Defibrilator.pptx
- 3. Defibrillator ? Defibrillators are devices that apply an electric charge or current to the heart to restore a normal heartbeat. ? A defibrillator is a device that provides an electric shock to the heart to allow it to get out of a potentially fatal abnormal heart rhythm, or arrhythmia, — ventricular tachycardia (with no pulse) or ventricular fibrillation — and back to a normal rhythm.
- 5. Defibrillation ? Defibrillation is the immediate administration of an electrical current to help restore normal cardiac function. ? Defibrillation is administered when the client does not have a pulse. ? The typical rhythms for defibrillation are ventricular fibrillation, and ventricular tachycardia (without a pulse).
- 6. Cardioversion ? Cardioversion involves the use of low-energy electrical shocks to resume the heart’s normal electrical rhythm. ? t is important to remember that cardioversion is only used for dysrhythmia in which the client has a pulse.
- 7. Types of Defibrillator ? Internal Defibrillator : I. Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator (ICD) ? External Defibrillator: I. Manual External Defibrillator II. Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
- 8. ICD
- 9. AED
- 11. Defibrillator Wave forms ? Monophasic wave form: Energgy is delivered through the patient’s chest in a “single direction”. ? Biphasic wave form: Energy is delivered through the patient’s chest in two directions.
- 12. Energy Levels for Defibrillation ? Defibrillation for Ventricular fibrillation and Pulse less ventricular tachycardia: I. Monophasic : 360 J II. Biphasic : 120-200 J III. If unknown: use maximum available dose (manufacturer recommended.)
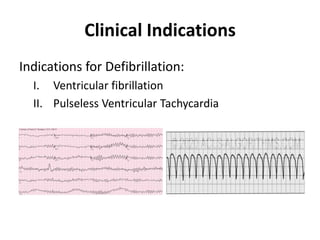
- 13. Clinical Indications Indications for Defibrillation: I. Ventricular fibrillation II. Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia
- 14. Clinical Indications Indications for Cardioversion: I. Supraventricular tachycardia II. Atrial fibrillation III. Atrial flutter IV. Ventricular Tachycardia with pulse
- 15. Electrode Position ? The anterior electrode is placed on the right, below the clavicle. ?The apex electrode is applied to the left side of the patient, just below and to the left of the pectoral muscle.
- 16. SPECIAL EQUIPMENT ? Defibrillator ? Conductive medium- defibrillator pads ? Cardiac monitor with recorder ? Emergency cart and medications ? Emergency pacing equipment
- 17. Thank You