Decision points - Repurposing Function Points for Decision Making
- 1. Decision Points Function Point Analysis for Project Decisions Management? Can we repurpose A MetroNorth Roundtable Presentation 14 slides. 35-40 minutes.
- 2. Why so many start-ups? After 20 years of trying to manage projectsŌĆ” Why are you interested in decision making? Hello. My name is David
- 3. Size Complexity CostTime What are function points? ŌĆ”and a tool for examining the mean, medium, and mode. A way of estimatingŌĆ”
- 4. There are several approaches to function points. Some are standards Systematic simplification to How do function points work? See http://www.ifpug.org 5things
- 5. Identify atomic units of full-stack functionality and ratio the average effort required across team functions What would I do? This works pretty well in web development 1 Point
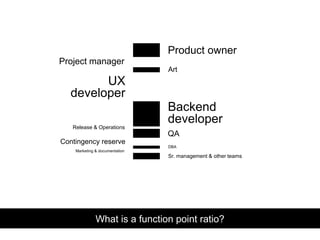
- 6. Product owner Project manager UX developer Backend developer QA Release & Operations Sr. management & other teams Contingency reserve Art DBA Marketing & documentation What is a function point ratio?
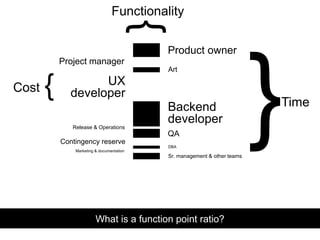
- 7. Product owner Project manager UX developer Backend developer QA Release & Operations Sr. management & other teams Contingency reserve Art DBA Marketing & documentation What is a function point ratio? Time } Functionality {Cost
- 8. ? ? ? What does this have to do with decisions?
- 9. Decisions are often chaotic, caustic, and costly Many decisions looked at togetheroften lack consistency Why is good decision making hard?
- 10. Plan ’é¤ Monitor ’é¤ Control ’é¤ QA How can decision making be less risky? Processization is often doable.
- 11. The logic of function point estimation maps well to estimating decision making What is the basis for estimating a decision?
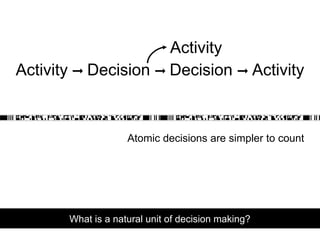
- 12. What is a natural unit of decision making? Activity Ō×× Decision Ō×× Decision Ō×× Activity Atomic decisions are simpler to count Activity
- 13. Can decisions can be broken down for estimation? ŌĆ”may be an input or output ŌĆ”may require inputs or outputs ŌĆ”may have dependencies
- 14. Decisions usually have regular iterations Is decision making workflow regular? Resolution stages Workflow steps Physical deliverables Why donŌĆÖt we see ads like ŌĆ£full stack decision maker skilled in Java, Python and consensus buildingŌĆØ?
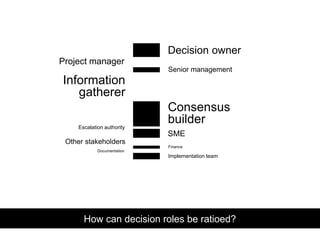
- 15. How can decision roles be ratioed? Decision owner Project manager Information gatherer Consensus builder SME Escalation authority Implementation team Other stakeholders Senior management Finance Documentation
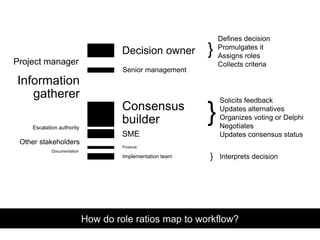
- 16. How do role ratios map to workflow? Decision owner Project manager Information gatherer Consensus builder SME Escalation authority Implementation team Other stakeholders Senior management Finance Documentation } Defines decision Promulgates it Assigns roles Collects criteria } Solicits feedback Updates alternatives Organizes voting or Delphi Negotiates Updates consensus status } Interprets decision
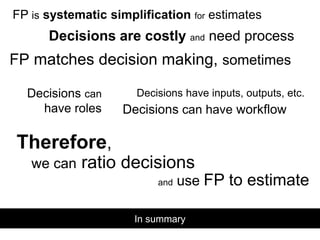
- 17. In summary FP is systematic simplification for estimates Decisions are costly and need process FP matches decision making, sometimes Decisions have inputs, outputs, etc.Decisions can have roles Decisions can have workflow Therefore, we can ratio decisions and use FP to estimate
Editor's Notes
- #3: I believe the most important process is group decision making Small new companies donŌĆÖt have accumulated bad habits IŌĆÖm going to talk about structured decision making and estimation THIS IS NOT AN INTRO TO FP
- #4: Helps think: 1. Quantize abstract work 2. Mean, median and mode Why a structured approach? 1. Consistency 2. Refinement over time 3. Explainability. ┬Ā
- #5: They can work. I have never met anyone who did strict FP Consistency is more important than immediate accuracy 5 things: Inputs Outputs Queries Local files Remote files ┬Ā
- #6: Start with end-user facing features What is ŌĆ£full stackŌĆØ? Caveat: if not ŌĆ£full-stackŌĆØ may not be so straightforward
- #7: Over time you can find the average time per role per feature Every slice may not in fact work for every feature ┬Ā
- #8: Cost Time Complexity over all function points
- #9: You might use FP-like thinking for many team activities Decision making is one possibility
- #10: Decisions are like software features: Abstract Malleable Hard to do well if unstructured Lots moving parts
- #11: You can always be more methodical FP doesnŌĆÖt work for all decisions Decision making isnŌĆÖt the biggest friction in some cases
- #12: How many people catalog and estimate their decisions? Decisions that touch all, most or many people are similar to features that touch all, most or many roles
- #13: FP is very dependent on good FP selection Decisions with embedded decisions can probably be broken down Example, platform selection
- #14: FP looks at: inputs, outputs, queries, local files, remote files Decisions are similar. They require inputs, outputs, investigation, assets, etc. The fit is good ŌĆō not forced
- #15: We can recognize a decision even if it is not methodical If decisions not reasonably regular FP would not work If we use FP the work becomes incrementally more regular
- #16: First we need to have roles Then make assumptions & improve them over time Think of the stack as being ŌĆ£end userŌĆØ down
- #17: We need roles and their activities need to be predictable That means everyone needs to know how decisions will be made