Data base
Download as pptx, pdf1 like332 views
A table is the primary unit of physical storage for data in a database. A key attribute or set of attributes uniquely identifies an entity instance. There are different types of keys including super keys, candidate keys, primary keys, foreign keys, and simple or composite keys. A simple key consists of a single attribute while a composite key consists of more than one attribute. The primary key uniquely identifies records in a table and cannot contain null values. A foreign key in one table references the primary key in another table and is used to define relationships between tables.
1 of 14
Download to read offline











Ad
Recommended
Icloud presentation
Icloud presentationSana Saleem
?
iCloud is Apple's cloud storage and cloud computing service that allows users to store and access their data across multiple Apple devices. It launched in 2011 and currently has over 320 million users. iCloud provides 5GB of free storage and allows syncing of data like music, photos, documents, notes, and device backups across iOS, macOS, and Windows devices. It is the latest rebranding of Apple's cloud services, which were previously called .Mac and MobileMe.The relational database model chapter 2
The relational database model chapter 2Nargis Ehsan
?
The document discusses the relational database model and its key concepts. It describes how the model focuses on logical representation of data using tables rather than physical storage. The main concepts covered are entities, attributes, tables, rows and columns, primary keys, foreign keys, and integrity rules. It also explains the common relational operators like select, project, join, union, intersect, difference, and product and provides examples of how they manipulate and combine table data. Finally, it discusses data dictionaries, system catalogs, and their role in metadata management.3. Relational Models in DBMS
3. Relational Models in DBMSkoolkampus
?
The document provides an overview of the relational model and relational algebra used in relational databases. It defines key concepts like relations, tuples, attributes, domains, schemas, instances, keys, and normal forms. It also explains the six basic relational algebra operations - select, project, union, difference, cartesian product, and rename - and how they can be composed to form complex queries. Examples of relations and queries involving operations like selection, projection, joins are provided to illustrate relational algebra.Database : Relational Data Model
Database : Relational Data ModelSmriti Jain
?
Edgar Codd at IBM invented the relational database model in 1970 based on 13 rules. A relational database management system (RDBMS) stores data in related tables. RDBMSs help make data easy to store, retrieve, and combine in useful ways. Common RDBMSs include Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, and PostgreSQL. Tables are related through primary and foreign keys, which help enforce referential integrity.Relational Database Design - Lecture 4 - Introduction to Databases (1007156ANR)
Relational Database Design - Lecture 4 - Introduction to Databases (1007156ANR)Beat Signer
?
This document discusses relational database design and normalization. It outlines two major design approaches: top-down design which develops a conceptual model like an ER diagram and maps it to relational schemas, and bottom-up design which uses normalization to iteratively decompose relations. The document then describes how to map different ER model concepts like entities, attributes, and relationships to relational schemas. It also discusses functional dependencies, normalization forms, and how normalization can be used to remove redundancies and anomalies from relational schemas.Relational Database Management System
Relational Database Management SystemFree Open Source Software Technology Lab
?
The document discusses relational database management systems and their advantages over traditional file processing systems. It describes some key disadvantages of file processing systems like data redundancy, difficulty in accessing data, integrity problems, and security issues. It then explains some core components and concepts of relational database management systems like data independence, data models, entity-relationship diagrams, relational algebra, relational calculus, SQL, and integrity constraints. The document provides an overview of relational database management systems and their design and querying capabilities.Keys and its types in DBMS
Keys and its types in DBMSSaqlain84
?
The document discusses keys in database management systems. It defines key types including super keys, candidate keys, primary keys and secondary keys. It provides examples of simple and composite keys. The primary key is chosen from candidate keys to uniquely identify records and cannot contain null values. Secondary keys provide alternative ways to access records.Database management systems cs403 power point slides lecture 08
Database management systems cs403 power point slides lecture 08Md.Abu Sayed
?
This document discusses different types of keys in a database management system including primary keys, candidate keys, super keys, composite keys, and alternate keys. It provides examples of each type of key using a table of student records with the primary key being the student ID. The key attributes uniquely identify records and are important for accessing and relating data in the database.B & c
B & cVaibhav Kathuria
?
RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. It stores data in tables with rows and columns and provides operators to manipulate the data. RDBMS uses SQL as its query language. The leading RDBMS products are Oracle, IBM DB2, and Microsoft SQL Server. Keys like primary keys and foreign keys are used to identify rows and relate tables through common columns. Data integrity rules constrain column values to ensure consistency.computer-210809080138.pdf
computer-210809080138.pdfrahulsharma571283
?
This document discusses different types of keys used in databases. It defines keys as attributes that help uniquely identify rows in tables. It then explains various key types including super keys, candidate keys, primary keys, alternate keys, unique keys, composite keys, foreign keys, natural keys and surrogate keys. For each key type, it provides examples from sample tables and discusses their properties and how they differ from each other. The document concludes that databases generally only contain primary, foreign, unique and surrogate keys, while other key types are conceptual, and that each table needs a unique key to guarantee reliable data access.Types Of Keys in DBMS
Types Of Keys in DBMSPadamNepal1
?
This document discusses different types of keys used in databases. It defines keys as attributes that uniquely identify rows in tables. It then explains various key types including primary keys, candidate keys, super keys, alternate keys, unique keys, composite keys, foreign keys, natural keys and surrogate keys. For each key type, it provides examples from sample tables and discusses their properties and how they differ from each other. The document concludes that databases generally only contain primary, foreign, unique and surrogate keys, while other key types are conceptual, and that each table requires a unique key to reliably access and identify data.Keys_in_DBMS_VALID_INFORMATION_IS_AVAILA
Keys_in_DBMS_VALID_INFORMATION_IS_AVAILAprashantkori7
?
The document discusses various types of keys in databases, including super keys, candidate keys, primary keys, alternate keys, unique keys, composite keys, foreign keys, natural keys, and surrogate keys. It explains their definitions, properties, and examples, emphasizing their role in uniquely identifying records in tables and establishing relationships between different tables. The conclusion highlights the necessity of keys for ensuring data integrity and reliability in database management.Keys in Database
Keys in DatabaseA. S. M. Shafi
?
Keys in a database help uniquely identify rows. Super keys can identify rows but may contain redundant attributes, while candidate keys are minimal sets of attributes that uniquely identify rows. The primary key is the chosen candidate key that uniquely identifies each row; foreign keys in one table refer to the primary key of another table to link the tables.2.2 keys
2.2 keysELIMENG
?
This document defines key database terms used in relational database management systems (RDBMS). It discusses different types of keys such as candidate keys, primary keys, foreign keys, and secondary/alternative keys. It also defines key terms like super key, simple key, compound key, and composite key. The primary purpose of keys is to uniquely identify each record in a database table and help establish relationships between tables.Keys.pptx
Keys.pptxrevathi s
?
Keys play an important role in relational databases by uniquely identifying rows and establishing relationships between tables. There are several types of keys including primary keys, super keys, candidate keys, alternate keys, foreign keys, compound keys, and composite keys. A primary key uniquely identifies each row in a table and cannot be null, while other keys like alternate and foreign keys link data between tables or can uniquely identify rows without being designated as the primary key.Advance database system (part 3)
Advance database system (part 3)Abdullah Khosa
?
The document provides an overview of the three-level ANSI-SPARC architecture for relational database management systems (RDBMS). It describes the external, conceptual, and internal levels of the architecture and how they provide logical and physical data independence. Keys such as primary keys, foreign keys, and alternate keys are also discussed as they relate to the relational data structure and ensuring data integrity across tables.DBMS key topic Presentation slide 1.pptx
DBMS key topic Presentation slide 1.pptxsonudhakad173
?
Keys are crucial in relational databases for establishing relationships between tables and uniquely identifying records. They come in various types including primary, candidate, foreign, super, alternate, and composite keys, each serving specific roles in data organization. The document explains the significance and examples of these keys to facilitate accurate data retrieval and management.Dbms keys
Dbms keysRUpaliLohar
?
The document discusses different types of keys used in database management systems. It defines primary keys as columns that uniquely identify rows in a table and cannot contain null values. It also describes candidate keys, super keys, foreign keys, alternate keys, composite keys, and surrogate keys. The key types allow tables to be linked together and ensure uniqueness and integrity of data in the tables.DBMS Structure of Relational Databases.pptx
DBMS Structure of Relational Databases.pptxssuser19199c
?
The document discusses the structure and principles of relational databases, covering concepts such as tables, rows, and integrity constraints like primary keys, foreign keys, and unique constraints. It also explains the conversion of ER diagrams to relational models and outlines SQL commands for creating tables with various data types and constraints. Additionally, it highlights the differences between primary and unique keys, as well as the implementation of not null and check constraints in SQL.Types of keys in dbms
Types of keys in dbmsdarshhingu
?
This document defines and explains different types of keys used in relational database management systems. It describes super keys as any set of attributes that uniquely identify a record, with primary keys being a single attribute that uniquely identifies each record. Candidate keys are minimal super keys, and alternate keys are candidate keys other than the primary key. Foreign keys link two tables by referencing the primary key of one table from another table.Database manamement system_keys_sheikh_monirul_hasan
Database manamement system_keys_sheikh_monirul_hasanSheikh Monirul Hasan
?
The presentation discusses the five types of keys in Database Management Systems (DBMS): primary key, unique key, super key, candidate key, and foreign key, each with distinct functionalities and properties. It provides examples illustrating how these keys are used to uniquely identify records within a database. Additionally, it touches on composite keys that arise from combining two or more columns to create a unique identifier.Relational database Management system.pptx
Relational database Management system.pptxRevathiNCommerceCSCA
?
Relational database management systemKey and its different types
Key and its different typesUmair Shakir
?
This document defines and provides examples of different types of keys in a database table:
1) A super key is an attribute or combination of attributes that can identify records, but it may contain redundant data. A candidate key is a minimal super key that uniquely identifies each record.
2) The primary key is the candidate key chosen by the database designer to uniquely identify each record. It can consist of one or more attributes.
3) A foreign key is an attribute in one table that references the primary key of another table, enforcing referential integrity between the tables.
4) If the primary key contains multiple attributes, it is called a composite or compound key.Presentation OF DBMS-2.pptx
Presentation OF DBMS-2.pptxShumailaSajjad
?
The document discusses different types of keys used in database management systems (DBMS) to uniquely identify and relate data between tables. It defines keys such as primary keys, foreign keys, candidate keys, surrogate keys, composite keys and others. For example, it states that a primary key uniquely identifies each row in a table and cannot be duplicate, while a foreign key creates a relationship between two tables by referencing the primary key of another table.relational data model in RDBMS USING KEYS.pptx
relational data model in RDBMS USING KEYS.pptxurvashipundir04
?
The document outlines the foundational concepts of the relational database model, which organizes data into tables consisting of rows and columns. It details key terminologies such as attributes, relation schema, tuples, and various types of keys including primary, candidate, foreign, alternate, and composite keys. Furthermore, it discusses rules for defining primary keys and provides the syntax for creating tables with primary and foreign keys.relational data model In rdbms keys.pptx
relational data model In rdbms keys.pptxurvashipundir04
?
The document provides an overview of the relational database model, initially proposed by E.F. Codd, detailing how data is organized into tables with attributes. It explains key terminologies such as relation schema, tuples, keys (primary, candidate, foreign, and composite), and how they function to uniquely identify records within a table. The rules and examples for creating primary and foreign keys, along with the significance of maintaining data integrity in relational databases, are also discussed.relational data model in DBMS AND KEYS.pptx
relational data model in DBMS AND KEYS.pptxurvashipundir04
?
The document discusses the relational database model introduced by E.F. Codd in the 1970s, outlining its foundational concepts, including relations, attributes, tuples, keys, and their various types such as primary, foreign, candidate, and composite keys. It highlights the process of defining a relational schema, the role of keys in uniquely identifying records, and provides examples for better understanding. The document also explains syntactical aspects of creating tables and defining keys within a relational database.RELATIONALfsaaaaaaaaaaaakyagsgs MODEL.pptx
RELATIONALfsaaaaaaaaaaaakyagsgs MODEL.pptxsatish7588
?
The document provides an overview of the relational model and entity-relationship model for database design. It explains key concepts, such as attributes, tables, tuples, primary keys, foreign keys, and integrity constraints, emphasizing their roles in maintaining data relationships and ensuring data integrity. Overall, it highlights the simplicity and widespread use of the relational model in modern database products.More Related Content
Similar to Data base (20)
B & c
B & cVaibhav Kathuria
?
RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. It stores data in tables with rows and columns and provides operators to manipulate the data. RDBMS uses SQL as its query language. The leading RDBMS products are Oracle, IBM DB2, and Microsoft SQL Server. Keys like primary keys and foreign keys are used to identify rows and relate tables through common columns. Data integrity rules constrain column values to ensure consistency.computer-210809080138.pdf
computer-210809080138.pdfrahulsharma571283
?
This document discusses different types of keys used in databases. It defines keys as attributes that help uniquely identify rows in tables. It then explains various key types including super keys, candidate keys, primary keys, alternate keys, unique keys, composite keys, foreign keys, natural keys and surrogate keys. For each key type, it provides examples from sample tables and discusses their properties and how they differ from each other. The document concludes that databases generally only contain primary, foreign, unique and surrogate keys, while other key types are conceptual, and that each table needs a unique key to guarantee reliable data access.Types Of Keys in DBMS
Types Of Keys in DBMSPadamNepal1
?
This document discusses different types of keys used in databases. It defines keys as attributes that uniquely identify rows in tables. It then explains various key types including primary keys, candidate keys, super keys, alternate keys, unique keys, composite keys, foreign keys, natural keys and surrogate keys. For each key type, it provides examples from sample tables and discusses their properties and how they differ from each other. The document concludes that databases generally only contain primary, foreign, unique and surrogate keys, while other key types are conceptual, and that each table requires a unique key to reliably access and identify data.Keys_in_DBMS_VALID_INFORMATION_IS_AVAILA
Keys_in_DBMS_VALID_INFORMATION_IS_AVAILAprashantkori7
?
The document discusses various types of keys in databases, including super keys, candidate keys, primary keys, alternate keys, unique keys, composite keys, foreign keys, natural keys, and surrogate keys. It explains their definitions, properties, and examples, emphasizing their role in uniquely identifying records in tables and establishing relationships between different tables. The conclusion highlights the necessity of keys for ensuring data integrity and reliability in database management.Keys in Database
Keys in DatabaseA. S. M. Shafi
?
Keys in a database help uniquely identify rows. Super keys can identify rows but may contain redundant attributes, while candidate keys are minimal sets of attributes that uniquely identify rows. The primary key is the chosen candidate key that uniquely identifies each row; foreign keys in one table refer to the primary key of another table to link the tables.2.2 keys
2.2 keysELIMENG
?
This document defines key database terms used in relational database management systems (RDBMS). It discusses different types of keys such as candidate keys, primary keys, foreign keys, and secondary/alternative keys. It also defines key terms like super key, simple key, compound key, and composite key. The primary purpose of keys is to uniquely identify each record in a database table and help establish relationships between tables.Keys.pptx
Keys.pptxrevathi s
?
Keys play an important role in relational databases by uniquely identifying rows and establishing relationships between tables. There are several types of keys including primary keys, super keys, candidate keys, alternate keys, foreign keys, compound keys, and composite keys. A primary key uniquely identifies each row in a table and cannot be null, while other keys like alternate and foreign keys link data between tables or can uniquely identify rows without being designated as the primary key.Advance database system (part 3)
Advance database system (part 3)Abdullah Khosa
?
The document provides an overview of the three-level ANSI-SPARC architecture for relational database management systems (RDBMS). It describes the external, conceptual, and internal levels of the architecture and how they provide logical and physical data independence. Keys such as primary keys, foreign keys, and alternate keys are also discussed as they relate to the relational data structure and ensuring data integrity across tables.DBMS key topic Presentation slide 1.pptx
DBMS key topic Presentation slide 1.pptxsonudhakad173
?
Keys are crucial in relational databases for establishing relationships between tables and uniquely identifying records. They come in various types including primary, candidate, foreign, super, alternate, and composite keys, each serving specific roles in data organization. The document explains the significance and examples of these keys to facilitate accurate data retrieval and management.Dbms keys
Dbms keysRUpaliLohar
?
The document discusses different types of keys used in database management systems. It defines primary keys as columns that uniquely identify rows in a table and cannot contain null values. It also describes candidate keys, super keys, foreign keys, alternate keys, composite keys, and surrogate keys. The key types allow tables to be linked together and ensure uniqueness and integrity of data in the tables.DBMS Structure of Relational Databases.pptx
DBMS Structure of Relational Databases.pptxssuser19199c
?
The document discusses the structure and principles of relational databases, covering concepts such as tables, rows, and integrity constraints like primary keys, foreign keys, and unique constraints. It also explains the conversion of ER diagrams to relational models and outlines SQL commands for creating tables with various data types and constraints. Additionally, it highlights the differences between primary and unique keys, as well as the implementation of not null and check constraints in SQL.Types of keys in dbms
Types of keys in dbmsdarshhingu
?
This document defines and explains different types of keys used in relational database management systems. It describes super keys as any set of attributes that uniquely identify a record, with primary keys being a single attribute that uniquely identifies each record. Candidate keys are minimal super keys, and alternate keys are candidate keys other than the primary key. Foreign keys link two tables by referencing the primary key of one table from another table.Database manamement system_keys_sheikh_monirul_hasan
Database manamement system_keys_sheikh_monirul_hasanSheikh Monirul Hasan
?
The presentation discusses the five types of keys in Database Management Systems (DBMS): primary key, unique key, super key, candidate key, and foreign key, each with distinct functionalities and properties. It provides examples illustrating how these keys are used to uniquely identify records within a database. Additionally, it touches on composite keys that arise from combining two or more columns to create a unique identifier.Relational database Management system.pptx
Relational database Management system.pptxRevathiNCommerceCSCA
?
Relational database management systemKey and its different types
Key and its different typesUmair Shakir
?
This document defines and provides examples of different types of keys in a database table:
1) A super key is an attribute or combination of attributes that can identify records, but it may contain redundant data. A candidate key is a minimal super key that uniquely identifies each record.
2) The primary key is the candidate key chosen by the database designer to uniquely identify each record. It can consist of one or more attributes.
3) A foreign key is an attribute in one table that references the primary key of another table, enforcing referential integrity between the tables.
4) If the primary key contains multiple attributes, it is called a composite or compound key.Presentation OF DBMS-2.pptx
Presentation OF DBMS-2.pptxShumailaSajjad
?
The document discusses different types of keys used in database management systems (DBMS) to uniquely identify and relate data between tables. It defines keys such as primary keys, foreign keys, candidate keys, surrogate keys, composite keys and others. For example, it states that a primary key uniquely identifies each row in a table and cannot be duplicate, while a foreign key creates a relationship between two tables by referencing the primary key of another table.relational data model in RDBMS USING KEYS.pptx
relational data model in RDBMS USING KEYS.pptxurvashipundir04
?
The document outlines the foundational concepts of the relational database model, which organizes data into tables consisting of rows and columns. It details key terminologies such as attributes, relation schema, tuples, and various types of keys including primary, candidate, foreign, alternate, and composite keys. Furthermore, it discusses rules for defining primary keys and provides the syntax for creating tables with primary and foreign keys.relational data model In rdbms keys.pptx
relational data model In rdbms keys.pptxurvashipundir04
?
The document provides an overview of the relational database model, initially proposed by E.F. Codd, detailing how data is organized into tables with attributes. It explains key terminologies such as relation schema, tuples, keys (primary, candidate, foreign, and composite), and how they function to uniquely identify records within a table. The rules and examples for creating primary and foreign keys, along with the significance of maintaining data integrity in relational databases, are also discussed.relational data model in DBMS AND KEYS.pptx
relational data model in DBMS AND KEYS.pptxurvashipundir04
?
The document discusses the relational database model introduced by E.F. Codd in the 1970s, outlining its foundational concepts, including relations, attributes, tuples, keys, and their various types such as primary, foreign, candidate, and composite keys. It highlights the process of defining a relational schema, the role of keys in uniquely identifying records, and provides examples for better understanding. The document also explains syntactical aspects of creating tables and defining keys within a relational database.RELATIONALfsaaaaaaaaaaaakyagsgs MODEL.pptx
RELATIONALfsaaaaaaaaaaaakyagsgs MODEL.pptxsatish7588
?
The document provides an overview of the relational model and entity-relationship model for database design. It explains key concepts, such as attributes, tables, tuples, primary keys, foreign keys, and integrity constraints, emphasizing their roles in maintaining data relationships and ensuring data integrity. Overall, it highlights the simplicity and widespread use of the relational model in modern database products.Recently uploaded (20)
Lesson-3_Program-Outcomes-and-Student-Learning-Outcomes_For-Students.pdf
Lesson-3_Program-Outcomes-and-Student-Learning-Outcomes_For-Students.pdfSarahMaeDuallo
?
tendency and variability. Data visualization techniques.最新版美国芝加哥大学毕业证(鲍颁丑颈肠补驳辞毕业证书)原版定制
最新版美国芝加哥大学毕业证(鲍颁丑颈肠补驳辞毕业证书)原版定制taqyea
?
2025原版芝加哥大学毕业证书pdf电子版【q薇1954292140】美国毕业证办理UChicago芝加哥大学毕业证书多少钱?【q薇1954292140】海外各大学Diploma版本,因为疫情学校推迟发放证书、证书原件丢失补办、没有正常毕业未能认证学历面临就业提供解决办法。当遭遇挂科、旷课导致无法修满学分,或者直接被学校退学,最后无法毕业拿不到毕业证。此时的你一定手足无措,因为留学一场,没有获得毕业证以及学历证明肯定是无法给自己和父母一个交代的。
【复刻芝加哥大学成绩单信封,Buy The University of Chicago Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
芝加哥大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括芝加哥大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
我们承诺采用的是学校原版纸张(原版纸质、底色、纹路)我们工厂拥有全套进口原装设备,特殊工艺都是采用不同机器制作,仿真度基本可以达到100%,所有成品以及工艺效果都可提前给客户展示,不满意可以根据客户要求进行调整,直到满意为止!
【主营项目】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理毕业证|办理文凭: 买大学毕业证|买大学文凭【q薇1954292140】芝加哥大学学位证明书如何办理申请?
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理美国成绩单芝加哥大学毕业证【q薇1954292140】国外大学毕业证, 文凭办理, 国外文凭办理, 留信网认证NVIDIA Triton Inference Server, a game-changing platform for deploying AI mod...
NVIDIA Triton Inference Server, a game-changing platform for deploying AI mod...Tamanna36
?
NVIDIA Triton Inference Server! ?
Learn how Triton streamlines AI model deployment with dynamic batching, support for TensorFlow, PyTorch, ONNX, and more, plus GPU-optimized performance. From YOLO11 object detection to NVIDIA Dynamo’s future, it’s your guide to scalable AI inference.
Check out the slides and share your thoughts! ?
#AI #NVIDIA #TritonInferenceServer #MachineLearning一比一原版(罢鲍颁毕业证书)开姆尼茨工业大学毕业证如何办理
一比一原版(罢鲍颁毕业证书)开姆尼茨工业大学毕业证如何办理taqyed
?
鉴于此,办理TUC大学毕业证开姆尼茨工业大学毕业证书【q薇1954292140】留学一站式办理学历文凭直通车(开姆尼茨工业大学毕业证TUC成绩单原版开姆尼茨工业大学学位证假文凭)未能正常毕业?【q薇1954292140】办理开姆尼茨工业大学毕业证成绩单/留信学历认证/学历文凭/使馆认证/留学回国人员证明/录取通知书/Offer/在读证明/成绩单/网上存档永久可查!
如果您处于以下几种情况:
◇在校期间,因各种原因未能顺利毕业……拿不到官方毕业证
◇面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
◇不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
◇回国时间很长,忘记办理;
◇回国马上就要找工作,办给用人单位看;
◇企事业单位必须要求办理的
◇需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口
◇申请留学生创业基金
【办理开姆尼茨工业大学成绩单Buy Technische Universit?t Chemnitz Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
开姆尼茨工业大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括开姆尼茨工业大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!定制翱颁础顿学生卡加拿大安大略艺术与设计大学成绩单范本,翱颁础顿成绩单复刻
定制翱颁础顿学生卡加拿大安大略艺术与设计大学成绩单范本,翱颁础顿成绩单复刻taqyed
?
2025年极速办安大略艺术与设计大学毕业证【q薇1954292140】学历认证流程安大略艺术与设计大学毕业证加拿大本科成绩单制作【q薇1954292140】海外各大学Diploma版本,因为疫情学校推迟发放证书、证书原件丢失补办、没有正常毕业未能认证学历面临就业提供解决办法。当遭遇挂科、旷课导致无法修满学分,或者直接被学校退学,最后无法毕业拿不到毕业证。此时的你一定手足无措,因为留学一场,没有获得毕业证以及学历证明肯定是无法给自己和父母一个交代的。
【复刻安大略艺术与设计大学成绩单信封,Buy OCAD University Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
安大略艺术与设计大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括安大略艺术与设计大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
我们承诺采用的是学校原版纸张(原版纸质、底色、纹路)我们工厂拥有全套进口原装设备,特殊工艺都是采用不同机器制作,仿真度基本可以达到100%,所有成品以及工艺效果都可提前给客户展示,不满意可以根据客户要求进行调整,直到满意为止!
【主营项目】
一.安大略艺术与设计大学毕业证【q微1954292140】安大略艺术与设计大学成绩单、留信认证、使馆认证、教育部认证、雅思托福成绩单、学生卡等!
二.真实使馆公证(即留学回国人员证明,不成功不收费)
三.真实教育部学历学位认证(教育部存档!教育部留服网站永久可查)
四.办理国外各大学文凭(一对一专业服务,可全程监控跟踪进度)Flextronics Employee Safety Data-Project-2.pptx
Flextronics Employee Safety Data-Project-2.pptxkilarihemadri
?
This PPT are using to show employee safetyResidential Zone 4 for industrial village
Residential Zone 4 for industrial villageMdYasinArafat13
?
based on assumption that failure of such a weld is by shear on the
effective area whether the shear transfer is parallel to or
perpendicular to the axis of the line of fillet weld. In fact, the
strength is greater for shear transfer perpendicular to the weld axis;
however, for simplicity the situations are treated the same.Starbucks in the Indian market through its joint venture.
Starbucks in the Indian market through its joint venture.sales480687
?
This topic focuses on the growth and challenges of Starbucks in the Indian market through its joint venture with Tata. It covers localization strategies, menu adaptations, expansion goals, and financial performance. The topic also examines consumer perceptions, market competition, and how Starbucks navigates economic and cultural factors in one of its most promising international markets.英国毕业证范本利物浦约翰摩尔斯大学成绩单底纹防伪尝闯惭鲍学生证办理学历认证
英国毕业证范本利物浦约翰摩尔斯大学成绩单底纹防伪尝闯惭鲍学生证办理学历认证 taqyed
?
LJMU利物浦约翰摩尔斯大学毕业证书多少钱【q薇1954292140】1:1原版利物浦约翰摩尔斯大学毕业证+LJMU成绩单【q薇1954292140】完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。
【主营项目】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理毕业证|办理文凭: 买大学毕业证|买大学文凭【q薇1954292140】学位证明书如何办理申请?
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理利物浦约翰摩尔斯大学毕业证|LJMU成绩单【q薇1954292140】国外大学毕业证, 文凭办理, 国外文凭办理, 留信网认证
三.材料咨询办理、认证咨询办理请加学历顾问【微信:1954292140】毕业证购买指大学文凭购买,毕业证办理和文凭办理。学院文凭定制,学校原版文凭补办,扫描件文凭定做,100%文凭复刻。最新版意大利米兰大学毕业证(鲍狈滨惭滨毕业证书)原版定制
最新版意大利米兰大学毕业证(鲍狈滨惭滨毕业证书)原版定制taqyea
?
2025原版米兰大学毕业证书pdf电子版【q薇1954292140】意大利毕业证办理UNIMI米兰大学毕业证书多少钱?【q薇1954292140】海外各大学Diploma版本,因为疫情学校推迟发放证书、证书原件丢失补办、没有正常毕业未能认证学历面临就业提供解决办法。当遭遇挂科、旷课导致无法修满学分,或者直接被学校退学,最后无法毕业拿不到毕业证。此时的你一定手足无措,因为留学一场,没有获得毕业证以及学历证明肯定是无法给自己和父母一个交代的。
【复刻米兰大学成绩单信封,Buy Università degli Studi di MILANO Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
米兰大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括米兰大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
我们承诺采用的是学校原版纸张(原版纸质、底色、纹路)我们工厂拥有全套进口原装设备,特殊工艺都是采用不同机器制作,仿真度基本可以达到100%,所有成品以及工艺效果都可提前给客户展示,不满意可以根据客户要求进行调整,直到满意为止!
【主营项目】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理毕业证|办理文凭: 买大学毕业证|买大学文凭【q薇1954292140】米兰大学学位证明书如何办理申请?
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理意大利成绩单米兰大学毕业证【q薇1954292140】国外大学毕业证, 文凭办理, 国外文凭办理, 留信网认证Ad
Data base
- 1. “Data Base “ Name: Sana Salim Dept: IT M.Cs 3rd Topic: Relational Keys
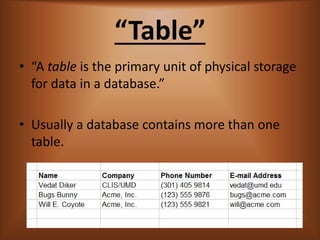
- 2. “Table” ? “A table is the primary unit of physical storage for data in a database.” ? Usually a database contains more than one table.
- 3. “Key Attributes” ? An attribute or set of attributes to identify an entity instance uniquely ? Types: – Super key – Candidate key – Primary key – Foreign Key – Simple or Composite Key
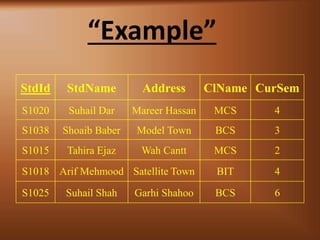
- 4. “Example of Key” StdId StdName Address ClName CurSem S1020 Suhail Dar Mareer Hassan MCS 4 S1038 Shoaib Baber Model Town BCS 3 S1015 Tahira Ejaz Wah Cantt MCS 2 S1018 Arif Mehmood Satellite Town BIT 4 S1025 Suhail Shah Garhi Shahoo BCS 6
- 5. “Simple or Composite Key” ? A key consisting of single attribute is called simple key, e.g., StudID, itemNo ? A key consisting of more than one attribute is known as composite key, like {Program_Code, Course_Code}
- 6. ProgCode CourseCode MarksAlloc CrHrs MCS DS 100 3 MCS DBS 100 3 MBA DBS 100 3 BCS NW 100 3 OFFERING “Example”
- 7. “Primary Key” ? Primary key is a unique identifier of records in a table. ? None of its attributes can have NULL values ? Primary key values may be generated manually or automatically. ? A primary key can consist of more than one field.
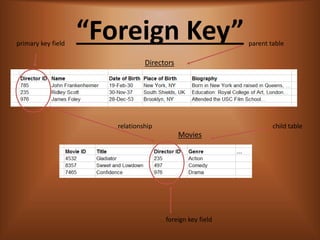
- 8. “Foreign Key” foreign key field primary key field parent table Directors Movies child tablerelationship
- 9. “Relationship Types” ? One-to-one ? One-to-many ? Many-to-many
- 10. “Super Key” ? Any set of attributes containing a super key is also a super key since it too uniquely identifies an entity e.g. {StudID, major} ? For example, for EMPLOYEE and STUDENT entity types EmpID and StudID are the superkeys respectively.
- 11. “Example” StdId StdName Address ClName CurSem S1020 Suhail Dar Mareer Hassan MCS 4 S1038 Shoaib Baber Model Town BCS 3 S1015 Tahira Ejaz Wah Cantt MCS 2 S1018 Arif Mehmood Satellite Town BIT 4 S1025 Suhail Shah Garhi Shahoo BCS 6
- 12. “Candidate Key” ? A candidate key is the super key that does not contain extra attributes. ? It might have more than one attribute that uniquely identifies an entity. e.g {name, address}
- 13. “Example” StdId StdName Address ClName CurSem S1020 Suhail Dar Mareer Hassan MCS 4 S1038 Shoaib Baber Model Town BCS 3 S1015 Tahira Ejaz Wah Cantt MCS 2 S1018 Arif Mehmood Satellite Town BIT 4 S1025 Suhail Shah Garhi Shahoo BCS 6
- 14. Thank you!
