experience Opportunities Persona Scenario The Journey Mapping Framework Channels & Touch-points
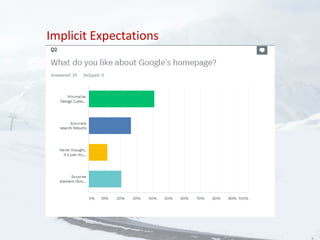
- 20. Explicit Expectations Implicit Expectations Static-performance Expectation Dynamic-performance Expectation Inter-personal Expectations
- 23. Customer Thoughts/ Emotional Response Journey Phases Journey Steps Estimated Impact (KPIs) Customer Expectations Root Cause of Pain Experience Opportunities Persona Scenario The Journey Mapping Framework Channels & Touch-points
- 24. Peak-end Rule PIG (Pain-is-good) Strategy
- 26. Customer Thoughts/ Emotional Response Journey Phases Journey Steps Estimated Impact (UX KPIs) Customer Expectations Root Cause of Pain Experience Opportunities Persona Scenario The Journey Mapping Framework Channels & Touch-points
- 27. Quantitative UX KPIs Interaction flow success rate Time to complete a sub-journey Use of Search vs. Navigation User error rate Qualitative UX KPIs Reported expectations and performance Overall satisfaction
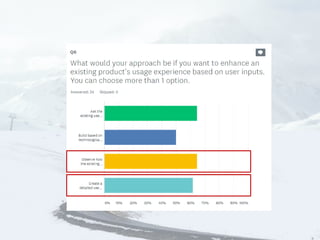
- 28. What kind of journey do you want to map? Current (as-is) vs. Future (to-be) Hypothesis vs. Research Low-fidelity vs. High-fidelity Before beginning any mapping effort 3 decisions must be made
- 29. What we have worked upon so far¡ Current (as-is) + Future (to-be) Hypothesis Low-fidelity
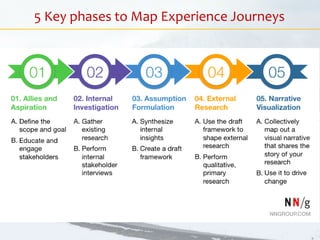
- 30. 5 Key phases to Map Experience Journeys