Decimation in Time
- 1. Decimation-In-Time Suraj Kumar Saini ID: 2015KUEC2015 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Information Technology Kota Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 1 / 13
- 2. Overview 1 Discrete Fourier Transform 2 Decimation-In-Time 3 Radix-2 DFT Algorithm 4 ButterïŽy Structure 5 Complexity in DIT 6 Inverse Discrete Fourier Transform Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 2 / 13
- 3. Discrete Fourier Transform The DFT pair was given as : X[k] = Nâ1 n=0 x[n]eâj(2Ï/N)kn x[n] = 1 N Nâ1 k=0 X[k]ej(2Ï/N)kn Baseline for computational complexity: Each DFT coeïŽcient requires N complex multiplications N-1 complex additions All N DFT coeïŽcients require N2 complex multiplications N(N-1) complex additions Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 3 / 13
- 4. Continue... Most fast methods are based on symmetry properties Symmetry: W k N [N â n] = W âkn N = (W kn N )â Periodicity in n and k: W kn N = W k[n+N] N = W [k+N]n N Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 4 / 13
- 5. Decimation-In-Time DIT algorithm is used to calculate the DFT of a N-point sequence. First step of process of decimation is splitting a sequence in smaller sequences. A sequence of 16 numbers can be splitted in 2 sequences of 8. Further, Each sequence of 8 can be be splitted in two sequences of 4. Subsequently each sequence of 4 can be splitted in two sequences of two. Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 5 / 13
- 6. Decimation-In-Time Separate x[n] into two sequence of length N/2 sequence. Even indexed samples in the ïŽrst sequence Odd indexed samples in the other sequence X[k] = Nâ1 n=0 x[n]eâj(2Ï/N)kn = Nâ1 n,even x[n]eâj(2Ï/N)kn + Nâ1 n,odd x[n]eâj(2Ï/N)kn Substitute variables n=2r for n even and n=2r+1 for odd X[k] = N/2â1 r=0 x[2r]W 2rk N + N/2â1 r=0 x[2r + 1]W (2r+1)k N = G[k] + W k NH[k] Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 6 / 13
- 7. 8-point Radix-2 DFT Algorithm Repeat until were left with two-point DFTs Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 7 / 13
- 8. Continue... Final ïŽow graph for 8-point decimation in time Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 8 / 13
- 9. ButterïŽy Structure Cross feed of G[k] and H[k] in ïŽow diagram is called a butterïŽy, due to shape We can implement each butterïŽy with one multiplication Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 9 / 13
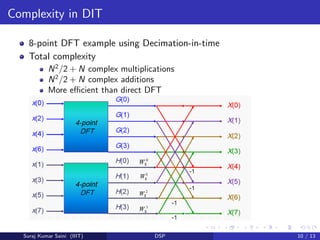
- 10. Complexity in DIT 8-point DFT example using Decimation-in-time Total complexity N2 /2 + N complex multiplications N2 /2 + N complex additions More eïŽcient than direct DFT Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 10 / 13
- 11. Example Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 11 / 13
- 12. Inverse Discrete Fourier Transform Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 12 / 13
- 13. Thank you! Questions and Suggestions Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 13 / 13


![Discrete Fourier Transform
The DFT pair was given as :
X[k] =
Nâ1
n=0
x[n]eâj(2Ï/N)kn
x[n] =
1
N
Nâ1
k=0
X[k]ej(2Ï/N)kn
Baseline for computational complexity:
Each DFT coeïŽcient requires
N complex multiplications
N-1 complex additions
All N DFT coeïŽcients require
N2
complex multiplications
N(N-1) complex additions
Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 3 / 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015kuec2015ppt-180513180657/85/Decimation-in-Time-3-320.jpg)
![Continue...
Most fast methods are based on symmetry properties
Symmetry:
W k
N [N â n] = W âkn
N = (W kn
N )â
Periodicity in n and k:
W kn
N = W
k[n+N]
N = W
[k+N]n
N
Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 4 / 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015kuec2015ppt-180513180657/85/Decimation-in-Time-4-320.jpg)
![Decimation-In-Time
Separate x[n] into two sequence of length N/2 sequence.
Even indexed samples in the ïŽrst sequence
Odd indexed samples in the other sequence
X[k] =
Nâ1
n=0
x[n]eâj(2Ï/N)kn
=
Nâ1
n,even
x[n]eâj(2Ï/N)kn
+
Nâ1
n,odd
x[n]eâj(2Ï/N)kn
Substitute variables n=2r for n even and n=2r+1 for odd
X[k] =
N/2â1
r=0
x[2r]W 2rk
N +
N/2â1
r=0
x[2r + 1]W
(2r+1)k
N
= G[k] + W k
NH[k]
Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 6 / 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015kuec2015ppt-180513180657/85/Decimation-in-Time-6-320.jpg)


![ButterïŽy Structure
Cross feed of G[k] and H[k] in ïŽow diagram is called a butterïŽy, due
to shape
We can implement each butterïŽy with one multiplication
Suraj Kumar Saini (IIIT) DSP 9 / 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015kuec2015ppt-180513180657/85/Decimation-in-Time-9-320.jpg)