DBMS-2.pptx
- 1. Dr. Pradeep Kumar Mallick Associate Professor [II] School of Computer Engineering, Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology (KIIT), Deemed to be University,Odisha Database Management Systems (CS 2004) KALINGA INSTITUTE OF INDUSTRIAL TECHNOLOGY School Of Computer Engineering 4 Credit Lecture Note 02
- 2. ’āś Data model is a collection of conceptual tools for describing data, data relationships, data semantics and consistency constraints. That means a data model provides a way to describe the design of a database. ’ā╝ It is relatively simple representation, usually graphical, of complex real- world data structures. ’ā╝ Data modeling is considered as the most important part of the database design process. 2 Data Model
- 3. ’ā╝ Entity: An entity can be a real-world object, either animate or inanimate, that can be easily identifiable. For example, in a school database, students, teachers, classes, and courses offered can be considered as entities. All these entities have some attributes or properties that give them their identity. ’ā╝ Entity Set: An entity set is a collection of similar types of entities. An entity set may contain entities with attribute sharing similar values. For example, a Students set may contain all the students of a school; likewise a Teachers set may contain all the teachers of a school from all faculties. ’ā╝ Attribute: Entities are represented by means of their properties, called attributes. All attributes have values. For example, a student entity may have name, class, and age as attributes. ’ā╝ Constraints: A constraint is a restriction placed on the data. Constraints are important because they help to ensure data integrity 3 Data Model Basic Building Blocks
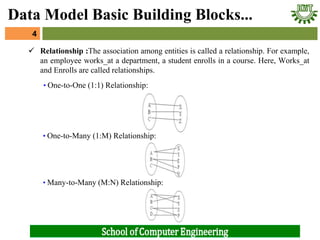
- 4. ’ā╝ Relationship :The association among entities is called a relationship. For example, an employee works_at a department, a student enrolls in a course. Here, Works_at and Enrolls are called relationships. 4 4 Data Model Basic Building Blocks... ŌĆó One-to-One (1:1) Relationship: ŌĆó One-to-Many (1:M) Relationship: ŌĆó Many-to-Many (M:N) Relationship:
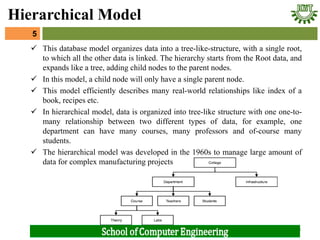
- 5. ’ā╝ This database model organizes data into a tree-like-structure, with a single root, to which all the other data is linked. The hierarchy starts from the Root data, and expands like a tree, adding child nodes to the parent nodes. ’ā╝ In this model, a child node will only have a single parent node. ’ā╝ This model efficiently describes many real-world relationships like index of a book, recipes etc. ’ā╝ In hierarchical model, data is organized into tree-like structure with one one-to- many relationship between two different types of data, for example, one department can have many courses, many professors and of-course many students. ’ā╝ The hierarchical model was developed in the 1960s to manage large amount of data for complex manufacturing projects 5 5 Hierarchical Model
- 6. ’āś Advantages: ’ā╝ Efficient storage for data that have a clear hierarchy ’ā╝ Parent/child relationship promotes conceptual simplicity & data integrity ’ā╝ It is efficient with 1:M relationships ’ā╝ It promotes data sharing ’āś Disadvantages: ’ā╝ It is complex to implement ’ā╝ It is difficult to manage ’ā╝ There are implementation limitations, that means it canŌĆÖt represent M:N relationships ’ā╝ There is no DDL and DML ’ā╝ There is lack of standards 6 Hierarchical ModelŌĆ”
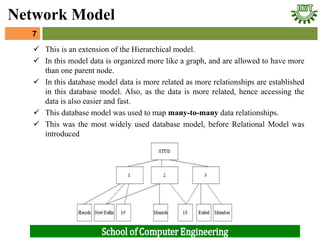
- 7. ’ā╝ This is an extension of the Hierarchical model. ’ā╝ In this model data is organized more like a graph, and are allowed to have more than one parent node. ’ā╝ In this database model data is more related as more relationships are established in this database model. Also, as the data is more related, hence accessing the data is also easier and fast. ’ā╝ This database model was used to map many-to-many data relationships. ’ā╝ This was the most widely used database model, before Relational Model was introduced 7 Network Model
- 8. ’āś Advantages: ’ā╝ It represents complex data relationships better than hierarchical models ’ā╝ It handles more relationship types, such as M: N and multi-parent ’ā╝ Data access is more flexible than hierarchical model ’ā╝ Improved database performance ’ā╝ It includes DDL and DML ’āś Disadvantages: ’ā╝ System complexity limits efficiency ’ā╝ Navigational system yields complex implementation and management ’ā╝ Structural changes require changes in all application programs ’ā╝ Database contains a complex array of pointers that thread through a set of records ’ā╝ Put heavy pressure on programmers due the complex structure ’ā╝ Networks can become chaotic unless planned carefully 8 Network ModelŌĆ”.
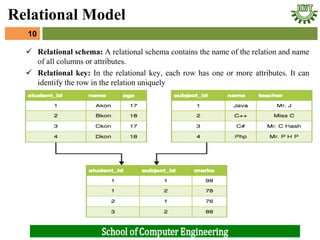
- 9. ’ā╝ In this model, data is organised in two-dimensional tables and the relationship is maintained by storing a common field. ’ā╝ This model was introduced by E.F Codd in 1970, and since then it has been the most widely used database model, infact, we can say the only database model used around the world. ’ā╝ The basic structure of data in the relational model is tables. All the information related to a particular type is stored in rows of that table. ’ā╝ Hence, tables are also known as relations in relational model. ’ā╝ Domain: It contains a set of atomic values that an attribute can take. ’ā╝ Attribute: It contains the name of a column in a particular table. Each attribute Ai must have a domain, dom(Ai) ’ā╝ Relational instance: In the relational database system, the relational instance is represented by a finite set of tuples. Relation instances do not have duplicate tuples. 9 Relational Model
- 10. 10 Relational Model ’ā╝ Relational schema: A relational schema contains the name of the relation and name of all columns or attributes. ’ā╝ Relational key: In the relational key, each row has one or more attributes. It can identify the row in the relation uniquely
- 11. ’āś Advantages: ’ā╝ Changes in a tableŌĆÖs structure do not affect data access or application programs ’ā╝ Tabular view substantially improves conceptual simplicity, thereby promoting easier database design, implementation, management and use ’ā╝ Have referential integrity controls ensure data consistency ’ā╝ RDBMS isolates the end-users from physical level details and improves implementation and management simplicity ’āś Disadvantages: ’ā╝ Conceptual simplicity gives relatively untrained people the tools to use a good system poorly ’ā╝ It may promote islands of information problems as individuals and departments can easily develop their own applications 11 Relational Model
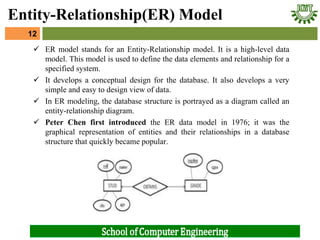
- 12. ’ā╝ ER model stands for an Entity-Relationship model. It is a high-level data model. This model is used to define the data elements and relationship for a specified system. ’ā╝ It develops a conceptual design for the database. It also develops a very simple and easy to design view of data. ’ā╝ In ER modeling, the database structure is portrayed as a diagram called an entity-relationship diagram. ’ā╝ Peter Chen first introduced the ER data model in 1976; it was the graphical representation of entities and their relationships in a database structure that quickly became popular. 12 Entity-Relationship(ER) Model
- 13. ’āś Advantages: ’ā╝ Visual modeling yields exceptional conceptual simplicity ’ā╝ Visual representation makes it an effective communication tool ’ā╝ It is integrated with dominant relational model ’āś Disadvantages: ’ā╝ There is limited constraint representation ’ā╝ There is limited relationship representation ’ā╝ There is no DML ’ā╝ Loss of information content when attributes are removed from entities to avoid crowded displays 13 Entity-Relationship(ER) Model
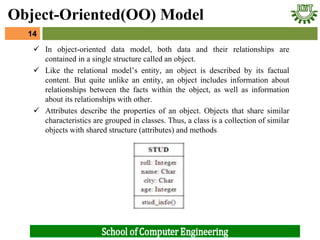
- 14. ’ā╝ In object-oriented data model, both data and their relationships are contained in a single structure called an object. ’ā╝ Like the relational modelŌĆÖs entity, an object is described by its factual content. But quite unlike an entity, an object includes information about relationships between the facts within the object, as well as information about its relationships with other. ’ā╝ Attributes describe the properties of an object. Objects that share similar characteristics are grouped in classes. Thus, a class is a collection of similar objects with shared structure (attributes) and methods 14 Object-Oriented(OO) Model
- 15. ’āś Advantages: ’ā╝ Semantic content is added ’ā╝ Support for complex objects ’ā╝ Visual representation includes semantic content ’ā╝ Inheritance promotes data integrity ’āś Disadvantages: ’ā╝ It is a complex navigational system ’ā╝ High system overheads slow transactions ’ā╝ Slow development of standards caused vendors to supply their own enhancements, thus eliminating a widely accepted standard. 15 Object-Oriented(OO) Model
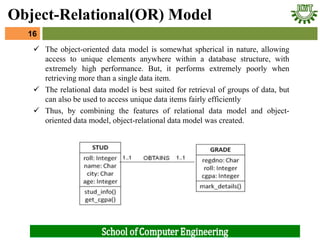
- 16. ’ā╝ The object-oriented data model is somewhat spherical in nature, allowing access to unique elements anywhere within a database structure, with extremely high performance. But, it performs extremely poorly when retrieving more than a single data item. ’ā╝ The relational data model is best suited for retrieval of groups of data, but can also be used to access unique data items fairly efficiently ’ā╝ Thus, by combining the features of relational data model and object- oriented data model, object-relational data model was created. 16 Object-Relational(OR) Model
- 17. ’ā╝ The semi-structured data model permits the specification of data where individual data items of the same type may have different sets of attributes. The XML (Extensible Markup Language) is widely used to represent semi- structured data. It supports unstructured data. 17 Semi-structured Model
- 18. 18
![Dr. Pradeep Kumar Mallick
Associate Professor [II]
School of Computer Engineering,
Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology (KIIT),
Deemed to be University,Odisha
Database Management Systems (CS 2004)
KALINGA INSTITUTE OF INDUSTRIAL
TECHNOLOGY
School Of Computer
Engineering
4 Credit Lecture Note 02](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dbms-2-221101032839-37103ada/85/DBMS-2-pptx-1-320.jpg)