Database Management System Introduction to DBMS.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes5 views
Introduction to DMBS part 1
1 of 16
Download to read offline










Recommended
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM



DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMAdarsh College, Hingoli
Ěý
A DBMS is system software that manages data storage, access, modification, and integrity in a structured database. It allows users to create, read, update and delete data systematically and serves as an interface between users and the database. Common applications of DBMS include banking, airlines, universities, telecommunications, finance, sales, manufacturing, and human resources. The most widely used type of DBMS is the relational DBMS which stores data in tables that can be related through joins. Other types include hierarchical, network, and object-oriented DBMS.Database management system 



Database management system Shashikumar_chari
Ěý
A database management system (DBMS) is software that allows users to create, access, modify, and manage data in a structured database. A DBMS provides an interface between users and the database, ensuring data is organized and accessible. Common applications of DBMSs include banking, airlines, universities, telecommunications, finance, sales, manufacturing, and human resources. The top 10 DBMS software programs are Oracle, IBM DB2, Microsoft SQL Server, SAP Sybase ASE, Teradata, ADABAS, MySQL, FileMaker, Microsoft Access, and Informix. The main types of DBMSs are relational, hierarchical, network, and object-oriented. Relational DBMSs are the most widelyDatabase management system 



Database management system 9535814851
Ěý
A database management system (DBMS) is system software that manages organization, storage, access, modification and integrity of data in a structured database. A DBMS allows end users to create, read, update and delete data systematically and serves as an interface between the database and end users. Common applications of DBMS include banking, airlines, universities, telecommunications, finance, sales, manufacturing and human resources. Popular DBMS software includes Oracle, IBM DB2, Microsoft SQL Server, SAP Sybase ASE, Teradata, ADABAS, MySQL, FileMaker, Microsoft Access and Informix. Common types of DBMS are relational, hierarchical, network and object-oriented.Basic of Database Management System(DBMS)



Basic of Database Management System(DBMS)anjanasharma77573
Ěý
Basic of Database Management System(DBMS)1677091759369776.pdf



1677091759369776.pdfJanoakre
Ěý
This document discusses database management systems (DBMS). It defines a DBMS as software that manages databases and provides interfaces for creating, storing, updating, and securing data. The document outlines the key functions of a DBMS, including data definition, updation, retrieval, and user administration. It also discusses the characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, popular types (hierarchical, network, relational, object-oriented), software, and applications of DBMS.Lecture#5



Lecture#5TolganayAnarbekova
Ěý
The document discusses databases and database management systems (DBMS). It defines a database as an organized collection of data that can be used alone or combined for multiple purposes. A DBMS is a collection of programs that enables storing, modifying, and extracting data from a database. The document then discusses key characteristics, purposes, advantages, types and components of DBMS.Database



Databasesahil shinwari
Ěý
A database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. A database management system (DBMS) is software that allows users to define, create, maintain and control access to the database. Well-known DBMSs include MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server and IBM DB2. A DBMS manages storage, security, querying and integrity of the data in the database. The most popular database model since the 1980s has been the relational model which represents data in tables related through keys.Database and Database Management (DBM): Health Informatics



Database and Database Management (DBM): Health InformaticsZulfiquer Ahmed Amin
Ěý
A database is an organized collection of related data that can be used alone or combined with other data for multiple purposes. A database management system (DBMS) enables users to store, modify, and extract information from a database. Key characteristics of a DBMS include performance, sharing data access, security, removing redundancy, and concurrent access. DBMS were developed to address difficulties with typical file processing systems like data redundancy, inconsistent access, and security problems.DBMS characteristics in Information Management System.pptx



DBMS characteristics in Information Management System.pptxRajiRagukumar2
Ěý
DBMS CHARACTERISTIC IN INFORMANTION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM PRESENTATION BY RAJESHWARI.M ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PSR ENGINEERING COLLEGE SIVAKASIWhat is Database Management.pdf



What is Database Management.pdfKonverge Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Ěý
Database Management allow person to organize, store and retrieve data from a computer. How database management contributes to achieving your business growth.
For more details visit: https://www.konverge.co.in/what-is-database-management/jose rizal



jose rizalRio Hemelgo
Ěý
A database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. A database management system (DBMS) is software that allows users to define, create, query, update, and administer a database. Well-known DBMSs include MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, and IBM DB2. A DBMS manages access to the database, maintains its organization and security, and recovers information if the system fails.SQL (Scratch to Advance).pptx



SQL (Scratch to Advance).pptxHitesh670643
Ěý
SQL is a standard language for accessing and manipulating databases. It allows users to store, organize and analyze data in databases. There are many types of databases including relational, object-oriented, distributed, cloud, and NoSQL databases. Each database has a different structure and is suited for different purposes. A database management system (DBMS) is software that allows users to create, access, manage and control databases. It provides advantages like efficient data storage, sharing and administration but also has disadvantages like high costs and complexity.DBMS - Database Management System 



DBMS - Database Management System Krishna Patel
Ěý
DBMS - Database Management System, Data and Database, DBMS meaning, Why DBMS?, Characteristics of DBMS, Types of DBMS- Hierarchical DBMS, Network DBMS, Relational DBMS, Object-oriented DBMS, Applications of DBMS, Popular DBMS Software, Advantages of DBMS, disadvantages of DBMS.Database management system



Database management systemkhagendrabasnet4
Ěý
A database management system (DBMS) is a collection of software programs that manage data stored in a database. It allows for data storage, organization, manipulation, and retrieval. Popular DBMS programs include MS Access, Oracle, MySQL, and SQL Server. The relational database model organizes data into tables with rows and columns and defines relationships between tables. A relational database management system (RDBMS) uses this model and provides security, concurrency control, and other features to make database access and management easier.Database management system overview



Database management system overviewNj Saini
Ěý
This document provides an overview of database management systems (DBMS). It discusses key concepts such as the components of a database system including hardware, software, people and procedures. It also describes different database models like hierarchical, network and relational models. The document explains database languages for data definition (DDL) and data manipulation (DML). It discusses database users and administrators and their roles. Some common applications of DBMS and advantages like improved data sharing and integrity are highlighted. Disadvantages like increased costs are also mentioned.Uses of dbms



Uses of dbmsMISY
Ěý
The document provides an overview of database management systems, including what they are, their benefits, examples, and types of database models. It discusses that a database is a structured collection of records stored in a computer system, and a database management system (DBMS) is software used to organize, analyze, and modify the stored data. Benefits of DBMS include increased productivity, consolidated data, and the ability to easily change information systems. Examples provided are Oracle, Microsoft Access, and SQL Server. Types of database models described are distributed, network, object-oriented, hierarchical, and relational. The document also briefly mentions data security.DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM-MRS. LAXMI B PANDYA FOR 25TH AUGUST,2022.pptx



DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM-MRS. LAXMI B PANDYA FOR 25TH AUGUST,2022.pptxLaxmi Pandya
Ěý
The document discusses database management systems and provides examples of different types of databases including relational, non-relational, centralized, distributed and object-oriented databases. It describes key components of databases like fields, records, tables and the core functions of adding, deleting, modifying and retrieving records. The document also explains concepts like database languages, database models, database examples, database features and integrity constraints.Introduction to Database Management Systems



Introduction to Database Management SystemsBackiyalakshmiVenkat
Ěý
Introduction to DBMS, its type and modelsMis chapter 7 database systems



Mis chapter 7 database systemsFilmon Habtemichael Tesfai
Ěý
This document provides an overview of database concepts. It discusses the traditional approach to data management versus the database approach. The traditional approach leads to problems like data redundancy, inconsistency, and inability to share data. A database management system addresses these issues by allowing centralized data storage and shared access. Key topics covered include data modeling, the relational database model, database administration, popular DBMSs, and emerging concepts like data warehousing, data mining and business intelligence.data base system to new data science lerne



data base system to new data science lernetarunprajapati0t
Ěý
Databases are organized collections of data that allow for efficient data access and management. There are different types of databases including relational databases, NoSQL databases, object-oriented databases, and graph databases. Databases have evolved over time from flat file systems to hierarchical, network, relational, and modern cloud-based systems. A database management system provides tools for creating, accessing, and managing databases and ensures security, integrity, and consistency of stored data.Database management system



Database management systemRizwanHafeez
Ěý
The document provides information about database management systems. It defines a DBMS as software that allows storage, retrieval, modification and deletion of data from a database. It then discusses different types of DBMS like hierarchical, network, relational, flat file and object oriented. Examples of popular DBMS are also listed including SQL, Oracle, FoxPro, MS Access and MySQL. Key advantages of DBMS are efficient data storage, security, concurrent access and integrity maintenance.Database Management Systems (Mcom Ecommerce)



Database Management Systems (Mcom Ecommerce)Rupen Parte
Ěý
The document discusses database management systems (DBMS) and their architecture. It describes the three levels of the ANSI-SPARC DBMS architecture model: 1) the internal level deals with how data is physically stored, 2) the conceptual level provides a logical view of how data is structured and related, and 3) the external level presents customized views of the data to users and applications. The model provides abstraction between these levels to hide complex implementation details and support multiple simultaneous users.US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
Ěý
Preface: The ReGenX Generator innovation operates with a US Patented Frequency Dependent Load Current Delay which delays the creation and storage of created Electromagnetic Field Energy around the exterior of the generator coil. The result is the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs any magnitude of Positive Electro-Mechanical Work at infinite efficiency on the generator's Rotating Magnetic Field, increasing its Kinetic Energy and increasing the Kinetic Energy of an EV or ICE Vehicle to any magnitude without requiring any Externally Supplied Input Energy. In Electricity Generation applications the ReGenX Generator innovation now allows all electricity to be generated at infinite efficiency requiring zero Input Energy, zero Input Energy Cost, while producing zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions, zero Air Pollution and zero Nuclear Waste during the Electricity Generation Phase. In Electric Motor operation the ReGen-X Quantum Motor now allows any magnitude of Work to be performed with zero Electric Input Energy.
Demonstration Protocol: The demonstration protocol involves three prototypes;
1. Protytpe #1, demonstrates the ReGenX Generator's Load Current Time Delay when compared to the instantaneous Load Current Sine Wave for a Conventional Generator Coil.
2. In the Conventional Faraday Generator operation the created Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Negative Work at infinite efficiency and it reduces the Kinetic Energy of the system.
3. The Magnitude of the Negative Work / System Kinetic Energy Reduction (in Joules) is equal to the Magnitude of the created Electromagnetic Field Energy (also in Joules).
4. When the Conventional Faraday Generator is placed On-Load, Negative Work is performed and the speed of the system decreases according to Lenz's Law of Induction.
5. In order to maintain the System Speed and the Electric Power magnitude to the Loads, additional Input Power must be supplied to the Prime Mover and additional Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft.
6. For example, if 100 Watts of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >100 Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
7. If 1 MW of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >1 MW Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
8. Generally speaking the ratio is 2 Watts of Mechanical Input Power to every 1 Watt of Electric Output Power generated.
9. The increase in Drive Shaft Mechanical Input Power is provided by the Prime Mover and the Input Energy Source which powers the Prime Mover.
10. In the Heins ReGenX Generator operation the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Positive Work at infinite efficiency and it increases the Kinetic Energy of the system.Best KNow Hydrogen Fuel Production in the World The cost in USD kwh for H2



Best KNow Hydrogen Fuel Production in the World The cost in USD kwh for H2Daniel Donatelli
Ěý
The cost in USD/kwh for H2
Daniel Donatelli
Secure Supplies Group
Index
• Introduction - Page 3
• The Need for Hydrogen Fueling - Page 5
• Pure H2 Fueling Technology - Page 7
• Blend Gas Fueling: A Transition Strategy - Page 10
• Performance Metrics: H2 vs. Fossil Fuels - Page 12
• Cost Analysis and Economic Viability - Page 15
• Innovations Driving Leadership - Page 18
• Laminar Flame Speed Adjustment
• Heat Management Systems
• The Donatelli Cycle
• Non-Carnot Cycle Applications
• Case Studies and Real-World Applications - Page 22
• Conclusion: Secure Supplies’ Leadership in Hydrogen Fueling - Page 27
More Related Content
Similar to Database Management System Introduction to DBMS.pptx (20)
Database and Database Management (DBM): Health Informatics



Database and Database Management (DBM): Health InformaticsZulfiquer Ahmed Amin
Ěý
A database is an organized collection of related data that can be used alone or combined with other data for multiple purposes. A database management system (DBMS) enables users to store, modify, and extract information from a database. Key characteristics of a DBMS include performance, sharing data access, security, removing redundancy, and concurrent access. DBMS were developed to address difficulties with typical file processing systems like data redundancy, inconsistent access, and security problems.DBMS characteristics in Information Management System.pptx



DBMS characteristics in Information Management System.pptxRajiRagukumar2
Ěý
DBMS CHARACTERISTIC IN INFORMANTION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM PRESENTATION BY RAJESHWARI.M ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PSR ENGINEERING COLLEGE SIVAKASIWhat is Database Management.pdf



What is Database Management.pdfKonverge Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Ěý
Database Management allow person to organize, store and retrieve data from a computer. How database management contributes to achieving your business growth.
For more details visit: https://www.konverge.co.in/what-is-database-management/jose rizal



jose rizalRio Hemelgo
Ěý
A database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. A database management system (DBMS) is software that allows users to define, create, query, update, and administer a database. Well-known DBMSs include MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, and IBM DB2. A DBMS manages access to the database, maintains its organization and security, and recovers information if the system fails.SQL (Scratch to Advance).pptx



SQL (Scratch to Advance).pptxHitesh670643
Ěý
SQL is a standard language for accessing and manipulating databases. It allows users to store, organize and analyze data in databases. There are many types of databases including relational, object-oriented, distributed, cloud, and NoSQL databases. Each database has a different structure and is suited for different purposes. A database management system (DBMS) is software that allows users to create, access, manage and control databases. It provides advantages like efficient data storage, sharing and administration but also has disadvantages like high costs and complexity.DBMS - Database Management System 



DBMS - Database Management System Krishna Patel
Ěý
DBMS - Database Management System, Data and Database, DBMS meaning, Why DBMS?, Characteristics of DBMS, Types of DBMS- Hierarchical DBMS, Network DBMS, Relational DBMS, Object-oriented DBMS, Applications of DBMS, Popular DBMS Software, Advantages of DBMS, disadvantages of DBMS.Database management system



Database management systemkhagendrabasnet4
Ěý
A database management system (DBMS) is a collection of software programs that manage data stored in a database. It allows for data storage, organization, manipulation, and retrieval. Popular DBMS programs include MS Access, Oracle, MySQL, and SQL Server. The relational database model organizes data into tables with rows and columns and defines relationships between tables. A relational database management system (RDBMS) uses this model and provides security, concurrency control, and other features to make database access and management easier.Database management system overview



Database management system overviewNj Saini
Ěý
This document provides an overview of database management systems (DBMS). It discusses key concepts such as the components of a database system including hardware, software, people and procedures. It also describes different database models like hierarchical, network and relational models. The document explains database languages for data definition (DDL) and data manipulation (DML). It discusses database users and administrators and their roles. Some common applications of DBMS and advantages like improved data sharing and integrity are highlighted. Disadvantages like increased costs are also mentioned.Uses of dbms



Uses of dbmsMISY
Ěý
The document provides an overview of database management systems, including what they are, their benefits, examples, and types of database models. It discusses that a database is a structured collection of records stored in a computer system, and a database management system (DBMS) is software used to organize, analyze, and modify the stored data. Benefits of DBMS include increased productivity, consolidated data, and the ability to easily change information systems. Examples provided are Oracle, Microsoft Access, and SQL Server. Types of database models described are distributed, network, object-oriented, hierarchical, and relational. The document also briefly mentions data security.DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM-MRS. LAXMI B PANDYA FOR 25TH AUGUST,2022.pptx



DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM-MRS. LAXMI B PANDYA FOR 25TH AUGUST,2022.pptxLaxmi Pandya
Ěý
The document discusses database management systems and provides examples of different types of databases including relational, non-relational, centralized, distributed and object-oriented databases. It describes key components of databases like fields, records, tables and the core functions of adding, deleting, modifying and retrieving records. The document also explains concepts like database languages, database models, database examples, database features and integrity constraints.Introduction to Database Management Systems



Introduction to Database Management SystemsBackiyalakshmiVenkat
Ěý
Introduction to DBMS, its type and modelsMis chapter 7 database systems



Mis chapter 7 database systemsFilmon Habtemichael Tesfai
Ěý
This document provides an overview of database concepts. It discusses the traditional approach to data management versus the database approach. The traditional approach leads to problems like data redundancy, inconsistency, and inability to share data. A database management system addresses these issues by allowing centralized data storage and shared access. Key topics covered include data modeling, the relational database model, database administration, popular DBMSs, and emerging concepts like data warehousing, data mining and business intelligence.data base system to new data science lerne



data base system to new data science lernetarunprajapati0t
Ěý
Databases are organized collections of data that allow for efficient data access and management. There are different types of databases including relational databases, NoSQL databases, object-oriented databases, and graph databases. Databases have evolved over time from flat file systems to hierarchical, network, relational, and modern cloud-based systems. A database management system provides tools for creating, accessing, and managing databases and ensures security, integrity, and consistency of stored data.Database management system



Database management systemRizwanHafeez
Ěý
The document provides information about database management systems. It defines a DBMS as software that allows storage, retrieval, modification and deletion of data from a database. It then discusses different types of DBMS like hierarchical, network, relational, flat file and object oriented. Examples of popular DBMS are also listed including SQL, Oracle, FoxPro, MS Access and MySQL. Key advantages of DBMS are efficient data storage, security, concurrent access and integrity maintenance.Database Management Systems (Mcom Ecommerce)



Database Management Systems (Mcom Ecommerce)Rupen Parte
Ěý
The document discusses database management systems (DBMS) and their architecture. It describes the three levels of the ANSI-SPARC DBMS architecture model: 1) the internal level deals with how data is physically stored, 2) the conceptual level provides a logical view of how data is structured and related, and 3) the external level presents customized views of the data to users and applications. The model provides abstraction between these levels to hide complex implementation details and support multiple simultaneous users.Recently uploaded (20)
US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
Ěý
Preface: The ReGenX Generator innovation operates with a US Patented Frequency Dependent Load Current Delay which delays the creation and storage of created Electromagnetic Field Energy around the exterior of the generator coil. The result is the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs any magnitude of Positive Electro-Mechanical Work at infinite efficiency on the generator's Rotating Magnetic Field, increasing its Kinetic Energy and increasing the Kinetic Energy of an EV or ICE Vehicle to any magnitude without requiring any Externally Supplied Input Energy. In Electricity Generation applications the ReGenX Generator innovation now allows all electricity to be generated at infinite efficiency requiring zero Input Energy, zero Input Energy Cost, while producing zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions, zero Air Pollution and zero Nuclear Waste during the Electricity Generation Phase. In Electric Motor operation the ReGen-X Quantum Motor now allows any magnitude of Work to be performed with zero Electric Input Energy.
Demonstration Protocol: The demonstration protocol involves three prototypes;
1. Protytpe #1, demonstrates the ReGenX Generator's Load Current Time Delay when compared to the instantaneous Load Current Sine Wave for a Conventional Generator Coil.
2. In the Conventional Faraday Generator operation the created Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Negative Work at infinite efficiency and it reduces the Kinetic Energy of the system.
3. The Magnitude of the Negative Work / System Kinetic Energy Reduction (in Joules) is equal to the Magnitude of the created Electromagnetic Field Energy (also in Joules).
4. When the Conventional Faraday Generator is placed On-Load, Negative Work is performed and the speed of the system decreases according to Lenz's Law of Induction.
5. In order to maintain the System Speed and the Electric Power magnitude to the Loads, additional Input Power must be supplied to the Prime Mover and additional Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft.
6. For example, if 100 Watts of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >100 Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
7. If 1 MW of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >1 MW Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
8. Generally speaking the ratio is 2 Watts of Mechanical Input Power to every 1 Watt of Electric Output Power generated.
9. The increase in Drive Shaft Mechanical Input Power is provided by the Prime Mover and the Input Energy Source which powers the Prime Mover.
10. In the Heins ReGenX Generator operation the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Positive Work at infinite efficiency and it increases the Kinetic Energy of the system.Best KNow Hydrogen Fuel Production in the World The cost in USD kwh for H2



Best KNow Hydrogen Fuel Production in the World The cost in USD kwh for H2Daniel Donatelli
Ěý
The cost in USD/kwh for H2
Daniel Donatelli
Secure Supplies Group
Index
• Introduction - Page 3
• The Need for Hydrogen Fueling - Page 5
• Pure H2 Fueling Technology - Page 7
• Blend Gas Fueling: A Transition Strategy - Page 10
• Performance Metrics: H2 vs. Fossil Fuels - Page 12
• Cost Analysis and Economic Viability - Page 15
• Innovations Driving Leadership - Page 18
• Laminar Flame Speed Adjustment
• Heat Management Systems
• The Donatelli Cycle
• Non-Carnot Cycle Applications
• Case Studies and Real-World Applications - Page 22
• Conclusion: Secure Supplies’ Leadership in Hydrogen Fueling - Page 27
Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdf



Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdfTotok Sulistiyanto
Ěý
High Efficiency Chiller System in HVACUNIT 1FUNDAMENTALS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS.pptx



UNIT 1FUNDAMENTALS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS.pptxKesavanT10
Ěý
UNIT 1FUNDAMENTALS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS.pptxIPC-9716_2024 Requirements for Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) Process Con...



IPC-9716_2024 Requirements for Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) Process Con...ssuserd9338b
Ěý
IPC-9716_2024 Requirements for Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) Process Control for Printed Board Assemblies.pdfG8 mini project for alcohol detection and engine lock system with GPS tracki...



G8 mini project for alcohol detection and engine lock system with GPS tracki...sahillanjewar294
Ěý
b.tech final year projects report for cseHow to Make an RFID Door Lock System using Arduino



How to Make an RFID Door Lock System using ArduinoCircuitDigest
Ěý
Learn how to build an RFID-based door lock system using Arduino to enhance security with contactless access control.15. Smart Cities Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New Utopia.pdf



15. Smart Cities Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New Utopia.pdfNgocThang9
Ěý
Smart Cities Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New UtopiaSoil Properties and Methods of Determination



Soil Properties and Methods of DeterminationRajani Vyawahare
Ěý
This PPT covers the index and engineering properties of soil. It includes details on index properties, along with their methods of determination. Various important terms related to soil behavior are explained in detail. The presentation also outlines the experimental procedures for determining soil properties such as water content, specific gravity, plastic limit, and liquid limit, along with the necessary calculations and graph plotting. Additionally, it provides insights to understand the importance of these properties in geotechnical engineering applications.Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
Ěý
Welcome to the March 2025 issue of WIPAC Monthly the magazine brought to you by the LinkedIn Group WIPAC Monthly.
In this month's edition, on top of the month's news from the water industry we cover subjects from the intelligent use of wastewater networks, the use of machine learning in water quality as well as how, we as an industry, need to develop the skills base in developing areas such as Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence.
Enjoy the latest editionHow to Build a Maze Solving Robot Using Arduino



How to Build a Maze Solving Robot Using ArduinoCircuitDigest
Ěý
Learn how to make an Arduino-powered robot that can navigate mazes on its own using IR sensors and "Hand on the wall" algorithm.
This step-by-step guide will show you how to build your own maze-solving robot using Arduino UNO, three IR sensors, and basic components that you can easily find in your local electronics shop.US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
Ěý
Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
Ěý
Database Management System Introduction to DBMS.pptx
- 1. DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM By: Raj Vardhan
- 2. INTRODUCTION A Database Management System (DBMS) is system software used to manage the organization by storage, access, modify and integrity of data in structured database. a A DBMS makes it possible for end users to create, read, update and delete data in a database systematically. The DBMS essentially serves as an interface between the database and end users, ensuring that data is consistently organized and remains easily accessible.
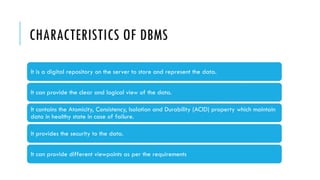
- 3. CHARACTERISTICS OF DBMS It is a digital repository on the server to store and represent the data. It can provide the clear and logical view of the data. It contains the Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation and Durability (ACID) property which maintain data in healthy state in case of failure. It provides the security to the data. It can provide different viewpoints as per the requirements
- 4. APPLICATION OF DBMS BANKING For customer information, accounts, payments, deposits, loans and banking transactions. AIRLINES: For reservations and schedule information. Airlines were among the first to use databases in geographically a distributed manner. Terminals situated around the world accessed through the central database system. TELECOMMUNICATION: For keeping records of calls made, generating monthly bills, maintaining balances and storing information about the communication networks. FINANCE: For storing information about holdings, sales, and purchases of financial instruments such as stocks and bonds. UNIVERSITIES: For student information, course registrations, colleges and grades. SALES: For storing customer, product & sales information.
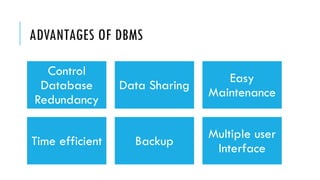
- 5. ADVANTAGES OF DBMS Control Database Redundancy Data Sharing Easy Maintenance Time efficient Backup Multiple user Interface
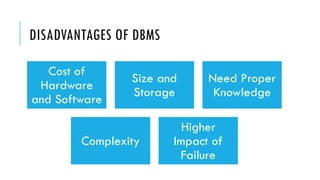
- 6. DISADVANTAGES OF DBMS Cost of Hardware and Software Size and Storage Need Proper Knowledge Complexity Higher Impact of Failure
- 8. RELATIONAL DBMS Relational DBMS are the most widely used database management systems today. They are relatively easy to use. The relational model relies on normalizing data within rows and columns in tables. The data can be related to other data in the same table or other tables which has to be correctly managed by joining one or more tables. Data in this type of model is stored is fixed predefined structures and are usually manipulated using Structured Query Language (SQL). Relational database management systems include Oracle, SQL Server, IBM DB2, mySQL & others.
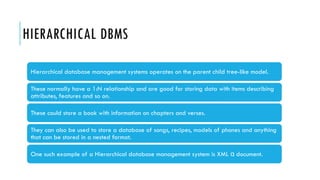
- 10. HIERARCHICAL DBMS Hierarchical database management systems operates on the parent child tree-like model. These normally have a 1:N relationship and are good for storing data with items describing attributes, features and so on. These could store a book with information on chapters and verses. They can also be used to store a database of songs, recipes, models of phones and anything that can be stored in a nested format. One such example of a Hierarchical database management system is XML document. α
- 12. NETWORK DBMS A Network database management system uses a data model similar to Hierarchical database management systems. The major difference here is that the tree structure in the Network models can have a many parent to many child relational model. The Network model structure is based on records and sets and most of these databases use SQL for manipulation of their data. Network database management systems tend to be very flexible but are rarely used and were very quite common in the 1960s and 1970s
- 13. NETWORK DBMS
- 14. OBJECT ORIENTED DBMS Object-oriented DBMS borrow from the model of the Object-oriented programming paradigm. In this database model, the Object and its data or attributes are seen as one and accessed through pointers rather than stored in relational table models. Object-oriented database models consist of diverse structures and is quite extensible. This data model was designed to work closely with programs built with Object-oriented programming languages thereby almost making the data and the program operate as one. There is little commercial implementation of this database model as it is still developing. Examples of Object-oriented DBMS include IBM DB4 and DTS/S1.





![Presentation AICT Improved version[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/presentationaictimprovedversion1-241213140004-f34d119f-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)








