demonstration-balancing equation.pptx
- 3. UNLOCKING OF TERMS ŌĆó Matter ŌĆó Pure Substance ŌĆó Elements ŌĆó Compounds ŌĆó Chemical Reaction ŌĆó Chemical Equation
- 4. TERMS MATTER - anything that has space and occupies mass PURE SUBSTANCE - sample of matter that has definite chemical and physical properties.
- 5. TERMS ELEMENT - Simplest from of pure substance COMPOUND - pure substance that is made up of two or more elements bonded chemically
- 6. MOLECULAR SHAPES Pure Substances Made of one type of matter Elements Made of one type of atom Compounds Made of 2 or More atoms bonded together Homogeneous one phase MATTER Made of Atoms Has Mass & takes up Space Heterogeneous Made of more than one phase Can be separated Mixtures Made of more than one type of matter Atom + Atom = Element Molecule + Molecule = Compound Atom + Atom = Molecule Example: Juice Examples: Trail Mix Salad
- 7. TERMS CHEMICAL REACTIONS - process in which the physical and chemical properties of the original substances change as new substances with different physical and chemical properties are formed. CHEMICAL EQUATION - symbolic representation of a chemical reaction in the form of symbols and chemical formulas
- 8. H2 + O2 ’āĀ H2O H O H2O Reactant Product Beginning of the reaction Formed after the reaction
- 9. H2 + O2 ’āĀ H2O H O H2O + ’āĀ H H H H O O O
- 10. LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MASS During chemical reaction, atoms are neither created nor destroyed. The number of atoms remains constant throughout the reaction. Since the number of atoms doesnŌĆÖt change, the mass must remain constant as well.
- 11. H2 + O2 ’āĀ H2O
- 12. H2 + O2 ’āĀ H2O H O H2O + ’āĀ + ’āĀ H H O O H H O H H
- 13. H2 + O2 ’āĀ H2O H O H2O + ’āĀ + ’āĀ H H O O H H O H H H H O
- 14. H2 + O2 ’āĀ H2O H H H H O O H H O
- 15. 2H2 + O2 ’āĀ 2H2O H H H H O O H H O
- 16. 2H2 + O2 ’āĀ 2H2O BALANCED EQUATION + ’āĀ H H O O H H O H H H H O
- 17. 2H2 O2 Na 2H2O
- 20. Na + FeCl2 ’āĀ NaCl + Fe When sodium metal reacts with iron (II) chloride, iron metal and sodium chloride are formed.
- 21. Na + FeCl2 ’āĀ NaCl + Fe Na Cl Fe
- 22. Na + FeCl2 ’āĀ NaCl + Fe Step 1. Identify the reactant and the product. Reactant: Na + FeCl2 Product: NaCl+ Fe
- 23. Na + FeCl2 ’āĀ NaCl + Fe Step 2. List all the elements found on the chemical equation __ Na + __ FeCl2 ’āĀ __ NaCl + __Fe -Na- -Fe- -Cl-
- 24. Na + FeCl2 ’āĀ NaCl + Fe Step 3. Identify the number of atoms present in every element in the reactant side __ Na + __ FeCl2 ’āĀ __ NaCl + __Fe 1 -Na- 1 -Fe- 2 -Cl-
- 25. Na + FeCl2 ’āĀ NaCl + Fe Step 4. Identify the number of atoms present in every element in the product side __ Na + __ FeCl2 ’āĀ __ NaCl + __Fe -Na- 1 -Fe- 1 -Cl- 1
- 26. Na + FeCl2 ’āĀ NaCl + Fe Step 5. Check if the number of atoms on both reactant and product side is the same/balanced __ Na + __ FeCl2 ’āĀ __ NaCl + __Fe 1 -Na- 1 1 -Fe- 1 2 -Cl- 1
- 27. Na + FeCl2 ’āĀ NaCl + Fe Step 6. Write coefficient in each element/compound to change the number of atoms in an element and check if the number of atoms on both reactant and product side is the same/balanced __ Na + __ FeCl2 ’āĀ 2NaCl + __Fe 1 -Na- 1 1 -Fe- 1 2 -Cl- 1
- 28. Na + FeCl2 ’āĀ NaCl + Fe Step 6. Write coefficient in each element/compound to change the number of atoms in an element and check if the number of atoms on both reactant and product side is the same/balanced __ Na + __ FeCl2 ’āĀ 2NaCl + __Fe 1 -Na- 1 1 -Fe- 1 2 -Cl- 2
- 29. Na + FeCl2 ’āĀ NaCl + Fe Step 6. Write coefficient in each element/compound to change the number of atoms in an element and check if the number of atoms on both reactant and product side is the same/balanced __ Na + __ FeCl2 ’āĀ 2NaCl + __Fe 1 -Na- 2 1 -Fe- 1 2 -Cl- 2
- 30. Na + FeCl2 ’āĀ NaCl + Fe Step 6. Write coefficient in each element/compound to change the number of atoms in an element and check if the number of atoms on both reactant and product side is the same/balanced 2Na + FeCl2 ’āĀ 2NaCl + Fe 2 -Na- 2 1 -Fe- 1 2 -Cl- 2
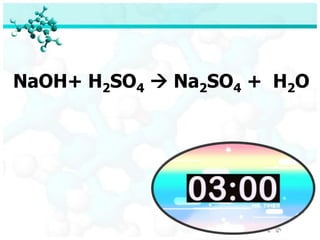
- 31. NaOH + H2SO4 ’āĀ Na2SO4 + H2O When dissolved sodium hydroxide reacts with sulfuric acid, aqueous sodium sulfate and water are formed.
- 32. NaOH+ H2SO4 ’āĀ Na2SO4 + H2O
- 33. NaOH+ H2SO4 ’āĀ Na2SO4 + H2O Step 1. Identify the reactant and the product. Reactant: NaOH+ H2SO4 Product: Na2SO4 + H2O
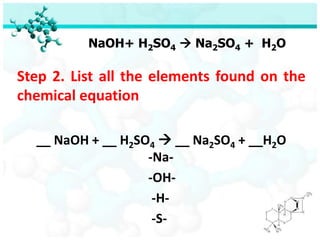
- 34. NaOH+ H2SO4 ’āĀ Na2SO4 + H2O Step 2. List all the elements found on the chemical equation __ NaOH + __ H2SO4 ’āĀ __ Na2SO4 + __H2O -Na- -OH- -H- -S-
- 35. NaOH+ H2SO4 ’āĀ Na2SO4 + H2O Step 3. Identify the number of atoms present in every element in the reactant side __ NaOH + __ H2SO4 ’āĀ __ Na2SO4 + __H2O 1 -Na- 6 -O- 3 -H- 4 -S-
- 36. NaOH+ H2SO4 ’āĀ Na2SO4 + H2O Step 4. Identify the number of atoms present in every element in the product side __ NaOH + __ H2SO4 ’āĀ __ Na2SO4 + __H2O -Na- 2 -O- 5 -H- 2 -S- 1
- 37. NaOH+ H2SO4 ’āĀ Na2SO4 + H2O Step 5. Check if the number of atoms on both reactant and product side is the same/balanced __ NaOH + __ H2SO4 ’āĀ __ Na2SO4 + __H2O 1 -Na- 2 5 -O- 5 3 -H- 2 1 -S- 1
- 38. NaOH+ H2SO4 ’āĀ Na2SO4 + H2O Step 6. Write coefficient in each element/compound to change the number of atoms in an element and check if the number of atoms on both reactant and product side is the same/balanced 2 NaOH + H2SO4 ’āĀ Na2SO4 + 2 H2O 2 -Na- 2 5 -O- 5 3 -H- 2 1 -S- 1
- 39. NaOH+ H2SO4 ’āĀ Na2SO4 + H2O Step 6. Write coefficient in each element/compound to change the number of atoms in an element and check if the number of atoms on both reactant and product side is the same/balanced 2 NaOH + H2SO4 ’āĀ Na2SO4 + 2 H2O 2 -Na- 2 6 -O- 6 4 -H- 4 1 -S- 1
- 40. BALANCE A B C
- 43. QUIZ TIME
- 44. Test I. Balanced Unbalanced 1AlBr3 + 6K ’āĀ 3KBr + 2Al 1FeO + 1PdF2 ’āĀ 1FeF2 + 1PdO 1P4 + 6Br2 ’āĀ 4PBr3 2LiCl + 1Br2 ’āĀ LiBr + 1Cl2 1PbBr2 + 2HCl ’āĀ 2HBr + 1PbCl2
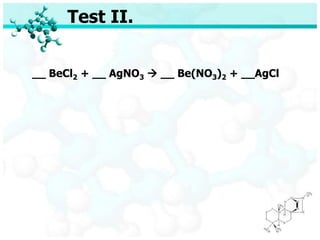
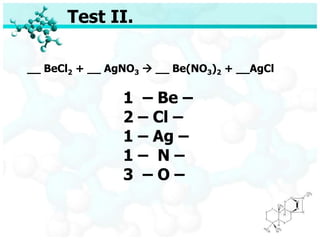
- 45. Test II. __ BeCl2 + __ AgNO3 ’āĀ __ Be(NO3)2 + __AgCl
- 46. QUIZ TIME
- 47. Test I. Balanced Unbalanced 1AlBr3 + 6K ’āĀ 3KBr + 2Al 1FeO + 1PdF2 ’āĀ 1FeF2 + 1PdO 1P4 + 6Br2 ’āĀ 4PBr3 2LiCl + 1Br2 ’āĀ LiBr + 1Cl2 1PbBr2 + 2HCl ’āĀ 2HBr + 1PbCl2
- 48. Test I. 1FeO + 1PdF2 ’āĀ 1FeF2 + 1PdO 1P4 + 6Br2 ’āĀ 4PBr3 2LiCl + 1Br2 ’āĀ LiBr + 1Cl2 1PbBr2 + 2HCl ’āĀ 2HBr + 1PbCl2 Balanced Unbalanced 1AlBr3 + 6K ’āĀ 3KBr + 2Al
- 49. Test I. Balanced Unbalanced 1FeO + 1PdF2 ’āĀ 1FeF2 + 1PdO 1AlBr3 + 6K ’āĀ 3KBr + 2Al 2LiCl + 1Br2 ’āĀ LiBr + 1Cl2 1PbBr2 + 2HCl ’āĀ 2HBr + 1PbCl2
- 50. Test I. Balanced Unbalanced 1FeO + 1PdF2 ’āĀ 1FeF2 + 1PdO 1P4 + 6Br2 ’āĀ 4PBr3 1AlBr3 + 6K ’āĀ 3KBr + 2Al 2LiCl + 1Br2 ’āĀ LiBr + 1Cl2 1PbBr2 + 2HCl ’āĀ 2HBr + 1PbCl2
- 51. Test I. Balanced Unbalanced 1FeO + 1PdF2 ’āĀ 1FeF2 + 1PdO 1P4 + 6Br2 ’āĀ 4PBr3 1AlBr3 + 6K ’āĀ 3KBr + 2Al 2LiCl + 1Br2 ’āĀ LiBr + 1Cl2 1PbBr2 + 2HCl ’āĀ 2HBr + 1PbCl2
- 52. Test I. Balanced Unbalanced 1FeO + 1PdF2 ’āĀ 1FeF2 + 1PdO 1P4 + 6Br2 ’āĀ 4PBr3 1PbBr2 + 2HCl ’āĀ 2HBr + 1PbCl2 1AlBr3 + 6K ’āĀ 3KBr + 2Al 2LiCl + 1Br2 ’āĀ LiBr + 1Cl2
- 53. Test II. __ BeCl2 + __ AgNO3 ’āĀ __ Be(NO3)2 + __AgCl
- 54. Test II. __ BeCl2 + __ AgNO3 ’āĀ __ Be(NO3)2 + __AgCl ŌĆō Be ŌĆō ŌĆō Cl ŌĆō ŌĆō Ag ŌĆō ŌĆō N ŌĆō ŌĆō O ŌĆō
- 55. Test II. __ BeCl2 + __ AgNO3 ’āĀ __ Be(NO3)2 + __AgCl 1 ŌĆō Be ŌĆō 2 ŌĆō Cl ŌĆō 1 ŌĆō Ag ŌĆō 1 ŌĆō N ŌĆō 3 ŌĆō O ŌĆō
- 56. Test II. __ BeCl2 + __ AgNO3 ’āĀ __ Be(NO3)2 + __AgCl 1 ŌĆō Be ŌĆō 1 2 ŌĆō Cl ŌĆō 1 1 ŌĆō Ag ŌĆō 1 1 ŌĆō N ŌĆō 2 3 ŌĆō O ŌĆō 6
- 57. Test II. __ BeCl2 + __ AgNO3 ’āĀ __ Be(NO3)2 + 2AgCl 1 ŌĆō Be ŌĆō 1 2 ŌĆō Cl ŌĆō 1x2=2 1 ŌĆō Ag ŌĆō 1x2=2 1 ŌĆō N ŌĆō 2 3 ŌĆō O ŌĆō 6
- 58. Test II. __ BeCl2 + 2AgNO3 ’āĀ __ Be(NO3)2 + 2AgCl 1 ŌĆō Be ŌĆō 1 2 ŌĆō Cl ŌĆō 1x2=2 2=2x1 ŌĆō Ag ŌĆō 1x2=2 2=2x1 ŌĆō N ŌĆō 2 6=2x3 ŌĆō O ŌĆō 6
- 59. Test II. Balanced Equation: 1BeCl2 + 2AgNO3 ’āĀ 1Be(NO3)2 + 2AgCl or BeCl2 + 2AgNO3 ’āĀ Be(NO3)2 + 2AgCl
- 60. THE END!