DATA LOGGING SSI 3013
- 1. PREPARED BY NAME ID NUMBER NORHAFIZAH BINTI NORDIN D20101037456 NURSYAHIRA AYUNI BINTI AHMAD D20101037457 ZAMRI AIN NABILA BINTI ABD. MALEK D20101037463
- 2. TITLE: THE EFFECT OF SALT ON THE RATE OF CORROSION
- 3. ENGAGE Nail A Nail B ÔÇó These two nails were located at same place. ÔÇó Nail A was immersed in salt water while nail B was immersed in plain water. ÔÇó Which nails will more corrosive?
- 4. Questions Which nail is more Why? corrosive? From the situation, what Can you happen to explain? both nails?
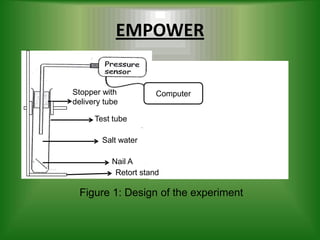
- 5. EMPOWER Stopper with Computer delivery tube Test tube Salt water Nail A Retort stand Figure 1: Design of the experiment
- 6. Plan of the experiment Objective ÔÇó To investigate the effect of salt on the rate of corrosion. Hypothesis ÔÇó Salt water increase the rate of corrosion Variables ÔÇó Manipulated variable: Type of water ÔÇó Responding variable: The rate of corrosion ÔÇó Fixed variable: Temperature
- 7. Plan of the experiment Apparatus ÔÇó Nails ÔÇó Salt water ÔÇó Plain water ÔÇó A delivery tube ÔÇó Cork ÔÇó Pressure sensor ÔÇó Retort stand
- 8. Plan of the experiment Methods 1. Prepare 2 test tubes labeled A and B. 2. Set up the apparatus as shown in Figure 1. 3. Place a nail in each test tube. 4. Pour salt water in test tube A and plain water in the test tube B. 5. The water is pored until it overflow from the test tube. 6. Insert the stopper with delivery tube. 7. Make sure there is no air bubble in the test tube. 8. Connect the pressure sensor at delivery tube. 9. The pressure sensor is connected at computer. 10. Measure the pressure change of both test tube over 7 days.
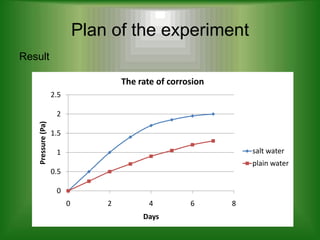
- 9. Plan of the experiment Result The rate of corrosion 2.5 2 Pressure (Pa) 1.5 1 salt water plain water 0.5 0 0 2 4 6 8 Days
- 10. Plan of the experiment Discussion ÔÇó Based on the result, nail A that immersed in salt water is more corrosive than nail B that immersed in plain water. ÔÇó This is because, oxygen present in water and salt causes corrosion. Salt is hygroscopic in nature and it attracts the water. Water is required for corrosion and salt speeds up the process. ÔÇó The salt speeds up the corrosion by improves the capability of water to carry electron through redox reactions. ÔÇó Rusting in metals undergoes an electrochemical process in which iron loses electrons by oxidation causing the water to break into hydroxide ions and oxygen. The metal that has oxidized reacts with the hydroxide ions and oxygen to form metal oxide. These salts remain even if the water is gone and they again start rusting whenever they come in contact with moisture.
- 11. Plan of the experiment Conclusion ÔÇó The salt water increase the rate of corrosion compare with plain water.
- 12. ENHANCE A- House at Pantai Teluk Lipat B-House at Putrajaya ÔÇó From the above pictures, predict the condition of gate after 10 years based on the locations? ÔÇó Give the reasons to support your predictions. ÔÇó Explain the changes process.
- 13. EXTENSION Ship A Ship B ÔÇó According to the pictures, ship A is more corrosive than ship B. ÔÇó How to reduce the ship A from keep corrosive? Explain. ÔÇó Does humidity also affect the corrosion process? If yes, give the explanation.