Deciduous maxillary & mandibular 2 nd molar
- 1. DECIDUOUS MAXILLARY 2ND MOLAR Made by: Jubin Babu, 3rd year BDS
- 3. BUCCAL ASPECT  The characteristics resembles those of the permanent maxillary 1st molar, but it is smaller  The buccal view of this tooth shows two well-defined buccal cusps with a buccal developmental groove between them.  The crown is narrow at the cervix in comparison with its M-D measurement at the contact areas.  The crown is much larger than that of the first primary molar.
- 4. Buccal aspect contd..  The root are slender, are much longer and heavier than those of maxillary first molar.  The point of bifurcation between the buccal roots is close to the cervical lone of the crown.  The two buccal cusp are more nearly equal in size and development than those of permanent maxillary 1st molar.
- 5. LINGUAL ASPECT Lingually , the crown shows the following three cusps; 1. The mesiolingual cusp, which is large and well developed 2. The distolingual cusp, which is well developed (more than primary 1st molar) and 3. A third supplemental cusp, which is apical to the mesiolingual cusp sometimes called the tubercle of carabelli , or the fifth cusp
- 6. Lingual aspect contd..  A well-defined developmental groove separates the mesiolingual cusp from the distolingual cusp and connects with the developmental groove, which outlines the fifth cusp.  All three roots are visible from this aspect.  Lingual root is large and thick in comparison with other two roots.
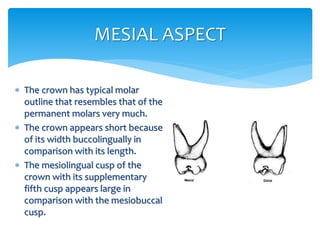
- 7. MESIAL ASPECT  The crown has typical molar outline that resembles that of the permanent molars very much.  The crown appears short because of its width buccolingually in comparison with its length.  The mesiolingual cusp of the crown with its supplementary fifth cusp appears large in comparison with the mesiobuccal cusp.
- 8. Mesial aspect contd.  Mesiobucaal root from this aspect is broad and flat.  The lingual root has somewhat same curvature as of 1st molar.  The mesiobuccal root extends lingually far out beyond the crown outline.  The point of bifurcation between the mesiobuccal root and the lingual root is 2 or 3 mm apical to the cervical line of the crown
- 9. DISTAL ASPECT  From both the distal and the mesial aspect the outline of the crown lingually creates a smooth, rounded line, whereas a line describing the buccal surface is almost straight from the crest of curvature to the tip of the buccal cusp.  The distobuccal cusp and the distolingual cusp are about the same in length. The cervical line is approximately straight , as was found mesially.
- 10. Distal aspect contd..  All three roots are seen from this aspect, although only apart of the outline of mesiobuccal root may be seen, since the distobuccal root is superimposed over it.  The distobuccal root is shorter and narrower than the other roots.  The point of bifurcation between the distobuccal root and the lingual root is more apical in location than any of the other point of bifurcation.
- 11. OCCLUSAL ASPECT  From the occlusal aspect, the tooth resemble the permanent first molar.  It is somewhat rhomboidal and has four well developed cusp: mesiobuccal, distobuccal, mesiolingual, distolingual and fifth supplemental cusp  The buccal surface is rather flat with the developmental groove between the cusp less marked than that found on the first permanent molar.
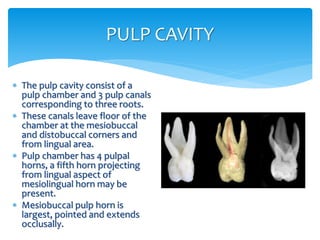
- 12. PULP CAVITY  The pulp cavity consist of a pulp chamber and 3 pulp canals corresponding to three roots.  These canals leave floor of the chamber at the mesiobuccal and distobuccal corners and from lingual area.  Pulp chamber has 4 pulpal horns, a fifth horn projecting from lingual aspect of mesiolingual horn may be present.  Mesiobuccal pulp horn is largest, pointed and extends occlusally.
- 13.  Mesiolingual pulp horn is second in size, when combined with fifth horn it presents a bulky appearance.  Distobuccal pulp horn is third in size, joining mesiolingual pulp horn as slight elevation.  Distolingual pulp horn is shortest and extends only slightly above occlusal level.
- 14. DECIDUOUS MANDIBULAR 2ND MOLAR It has characteristics that resemble those of the permanent mandibular first molar, although its dimensions differ.
- 15. BUCCAL ASPECT  How it differs from first molars?  It has a narrow M-D calibration at the cervical portion of the crown than at contact level.  The mandibular first permanent molar, accordingly, is wider at the cervical portion.  The roots are slender and long.  They have a characteristic flare mesiodistally at middle and apical thirds.  The point of bifurcation of the roots starts immediately below the CEJ.
- 16. LINGUAL ASPECT  Two cusps of almost equal dimensions seen, a short, lingual groove is between them.  The cervical line is relatively straight.  The mesial portion of the crown seems to be a little higher than the distal portion, thus appears tipped distally.
- 17. MESIAL ASPECT  Outline of the crown resembles permanent mandibular first molar.  The crest of contour buccally is more prominent  Marginal ridge is high  the lingual cusp is longer, or higher, than the buccal cusp.  The cervical line is regular  The mesial root is unusually broad and flat with a blunt & apex sometimes serrated
- 18. DISTAL ASPECT  The crown is not as wide distally as it is mesially; therefore, the mesiobuccal and distobuccal cusp from the distal aspect.  The distolingual cusp appears well developed, and the triangular ridge is seen over the distal marginal ridge.  The distal marginal ridge dips down more sharply and is shorter buccolingually than the mesial marginal ridge.  This cervical line of the crown is regular
- 20. Distal aspect contd..  The distal root is almost as broad as the mesial root is flattened on the distal surface.  The distal root tapers more at the apical end than does the mesial root
- 21. OCCLUSAL ASPECT  The occlusal outline is somewhat rectangular  The three buccal cusps are similar is size.  The two lingual cusps are also equally matched.  Well-defined triangular ridges seen  The distal triangular fossa is not as well defined as the mesial triangular fossa.  The mesial marginal ridge is better developed and more pronounced than the distal marginal ridge
- 22. PULP CAVITY  Pulp cavity is made up of a chamber & usually 3 pulp canals.  The two mesial pulp canals are confluent as they leave floor of pulp chamber through a common orifice.  Distal canal is constricted in the centre.
- 23.  Pulp chamber has 5 pulpal horns corresponding to 5 cusps.  Mesiobuccal and mesiolingual pulp horns are largest.  Distobuccal horn is smaller than mesial horns.  The distal horn is shortest and smallest occupying a position distal to distobuccal horn.
- 24. How its different from permanent ?  In the deciduous molar the mesiobuccal, distobuccal and distal cusp are almost equal in size and development.  The distal cusp of the permanent molar is smaller than the other two.  Because of the small buccal cusps, the deciduous tooth crown is narrower buccolingually, in comparison with its mesiodistal measurement , than is the permanent tooth.