Data Analysis in Engineering
- 1. Fast Data Analysis in Automotive Engineering. Dr. Ahmed Rezk 1
- 2. Data Analysis. Data analysis work flow. Access Data Pre-process Data Data Analysis Model Model Deployment Data file Strain sensor Temp. sensor Sound sensor Press. sensor Working with messy data Data Reduction Efficiency quality Cost Optimisation 0.064 0.066 0.068 0.07 0.072 0.074 0.076 0.078 0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 MassflowRate[kg/s] Time[ s ] Test Data Pred Data Prediction Scripting for similar use Validation - Platform with statistical capability is required - User interface software is preferable, for fast processing Coding required System Data analysis model Other Model or Hardware Interface Regression 2
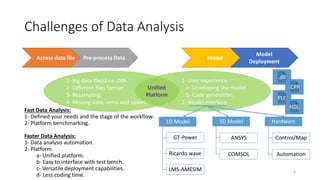
- 3. Challenges of Data Analysis Access data file Pre-process Data Model Model Deployment 1- User experience. a- Developing the model. b- Code generation. 2- Model interface. 1- Big data file(s) i.e. DBF. 2- Different files format. 3- Resampling. 4- Missing data, zeros and spikes. Unified Platform 1D Model GT-Power Ricardo wave LMS-AMESIM 3D Model ANSYS COMSOL Hardware Control/Map Automation .dll .CPP PLC HDL Fast Data Analysis: 1- Defined your needs and the stage of the workflow. 2- Platform benchmarking. Faster Data Analysis: 1- Data analysis automation. 2- Platform. a- Unified platform. b- Easy to interface with test bench. c- Versatile deployment capabilities. d- Less coding time. 3

![Data Analysis.
Data analysis work flow.
Access Data Pre-process Data
Data Analysis
Model
Model
Deployment
Data file
Strain sensor Temp. sensor
Sound sensor Press. sensor
Working with
messy data
Data Reduction
Efficiency quality Cost
Optimisation
0.064
0.066
0.068
0.07
0.072
0.074
0.076
0.078
0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08
MassflowRate[kg/s]
Time[ s ]
Test Data
Pred Data
Prediction Scripting for similar use
Validation
- Platform with statistical
capability is required
- User interface software is
preferable, for fast processing
Coding required
System
Data
analysis
model
Other
Model or
Hardware
Interface
Regression 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataanalaysispresentationupload-170726092206/85/Data-Analysis-in-Engineering-2-320.jpg)