Cyber forensics and investigations
- 1. Jay Mehta
- 4. Forensics Investigator ? ŌĆó Identifying the crime scene ŌĆó Protecting the crime scene ŌĆó Preserving temporary and fragile evidence ŌĆó Collecting complete information about the incident ŌĆó Documenting all findings ŌĆó Packaging and transporting the electronic evidence ŌĆó Gather preliminary information at the scene
- 5. Why Cyber Forensics ?
- 7. Digital Evidence ? ŌĆó Latent/Hidden ŌĆó Crosses jurisdictional borders quickly and easily ŌĆó Can be altered, damaged, or destroyed easily ŌĆó Can be time sensitive
- 8. Chain of Custody ? ŌĆó A list of all devices that were secured from the crime scene for further Investigation ŌĆó Accurate information about the devices that has been copied, transferred, and collected ŌĆó Timestamp of all the collected evidence ŌĆó Who processed the item? ŌĆó Who is the owner of the item? ŌĆó Where was it taken or seized from? ŌĆó All electronic evidence that was collected from the crime scene must be properly documented each time that evidence is viewed ŌĆó Such documentation must be made available, if requested by the client, throughout the pre-trial discovery phase.
- 9. Forensic Investigation Challenges ŌĆó Inadequate chain of custody ŌĆó Not maintaining legal procedures ŌĆó Inadequate evidential integrity ŌĆó Inadequate evidence gathering and maintaining accuracy, authenticity, completeness
- 10. Who uses Cyber Forensics ? ŌĆó Criminal Prosecutors ŌĆó Civil Litigations ŌĆó Insurance Companies ŌĆó Private Corporations ŌĆó Law Enforcement Officials ŌĆó Individual/Private Citizens
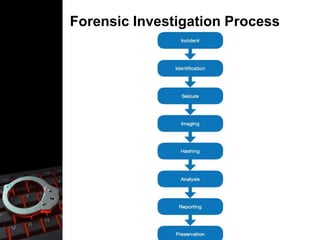
- 11. Evidence Processing Guidelines ŌĆó Step 1: Shut down the computer ŌĆó Step 2: Document the Hardware Configuration of The System ŌĆó Step 3: Transport the Computer System to A Secure Location ŌĆó Step 4: Make Bit Stream Backups of Hard Disks and Floppy Disks ŌĆó Step 5: Mathematically Authenticate Data on All Storage Devices ŌĆó Step 6: Document the System Date and Time ŌĆó Step 7: Make a List of Key Search Words ŌĆó Step 8: Evaluate Unallocated Space (Erased Files) ŌĆó Step 9: Document File Names, Dates and Times ŌĆó Step 10: Identify File, Program and Storage Anomalies ŌĆó Step 11: Evaluate Program Functionality ŌĆó Step 12: Document Your Findings ŌĆó Step 13: Retain Copies of Software Used
- 12. Types of Cyber Forensics ŌĆó Database forensics ŌĆó Email forensics ŌĆó Malware forensics ŌĆó Memory forensics ŌĆó Mobile forensics ŌĆó Network forensics