Demand and supply factors
- 1. DEMAND AND SUPPLY FACTORS UNDERSTANDING CUSTOMER ADOPTION PROCESS
- 3. MEANING The business dictionary defines the consumer adoption process as the product adoption process. This term is also known similarly as the diffusion of innovations. A company produces a product or service and announces it to the market. At that point the consumer adoption process begins. This is where the consumer decides to become a new customer and purchase or reject the product.
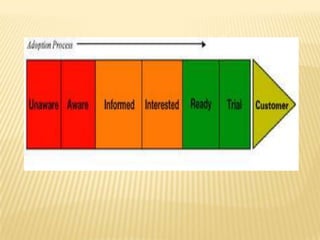
- 6. AWARENESS ’āÆ The first stage, Awareness, is most important and is also where marketers put a lot of effort and money. If consumers are not aware that the product or service exists, how can the company expect the consumers to buy it?
- 7. INTEREST ’āÆ The second stage is Interest. This stage is when the consumer becomes aware of the product and searches out information. A popular of searching out information is method the internet.
- 8. EVALUATION ’āÆ In this stage, the consumer has enough knowledge about the product and he considers its relative benefits and evaluates it in terms of various factors as cost, competitorsŌĆÖ offering, etc.
- 9. TRAIL This is the stage when the consumer experiences the product and judges whether the claims are correct or not. Trials can be generated by sampling or by the consumer himself buying the product. Many new brands aim to reach this stage as soon as possible.
- 10. ADOPTION OR REJECTION DECISION This is the stage when the consumer has made up her mind whether to remain with the product or switch back to her earlier product.
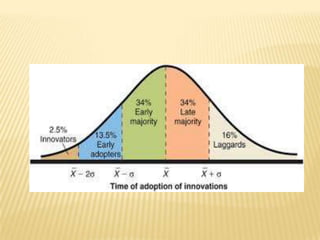
- 13. EARLY ADOPTERS ’āÆ The early adopters are very quick to respond to new product launches and innovative offers from the marketers. Such people are always willing to try new ideas.
- 14. EARLY MAJORITY ’āÆ The early majority keenly observes the innovators and finds out whether the new product or innovations offer any value and have stood the test of times. If the product proves to be useful and is said to be a good offer, that is novel and different from other products- the product will witness a surge in demand.
- 15. LATE MAJORITY ’āÆ The late majority tends to buy the product later than the average individual. They are slow to catch on to the popularity of new products, services or ideas. Marketing will still enjoy the advantage of mass consumption , but it begins to end after a while.
- 16. LAGGARDS ’āÆ Laggards are not the trendsetters. They do not even follow the large majority quickly. They are the last ones to get into the ship. For marketers, there is a profit to be made from these consumers.