Cytokines and metabolic syndrome
- 1. Citochine e Sindrome Metabolica Luigi Landolfi
- 2. Criteri per la diagnosi di Sindrome Metabolica
- 3. Obesity Is Caused by Long-Term Positive Energy Balance FatFat StoresStores
- 4. Balancing Intake vs Expenditure Changes in the environment Energy dense food overabundant Opportunity for expenditure reduced
- 5. Energy expenditure Energy intake Leptin Insulin (+) (+) (+) (-) (-) Fat stores Ghrelin Others (?) Satiety Signals from the Gut: CCK, GLP-1, PYY
- 6. Physiology: Central Pathways ’ü« Leptin ’ü« ╬▒-MSH ’ü« CART ’ü« GLP-1 ’ü« C-NTF ’ü« CRH/Urocortin ’ü« Neuromedin U ’ü« Serotonin ’ü« CCK ’ü« Insulin ’ü« Bombesin ’ü« Calcitonin ’ü« Enterostatin ’ü« TRH ’ü« IL-1╬Æ ’ü« Neurotensin ’ü« Oxytocin ’ü« Vasopressin ’ü« Neuropeptide Y ’ü« MCH ’ü« AGRP ’ü« Orexin A, B (Hypocretin 1,3) ’ü« Galanin ’ü« Dynomorphin ’ü« Norepinephrine ’ü« ╬Æ-endorphin Anorexigenic Orexigenic Important to know that complex regulation exists, do not need to know individual factors. Identify Leptin as important.
- 7. Genetic bases of obesity
- 8. Genetic bases of obesity ŌĆó Il GENE ŌĆ£FTOŌĆØ: FTO (Fat Mass- And Obesity- Associated Gene) la sua espressione genica ├© elevata in sede ipotalamica e il livello di questa espressione ├© regolata dallŌĆÖintroito calorico. Il gene FTO ha un alto polimorfismo genico ma con alcune varianti (alleli) correlate al fenotipo dellŌĆÖobesit├Ā. ŌĆó Gene IRX3 : ├© influenzato dalle mutazioni di FTO ; controlla la percentuale di grasso corporeo agendo sullŌĆÖipotamano ŌĆó Qualunque associazione tra FTO e obesit├Ā appare mediata da IRX3
- 9. Genetic bases of obesity Le forme a eredit├Ā mendeliana non sindromica pi├╣ studiate sono essenzialmente tre: ŌĆó Deficit del recettore della melanocortina-4 (MC4R) ŌĆó Deficit congenito di leptina (LEP) ŌĆó Deficit del recettore della leptina (LEPR)
- 10. Endocrine Causes of Obesity ’ü«Hypothalamic injury or tumor ’ü«CushingŌĆÖs syndrome ’ü«Hypothyroidism ’ü«Hypogonadism ’ü«Growth hormone deficiency ’ü«Polycystic ovarian syndrome ’ü«Manifestation of obesity versus cause
- 11. Adiponectin Angiotensinogen Resistin IL-6 TNF-╬▒ Leptin other Adipose Tissue: An Endocrine OrganAdipose Tissue: An Endocrine Organ CC:BY 3.0 BY: Regents of the University of Michigan
- 15. Obesity and cytokinesObesity and cytokines
- 17. TNFŌĆō╬▒ ?
- 19. Il Ruolo del TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ nel metabolismo degli adipocitiIl Ruolo del TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ nel metabolismo degli adipociti Modula il metabolismo lipidico : Riduce lŌĆÖuptake dei FFA e la sintesi dei trigliceridi (lipogenesi) Incrementa la lipolisi
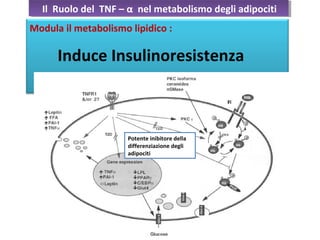
- 20. Il Ruolo del TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ nel metabolismo degli adipocitiIl Ruolo del TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ nel metabolismo degli adipociti Modula il metabolismo lipidico : Induce Insulinoresistenza
- 21. Il Ruolo del TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ nel metabolismo degli adipocitiIl Ruolo del TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ nel metabolismo degli adipociti Modula il metabolismo lipidico : Induce Insulinoresistenza Regola la produzione di leptina
- 22. Il Ruolo del TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ nel metabolismo degli adipocitiIl Ruolo del TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ nel metabolismo degli adipociti Modula il metabolismo lipidico : Induce Insulinoresistenza > Livelli di PAI-1 adipocitari e circolanti plasminogen activator inhibitor PAI-1.
- 23. Il Ruolo del TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ nel metabolismo degli adipocitiIl Ruolo del TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ nel metabolismo degli adipociti Modula il metabolismo lipidico : Induce Insulinoresistenza Potente inibitore della differenziazione degli adipociti
- 24. Il Ruolo del TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ nel metabolismo degli adipocitiIl Ruolo del TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ nel metabolismo degli adipociti Modula il metabolismo lipidico : Induce Insulinoresistenza > lŌĆÖapoptosi nel tessuto adiposo
- 25. Obesit├Ā Infiammazione e InsulinoresistenzaObesit├Ā Infiammazione e Insulinoresistenza Adipokine expression and secretion by adipose tissue in lean subjects
- 26. Obesit├Ā Infiammazione e InsulinoresistenzaObesit├Ā Infiammazione e Insulinoresistenza Obese subjects
- 28. Insulin Resistance Mortality / Morbidity
- 30. Expression of TNF-╬▒ mRNA in adipose tissue from lean and obese female human subjects .
- 32. INFIAMMAZIONE Adipose tissue inflammation The increase in fat cell size is accompanied by the increased infiltration of immune cells including macrophages (arrows).
- 33. Lipidi e mediatori dellŌĆÖinfiammazione : integrazione delle risposte metaboliche e immunitarie in adipociti e macrofagi attraverso meccanismi condivisi
- 36. Time course of hypothalamic inflammation after the onset of HFD feeding.
- 37. Radiologic evidence of gliosis in the MBH of obese humans
- 39. Implications and future directions This finding advances knowledge about the pathological changes affecting the central nervous system during the development of metabolic syndrome, and provides support for the idea that hypothalamic neuropathy contributes to the condition.
- 40. TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ e insulinoresistenza in obesi con DM 2TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ e insulinoresistenza in obesi con DM 2
- 41. TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ e insulinoresistenza in obesi con DM 2TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ e insulinoresistenza in obesi con DM 2
- 58. Ipoglicemia come nuovo fattore di rischio cardiovascolare LŌĆÖipoglicemia attiva gli stessi meccanismi indotti dallŌĆÖiperglicemia
- 65. Date of download: 11/16/2014 Copyright ┬® American College of Chest Physicians. All rights reserved. From: Expression of the Atypical Chemokine Receptor D6 in Human Alveolar Macrophages in COPDD6 Upregulation in COPD Chest. 2013;143(1):98-106. doi:10.1378/chest.11-3220 A-D, When all subjects were considered as a group, D6 expression was positively correlated with the markers of immune activation: CD8+ cells infiltrating the alveolar walls (A), IL-32 (B), and TNF- (C) and negatively correlated with╬▒ lung function parameters (FEV1/FVC) (D). E, F, When stratified according to the expression of D6 (above or below the median value), patients with COPD with high D6 levels showed levels of IL-32 and TNF- significantly higher than╬▒ patients with COPD with low D6 levels in which the levels of these cytokines were scattered. P values (Mann-Whitney U test): *P < .05, **P = .01. TNF = tumor necrosis factor. Figure Legend:
- 73. Comparison of serum NO, TNF-╬▒, IL-1╬▓, sIL-2R, IL-6 and IL-8 levels with grades of retinopathy in patients with diabetes mellitus S Doganay, C Evereklioglu, H Er, Y T├╝rk├Čz, A Sevin├¦, N Mehmet and H ┼×avli
- 74. Regular Physical Exercise as a Strategy to Improve Antioxidant and Anti- Inflammatory Status: Benefits in Type 2 DiabetesMellitus Adiponectina TNF-╬▒ CRP IL-6
- 77. ŌŚÅ TNF ŌĆō ╬▒ ŌŚÅ IL ŌĆō 6 ŌŚÅ IL ŌĆō 18 ŌŚÅ CRP
Editor's Notes
- #4: Obesity is caused by long-term positive energy balance Obesity is caused by ingesting more energy than is expended over a long period of time. The excess calories that are consumed lead to an accumulation of body fat either by being stored as fat or preventing the mobilization and oxidation of endogenous fat. In general, ingesting 3500 kcal more (or less) than expended will lead to a gain (or loss) of approximately 1 lb of fat. Genetic factors may influence the amount of weight gained with overfeeding. In one study, weight gain varied greatly among 12 monozygotic twin pairs who were chronically overfed 1000 kcal/d [1]. However, weight gains were very similar within each member of a twin pair. In another study, body fat gain after 8 weeks of overfeeding also varied among study subjects but was inversely related to changes in non-volitional energy expenditure, such as fidgeting, which may be determined genetically [2]. Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Despres JP, et al. The response to long-term overfeeding in identical twins. N Engl J Med 1990;322:1477-1482. Levine JA, Eberhardt NL, Jensen MD. Role of nonexercise activity thermogenesis in resistance to fat gain in humans. Science 1999;282:212-214.
- #30: DallŌĆÖaccumulo delle cellule schiumose nellŌĆÖintima della parte arteriosa lo sviluppo della placca aterosclerotica si realizza nel tempo. La complicazione della placca come rottura, trombosi per esempio ├© rapida. La sindrome coronarica acuta e le sue conseguenze si scatenano in relazione a fattori che vengono indicati come triggers: per esempio le ore dellŌĆÖalba, temperature ambientali estreme, emozioni intense acute, esercizi fisici inusuali, pasti copiosi ricchi in grassi, sospensione farmacologica delle statine. E anche lŌĆÖinfezione influenzale.