Cyclovertical deviation
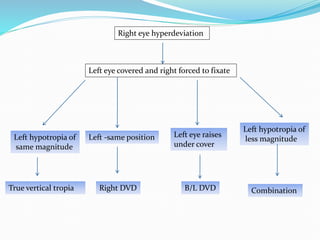
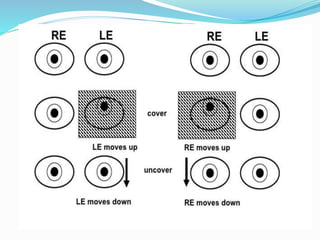
- 2. Right eye hyperdeviation Left eye covered and right forced to fixate Left hypotropia of same magnitude True vertical tropia Left -same position Right DVD Left eye raises under cover B/L DVD Left hypotropia of less magnitude Combination
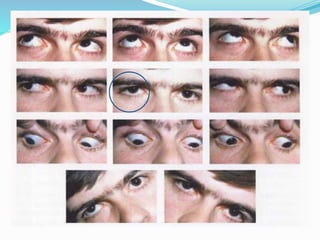
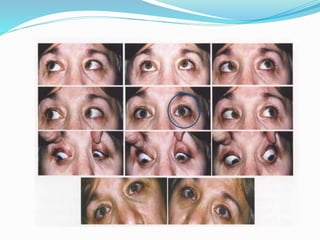
- 3. Principles in cyclovertical deviations ? Incomitant hyperdeviation in horizontal plane -Oblique muscle ? Comitant hyperdeviation in horizontal plane - Vertical rectus ? Most common causes of a true vertical tropia - fourth nerve palsy. ? If the deviation is incomitant in the horizontal plane or is long- standing and comitant, perform a head-tilt test . ? In a case of superior oblique palsy, the clinician must assume the palsy is bilateral until it is proven otherwise
- 4. Park 3 step test ? Primary position ®C which eye ? ? Gaze ? ? Head tilt ? Sensitivity -70%(1) Sensitivity of the three-step test in diagnosis of superior oblique palsy Ajay M. Manchandia et al J AAPOS. 2014 December ; 18(6): 567®C571. doi:10.1016/j.jaapos.2014.08.007.
- 7. Classification ? Dissociated vertical deviation ? Incomitant vertical deviation 1. IO overaction 2. SO overaction 3. SO underaction 4. IO underaction ? Comitant vertical deviation
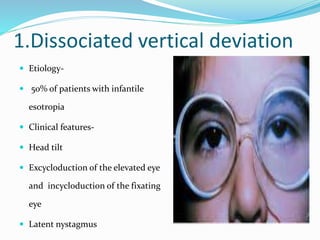
- 8. 1.Dissociated vertical deviation ? Etiology- ? 50% of patients with infantile esotropia ? Clinical features- ? Head tilt ? Excycloduction of the elevated eye and incycloduction of the fixating eye ? Latent nystagmus
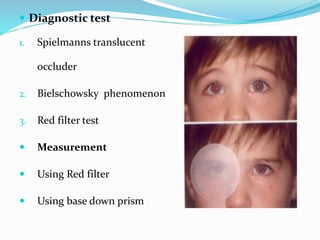
- 10. ? Diagnostic test 1. Spielmanns translucent occluder 2. Bielschowsky phenomenon 3. Red filter test ? Measurement ? Using Red filter ? Using base down prism
- 11. ?Treatment Medical 1. Refractive error 2. Occlusion 3. Prisms Surgical 1. When ? 2. What ?
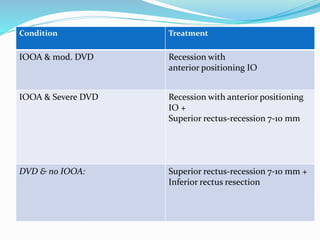
- 12. Condition Treatment IOOA & mod. DVD Recession with anterior positioning IO IOOA & Severe DVD Recession with anterior positioning IO + Superior rectus-recession 7-10 mm DVD & no IOOA: Superior rectus-recession 7-10 mm + Inferior rectus resection
- 13. Inferior Oblique Muscle Over action ? Etiology 1. Primary 2. Secondary ? Clinical Features ? Management ? Weakening procedure on the inferior oblique muscle
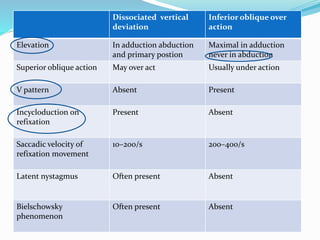
- 14. Dissociated vertical deviation Inferior oblique over action Elevation In adduction abduction and primary postion Maximal in adduction never in abduction Superior oblique action May over act Usually under action V pattern Absent Present Incycloduction on refixation Present Absent Saccadic velocity of refixation movement 10®C200/s 200®C400/s Latent nystagmus Often present Absent Bielschowsky phenomenon Often present Absent
- 15. Superior Oblique Muscle Over action ? Clinical Features 1. Overdepression in adduction. 2. Associated with exo ? Management ? Superior oblique tendon weakening procedure
- 16. 4.Superior Oblique Muscle Paralysis ? Most common Single cyclovertical muscle paralysis. ? Etiology ? Congenital vs acquired ? Head trauma ? Vascular problems of the central nervous system, ? Diabetes mellitus, or a brain tumor
- 17. Clinical features ? Head tilt ? Hypertropia ? Excyclotorsion ? Esotropia
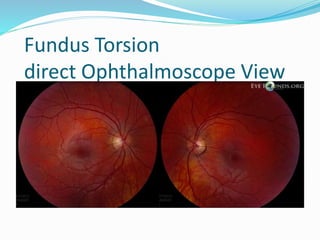
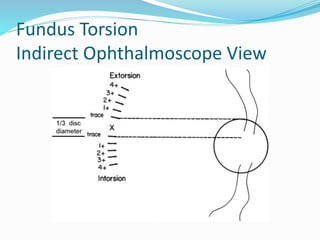
- 18. Fundus Torsion direct Ophthalmoscope View
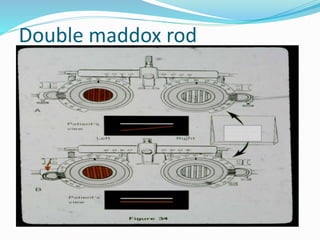
- 21. Maddox wing ? The amount of cyclophoria is determined by asking the patient to move the red arrow so that it is parallel with the horizontal row of numbers
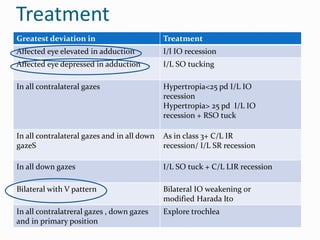
- 23. Treatment Greatest deviation in Treatment Affected eye elevated in adduction I/l IO recession Affected eye depressed in adduction I/L SO tucking In all contralateral gazes Hypertropia<25 pd I/L IO recession Hypertropia> 25 pd I/L IO recession + RSO tuck In all contralateral gazes and in all down gazeS As in class 3+ C/L IR recession/ I/L SR recession In all down gazes I/L SO tuck + C/L LIR recession Bilateral with V pattern Bilateral IO weakening or modified Harada Ito In all contralatreral gazes , down gazes and in primary position Explore trochlea
- 24. 4.Inferior Oblique Muscle Paralysis
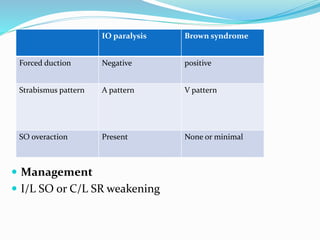
- 25. IO paralysis Brown syndrome Forced duction Negative positive Strabismus pattern A pattern V pattern SO overaction Present None or minimal ? Management ? I/L SO or C/L SR weakening
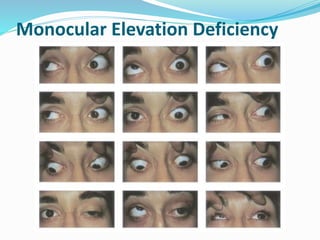
- 27. Three forms of monocular elevation deficiency are as follows: 1. Restriction 2. Elevator muscle innervational deficit 3. Combination Management Restrictive ®Crecession of IR No restriction ®C Knapp procedure
- 28. Refernces ? Binocular vision and occular motility - Von noorden 5th edition ? Handbook of Pediatric Strabismus and Amblyopia Kenneth W. Wright, MD ? PEDIATRIC Ophthalmologyand Strabismus - Creig S Hoyt -4thedition ? Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus -Section 6 2015-2016- American academy of ophthalmology.