Demand
Download as ppt, pdf2 likes968 views
This document discusses key concepts related to demand in microeconomics, including: 1. Demand refers to the desire and willingness to pay for a product. It is influenced by factors like income, tastes, substitutes, expectations, and number of consumers. 2. The law of demand states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa. This inverse relationship is shown on a demand curve or schedule. 3. Elasticity of demand measures how responsive quantity demanded is to changes in price. Demand is more elastic if close substitutes exist or a product is a luxury versus necessity.
1 of 31
Downloaded 55 times




























Ad
Recommended
Demand and supply law
Demand and supply lawALEX CUESTA SALAZAR
Ěý
This document discusses the fundamental economic concepts of supply and demand. It explains that demand refers to how much of a product is wanted by consumers and that supply is how much is produced. The price of a good or service is determined by the point at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. The law of demand states that as price increases, demand decreases, resulting in a downward sloping demand curve. Conversely, the law of supply shows that as price increases, supply increases too, depicted by an upward sloping supply curve.Elasticity Of Demand
Elasticity Of DemandDan Ewert
Ěý
The document discusses elasticity of demand, which refers to how much consumer demand for a product changes when the price changes. If demand does not change much when the price increases, demand is said to be inelastic. Inelastic demand occurs for necessities like insulin for diabetics - even if the price rises, diabetics' demand will not decrease much as they need it. Factors that impact elasticity include availability of substitutes, importance of the product in the consumer's budget, whether it is considered a necessity or luxury, and potential for substitutes over time. Companies must consider elasticity and the demand curve for their product to determine optimal pricing that maximizes revenue.Theory of demand
Theory of demandPJ123456789
Ěý
The document discusses the theory of demand. It defines demand as the quantity of goods and services that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices over a period of time. It describes how demand is generated from need to want to desire. The law of demand states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, assuming all other factors remain constant. A demand schedule shows the relationship between price and quantity demanded in a table, while a demand curve illustrates this relationship graphically with a downward sloping curve. The document also discusses different types of demand and the conditions that affect demand for a product or service.How do we determine prices?
How do we determine prices?Susanna Pierce
Ěý
1) Supply and demand determine price in a competitive market. The decisions of individual buyers and sellers interact through the mechanism of price.
2) The law of demand and law of supply show the inverse and direct relationships between price and quantity, respectively. A change in price causes a movement along the curves, while a change in external factors can cause a shift in the curves.
3) The five determinants of demand and six determinants of supply that can shift the curves are tastes, income, population, expectations, related goods' prices for demand and number of sellers, productivity, input prices, expectations, related goods' prices, and taxes/subsidies for supply.Demand and supply presentation
Demand and supply presentationSheeraz Latif
Ěý
1. The document discusses the economic concepts of demand, supply, and equilibrium.
2. It explains that demand is represented by a demand curve showing the relationship between price and quantity demanded, and that it typically slopes downward as price increases according to the law of demand. Supply is represented similarly by a supply curve.
3. The document also introduces the concept of market equilibrium, which occurs where the supply and demand curves intersect and quantity supplied equals quantity demanded.Economics chapter 5
Economics chapter 5Autumn Bilbao
Ěý
This document summarizes key aspects of prices and the price system from an economics textbook. It discusses the role and benefits of the price system in guiding supply and demand, and its limitations such as externalities and public goods. Market equilibrium occurs when supply and demand are balanced. Surpluses and shortages cause prices to change to restore equilibrium. Shifts in supply or demand also shift the equilibrium point. Governments sometimes set prices to address market limitations or for other reasons, but this interferes with market forces. Price floors, ceilings, and rationing are used to establish boundaries but can prevent equilibrium.Elasticity of Demand
Elasticity of Demanditutor
Ěý
This document discusses elasticity, which measures how responsive buyers and sellers are to changes in market conditions like price. It defines price elasticity of demand as the percentage change in quantity demanded given a percentage change in price. Demand can be elastic, inelastic, or unit elastic depending on how much quantities change relative to price changes. The document then examines factors that determine a good's elasticity like availability of substitutes, percentage of income spent, and whether it is a necessity or luxury. It also defines income elasticity as the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in consumer income.Why we love demand!
Why we love demand!Emily Holmes
Ěý
This document provides an overview of key concepts in demand economics, including the law of demand, income and substitution effects, demand curves and shifts in demand curves. It discusses factors that can cause a shift in demand, such as income, population changes, tastes, advertising, and expectations. It also defines normal goods and inferior goods and how income affects demand for each. Finally, it briefly mentions complements, substitutes, scarcity, and how economies deal with demand.Theory of demand
Theory of demandeconomicsharbour
Ěý
The document discusses the theory of demand. It defines demand and quantity demanded, and explains that demand is represented by demand schedules and curves. The law of demand states that, other things remaining equal, quantity demanded varies inversely with price. A demand curve slopes downward due to the law of diminishing marginal utility and substitution and income effects. Exceptions to the law of demand include Giffen goods. Changes in demand can occur due to changes in income, prices of related goods, or tastes and preferences.Introduction to Economics,
Theory of Demand and Supply
Introduction to Economics,
Theory of Demand and SupplyYog's Malani
Ěý
The document discusses key concepts in economics including:
1) Economics is defined as the management of household resources, with different economists providing varying definitions focused on wealth, welfare, or scarcity.
2) Microeconomics examines decision-making by individuals and firms, while macroeconomics studies aggregate economic indicators like GDP and unemployment rates.
3) The law of demand states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa. The supply curve slopes upward to show quantity supplied increases with rising price.Theory of demand
Theory of demandUmamaheswari Gopal
Ěý
This document discusses demand theory and the factors that influence demand. It defines demand as the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price. The key points are:
1) Demand depends on a good's utility and consumers' ability to pay. It relates inversely to price - as price rises, demand falls, and vice versa.
2) The demand curve graphs this inverse relationship, with a downward slope. A change in demand results from non-price factors like income, tastes, or preferences.
3) Equilibrium occurs when supply equals demand. Prices adjust upwards when demand exceeds supply, and downwards when supply exceeds demand.Economics
Economicsakdm28
Ěý
This document discusses the principles of supply and demand in economics. It explains that in a free market system, consumers decide which products and businesses succeed by choosing to purchase certain goods. Supply and demand interact to determine price: when demand is high and supply is low, price will rise, and when demand is low and supply is high, price will fall. The document outlines the laws of supply and demand and how equilibrium is reached when supply equals demand, benefiting both consumers and producers.Demand and supply
Demand and supplywphaneuf
Ěý
The document explains the laws of supply and demand, highlighting the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, and a direct relationship between price and quantity supplied. It discusses market equilibrium, how shifts in demand and supply curves affect prices and quantities, and introduces concepts of shortages and surpluses, as well as price ceilings and floors. Examples include equilibrium at specified prices, as well as scenarios resulting from changes in consumer income and related goods.Price ceilings thurs04172014
Price ceilings thurs04172014Travis Klein
Ěý
This document provides instructions and guidance for a student project on identifying the effects of price ceilings in a selected market. Students are asked to choose a market, identify major corporations, determine demand elasticity, evaluate the impact of a price ceiling, cite sources on supply/demand changes, draw graphs showing the effects, and create a color poster/pamphlet/website to present their findings. Rubrics are provided on content requirements and points will be deducted for missing or insufficient elements.Unit 2 lesson 2 presentation
Unit 2 lesson 2 presentationDerek D'Angelo
Ěý
The document discusses the determinants of demand. It identifies six key determinants: (1) changes in income, (2) changes in prices of related goods like substitutes and complements, (3) changes in population size or composition, (4) changes in price expectations, (5) changes in tastes/preferences, and (6) changes in consumer expectations about health effects. It provides examples showing how an increase or decrease in these determinants would shift a demand curve, representing a change in the quantity demanded at each price level rather than a movement along the curve.Demand Theory
Demand TheoryJitin Kollamkudy
Ěý
The document discusses the concepts of demand, supply, and elasticity. It defines demand as being determined by desire, ability to pay, and willingness to pay. The key factors that influence demand are identified as price, income, tastes, prices of related goods, and other economic and social factors. The law of demand states that demand is inversely related to price. Elasticity is introduced as a measure of responsiveness of one variable to changes in another. The three main types of elasticity discussed are price elasticity of demand, income elasticity of demand, and cross elasticity of demand. Supply is defined as the amount of a good producers are willing to provide at different price levels, and is determined by input prices, technologyEconomics
EconomicsScelo1
Ěý
Economics studies how people and societies cope with scarce resources. There are two types: microeconomics focuses on individuals and businesses while macroeconomics looks at entire economies. Economics depends on four factors of production - land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. Demand and supply determine price and quantity. The law of demand states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa. Factors like income, population, and preferences can impact demand. The law of supply states that as price increases, quantity supplied also increases, and vice versa. Factors like costs, technology, and the number of suppliers impact supply. Elasticity measures responsiveness of quantity to price changes.Definition, Determinants and Nature or Types of Demand
Definition, Determinants and Nature or Types of DemandHarinadh Karimikonda
Ěý
Demand is the basis for starting a business, as the product decision and amount produced depends on prevailing market demand. Demand indirectly determines the factors of production required.
Demand is defined as the various quantities of a commodity that consumers will purchase in a given market period at different prices. For there to be demand, there must be a desire for the commodity, sufficient resources to purchase it, a willingness to spend on it, and its availability at a certain price, place, and time.
The determinants of demand include price of the product, consumer income, tastes and preferences, prices of substitutes and complements, consumer expectations, population, climate, and advertising. Demand is expressed as a function of these factors3.1 nature of demand
3.1 nature of demandAsser Agina
Ěý
1. The document discusses the concepts of demand, including the law of demand which states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa.
2. It defines demand as the amount that consumers are willing and able to purchase within a given time period. Quantity demanded refers to the amount purchased at a specific price.
3. A demand schedule shows the relationship between price and quantity demanded in a table, while a demand curve illustrates this relationship graphically with price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis.Nature of demand
Nature of demandEconomic Lessons
Ěý
This document discusses key concepts related to demand, including that demand is the amount of a good consumers are willing and able to buy at a given price. It also covers the law of demand, which states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa. Additionally, it explains the concepts of income and substitution effects, marginal utility, and diminishing marginal utility in relation to demand. An example demand schedule for a TV at different future price points is also provided.HOME ASSIGNMENT
HOME ASSIGNMENTANIK KUMAR BHATTACHERJEE
Ěý
The document discusses various concepts related to demand including:
1. Demand is the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at a given price in a given time period. Effective demand is backed by an ability to pay, while latent demand exists without purchasing power.
2. Derived demand is demand for a product that is linked to demand for a related product. For example, steel demand is derived from vehicle demand.
3. Elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price, income, or the price of a related good. Price elasticity is defined as the percentage change in quantity divided by the percentage change in price.
4. The daily energy demandCross Price Elasticity of Demand
Cross Price Elasticity of Demandtutor2u
Ěý
Cross price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of the demand for good X to a change in the price of a related good Y. It can be positive for substitutes, where a rise in the price of one good increases demand for the other, or negative for complements, where a fall in the price of one good increases demand for the other. The closer the relationship between the two goods, the higher the coefficient of cross price elasticity.consumer's surplus, economics.
consumer's surplus, economics.kazihassanalbanna
Ěý
The document introduces a group of students and their IDs. It then discusses the concept of consumer surplus, how it is displaced when price changes, and some difficulties in measuring it. Specifically, it notes that consumer surplus is the difference between what consumers are willing and able to pay versus what they actually pay. It also discusses Professor Hicks' concept of consumer surplus and four variations. Finally, it outlines some practical uses of consumer surplus in areas like public finance, monopoly pricing, cost-benefit analysis, and measuring benefits from international trade.Chapter 4 1 and 4 2 notes 4 1
Chapter 4 1 and 4 2 notes 4 1Lisa Stack
Ěý
The document discusses key concepts in supply and demand including:
1) The law of demand which states that, all else being equal, as price increases demand decreases and vice versa due to an inverse relationship between price and demand.
2) The substitution and income effects which describe how consumers will substitute goods when prices change and how changes in prices can impact consumer's real income.
3) The demand curve which graphically represents the law of demand and shows the relationship between price and quantity demanded for a good.Elasticity of demand
Elasticity of demandIshan Kaushik
Ěý
Price elasticity of demand measures how responsive quantity demanded is to changes in price. It depends on factors like availability of substitutes, necessity of the good, budget share, and time period. Gasoline has relatively inelastic demand, meaning changes in price do not greatly affect quantity bought, while restaurant meals are very elastic with demand falling sharply in response to price increases. Elasticity is calculated as the percentage change in quantity divided by the percentage change in price, with values below 1 indicating inelastic demand and above 1 indicating elastic demand.Cross price elasticity
Cross price elasticitymattbentley34
Ěý
This document discusses cross price elasticity of demand, which measures the responsiveness of the demand for one good to a change in the price of a related good. It provides examples of substitutes, where a price increase of one good raises demand for the other, and complements, where a price decrease of one good increases demand for the other. It also shows calculations of cross price elasticity values and how the strength of the relationship between goods is indicated by the coefficient. Charts illustrate the relationships between substitutes and complements. Finally, it analyzes cross price elasticity factors for UK cinema ticket prices.Commercial customer presentation_mf072010
Commercial customer presentation_mf072010Jesse Jino
Ěý
The document provides information about energy deregulation and strategies for businesses to save money on electricity costs. It discusses how deregulation allows customers to choose between different energy suppliers. It then recommends choosing a fixed-rate contract to avoid volatility, and describes how an energy consulting company can analyze a business's usage and switch them to a new supplier to save 20-50% off peak rates over 3 years.Market demand and supply of coke
Market demand and supply of cokeThe Superior University, Lahore
Ěý
This document provides information about demand, supply, and market equilibrium for Coca-Cola. It discusses the history and invention of Coca-Cola, the basic concepts of demand and supply, factors that affect demand and supply, and the relationship between price, demand, and supply. Specifically, it explains that demand for Coca-Cola depends on factors like price, income, tastes, and policies while supply depends on price, technology, number of consumers, and input prices. It also illustrates the laws of demand and supply through demand and supply curves for Coca-Cola.Unit 2 demand
Unit 2 demandBethany Bryski
Ěý
1. Demand is determined by buyers and refers to their willingness and ability to purchase different quantities of a good at different prices during a specific time period.
2. The law of demand states that, all else equal, as price increases the quantity demanded decreases, and as price decreases the quantity demanded increases.
3. Individual demand curves represent one person's demand, while market demand curves are the sum of all individual demand curves and show the total quantity demanded of a good at different prices.demand& the elasticity and degrees of .PPT
demand& the elasticity and degrees of .PPTRichaGoel44
Ěý
The document explains the theory of demand, highlighting definitions, requisites, different kinds of demand, and factors affecting demand, such as prices and consumer income. It discusses the law of demand, elasticity of demand—including price, income, and cross elasticity—and their implications for purchasing behavior and market dynamics. Additionally, the document covers demand schedules, demand curves, and shifts versus movements along the demand curve.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Theory of demand
Theory of demandeconomicsharbour
Ěý
The document discusses the theory of demand. It defines demand and quantity demanded, and explains that demand is represented by demand schedules and curves. The law of demand states that, other things remaining equal, quantity demanded varies inversely with price. A demand curve slopes downward due to the law of diminishing marginal utility and substitution and income effects. Exceptions to the law of demand include Giffen goods. Changes in demand can occur due to changes in income, prices of related goods, or tastes and preferences.Introduction to Economics,
Theory of Demand and Supply
Introduction to Economics,
Theory of Demand and SupplyYog's Malani
Ěý
The document discusses key concepts in economics including:
1) Economics is defined as the management of household resources, with different economists providing varying definitions focused on wealth, welfare, or scarcity.
2) Microeconomics examines decision-making by individuals and firms, while macroeconomics studies aggregate economic indicators like GDP and unemployment rates.
3) The law of demand states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa. The supply curve slopes upward to show quantity supplied increases with rising price.Theory of demand
Theory of demandUmamaheswari Gopal
Ěý
This document discusses demand theory and the factors that influence demand. It defines demand as the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price. The key points are:
1) Demand depends on a good's utility and consumers' ability to pay. It relates inversely to price - as price rises, demand falls, and vice versa.
2) The demand curve graphs this inverse relationship, with a downward slope. A change in demand results from non-price factors like income, tastes, or preferences.
3) Equilibrium occurs when supply equals demand. Prices adjust upwards when demand exceeds supply, and downwards when supply exceeds demand.Economics
Economicsakdm28
Ěý
This document discusses the principles of supply and demand in economics. It explains that in a free market system, consumers decide which products and businesses succeed by choosing to purchase certain goods. Supply and demand interact to determine price: when demand is high and supply is low, price will rise, and when demand is low and supply is high, price will fall. The document outlines the laws of supply and demand and how equilibrium is reached when supply equals demand, benefiting both consumers and producers.Demand and supply
Demand and supplywphaneuf
Ěý
The document explains the laws of supply and demand, highlighting the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, and a direct relationship between price and quantity supplied. It discusses market equilibrium, how shifts in demand and supply curves affect prices and quantities, and introduces concepts of shortages and surpluses, as well as price ceilings and floors. Examples include equilibrium at specified prices, as well as scenarios resulting from changes in consumer income and related goods.Price ceilings thurs04172014
Price ceilings thurs04172014Travis Klein
Ěý
This document provides instructions and guidance for a student project on identifying the effects of price ceilings in a selected market. Students are asked to choose a market, identify major corporations, determine demand elasticity, evaluate the impact of a price ceiling, cite sources on supply/demand changes, draw graphs showing the effects, and create a color poster/pamphlet/website to present their findings. Rubrics are provided on content requirements and points will be deducted for missing or insufficient elements.Unit 2 lesson 2 presentation
Unit 2 lesson 2 presentationDerek D'Angelo
Ěý
The document discusses the determinants of demand. It identifies six key determinants: (1) changes in income, (2) changes in prices of related goods like substitutes and complements, (3) changes in population size or composition, (4) changes in price expectations, (5) changes in tastes/preferences, and (6) changes in consumer expectations about health effects. It provides examples showing how an increase or decrease in these determinants would shift a demand curve, representing a change in the quantity demanded at each price level rather than a movement along the curve.Demand Theory
Demand TheoryJitin Kollamkudy
Ěý
The document discusses the concepts of demand, supply, and elasticity. It defines demand as being determined by desire, ability to pay, and willingness to pay. The key factors that influence demand are identified as price, income, tastes, prices of related goods, and other economic and social factors. The law of demand states that demand is inversely related to price. Elasticity is introduced as a measure of responsiveness of one variable to changes in another. The three main types of elasticity discussed are price elasticity of demand, income elasticity of demand, and cross elasticity of demand. Supply is defined as the amount of a good producers are willing to provide at different price levels, and is determined by input prices, technologyEconomics
EconomicsScelo1
Ěý
Economics studies how people and societies cope with scarce resources. There are two types: microeconomics focuses on individuals and businesses while macroeconomics looks at entire economies. Economics depends on four factors of production - land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. Demand and supply determine price and quantity. The law of demand states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa. Factors like income, population, and preferences can impact demand. The law of supply states that as price increases, quantity supplied also increases, and vice versa. Factors like costs, technology, and the number of suppliers impact supply. Elasticity measures responsiveness of quantity to price changes.Definition, Determinants and Nature or Types of Demand
Definition, Determinants and Nature or Types of DemandHarinadh Karimikonda
Ěý
Demand is the basis for starting a business, as the product decision and amount produced depends on prevailing market demand. Demand indirectly determines the factors of production required.
Demand is defined as the various quantities of a commodity that consumers will purchase in a given market period at different prices. For there to be demand, there must be a desire for the commodity, sufficient resources to purchase it, a willingness to spend on it, and its availability at a certain price, place, and time.
The determinants of demand include price of the product, consumer income, tastes and preferences, prices of substitutes and complements, consumer expectations, population, climate, and advertising. Demand is expressed as a function of these factors3.1 nature of demand
3.1 nature of demandAsser Agina
Ěý
1. The document discusses the concepts of demand, including the law of demand which states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa.
2. It defines demand as the amount that consumers are willing and able to purchase within a given time period. Quantity demanded refers to the amount purchased at a specific price.
3. A demand schedule shows the relationship between price and quantity demanded in a table, while a demand curve illustrates this relationship graphically with price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis.Nature of demand
Nature of demandEconomic Lessons
Ěý
This document discusses key concepts related to demand, including that demand is the amount of a good consumers are willing and able to buy at a given price. It also covers the law of demand, which states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa. Additionally, it explains the concepts of income and substitution effects, marginal utility, and diminishing marginal utility in relation to demand. An example demand schedule for a TV at different future price points is also provided.HOME ASSIGNMENT
HOME ASSIGNMENTANIK KUMAR BHATTACHERJEE
Ěý
The document discusses various concepts related to demand including:
1. Demand is the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at a given price in a given time period. Effective demand is backed by an ability to pay, while latent demand exists without purchasing power.
2. Derived demand is demand for a product that is linked to demand for a related product. For example, steel demand is derived from vehicle demand.
3. Elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price, income, or the price of a related good. Price elasticity is defined as the percentage change in quantity divided by the percentage change in price.
4. The daily energy demandCross Price Elasticity of Demand
Cross Price Elasticity of Demandtutor2u
Ěý
Cross price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of the demand for good X to a change in the price of a related good Y. It can be positive for substitutes, where a rise in the price of one good increases demand for the other, or negative for complements, where a fall in the price of one good increases demand for the other. The closer the relationship between the two goods, the higher the coefficient of cross price elasticity.consumer's surplus, economics.
consumer's surplus, economics.kazihassanalbanna
Ěý
The document introduces a group of students and their IDs. It then discusses the concept of consumer surplus, how it is displaced when price changes, and some difficulties in measuring it. Specifically, it notes that consumer surplus is the difference between what consumers are willing and able to pay versus what they actually pay. It also discusses Professor Hicks' concept of consumer surplus and four variations. Finally, it outlines some practical uses of consumer surplus in areas like public finance, monopoly pricing, cost-benefit analysis, and measuring benefits from international trade.Chapter 4 1 and 4 2 notes 4 1
Chapter 4 1 and 4 2 notes 4 1Lisa Stack
Ěý
The document discusses key concepts in supply and demand including:
1) The law of demand which states that, all else being equal, as price increases demand decreases and vice versa due to an inverse relationship between price and demand.
2) The substitution and income effects which describe how consumers will substitute goods when prices change and how changes in prices can impact consumer's real income.
3) The demand curve which graphically represents the law of demand and shows the relationship between price and quantity demanded for a good.Elasticity of demand
Elasticity of demandIshan Kaushik
Ěý
Price elasticity of demand measures how responsive quantity demanded is to changes in price. It depends on factors like availability of substitutes, necessity of the good, budget share, and time period. Gasoline has relatively inelastic demand, meaning changes in price do not greatly affect quantity bought, while restaurant meals are very elastic with demand falling sharply in response to price increases. Elasticity is calculated as the percentage change in quantity divided by the percentage change in price, with values below 1 indicating inelastic demand and above 1 indicating elastic demand.Cross price elasticity
Cross price elasticitymattbentley34
Ěý
This document discusses cross price elasticity of demand, which measures the responsiveness of the demand for one good to a change in the price of a related good. It provides examples of substitutes, where a price increase of one good raises demand for the other, and complements, where a price decrease of one good increases demand for the other. It also shows calculations of cross price elasticity values and how the strength of the relationship between goods is indicated by the coefficient. Charts illustrate the relationships between substitutes and complements. Finally, it analyzes cross price elasticity factors for UK cinema ticket prices.Commercial customer presentation_mf072010
Commercial customer presentation_mf072010Jesse Jino
Ěý
The document provides information about energy deregulation and strategies for businesses to save money on electricity costs. It discusses how deregulation allows customers to choose between different energy suppliers. It then recommends choosing a fixed-rate contract to avoid volatility, and describes how an energy consulting company can analyze a business's usage and switch them to a new supplier to save 20-50% off peak rates over 3 years.Market demand and supply of coke
Market demand and supply of cokeThe Superior University, Lahore
Ěý
This document provides information about demand, supply, and market equilibrium for Coca-Cola. It discusses the history and invention of Coca-Cola, the basic concepts of demand and supply, factors that affect demand and supply, and the relationship between price, demand, and supply. Specifically, it explains that demand for Coca-Cola depends on factors like price, income, tastes, and policies while supply depends on price, technology, number of consumers, and input prices. It also illustrates the laws of demand and supply through demand and supply curves for Coca-Cola.Similar to Demand (20)
Unit 2 demand
Unit 2 demandBethany Bryski
Ěý
1. Demand is determined by buyers and refers to their willingness and ability to purchase different quantities of a good at different prices during a specific time period.
2. The law of demand states that, all else equal, as price increases the quantity demanded decreases, and as price decreases the quantity demanded increases.
3. Individual demand curves represent one person's demand, while market demand curves are the sum of all individual demand curves and show the total quantity demanded of a good at different prices.demand& the elasticity and degrees of .PPT
demand& the elasticity and degrees of .PPTRichaGoel44
Ěý
The document explains the theory of demand, highlighting definitions, requisites, different kinds of demand, and factors affecting demand, such as prices and consumer income. It discusses the law of demand, elasticity of demand—including price, income, and cross elasticity—and their implications for purchasing behavior and market dynamics. Additionally, the document covers demand schedules, demand curves, and shifts versus movements along the demand curve.Chapter 2 Demand
Chapter 2 DemandEjarn Jijan
Ěý
This document discusses different types of demand, including:
1. Conventional perspectives on free goods, public goods, and economic goods. Islamic perspectives on al-tayyibat and al-rizq.
2. The relationship between price and quantity demanded as shown through demand schedules and curves. Individual demand curves summing to market demand.
3. Factors that can cause shifts in the demand curve, such as changes in income, tastes, prices of related goods, expectations, and market size. The differences between changes in quantity demanded versus changes in demand.Econ ch04
Econ ch04alowry12
Ěý
The document discusses concepts related to demand, including the law of demand, demand schedules, demand curves, elasticity of demand, and how elasticity affects total revenue. Specifically, it explains that according to the law of demand, as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa. It provides examples of demand schedules and how they are used to construct demand curves. It also discusses factors that can cause a shift in the demand curve, such as changes in income, population, or prices of related goods. Finally, it explains the concept of elasticity of demand and how elastic versus inelastic demand impacts a firm's total revenue when price is changed.Demand and Supply IB1.pptx
Demand and Supply IB1.pptxANTHONYAKINYOSOYE1
Ěý
This document provides a summary of key concepts related to demand and price in economics. It defines a market and its forms, demand and the law of demand, demand schedules and curves. It explains individual and market demand, and the determinants of demand including price, income, tastes, and others. It also defines price elasticity of demand and the different types, and explains how price elasticity relates to total revenue. Income elasticity of demand is also defined and the importance of understanding income and price elasticities for businesses and governments is discussed.Unit 2 supply and demand f 2019
Unit 2 supply and demand f 2019AngelaWard43
Ěý
This document provides an overview of demand, supply, and equilibrium in markets. It defines key concepts such as:
- The law of demand, which states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases.
- Demand curves, which show the relationship between price and quantity demanded.
- Supply curves, which show the relationship between price and quantity supplied.
- Equilibrium, which is reached at the price where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
It also discusses factors that can cause demand and supply to shift, and the relationship between price elasticity and consumers' responsiveness to price changes.Econ Demand
Econ DemandMr. Philen
Ěý
The document discusses key concepts in microeconomics including demand, the law of demand, demand schedules, demand curves, determinants of demand, elasticity of demand, and how to measure elasticity. Specifically, it defines demand as the quantity of a good consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices in a given time period. It explains that the law of demand states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa. Demand schedules and curves illustrate the relationship between price and quantity demanded. Factors like income, tastes, prices of related goods, and expectations can cause shifts in the demand curve. Elasticity refers to the responsiveness of quantity demanded to price changes, and can be elastic, inelastic,Chapter 4 Demand
Chapter 4 DemandChristine Onwenu
Ěý
Chapter 4 discusses the law of demand, which states that lower prices lead to higher quantities demanded, and introduces concepts such as demand curves and marginal utility. It further explains factors affecting demand, including consumer income, preferences, and related products, and differentiates between changes in quantity demanded and changes in demand. The chapter also covers demand elasticity, highlighting how price changes impact consumer behavior regarding different products.Demand and Supply Analysis.pptx
Demand and Supply Analysis.pptxnishadeotale
Ěý
This document discusses concepts of demand and supply analysis. It defines demand as the quantity of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price per unit of time. Demand is determined by price of the good, income of consumers, prices of substitutes and complements, tastes, expectations, and other factors. The supply of a good depends on input prices, technology, and other supply shifters. Demand and supply curves show the relationship between price and quantity demanded/supplied in the market. The interaction of demand and supply determines the market equilibrium price and quantity.Demand factors
Demand factorskellycrowell
Ěý
This document discusses factors that affect demand, including changes in the number of consumers, incomes, tastes, expectations, and prices of related goods. It explains how demand curves shift left when demand decreases and right when demand increases. Specifically, it outlines how demand is impacted by changes in population size, incomes, consumption patterns, popularity of goods, expectations about the future, prices of substitutes and complements, and elasticity of demand for different types of products.Lesson 6--demand[1]
Lesson 6--demand[1]Ashley Birmingham
Ěý
Here are some examples of goods with different demand elasticities:
- Insulin (inelastic): People need it to live, so they will still buy it even if the price increases significantly.
- Sodas (elastic): People can more easily substitute with other drinks or water if the price increases, so even a small price change would significantly impact the quantity bought.
Let me know if you need any clarification or have additional questions!Business Economics - Unit-2 for IMBA, Osmania University
Business Economics - Unit-2 for IMBA, Osmania UniversityBalasri Kamarapu
Ěý
This document provides an overview of Business Economics as a course. It outlines 5 units that will be covered: 1) nature and scope of business economics, 2) demand concepts and elasticity of demand, 3) production and cost concepts, 4) budget line, and 5) market structures and pricing. Key concepts from Unit 2 on demand include the law of demand, determinants of demand, elasticity of demand including types and uses, the concept of supply, determinants of supply, and the law of supply. Elasticity of supply is also briefly discussed including different types.ME-Ch2.pptx
ME-Ch2.pptxTeshome48
Ěý
This document provides an overview of demand theory and analysis. It defines demand as a desire for a product backed by both willingness and ability to pay. Demand is determined by factors like price, income, tastes, and expectations. The law of demand and marginal utility are described. Elasticity measures responsiveness of demand to changes in factors like price and income. Demand estimation attempts to quantify links between demand and determinants, while forecasting predicts future demand levels. Methods for forecasting demand are discussed.Demand 1 introduction menaing scope importance
Demand 1 introduction menaing scope importancejaya315652
Ěý
The document provides an extensive overview of demand, including its definition, factors influencing it, and how it is graphically represented through demand schedules and curves. It discusses concepts like marginal utility, elasticity of demand, and how changes in income, tastes, and the prices of related goods can affect demand. Additionally, it explains various types of elasticity, including price, income, and cross-price elasticity, and their implications on consumer behavior and market dynamics.Revision-1 (1).pptx
Revision-1 (1).pptxLAKHANTRIVEDI8
Ěý
This document defines key concepts in microeconomics related to demand and supply, including elasticities. It explains the laws of demand and supply, and how non-price factors can cause shifts in demand and supply curves. It also defines different types of elasticities including price elasticity of demand, cross elasticity of demand, income elasticity of demand, and price elasticity of supply. Examples are provided to illustrate these concepts.BASIC LAWS OF CONSUPTION AND DEMAND ANALYSIS.ppt
BASIC LAWS OF CONSUPTION AND DEMAND ANALYSIS.pptDrSamsonChepuri1
Ěý
The document discusses key concepts in demand analysis and consumer behavior, including:
1) It outlines the basic laws of consumption, including the law of diminishing marginal utility, the law of equi-marginal utility, consumer surplus, indifference curves, and consumer equilibrium.
2) It then covers demand analysis, defining demand, the demand function, factors that influence demand, and the law of demand.
3) Finally, it discusses elasticity of demand - how responsive demand is to changes in price and other factors. It defines different types of elasticities and factors that influence elasticity.2015 day 4
2015 day 4Travis Klein
Ěý
This document contains a series of questions and prompts related to economics concepts like demand, elasticity, and determinants of demand. It includes examples of demand schedules and graphs to illustrate key ideas. Students are asked to analyze demand curves, identify price points that maximize revenue, and explain how changes described in various scenarios would impact demand. The document aims to help students learn how to apply concepts of demand, elasticity, and their determinants through examples, practice questions, and interactive activities on whiteboards and slates.Supply and Demand
Supply and Demand north819
Ěý
This document provides an overview of supply and demand concepts including:
- Demand is determined by consumers' willingness and ability to purchase goods at different price levels, while supply is determined by producers' willingness to provide goods at different price levels.
- The law of demand states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, while the law of supply states that as price increases, quantity supplied also increases.
- Demand and supply curves graphically represent these relationships, with demand curves sloping downward and supply curves sloping upward.
- Factors like income, population, tastes, prices of substitutes and complements can cause demand to shift, while costs of production and technology can cause supply shifts.Economics Analysis
Economics Analysis Mohammad Saif Alam
Ěý
The document provides a detailed analysis of demand in economics, covering its definition, components, determinants, and the law of demand, which states that price inversely affects demand. It also explains concepts such as utility, elasticity of demand, and the effects of various factors on the demand curve, including income and advertising. Additionally, it discusses different types of elasticity, including price, cross, income, and advertisement elasticity, highlighting their implications for market behavior and decision-making.Ad
More from benefieldshannon (13)
The legislative branch
The legislative branchbenefieldshannon
Ěý
The document provides an overview of the legislative branch and Congress, including:
- Congress is bicameral, consisting of the House of Representatives and Senate
- The House has 435 members elected every 2 years, while the Senate has 100 members elected every 6 years
- Congress has enumerated powers listed in the Constitution as well as implied powers, and it shares foreign relations and war powers with the President
- The legislative process involves bills being introduced, referred to committee, debated on the floor, and voted on before being sent to the other chamber and then potentially to the PresidentUnit 2
Unit 2benefieldshannon
Ěý
The document discusses several topics related to political parties in the United States including what they are, their functions, the origins of the two-party system, different types of party systems, and aspects of how U.S. political parties operate such as nominating candidates, funding campaigns, and enforcing campaign finance laws.Ch. 4 federalism
Ch. 4 federalismbenefieldshannon
Ěý
Federalism divides power between the national and state governments. The founders implemented federalism to balance power and prevent abuse, as the states initially joined the union reluctantly and sought to maintain autonomy. Federalism gives certain powers to the national government and reserves others for the states, allowing for local control over local matters and national control over broader issues. This division of power defines the relationship between federal, state, and local authorities.Ch. 3 the constitution
Ch. 3 the constitutionbenefieldshannon
Ěý
The document outlines the key principles and structure of the US Constitution. It establishes that the Constitution sets forth the basic principles of popular sovereignty, limited government, separation of powers, checks and balances, and federalism. It is comprised of a preamble and 7 articles, which establish the three branches of government and their powers, the relationship between federal and state governments, and the process for ratifying amendments. The Constitution can be formally amended through a process that involves approval by Congress and the states, or informally amended over time through legislation, executive actions, court decisions, political practices, and customs.Ch. 12 Congress In Action
Ch. 12 Congress In Actionbenefieldshannon
Ěý
The document provides an overview of how Congress is organized and functions. It discusses how Congress convenes, the roles of presiding officers like the Speaker of the House and President of the Senate, how party officers and committee chairmen are chosen, and how committees consider and advance legislation. It also summarizes the legislative process, including how a bill is introduced, moves through committees, comes to the floor for debate and votes, and is reconciled between the House and Senate before being sent to the President.Ch. 3 The Constitution
Ch. 3 The Constitutionbenefieldshannon
Ěý
The document summarizes the key components and principles of the US Constitution, including the three branches of government, amendments, and both formal and informal processes of constitutional change. It outlines the 27 amendments under categories such as the Bill of Rights, Civil War amendments, and 20th century amendments. The informal amendment process can occur through legislation, executive action, court decisions, political party practices, and custom.Ch. 8 Employment, Labor, And Wages
Ch. 8 Employment, Labor, And Wagesbenefieldshannon
Ěý
The document discusses the history and development of labor unions in the United States from the colonial period through modern times. It covers key events and legislation that impacted unions such as the Great Depression, World War II, the Taft-Hartley Act. The document also examines topics related to employment, wages, gender pay differences, and minimum wage.Ch. 9 Taxes
Ch. 9 Taxesbenefieldshannon
Ěý
Taxes impact the economy through their effects on resource allocation, consumer behavior, and national productivity and growth. Taxes are directly related to supply and demand and affect incentives to save, invest, and work. An effective tax system aims to be equitable, simple, and efficient while adhering to principles like benefit received and ability to pay. The U.S. federal government collects most of its tax revenue from individual income taxes, Social Security and Medicare taxes, corporate income taxes, and excise taxes. State governments rely heavily on intergovernmental transfers and sales taxes, while local governments' primary sources are also intergovernmental transfers and property taxes.Supply
Supplybenefieldshannon
Ěý
Supply refers to the quantity of a product offered for sale. The law of supply states that more of a product will be offered at a higher price and less at a lower price. Supply curves show the relationship between price and quantity supplied, and can be individual or market curves representing one firm or multiple firms. Factors that affect supply include costs of inputs, productivity, technology, taxes, expectations, government regulations, and number of sellers. When these factors change, the supply curve shifts representing a change in quantity supplied at each price level.Chapter 6 Price
Chapter 6 Pricebenefieldshannon
Ěý
Prices serve as a link between producers and consumers by communicating supply and demand information. Prices find equilibrium when the quantity supplied equals quantity demanded. When surpluses or shortages occur due to shifts in supply or demand, prices adjust to restore equilibrium. The government sometimes intervenes in markets through price controls, but these distort market signals and reduce efficiency. Agricultural price supports use target prices, loans, and deficiency payments to stabilize farm prices.Business Organizations
Business Organizationsbenefieldshannon
Ěý
The document discusses different forms of business organizations including proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. It outlines the advantages and disadvantages of each structure. It also discusses government regulation of business, mergers and acquisitions as ways for businesses to grow, and the roles of non-profits, cooperatives, labor unions, and government in the economy.The War In The Pacific
The War In The Pacificbenefieldshannon
Ěý
The document summarizes the key events and strategy of the US in the Pacific Theater during World War 2. It describes the roles of General Douglas MacArthur and Admiral Chester Nimitz in devising an island hopping strategy to push the Japanese out of crucial Pacific islands. It then outlines some of the major battles in chronological order, from the Battle of the Coral Sea in 1942 to the Battle of Okinawa in 1945, where the US employed the island hopping approach to ultimately defeat Japan.Life At Home
Life At Homebenefieldshannon
Ěý
The war caused Franklin Roosevelt to shift the US economy. The government took control of industries and production, asking companies to produce specific materials for the war effort like airplanes, tanks, ships, and weapons. This new production created many jobs that were filled by women as more men joined the armed forces. Women took on roles in factories and the military like the WAC, WASP, and WAVES organizations. At home, Americans supported the war through rationing of scarce resources, recycling, buying war bonds, and viewing propaganda posters featuring characters like Rosie the Riveter that promoted the war effort.Ad
Demand
- 2. Why would the broker recommend pitchforks? Would the pitchfork producers benefit from this? 3. What would you think would happen to the price of the pitchfork?
- 3. What is Demand? How do we account for buying a product? What is marginal utility? How do we graph demand?
- 4. What is Demand? The desire and willingness to pay for a product. Firms provide us with goods and services based on the demand for that particular good/service.
- 5. Microeconomics Deals with the basic unit in regards to economic activity. Economists are going to look at you buying products and why you buy them. This will reveal how prices are determined and how you make your decisions.
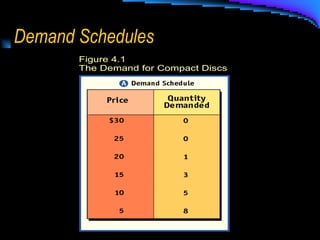
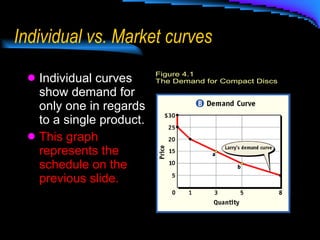
- 7. Individual vs. Market curves Individual curves show demand for only one in regards to a single product. This graph represents the schedule on the previous slide.
- 8. Market curves The market curve represents the demand of a product by everyone. Schedules will usually be larger than those of the individual demand.
- 9. The Law of Demand All of these concepts contribute to the law of demand. The law states that the quantity of goods (Q) demanded varies inversely with the price (P) of the product.
- 10. Law of Demand ct’d The inverse relationship between P & Q is something that we find in the market. When the price goes up, then demand usually goes down. Common sense and simple observation are consistent with Law of Demand.
- 11. Demand and Marginal Utility Marginal utility is important because it explains so much about the demand of products. Diminishing marginal utility is a prime example of this. When we use more and more of the product, the newness wears off and we want less of it.
- 13. D 4. C A Criticizes business for overcharging, stockholders, executives, and employees for greed, rationalizing low-quality products and for irresponsibility toward the environment, conservatives for attacking any criticism of business, and the hypocrisy of business interests in seeking subsidies.
- 14. Factors Affecting Demand What causes changes in demand? What are these factors? How are you going to account for them on a graph?
- 15. Changes in Quantity Demanded There are several factors that affect demand in the market. Income has a huge effect. Substitution impacts that market to.
- 16. Income effect When prices drop and you have money, you will buy it. If you are broke then you will not buy as much of the product .
- 17. Substitution effect This is where consumers substitute a good/service for a relatively similar one for a cheaper price. Examples would be if movie theaters cost $7 and the rental place costs $3, You will be more likely to stay in and rent.
- 18. Changes in Demand There are six major factors that affect the demand of a product. Consumer Income Consumer Tastes Substitutes and Complements Changes in Expectations Number of Consumers
- 19. Consumer Income When your income goes up, you can afford more stuff and you will buy it.
- 20. Consumer Tastes Not everyone wants the same stuff. This also plays a major role in the demand of a product. When a product is successfully advertised, its popularity increases and people buy more of it.
- 21. Substitutes and Complements Changes in price in related products will cause demand to change. Substitutes are similar products that will either benefit or not from changes in demand. Complements can cause demand shifts as well.
- 22. Expectations The speculations of consumers will directly affect the demand curve. If consumers hear about some new kind of technology or the development of a new product. They will, in turn, buy or hold off on specific products.
- 23. Number of Consumers Businesses will play the numbers game . The more consumers, the better chance that the demand will go up.
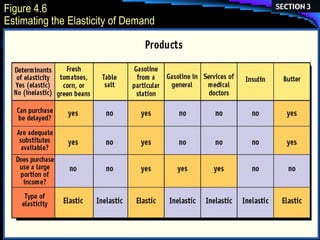
- 24. Elasticity of Demand What is elasticity? How does elasticity affect the demand of a product? What factors determine demand elasticity?
- 25. Elasticity Responsiveness Demand elasticity refers to the changes in demand due to the change in price.
- 26. Elastic Demand Change in (P) causes relatively larger changes in (Q) demanded. If P is lower, Q will be higher Increase in P = decrease in Q .
- 27. Demand Elasticity Demand tends to be more elastic if close substitutes are available. Demand is also more elastic if the good is a luxury, rather than a necessity. Buyers have substantial time to react to price change.
- 28. Inelastic demand Very little responsiveness to the change in P. Most inelastic changes occur to products that consumers value very little. (Ex. salt, sugar, etc.)
- 29. Unit Elasticity Occurs when the change in P will be proportional with changes in Q.
- 30. Section 3-15
- 31. Total Expenditures Test (P x Q) = total expenditures. Changes in expenditures depend on the elasticity of a demand curve— if change in price & expenditures move in opposite directions on the curve-- demand is elastic if they move in the same direction-- demand is inelastic if there is no change in expenditures-- demand is unit elastic.