dc ac inverters
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes553 views
1. A variable output voltage can be obtained from an inverter in two ways: by varying the input DC voltage or by adjusting the gain of the inverter using pulse width modulation control. 2. The output of an inverter is theoretically a sine wave but in reality is non-sinusoidal and contains harmonics that can be represented by Fourier series. 3. The fundamental component of the output voltage determines the useful power while harmonic components cause power loss and increased load temperature.
1 of 23
Download to read offline




















Recommended
Inverters (DC-AC)



Inverters (DC-AC)Taimur Ijaz
Ėý
1. An inverter refers to a power electronic device that converts DC input voltages to AC output voltages at the required magnitude and frequency.
2. There are three basic types of dc-ac converters depending on their AC output waveform: square wave, modified sine wave, and pure sine wave.
3. Inverters have applications in adjustable speed AC drives, electric vehicles, induction heating, aircraft power supplies, photovoltaic systems, UPS, and air conditioning units.Inverter PPT.ppt



Inverter PPT.pptAbhishekRanjan17318
Ėý
1. DC-AC converters called inverters change a DC input voltage into a symmetrical AC output voltage of desired magnitude and frequency.
2. Inverters can be single phase or three phase, and are widely used in applications like variable speed motor drives, induction heating, and HVDC power transmission.
3. The main types of inverters are single phase half bridge, single phase full bridge, and three phase inverters, which produce different output voltage waveforms and can be powered by batteries or other DC sources.DcâDc converters



DcâDc convertersBhulku Kalpak
Ėý
The document discusses dc-dc converters and their functions. Dc-dc converters are used to (1) convert a dc input voltage into a regulated dc output voltage against variations, (2) reduce ac voltage ripple on the output, and (3) optionally provide isolation between the input and load. Common types of dc-dc converters include buck, boost, buck-boost, forward, push-pull, half-bridge, full-bridge, flyback, and Cuk converters.A presentation on inverter by manoj



A presentation on inverter by manojIACM SmartLearn Ltd.
Ėý
This document provides information on inverters, including:
- Inverters convert DC input voltage into AC output voltage of desired magnitude and frequency. They are also known as DC-AC converters.
- Inverters can be classified as single-phase or three-phase, and by the type of switching device used (BJT, MOSFET, IGBT, GTO).
- Applications include variable speed AC motors, induction heating, UPS systems. Inputs can be batteries, fuel cells, solar cells.
- Circuit diagrams and operating principles are provided for single-phase half-bridge, full-bridge, and three-phase inverters using 1800 and 1200 conduction modes.Flying Capacitor Multi Level Inverter



Flying Capacitor Multi Level InverterSajid Sheikh
Ėý
It gives the basic Idea about Inverter than moving towards the advantages of Multilevel Inverter .In this PPT main focus on Flying Capacitor Multilevel Inverter.Chopper ppt



Chopper pptrnkiawasthi03
Ėý
A chopper, also known as a DC-DC converter, is a static device that is used to obtain a variable DC voltage from a constant DC voltage source. Choppers are widely used in applications like trolley cars, battery vehicles, motor control, and regenerative braking of DC motors. There are two types - step-down choppers that produce an output voltage lower than the input voltage, and step-up choppers that produce a higher output voltage. A step-down chopper works by using a thyristor switch to alternately connect and disconnect the load from the power supply voltage, generating a chopped output voltage waveform. Choppers are classified into different classes including Class A, B, C, D,DC DC Converter



DC DC ConverterMengstu Fentaw
Ėý
DC-DC converters are circuits that convert a DC voltage to another DC voltage level. They use switching elements like transistors and power switches to efficiently step up or step down voltage. The buck converter is a common DC-DC converter topology that can step down voltage. It uses a switch, inductor, diode, and capacitor. By periodically opening and closing the switch, the inductor filters the output to produce a lower average voltage. The output voltage of an ideal buck converter is equal to the input voltage multiplied by the duty cycle of the switch. Real converters have non-ideal components that cause additional voltage ripple. Proper component selection and design considerations are needed to minimize ripple.Current Source Inverter and Voltage Source Inverter 



Current Source Inverter and Voltage Source Inverter Sadanand Purohit
Ėý
The document discusses two types of inverters - current source inverters (CSI) and voltage source inverters (VSI). It describes the construction and working of CSI, which uses predetermined source current and load impedance to determine output voltage. VSI uses a constant DC input voltage and feedback diodes. The document also covers applications of CSI and VSI, such as use of CSI for AC motor drives due to regenerative capability, and use of VSI in UPS and AC drives. FACTS devices based on VSI are also summarized, including STATCOM, SSSC and UPFC for controlling transmission line parameters.dc to dc-converter



dc to dc-converterStudent
Ėý
This document discusses DC-DC converters known as choppers. It describes two types - step-down choppers and step-up choppers. A step-down chopper uses a thyristor switch to reduce input voltage to a lower output voltage for a load. Waveforms of the output voltage and current are shown. Different classes of choppers - Classes A through E - are defined based on the triggering schemes of the thyristors used. An example calculation is given to determine thyristor conduction period based on input voltage, output voltage, and operating frequency.Resonant Inverters



Resonant Invertersraviarmugam
Ėý
The document discusses different types of resonant pulse inverters. It begins by explaining the disadvantages of traditional pulse-width modulation controlled converters, such as high switching losses and electromagnetic interference. It then introduces resonant pulse converters which minimize these issues by forcing the voltage and current to zero during switching. The document outlines various resonant converter topologies, including series and parallel resonant inverters as well as classes of converters that achieve zero-voltage or zero-current switching. It provides examples of half-bridge and full-bridge configurations for series resonant inverters with both unidirectional and bidirectional switches. Finally, it briefly discusses the operation of parallel resonant inverters.TCSC



TCSCKaransinh Parmar
Ėý
This document provides an overview of the thyristor controlled series capacitor (TCSC). It begins with the basic TCSC scheme and equations showing how the variable inductive reactance XL can change the capacitive reactance XC. It then discusses the impedance characteristics of the TCSC and how the capacitor voltage is reversed by the thyristor controlled reactor (TCR). Next, it examines the TCSC operating in the capacitive and inductive regions and how it can provide phase advance or retard. The document also covers the attainable voltage-current characteristics and harmonic voltage generation in the TCSC. It describes the functional internal control schemes and concludes with notes on design considerations.Facts controller



Facts controllerDebayon Saha
Ėý
This document discusses Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) controllers. It defines FACTS controllers as power electronic devices that control parameters of AC transmission systems. The document describes several types of FACTS controllers including STATCOM, SVC, TCSC, SSSC, and UPFC. It explains how each type of controller works and its benefits such as increasing power transfer capability and network reliability.Pe dual converter ppt



Pe dual converter pptAdani Institute of Infrastructure Engineering College
Ėý
This document discusses dual converters, which comprise two converters - one that performs rectification and the other performs inversion. It begins with an introduction and provides a block diagram. It then explains the principles of operation in both non-circulating and circulating current modes. Four quadrant operation is also discussed. Ideal dual converters have ripple-free output voltage. The document concludes by covering types of dual converters (single and three-phase) and their applications such as controlling DC motor direction and speed.Unified Power Flow Controller(upfc)1



Unified Power Flow Controller(upfc)1JayakalyanReddy
Ėý
The Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) was proposed in 1991 as a device to control real and reactive power flow in AC transmission systems using two voltage sourced converters. The UPFC can independently control parameters like voltage, impedance, and phase angle to regulate power flow. It consists of two back-to-back converters connected by a DC link that allow bidirectional real power flow and independent reactive power control at each converter. The UPFC can perform functions like voltage regulation, series compensation, phase shifting, and multifunctional power flow control by injecting a controlled compensating voltage into the transmission line.ppt on inveters



ppt on invetersUrvashi Khandelwal
Ėý
Goals of a well designed inverter,Application,Types of power conveter,Introduction to inverters,Properties of an ideal inverter, Block diagram of an inverter ,Pulse Width Modulation,Inverter operation
Topic 2 - Switch Realization.pptx



Topic 2 - Switch Realization.pptxVanJasperCastillo
Ėý
The document discusses switch realization in power electronics. It begins with an overview of single-, two-, and four-quadrant switches and applications. It then surveys common power semiconductor devices used to realize switches, including diodes, MOSFETs, BJTs, IGBTs, and thyristors. Key aspects of transistor switching losses are examined for a clamped inductive load. Recovered charge in power diodes is also discussed. Realization of different types of switches using these devices is explored through examples like buck converters.Inverter



Inverterraguprince
Ėý
The document discusses different types of inverters, including half bridge and full bridge single phase inverters, series inverters, parallel inverters, and pulse width modulation (PWM) control methods. Series inverters have commutating components connected in series with the load and operate at high frequencies. Parallel inverters use a commutating capacitor connected in parallel with the load. PWM control varies the pulse width to regulate the output voltage without additional components. Single pulse width modulation controls one device per half cycle, while multiple pulse width modulation uses multiple pulses per half cycle to reduce harmonics.Power electronics Phase Controlled Rectifiers - SCR



Power electronics Phase Controlled Rectifiers - SCRBurdwan University
Ėý
This chapter introduces ideas on phase controlled SCR operated rectifiers. i.e. controlled rectifiers. INVERTERS PRESENTATION



INVERTERS PRESENTATIONRajesh V
Ėý
single phase half bridge inverter, full bridge inverter, parallel inverter, load commutated inverter with working and waveforms.
download and watch the animations. it will be effective.
single phase bridge inverter harmonic analysis.three phase inverter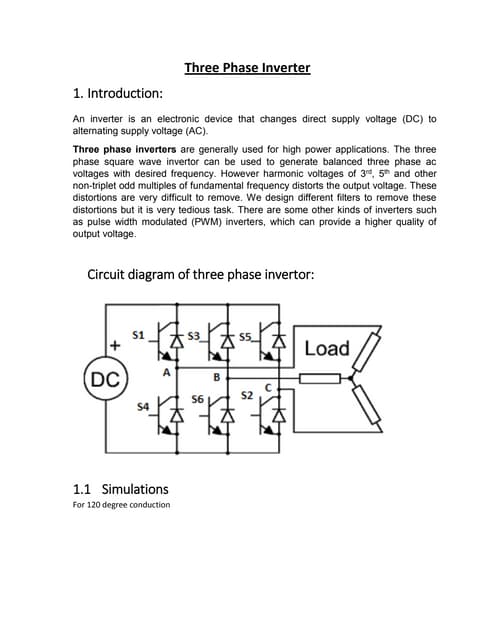



three phase inverterMalik Zaid
Ėý
This document describes a three phase inverter that converts DC voltage to AC voltage. There are two main modes of conduction for a three phase inverter - 180 degree conduction and 120 degree conduction. 180 degree conduction involves three switches being on at a time, while 120 degree conduction only has two switches on at a time. The document provides circuit diagrams and equations to calculate the output voltages under each conduction mode. Waveforms are also shown to illustrate the phase and line voltages.Cycloconverter 



Cycloconverter rohit kumar
Ėý
This document presents information on forced commutated cycloconverters. Cycloconverters directly convert AC power of one frequency to a different frequency. The document discusses types of cycloconverters including single phase to single phase and three phase configurations. It provides circuit diagrams and Simulink models of midpoint and bridge types. Applications include rolling mill drives, ship propulsion, and cement mill drives. Advantages are direct frequency conversion and regeneration capabilities. Disadvantages include complex control and large number of required thyristors. A research paper on cycloconverter-based double-ended microinverters for solar power is also summarized.Pwm techniques for converters



Pwm techniques for convertersABHINAV KUMAR BABUL
Ėý
Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) techniques are used to control output voltages of power converters. There are three main PWM methods: Sine PWM uses a reference sine wave compared to a triangular carrier wave to generate PWM signals; Hysteresis PWM uses a feedback control loop with variable switching frequency to maintain output within a hysteresis band; Space Vector PWM approximates the reference voltage vector using combinations of the eight switching states and their durations to reduce harmonic distortion and improve voltage utilization.Multilevel inverter technology



Multilevel inverter technologygmrit
Ėý
This ppt gives the basic idea about multilevel inverter.this ppt includes
1.Introduction
2.Advantages of multilevel inverters
3.Types of multilevel inverters
4.Working of multilevel inverters
5.Applications.Chapter 5 - DC-AC Conversion.pdf



Chapter 5 - DC-AC Conversion.pdfbenson215
Ėý
This document discusses DC to AC conversion using inverters. It describes various inverter topologies including single phase half bridge and full bridge inverters as well as three phase full bridge inverters. It discusses modulation techniques such as sinusoidal pulse width modulation to generate sinusoidal AC outputs. Examples of applications like motor drives and solar power generation are provided.Per unit system



Per unit systemMuhammad Kamran Shaikh
Ėý
Per unit analysis is used to normalize variables in power systems to avoid difficulties in referring impedances across transformers. It involves choosing base values for voltage, power, impedance and current, then expressing all quantities as ratios of their actual to base values. This allows transformer impedances to be treated as single values regardless of which side they are referred to. It also keeps per unit quantities within a narrow range and clearly shows their relative values. The procedure is demonstrated through an example circuit solved first using single phase and then three phase per unit analysis with the same result.Pulse width modulated inverter



Pulse width modulated inverterVSRAGHU
Ėý
This document discusses a 3-phase PWM inverter. It begins by defining an inverter as an electronic device that converts DC to AC. It then explains that PWM inverters use pulse width modulation technology to control the width of switching pulses and thereby regulate the output AC voltage. The document presents the block diagram of a 3-phase PWM inverter and describes how PWM signals are generated for each phase. It notes that 3-phase PWM inverters are used in applications like solar panels, motor speed control, and HVDC power transmission.Lecture-1 : Introduction to Power Electronics



Lecture-1 : Introduction to Power Electronicsrsamurti
Ėý
This is the first lecture on power electronics. This lecture has been targeted to under-graduate students of electrical and electronics engineering.Variable impedance type series compensators



Variable impedance type series compensatorsgundharchougule1
Ėý
This document discusses two types of variable impedance series compensators: the thyristor-controlled series capacitor (GCSC) and the thyristor-switched series capacitor (TSSC). It explains that the GCSC uses thyristors to control the voltage developed across a fixed capacitor, creating a variable reactive impedance. The TSSC uses thyristors to control the current in a fixed inductor from a constant voltage source, creating a variable reactive admittance. It also covers the operating control schemes for each device and discusses the phenomenon of sub-synchronous resonance.chapter4 DC to AC Converter.ppt



chapter4 DC to AC Converter.pptLiewChiaPing
Ėý
This document summarizes inverters and their operation. It begins with an introduction that defines inverters as devices that convert DC to AC power by switching the DC input voltage in a predetermined sequence. It then discusses the basic principles of inverters including single-phase half-bridge and full-bridge inverter circuits. Fourier series analysis is introduced as a tool to analyze the output waveforms of inverters in terms of harmonic components. The document concludes with a discussion of total harmonic distortion as a measure of output waveform quality.Chapter 4 Inverters.pdf



Chapter 4 Inverters.pdfLiewChiaPing
Ėý
This document summarizes inverters, which convert DC power to AC power by switching the DC input voltage in a predetermined sequence. It describes various types of inverters including single-phase half-bridge and full-bridge inverters, three-phase inverters, and discusses Fourier analysis of inverter output waveforms. Key concepts covered include the generation of output voltages from DC inputs, harmonic analysis using Fourier series, total harmonic distortion, and pulse-width modulation techniques for improving output waveform quality.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
dc to dc-converter



dc to dc-converterStudent
Ėý
This document discusses DC-DC converters known as choppers. It describes two types - step-down choppers and step-up choppers. A step-down chopper uses a thyristor switch to reduce input voltage to a lower output voltage for a load. Waveforms of the output voltage and current are shown. Different classes of choppers - Classes A through E - are defined based on the triggering schemes of the thyristors used. An example calculation is given to determine thyristor conduction period based on input voltage, output voltage, and operating frequency.Resonant Inverters



Resonant Invertersraviarmugam
Ėý
The document discusses different types of resonant pulse inverters. It begins by explaining the disadvantages of traditional pulse-width modulation controlled converters, such as high switching losses and electromagnetic interference. It then introduces resonant pulse converters which minimize these issues by forcing the voltage and current to zero during switching. The document outlines various resonant converter topologies, including series and parallel resonant inverters as well as classes of converters that achieve zero-voltage or zero-current switching. It provides examples of half-bridge and full-bridge configurations for series resonant inverters with both unidirectional and bidirectional switches. Finally, it briefly discusses the operation of parallel resonant inverters.TCSC



TCSCKaransinh Parmar
Ėý
This document provides an overview of the thyristor controlled series capacitor (TCSC). It begins with the basic TCSC scheme and equations showing how the variable inductive reactance XL can change the capacitive reactance XC. It then discusses the impedance characteristics of the TCSC and how the capacitor voltage is reversed by the thyristor controlled reactor (TCR). Next, it examines the TCSC operating in the capacitive and inductive regions and how it can provide phase advance or retard. The document also covers the attainable voltage-current characteristics and harmonic voltage generation in the TCSC. It describes the functional internal control schemes and concludes with notes on design considerations.Facts controller



Facts controllerDebayon Saha
Ėý
This document discusses Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) controllers. It defines FACTS controllers as power electronic devices that control parameters of AC transmission systems. The document describes several types of FACTS controllers including STATCOM, SVC, TCSC, SSSC, and UPFC. It explains how each type of controller works and its benefits such as increasing power transfer capability and network reliability.Pe dual converter ppt



Pe dual converter pptAdani Institute of Infrastructure Engineering College
Ėý
This document discusses dual converters, which comprise two converters - one that performs rectification and the other performs inversion. It begins with an introduction and provides a block diagram. It then explains the principles of operation in both non-circulating and circulating current modes. Four quadrant operation is also discussed. Ideal dual converters have ripple-free output voltage. The document concludes by covering types of dual converters (single and three-phase) and their applications such as controlling DC motor direction and speed.Unified Power Flow Controller(upfc)1



Unified Power Flow Controller(upfc)1JayakalyanReddy
Ėý
The Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) was proposed in 1991 as a device to control real and reactive power flow in AC transmission systems using two voltage sourced converters. The UPFC can independently control parameters like voltage, impedance, and phase angle to regulate power flow. It consists of two back-to-back converters connected by a DC link that allow bidirectional real power flow and independent reactive power control at each converter. The UPFC can perform functions like voltage regulation, series compensation, phase shifting, and multifunctional power flow control by injecting a controlled compensating voltage into the transmission line.ppt on inveters



ppt on invetersUrvashi Khandelwal
Ėý
Goals of a well designed inverter,Application,Types of power conveter,Introduction to inverters,Properties of an ideal inverter, Block diagram of an inverter ,Pulse Width Modulation,Inverter operation
Topic 2 - Switch Realization.pptx



Topic 2 - Switch Realization.pptxVanJasperCastillo
Ėý
The document discusses switch realization in power electronics. It begins with an overview of single-, two-, and four-quadrant switches and applications. It then surveys common power semiconductor devices used to realize switches, including diodes, MOSFETs, BJTs, IGBTs, and thyristors. Key aspects of transistor switching losses are examined for a clamped inductive load. Recovered charge in power diodes is also discussed. Realization of different types of switches using these devices is explored through examples like buck converters.Inverter



Inverterraguprince
Ėý
The document discusses different types of inverters, including half bridge and full bridge single phase inverters, series inverters, parallel inverters, and pulse width modulation (PWM) control methods. Series inverters have commutating components connected in series with the load and operate at high frequencies. Parallel inverters use a commutating capacitor connected in parallel with the load. PWM control varies the pulse width to regulate the output voltage without additional components. Single pulse width modulation controls one device per half cycle, while multiple pulse width modulation uses multiple pulses per half cycle to reduce harmonics.Power electronics Phase Controlled Rectifiers - SCR



Power electronics Phase Controlled Rectifiers - SCRBurdwan University
Ėý
This chapter introduces ideas on phase controlled SCR operated rectifiers. i.e. controlled rectifiers. INVERTERS PRESENTATION



INVERTERS PRESENTATIONRajesh V
Ėý
single phase half bridge inverter, full bridge inverter, parallel inverter, load commutated inverter with working and waveforms.
download and watch the animations. it will be effective.
single phase bridge inverter harmonic analysis.three phase inverter



three phase inverterMalik Zaid
Ėý
This document describes a three phase inverter that converts DC voltage to AC voltage. There are two main modes of conduction for a three phase inverter - 180 degree conduction and 120 degree conduction. 180 degree conduction involves three switches being on at a time, while 120 degree conduction only has two switches on at a time. The document provides circuit diagrams and equations to calculate the output voltages under each conduction mode. Waveforms are also shown to illustrate the phase and line voltages.Cycloconverter 



Cycloconverter rohit kumar
Ėý
This document presents information on forced commutated cycloconverters. Cycloconverters directly convert AC power of one frequency to a different frequency. The document discusses types of cycloconverters including single phase to single phase and three phase configurations. It provides circuit diagrams and Simulink models of midpoint and bridge types. Applications include rolling mill drives, ship propulsion, and cement mill drives. Advantages are direct frequency conversion and regeneration capabilities. Disadvantages include complex control and large number of required thyristors. A research paper on cycloconverter-based double-ended microinverters for solar power is also summarized.Pwm techniques for converters



Pwm techniques for convertersABHINAV KUMAR BABUL
Ėý
Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) techniques are used to control output voltages of power converters. There are three main PWM methods: Sine PWM uses a reference sine wave compared to a triangular carrier wave to generate PWM signals; Hysteresis PWM uses a feedback control loop with variable switching frequency to maintain output within a hysteresis band; Space Vector PWM approximates the reference voltage vector using combinations of the eight switching states and their durations to reduce harmonic distortion and improve voltage utilization.Multilevel inverter technology



Multilevel inverter technologygmrit
Ėý
This ppt gives the basic idea about multilevel inverter.this ppt includes
1.Introduction
2.Advantages of multilevel inverters
3.Types of multilevel inverters
4.Working of multilevel inverters
5.Applications.Chapter 5 - DC-AC Conversion.pdf



Chapter 5 - DC-AC Conversion.pdfbenson215
Ėý
This document discusses DC to AC conversion using inverters. It describes various inverter topologies including single phase half bridge and full bridge inverters as well as three phase full bridge inverters. It discusses modulation techniques such as sinusoidal pulse width modulation to generate sinusoidal AC outputs. Examples of applications like motor drives and solar power generation are provided.Per unit system



Per unit systemMuhammad Kamran Shaikh
Ėý
Per unit analysis is used to normalize variables in power systems to avoid difficulties in referring impedances across transformers. It involves choosing base values for voltage, power, impedance and current, then expressing all quantities as ratios of their actual to base values. This allows transformer impedances to be treated as single values regardless of which side they are referred to. It also keeps per unit quantities within a narrow range and clearly shows their relative values. The procedure is demonstrated through an example circuit solved first using single phase and then three phase per unit analysis with the same result.Pulse width modulated inverter



Pulse width modulated inverterVSRAGHU
Ėý
This document discusses a 3-phase PWM inverter. It begins by defining an inverter as an electronic device that converts DC to AC. It then explains that PWM inverters use pulse width modulation technology to control the width of switching pulses and thereby regulate the output AC voltage. The document presents the block diagram of a 3-phase PWM inverter and describes how PWM signals are generated for each phase. It notes that 3-phase PWM inverters are used in applications like solar panels, motor speed control, and HVDC power transmission.Lecture-1 : Introduction to Power Electronics



Lecture-1 : Introduction to Power Electronicsrsamurti
Ėý
This is the first lecture on power electronics. This lecture has been targeted to under-graduate students of electrical and electronics engineering.Variable impedance type series compensators



Variable impedance type series compensatorsgundharchougule1
Ėý
This document discusses two types of variable impedance series compensators: the thyristor-controlled series capacitor (GCSC) and the thyristor-switched series capacitor (TSSC). It explains that the GCSC uses thyristors to control the voltage developed across a fixed capacitor, creating a variable reactive impedance. The TSSC uses thyristors to control the current in a fixed inductor from a constant voltage source, creating a variable reactive admittance. It also covers the operating control schemes for each device and discusses the phenomenon of sub-synchronous resonance.Similar to dc ac inverters (20)
chapter4 DC to AC Converter.ppt



chapter4 DC to AC Converter.pptLiewChiaPing
Ėý
This document summarizes inverters and their operation. It begins with an introduction that defines inverters as devices that convert DC to AC power by switching the DC input voltage in a predetermined sequence. It then discusses the basic principles of inverters including single-phase half-bridge and full-bridge inverter circuits. Fourier series analysis is introduced as a tool to analyze the output waveforms of inverters in terms of harmonic components. The document concludes with a discussion of total harmonic distortion as a measure of output waveform quality.Chapter 4 Inverters.pdf



Chapter 4 Inverters.pdfLiewChiaPing
Ėý
This document summarizes inverters, which convert DC power to AC power by switching the DC input voltage in a predetermined sequence. It describes various types of inverters including single-phase half-bridge and full-bridge inverters, three-phase inverters, and discusses Fourier analysis of inverter output waveforms. Key concepts covered include the generation of output voltages from DC inputs, harmonic analysis using Fourier series, total harmonic distortion, and pulse-width modulation techniques for improving output waveform quality.Ppt 2



Ppt 2rnkiawasthi03
Ėý
An inverter converts DC input voltage into AC output voltage. There are various types of inverters including single-phase and three-phase inverters. Single-phase inverters include half-bridge and full-bridge configurations. Current source inverters directly control AC current instead of voltage. They use thyristors and commutating capacitors to generate quasi-square wave output current from a constant DC current source.Unit2



Unit2johny renoald
Ėý
This document discusses different types of phase controlled converters including single-phase and three-phase semiconverters, full converters, and dual converters. It provides equations and diagrams to describe the operation and analyze the performance of single-phase semiconverters and full converters with resistive-inductive loads. It also describes the operation of a three-phase half-wave converter with continuous and constant load current.Unit-2 AC-DC converter 



Unit-2 AC-DC converter johny renoald
Ėý
This document discusses various types of phase controlled converters including single-phase and three-phase semiconverters, full converters, and dual converters. It provides equations for the average and RMS output voltage of single-phase converters with resistive and RL loads. It also derives an expression for the average output voltage of a three-phase half wave converter with continuous and constant load current. Key aspects of three-phase half wave, full wave, and dual converters are summarized.chapter_2 AC to DC Converter.pptx



chapter_2 AC to DC Converter.pptxLiewChiaPing
Ėý
This document discusses single-phase and three-phase rectifiers. It describes how a single-phase half-wave rectifier works by only allowing current to flow during one half of the AC cycle. Waveforms are provided for the voltage and current. When an inductive load is used, the current remains continuous. Performance parameters for rectifiers include efficiency, form factor, ripple factor, and total harmonic distortion. Three-phase bridge rectifiers are also covered.3 Basic Electronics 3



3 Basic Electronics 3Kavin Paul
Ėý
The document provides an overview of basic electronics concepts including:
- Ohm's law defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
- Circuit diagrams use symbols to represent components like batteries, resistors, and capacitors connected by wires.
- Resistors can be connected in series or parallel configurations which changes how voltage and current are distributed.
- Capacitors store charge and can be used to filter signals with resistor-capacitor circuits functioning as low-pass or high-pass filters.
- Inductors involve relationships between voltage, current, and inductance and can also be used in filter circuits.07 basic-electronics



07 basic-electronicsSagar Bagwe
Ėý
The document provides an overview of basic electronics concepts including:
1) Ohm's law defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in circuits.
2) Schematics use symbols to represent circuit elements and show how they are connected.
3) Resistors in series and parallel follow specific rules to calculate total resistance.
4) Capacitors store charge and their behavior changes with frequency based on impedance.4. Rectifier.pptx



4. Rectifier.pptxDHANUSHKUMARKS
Ėý
A rectifier converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) using diodes. There are two main types: half-wave and full-wave rectifiers. Half-wave rectifiers use a single diode and only conduct during one half of the AC cycle, resulting in lower output. Full-wave rectifiers use either a center-tapped transformer or diode bridge to conduct on both halves of the cycle, providing higher efficiency and output. Rectifiers are used in applications that require DC power such as battery chargers, DC power supplies, welders, and motor drives.VCO_W.pdf VCO con IC aplicaciones del oscilador



VCO_W.pdf VCO con IC aplicaciones del osciladorJuan Pablo Martinez
Ėý
VCO_W.pdf VCO con IC aplicaciones del osciladorEe6378 linear regulators



Ee6378 linear regulatorsssuser2038c9
Ėý
The document discusses linear voltage regulators and their components. It describes voltage regulators as electronic circuits that provide a stable output voltage from an unregulated input supply. It then discusses the major functions, characteristics, and types of linear regulators including shunt and series regulators. Specific examples of zener diode and series regulators are analyzed in detail.fd6790bc-9642-4e63-8a17-f24f2ce7a6d9.pptx



fd6790bc-9642-4e63-8a17-f24f2ce7a6d9.pptxnagibmuhammad3
Ėý
this power point containts about inverter, an item that convert dc to ac electricity, it consist three part of stage, the first stage tells us about how to convert dc electricity to ac electricityThe Class-D Amplifier



The Class-D AmplifierTsuyoshi Horigome
Ėý
The document summarizes the operation of a class-D amplifier. It describes how class-D amplifiers use transistors as switches that are either fully on or fully off to achieve high efficiency. A comparator compares an audio signal to a high frequency triangle wave to generate a pulse width modulated square wave. A passive filter converts this into an analog output. Class-D amplifiers can be operated in a bridged configuration to increase output power without increasing voltage. Negative feedback is also used to improve performance.Chapter 20



Chapter 20Tha Mike
Ėý
The document discusses quasi-resonant converters and the half-wave zero-current-switching quasi-resonant switch cell. The switch cell uses a small resonant inductor and capacitor to achieve zero-current switching of the transistor. It operates in four subintervals per switching period: 1) transistor on, 2) resonant ringing, 3) capacitor discharging, 4) diode on. Mathematical analysis determines the waveforms and durations of each subinterval. Averaging the switch cell currents and voltages gives the conversion ratio, allowing the cell to be analyzed and incorporated into converter circuits.5



5Ramesh Kumar
Ėý
This document provides an overview of DC to AC converters known as inverters. It discusses various types of inverters including voltage source inverters and current source inverters. It covers topics such as commutation types, single phase and three phase inverter circuit configurations, quantitative analysis of output voltages, and methods for controlling output voltages. The document also discusses connecting multiple inverters in series to generate higher voltage output waveforms and the use of multi-level inverters to reduce harmonic distortion.Recently uploaded (20)
How Engineering Model Making Brings Designs to Life.pdf



How Engineering Model Making Brings Designs to Life.pdfMaadhu Creatives-Model Making Company
Ėý
This PDF highlights how engineering model making helps turn designs into functional prototypes, aiding in visualization, testing, and refinement. It covers different types of models used in industries like architecture, automotive, and aerospace, emphasizing cost and time efficiency.AI, Tariffs and Supply Chains in Knowledge Graphs



AI, Tariffs and Supply Chains in Knowledge GraphsMax De Marzi
Ėý
How tarrifs, supply chains and knowledge graphs combine.Unit II: Design of Static Equipment Foundations



Unit II: Design of Static Equipment FoundationsSanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon
Ėý
Design of Static Equipment, that is vertical vessels foundation.Env and Water Supply Engg._Dr. Hasan.pdf



Env and Water Supply Engg._Dr. Hasan.pdfMahmudHasan747870
Ėý
Core course, namely Environment and Water Supply Engineering. Full lecture notes are in book format for the BSc in Civil Engineering program. Integration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...



Integration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...ASHISHDESAI85
Ėý
Combining 3D printing with Internet of Things (IoT) enables the creation of smart, connected, and customizable objects that can monitor, control, and optimize their performance, potentially revolutionizing various industries. oT-enabled 3D printers can use sensors to monitor the quality of prints during the printing process. If any defects or deviations from the desired specifications are detected, the printer can adjust its parameters in real time to ensure that the final product meets the required standards.15. Smart Cities Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New Utopia.pdf



15. Smart Cities Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New Utopia.pdfNgocThang9
Ėý
Smart Cities Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New UtopiaUNIT 1FUNDAMENTALS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS.pptx



UNIT 1FUNDAMENTALS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS.pptxKesavanT10
Ėý
UNIT 1FUNDAMENTALS OF OPERATING SYSTEMS.pptxLessons learned when managing MySQL in the Cloud



Lessons learned when managing MySQL in the CloudIgor Donchovski
Ėý
Managing MySQL in the cloud introduces a new set of challenges compared to traditional on-premises setups, from ensuring optimal performance to handling unexpected outages. In this article, we delve into covering topics such as performance tuning, cost-effective scalability, and maintaining high availability. We also explore the importance of monitoring, automation, and best practices for disaster recovery to minimize downtime.US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
Ėý
Preface: The ReGenX Generator innovation operates with a US Patented Frequency Dependent Load Current Delay which delays the creation and storage of created Electromagnetic Field Energy around the exterior of the generator coil. The result is the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs any magnitude of Positive Electro-Mechanical Work at infinite efficiency on the generator's Rotating Magnetic Field, increasing its Kinetic Energy and increasing the Kinetic Energy of an EV or ICE Vehicle to any magnitude without requiring any Externally Supplied Input Energy. In Electricity Generation applications the ReGenX Generator innovation now allows all electricity to be generated at infinite efficiency requiring zero Input Energy, zero Input Energy Cost, while producing zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions, zero Air Pollution and zero Nuclear Waste during the Electricity Generation Phase. In Electric Motor operation the ReGen-X Quantum Motor now allows any magnitude of Work to be performed with zero Electric Input Energy.
Demonstration Protocol: The demonstration protocol involves three prototypes;
1. Protytpe #1, demonstrates the ReGenX Generator's Load Current Time Delay when compared to the instantaneous Load Current Sine Wave for a Conventional Generator Coil.
2. In the Conventional Faraday Generator operation the created Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Negative Work at infinite efficiency and it reduces the Kinetic Energy of the system.
3. The Magnitude of the Negative Work / System Kinetic Energy Reduction (in Joules) is equal to the Magnitude of the created Electromagnetic Field Energy (also in Joules).
4. When the Conventional Faraday Generator is placed On-Load, Negative Work is performed and the speed of the system decreases according to Lenz's Law of Induction.
5. In order to maintain the System Speed and the Electric Power magnitude to the Loads, additional Input Power must be supplied to the Prime Mover and additional Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft.
6. For example, if 100 Watts of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >100 Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
7. If 1 MW of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >1 MW Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
8. Generally speaking the ratio is 2 Watts of Mechanical Input Power to every 1 Watt of Electric Output Power generated.
9. The increase in Drive Shaft Mechanical Input Power is provided by the Prime Mover and the Input Energy Source which powers the Prime Mover.
10. In the Heins ReGenX Generator operation the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Positive Work at infinite efficiency and it increases the Kinetic Energy of the system.Engineering at Lovely Professional University (LPU).pdf



Engineering at Lovely Professional University (LPU).pdfSona
Ėý
LPUâs engineering programs provide students with the skills and knowledge to excel in the rapidly evolving tech industry, ensuring a bright and successful future. With world-class infrastructure, top-tier placements, and global exposure, LPU stands as a premier destination for aspiring engineers.US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
Ėý
Preface: The ReGenX Generator innovation operates with a US Patented Frequency Dependent Load
Current Delay which delays the creation and storage of created Electromagnetic Field Energy around
the exterior of the generator coil. The result is the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field
Energy performs any magnitude of Positive Electro-Mechanical Work at infinite efficiency on the
generator's Rotating Magnetic Field, increasing its Kinetic Energy and increasing the Kinetic Energy of
an EV or ICE Vehicle to any magnitude without requiring any Externally Supplied Input Energy. In
Electricity Generation applications the ReGenX Generator innovation now allows all electricity to be
generated at infinite efficiency requiring zero Input Energy, zero Input Energy Cost, while producing
zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions, zero Air Pollution and zero Nuclear Waste during the Electricity
Generation Phase. In Electric Motor operation the ReGen-X Quantum Motor now allows any
magnitude of Work to be performed with zero Electric Input Energy.
Demonstration Protocol: The demonstration protocol involves three prototypes;
1. Protytpe #1, demonstrates the ReGenX Generator's Load Current Time Delay when compared
to the instantaneous Load Current Sine Wave for a Conventional Generator Coil.
2. In the Conventional Faraday Generator operation the created Electromagnetic Field Energy
performs Negative Work at infinite efficiency and it reduces the Kinetic Energy of the system.
3. The Magnitude of the Negative Work / System Kinetic Energy Reduction (in Joules) is equal to
the Magnitude of the created Electromagnetic Field Energy (also in Joules).
4. When the Conventional Faraday Generator is placed On-Load, Negative Work is performed and
the speed of the system decreases according to Lenz's Law of Induction.
5. In order to maintain the System Speed and the Electric Power magnitude to the Loads,
additional Input Power must be supplied to the Prime Mover and additional Mechanical Input
Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft.
6. For example, if 100 Watts of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator,
an additional >100 Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive
Shaft by the Prime Mover.
7. If 1 MW of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >1
MW Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the
Prime Mover.
8. Generally speaking the ratio is 2 Watts of Mechanical Input Power to every 1 Watt of Electric
Output Power generated.
9. The increase in Drive Shaft Mechanical Input Power is provided by the Prime Mover and the
Input Energy Source which powers the Prime Mover.
10. In the Heins ReGenX Generator operation the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field
Energy performs Positive Work at infinite efficiency and it increases the Kinetic Energy of the
system.
decarbonization steel industry rev1.pptx



decarbonization steel industry rev1.pptxgonzalezolabarriaped
Ėý
Webinar Decarbonization steel industryWater Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
Ėý
Welcome to the March 2025 issue of WIPAC Monthly the magazine brought to you by the LinkedIn Group WIPAC Monthly.
In this month's edition, on top of the month's news from the water industry we cover subjects from the intelligent use of wastewater networks, the use of machine learning in water quality as well as how, we as an industry, need to develop the skills base in developing areas such as Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence.
Enjoy the latest editionIndustrial Valves, Instruments Products Profile



Industrial Valves, Instruments Products Profilezebcoeng
Ėý
Weâre excited to share our product profile, showcasing our expertise in Industrial Valves, Instrumentation, and Hydraulic & Pneumatic Solutions.
We also supply API-approved valves from globally trusted brands, ensuring top-notch quality and internationally certified solutions. Letâs explore valuable business opportunities together!
We specialize in:
âĒ Industrial Valves (Gate, Globe, Ball, Butterfly, Check)
âĒ Instrumentation (Pressure Gauges, Transmitters, Flow Meters)
âĒ Pneumatic Products (Cylinders, Solenoid Valves, Fittings)
As authorized partners of trusted global brands, we deliver high-quality solutions tailored to meet your industrial needs with seamless support.US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
Ėý
US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
Ėý
Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdf



Water Industry Process Automation & Control Monthly - March 2025.pdfWater Industry Process Automation & Control
Ėý
dc ac inverters
- 1. A variable output voltage may be obtained in two ways : 1. By varying the input dc voltage 2. By adjusting the gain of the inverter, usually done by PWM control. dc to ac converter (Inverter) It is a variable voltage ac source obtained from a fixed voltage dc source. Theoretically the output is a SINE wave. In real life the output is non- sinusoidal and contains harmonics.
- 2. Single phase half bridge inverter Vi t VS/2 VO t VS/2 T/2 T R Chopper VO + _ Chopper 2 V S 2 V S T/2 VS/2 ïš ïš ïš ïŧ ïđ ïŠ ïŠ ïŠ ïŦ ïĐ ï· ïļ ïķ ï§ ïĻ ïĶ ï ïŦ ï· ïļ ïķ ï§ ïĻ ïĶ ï― ïē ïē dt dt T 2 T 2 s 2 T 0 2 s s m r 2 V 2 V T 1 V The output rms voltage is given by 2 V V s o ï―
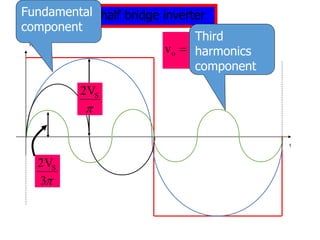
- 3. Single phase half bridge inverter VO t VS/2 T/2 T T/2 VS/2 Here we see that the output voltage wave is not a pure Sine wave. It can be represented as sum of n numbers of sine waves by Fourierâs series. t n n n ï· ï° sin V 2 v 5 , 3 , 1 s o ïĨ ïĩ ï― ï― ,.. 4 , 2 for , 0 vo ï― ï― n
- 4. Single phase half bridge inverter Vo t t n n n ï· ï° sin V 2 v 5 , 3 , 1 s o ïĨ ïĩ ï― ï― ï° S 2V ï° 3 2VS Fundamental component Third harmonics component
- 5. Single phase half bridge inverter VO t VS/2 T/2 T T/2 VS/2 t n n n ï· ï° sin V 2 v 5 , 3 , 1 s o ïĨ ïĩ ï― ï― For n=1, the fundamental component is s s 1 V 45 . 0 2 V 2 V ï― ïī ï― ï° t ï· ï° sin V 2 v s 1 ï― the rms fundamental component is
- 6. Single phase half bridge inverter VO t VS/2 T/2 T T/2 VS/2 In the output the power due to fundamental component is the useful power. s s 1 V 45 . 0 2 V 2 V ï― ïī ï― ï° The power due to harmonic components is dissipated as heat and increases the load temperature.
- 7. Single phase half bridge inverter The quality of the inverter output is evaluated by some parameters. Harmonic Factor of nth harmonic, HFn 1 n n V V HF ï― Total Harmonic distortion, THD ïĨ ïĩ ï― ï― 2,3 n 2 n 1 V V 1 THD Distortion Factor, DF ïĨ ïĩ ï― ï― 2,3 n 2 2 n 1 n V V 1 DF
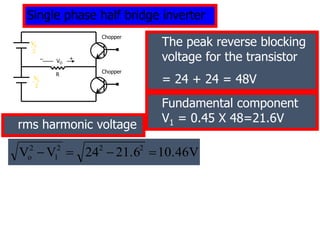
- 8. Single phase half bridge inverter Numerical Example : The dc input voltage of a single phase half bridge rectifier is 48 volt. It is supplying power to a 2.4ï resistor. Find (i) output voltage (ii) Fundamental component of output voltage (iii) output power (iv) peak and average current in each transistor (iv) peak reverse blocking voltage of each transistor (v) THD (vi) DF Given VS =48V and RL =2.4 ï Output voltage Vo=Vs/2=24V Output current Io=24/2.4=10A Output Power VoX Io=24X10=240W Each transistor conducts for 50% of time Transistor current = 10X0.5=5A
- 9. Single phase half bridge inverter The peak reverse blocking voltage for the transistor = 24 + 24 = 48V R Chopper VO + _ Chopper 2 V S 2 V S Fundamental component V1 = 0.45 X 48=21.6V rms harmonic voltage 10.46V 21.6 24 V V 2 2 2 1 2 o ï― ï ï― ï
- 10. R VS VO ï·t V Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 VB ï·t Q3 and Q4 Single phase bridge inverter VB ï·t Q1 and Q2 Vi ï·t VS H Bridge
- 11. Single phase bridge inverter Vi t VS VO t VS T/2 T T/2 VS ïĻ ïĐ ïĻ ïĐ ïš ïš ïš ïŧ ïđ ïŠ ïŠ ïŠ ïŦ ïĐ ï ïŦ ï― ïē ïē dt dt T 2 T 2 s 2 T 0 2 s s m r V V T 1 V The output rms voltage is given by s o V V ï― Students must do the integration in detail and find the result
- 12. VS VO t V Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 VB t Q3 and Q4 Single phase bridge inverter VB t Q1 and Q2 Vi t VS Inductive Load RL IL t IL
- 13. Single phase bridge inverter Vi t VS VO t VS T/2 T T/2 VS The frequency of the output voltage is given by T 1 f ï― Frequency can be chosen from the time period of the base signal
- 14. Single phase bridge inverter Vi t VS VO t VS T/2 T T/2 VS s o V V ï― Control of output voltage Single pulse width modulation Multiple pulse width modulation Sinusoidal pulse width modulation Modified Sinusoidal pulse width modulation Phase displacement control
- 15. Single phase bridge inverter Vi t VS Control of output voltage Single pulse width modulation VO ï·t V VB ï·t Q3 and Q4 VB ï·t Q1 and Q2 VO ï·t Vs VB ï·t VB ï·t Q1 and Q2 Q3 and Q4 (ï°-ïĪ)/2 0 ï° 2ï° The rms output voltage ïĻ ïĐ ïĻ ïĐ ïš ïš ïš ïŧ ïđ ïŠ ïŠ ïŠ ïŦ ïĐ ï ïŦ ï― ïē ïē ïŦ ï ïŦ ï dt dt 2 3 2 3 2 s 2 2 2 s s m r V V 2 1 V ïĪ ï° ïĪ ï° ïĪ ï° ïĪ ï° ï° ïĪ ïĪ ï° ïĪ S s m r V V ï― The output voltage can be controlled by controlling the value of ïĪ
- 16. Single phase bridge inverter Vi t VS Control of output voltage Multiple pulse width modulation VO ï·t Vs VB ï·t VB ï·t 0 ï° 2ï° ï° ïĪ p V V S s m r ï― ïĪ ïĪ Is the width of single pulse p Is the number of pulses per half cycle ïĪ and p both can be adjusted to control the output voltage
- 17. Single phase bridge inverter Vi t VS VO t VB t VB t 0 ï° 2ï° Q1 and Q2 Q3 and Q4 ïĨ ï― ï― 3 , 2 , 1 S s m r V V m m ï° ïĪ The duration of individual pulse can be adjusted to different desired values, so that the lower order harmonics are eliminated and a pure/near sine wave could be obtained
- 18. Modified PWM inververter VO t VB t 10ms 10ms 50Hz f ï― Suppose Carrier frequency =20kHz No of pulses per 10ms = 200 VB t VB t All the pulses are present 11111111 Alternate pulses are present 1010101010 pulses at desired pattern 1011011101101 Keep on trying with different patterns of pulses until a (i)sine wave of desired (ii)frequency and (iii)voltage magnitude is obtained.
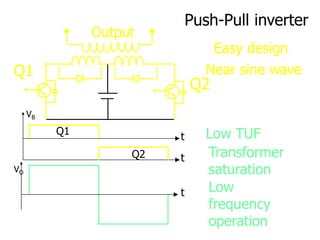
- 19. Push-Pull inverter Q1 Q2 Q1 t Q2 t VB Output Easy design Near sine wave t VO Low TUF Transformer saturation Low frequency operation
- 21. Three phase inverter Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Primary A Primary B Primary C Q5 Q6 Q7 Q8 Q9 Q10 Q11 Q12
- 22. Three phase inverter firing sequence 0 1800 3600 T t t t t t t VB t Q3 and Q4 1200 1200 Q5 and Q6 Q9 and Q10 Q7 and Q8 Q11 and Q12 Q11 and Q12 600 Q1 and Q2 Sequence : Q1 and Q2 Q11 and Q12 Q5 and Q6 Q3 and Q4 Q9 and Q10 Q7 and Q8
- 23. Three phase inverter output voltage Primary side 0 1800 3600 T t t t VP t Phase A Phase B Phase C 1200 1200










