Design of Bucket Elevator & Cage Elevator
- 1. ŌĆó Introduction, ŌĆó Types of Bucket Elevator, ŌĆó Design of Bucket Elevator- loading and bucket arrangements, ŌĆó Cage elevators, shaft way, guides, counter weights Design of Bucket Elevator & Cage Elevator
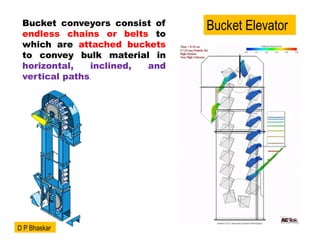
- 2. Bucket conveyors consist of endless chains or belts to which are attached buckets to convey bulk material in horizontal, inclined, and vertical paths. Bucket Elevator D P Bhaskar
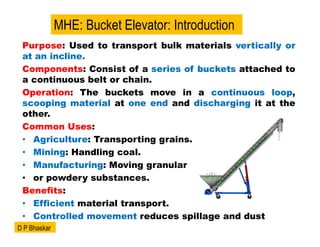
- 3. Purpose: Used to transport bulk materials vertically or at an incline. Components: Consist of a series of buckets attached to a continuous belt or chain. Operation: The buckets move in a continuous loop, scooping material at one end and discharging it at the other. Common Uses: ŌĆó Agriculture: Transporting grains. ŌĆó Mining: Handling coal. ŌĆó Manufacturing: Moving granular ŌĆó or powdery substances. Benefits: ŌĆó Efficient material transport. ŌĆó Controlled movement reduces spillage and dust MHE: Bucket Elevator: Introduction D P Bhaskar
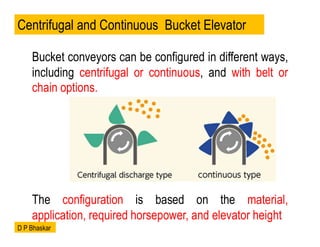
- 4. Bucket conveyors can be configured in different ways, including centrifugal or continuous, and with belt or chain options. The configuration is based on the material, application, required horsepower, and elevator height Centrifugal and Continuous Bucket Elevator D P Bhaskar
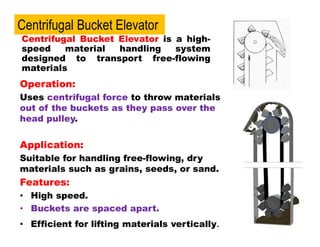
- 5. Operation: Uses centrifugal force to throw materials out of the buckets as they pass over the head pulley. Application: Suitable for handling free-flowing, dry materials such as grains, seeds, or sand. Features: ŌĆó High speed. ŌĆó Buckets are spaced apart. ŌĆó Efficient for lifting materials vertically. Centrifugal Bucket Elevator is a high- speed material handling system designed to transport free-flowing materials Centrifugal Bucket Elevator
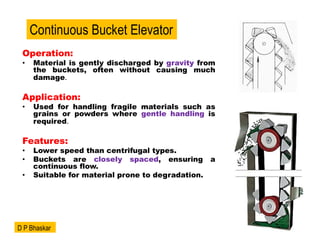
- 6. Operation: ŌĆó Material is gently discharged by gravity from the buckets, often without causing much damage. Application: ŌĆó Used for handling fragile materials such as grains or powders where gentle handling is required. Features: ŌĆó Lower speed than centrifugal types. ŌĆó Buckets are closely spaced, ensuring a continuous flow. ŌĆó Suitable for material prone to degradation. Continuous Bucket Elevator D P Bhaskar
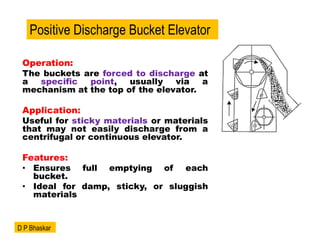
- 7. Operation: The buckets are forced to discharge at a specific point, usually via a mechanism at the top of the elevator. Application: Useful for sticky materials or materials that may not easily discharge from a centrifugal or continuous elevator. Features: ŌĆó Ensures full emptying of each bucket. ŌĆó Ideal for damp, sticky, or sluggish materials Positive Discharge Bucket Elevator D P Bhaskar
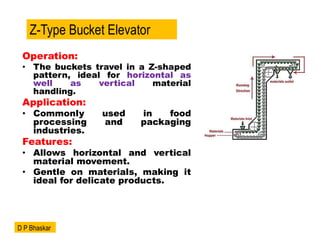
- 8. Operation: ŌĆó The buckets travel in a Z-shaped pattern, ideal for horizontal as well as vertical material handling. Application: ŌĆó Commonly used in food processing and packaging industries. Features: ŌĆó Allows horizontal and vertical material movement. ŌĆó Gentle on materials, making it ideal for delicate products. Z-Type Bucket Elevator D P Bhaskar
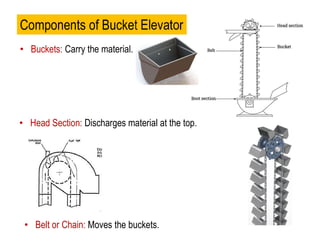
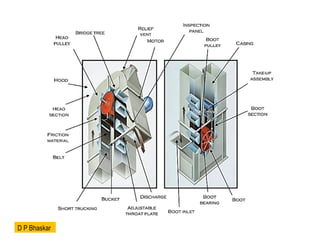
- 9. ŌĆó Head Section: Discharges material at the top. Components of Bucket Elevator ŌĆó Buckets: Carry the material. ŌĆó Belt or Chain: Moves the buckets.
- 10. D P Bhaskar
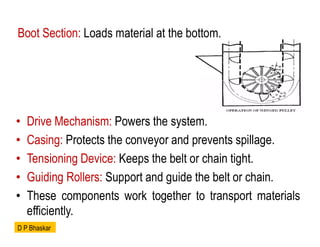
- 11. ŌĆó Drive Mechanism: Powers the system. ŌĆó Casing: Protects the conveyor and prevents spillage. ŌĆó Tensioning Device: Keeps the belt or chain tight. ŌĆó Guiding Rollers: Support and guide the belt or chain. ŌĆó These components work together to transport materials efficiently. Boot Section: Loads material at the bottom. D P Bhaskar
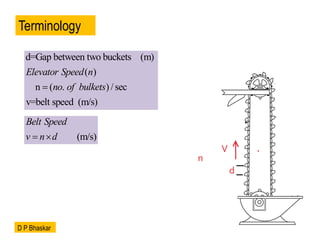
- 12. Terminology d=Gap between two buckets (m) ( ) n ( . ) /sec v=belt speed (m/s) Elevator Speed n no of bulkets ’ĆĮ (m/s) Belt Speed v n d ’ĆĮ ’é┤ D P Bhaskar
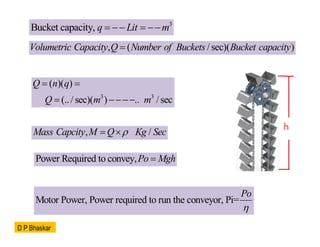
- 13. 3 Bucket capacity, q Lit m ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ , ( /sec)( ) Volumetric Capacity Q Number of Buckets Bucket capacity ’ĆĮ 3 3 ( )( ) (../ sec)( ) .. /sec Q n q Q m m ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ , / Mass Capcity M Q Kg Sec ’ü▓ ’ĆĮ ’é┤ Power Required to convey,Po Mgh ’ĆĮ Motor Power, Power required to run the conveyor, Pi= Po ’ü© D P Bhaskar
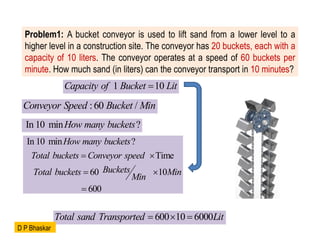
- 14. Problem1: A bucket conveyor is used to lift sand from a lower level to a higher level in a construction site. The conveyor has 20 buckets, each with a capacity of 10 liters. The conveyor operates at a speed of 60 buckets per minute. How much sand (in liters) can the conveyor transport in 10 minutes? 1 10 Capacity of Bucket Lit ’ĆĮ :60 / Conveyor Speed Bucket Min In 10 min ? How many buckets In 10 min ? Time 60 10 600 How many buckets Total buckets Conveyor speed Buckets Total buckets Min Min ’ĆĮ ’é┤ ’ĆĮ ’é┤ ’ĆĮ 600 10 6000 Total sand Transported Lit ’ĆĮ ’é┤ ’ĆĮ D P Bhaskar
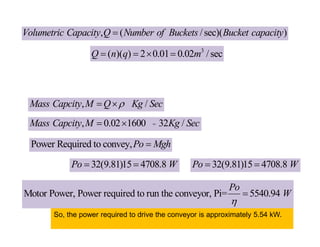
- 15. Problem2: A bucket conveyor is used to lift sand from ground level to a storage bin 15 meters high. The conveyor is inclined at an angle of 30┬░ to the horizontal. Each bucket has a capacity of 10 liters and is spaced 0.5 meters apart. The conveyor runs at a speed of 1 meter per second. The bulk density of the sand is 1600 kg/m┬│. Calculate: The volumetric capacity of the conveyor in liters per second. The mass capacity of the conveyor in kg per second. The power required to drive the conveyor if the efficiency is 85%. n=(Number of Buckets passing) per sec 3 3 1 / sec Bucket capacity, 10 0.01 1600 / v m q Lit m Kg m ’ü▓ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ( ) 1 /sec n= ( ) 0.5 Speed v m Spacing d m ’ĆĮ n=2 /sec Buckets Power Required to convey, ( /sec)( )( ) Po Mgh Kg g m Watt ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ (m/s) Belt Speed v n d ’ĆĮ ’é┤
- 16. , / Mass Capcity M Q Kg Sec ’ü▓ ’ĆĮ ’é┤ = , 0.02 1600 32 / Mass Capcity M Kg Sec ’ĆĮ ’é┤ Power Required to convey,Po Mgh ’ĆĮ 32(9.81)15 4708.8 Po W ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ 32(9.81)15 4708.8 Po W ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ Motor Power, Power required to run the conveyor, Pi= 5540.94 Po W ’ü© ’ĆĮ So, the power required to drive the conveyor is approximately 5.54 kW. , ( /sec)( ) Volumetric Capacity Q Number of Buckets Bucket capacity ’ĆĮ 3 ( )( ) 2 0.01 0.02 /sec Q n q m ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’é┤ ’ĆĮ
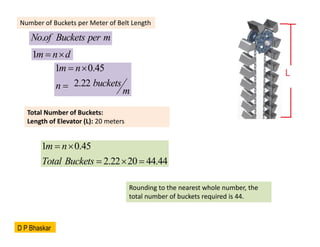
- 17. Problem3: A centrifugal bucket elevator is designed to handle 50 tons of sand per hour. The sand has a bulk density of 1600 kg/m┬│. Each bucket has a capacity of 12 liters, and the buckets are spaced 0.45 meters apart. The elevator is inclined at an angle of 30┬░. Calculate: The required belt speed in meters per second. The number of buckets required per meter of belt length. The total number of buckets required if the total length of the elevator is 20 meters. , 15 / Mass Capcity M Ton Hr ’ĆĮ 13.88 / M Kg Sec ’ĆĮ / M Q Kg Sec ’ü▓ ’ĆĮ ’é┤ 3 1600 / Kg m ’ü▓ ’ĆĮ 3 0.008680 / Volumetric Capacity Q m s ’ĆĮ ( )( ) Q n q ’ĆĮ 3 12 0.012 q Lit m ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ 0.723 /sec n buckets ’ĆĮ Belt Speed v n d ’ĆĮ ’é┤ 0.45 0.3255 /sec v n m ’ĆĮ ’é┤ ’ĆĮ
- 18. . Noof Buckets per m 1m n d ’ĆĮ ’é┤ Number of Buckets per Meter of Belt Length 1 0.45 2.22 m n buckets n m ’ĆĮ ’é┤ ’ĆĮ Total Number of Buckets: Length of Elevator (L): 20 meters 1 0.45 2.22 20 44.44 m n Total Buckets ’ĆĮ ’é┤ ’ĆĮ ’é┤ ’ĆĮ Rounding to the nearest whole number, the total number of buckets required is 44. D P Bhaskar
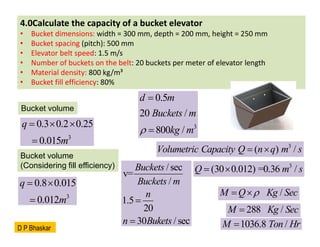
- 19. 4.0Calculate the capacity of a bucket elevator ŌĆó Bucket dimensions: width = 300 mm, depth = 200 mm, height = 250 mm ŌĆó Bucket spacing (pitch): 500 mm ŌĆó Elevator belt speed: 1.5 m/s ŌĆó Number of buckets on the belt: 20 buckets per meter of elevator length ŌĆó Material density: 800 kg/m┬│ ŌĆó Bucket fill efficiency: 80% Bucket volume 3 0.3 0.2 0.25 0.015 q m ’ĆĮ ’é┤ ’é┤ ’ĆĮ Bucket volume (Considering fill efficiency) 3 0.8 0.015 0.012 q m ’ĆĮ ’é┤ ’ĆĮ 3 0.5 20 / 800 / d m Buckets m kg m ’ü▓ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ 3 ( ) / Volumetric Capacity Q n q m s ’ĆĮ ’é┤ 3 (30 0.012) =0.36 / Q m s ’ĆĮ ’é┤ /sec v= / 1.5 20 30 / sec Buckets Buckets m n n Bukets ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ / M Q Kg Sec ’ü▓ ’ĆĮ ’é┤ 288 / M Kg Sec ’ĆĮ 1036.8 / M Ton Hr ’ĆĮ D P Bhaskar
- 20. Cage Elevator ŌĆó A cage elevator, also known as a cage lift or mine cage elevator, used in mining operations or construction sites to transport people, equipment, or materials vertically. ŌĆó It consists of an enclosed or semi-enclosed cage or platform that moves within a shaft, guided by rails, and powered by an electric or hydraulic mechanism. D P Bhaskar
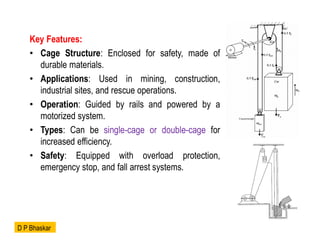
- 21. Key Features: ŌĆó Cage Structure: Enclosed for safety, made of durable materials. ŌĆó Applications: Used in mining, construction, industrial sites, and rescue operations. ŌĆó Operation: Guided by rails and powered by a motorized system. ŌĆó Types: Can be single-cage or double-cage for increased efficiency. ŌĆó Safety: Equipped with overload protection, emergency stop, and fall arrest systems. D P Bhaskar
- 22. Advantages: ŌĆó Designed for heavy load handling. ŌĆó Highly durable with advanced safety features. Disadvantages: ŌĆó Slower than modern passenger elevators. ŌĆó Requires significant space for the shaft. D P Bhaskar
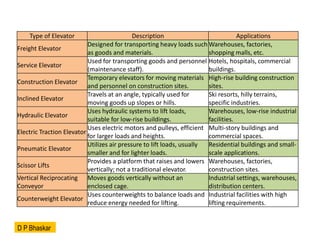
- 23. Type of Elevator Description Applications Freight Elevator Designed for transporting heavy loads such as goods and materials. Warehouses, factories, shopping malls, etc. Service Elevator Used for transporting goods and personnel (maintenance staff). Hotels, hospitals, commercial buildings. Construction Elevator Temporary elevators for moving materials and personnel on construction sites. High-rise building construction sites. Inclined Elevator Travels at an angle, typically used for moving goods up slopes or hills. Ski resorts, hilly terrains, specific industries. Hydraulic Elevator Uses hydraulic systems to lift loads, suitable for low-rise buildings. Warehouses, low-rise industrial facilities. Electric Traction Elevator Uses electric motors and pulleys, efficient for larger loads and heights. Multi-story buildings and commercial spaces. Pneumatic Elevator Utilizes air pressure to lift loads, usually smaller and for lighter loads. Residential buildings and small- scale applications. Scissor Lifts Provides a platform that raises and lowers vertically; not a traditional elevator. Warehouses, factories, construction sites. Vertical Reciprocating Conveyor Moves goods vertically without an enclosed cage. Industrial settings, warehouses, distribution centers. Counterweight Elevator Uses counterweights to balance loads and reduce energy needed for lifting. Industrial facilities with high lifting requirements. D P Bhaskar
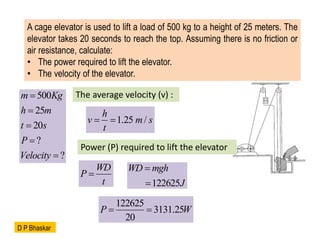
- 24. A cage elevator is used to lift a load of 500 kg to a height of 25 meters. The elevator takes 20 seconds to reach the top. Assuming there is no friction or air resistance, calculate: ŌĆó The power required to lift the elevator. ŌĆó The velocity of the elevator. 500 25 20 ? ? m Kg h m t s P Velocity ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ The average velocity (v) : 1.25 / h v m s t ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ Power (P) required to lift the elevator WD P t ’ĆĮ 122625 WD mgh J ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ 122625 3131.25 20 P W ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ D P Bhaskar
- 25. A cage elevator is designed to lift a load of 1,000 kg to a height of 40 meters. The elevator uses a pulley system that provides a mechanical advantage of 4. The total weight of the elevator cage, including its components, is 200 kg. The elevator operates with an efficiency of 90%. Calculate: ŌĆó The force required to lift the load. ŌĆó The work done in lifting the load and the elevator cage. ŌĆó The total power required from the motor. ŌĆó The actual power output of the motor, considering efficiency. . 1000 40 4 200 0.9 cage m Kg h m MA m Kg ’ü© ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ D P Bhaskar
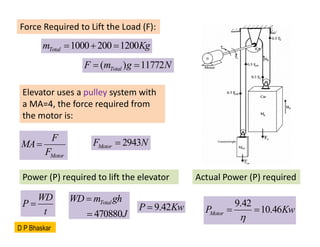
- 26. 1000 200 1200 Total m Kg ’ĆĮ ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ Force Required to Lift the Load (F): ( ) 11772 Total F m g N ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ Elevator uses a pulley system with a MA=4, the force required from the motor is: Motor F MA F ’ĆĮ 2943 Motor F N ’ĆĮ Power (P) required to lift the elevator WD P t ’ĆĮ 470880 Total WD m gh J ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ 9.42 P Kw ’ĆĮ Actual Power (P) required 9.42 10.46 Motor P Kw ’ü© ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ D P Bhaskar
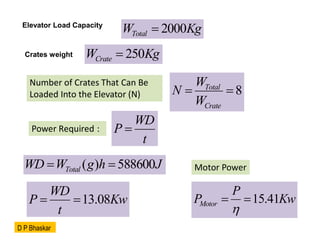
- 27. A freight elevator is designed to lift heavy goods in a warehouse. The elevator has the following specifications: Load Capacity: 2,000 kg Height of Lift: 30 meters Time to Lift Load: 45 seconds Efficiency of the Motor: 85% The elevator is used to lift crates, each weighing 250 kg. Calculate: The total weight of the load being lifted when the elevator is at maximum capacity. The work done in lifting the maximum load to the specified height. The total power required from the motor to lift the maximum load. The actual power output of the motor considering its efficiency. The number of crates that can be loaded into the elevator when operating at maximum capacity. D P Bhaskar
- 28. 2000 Total W Kg ’ĆĮ Elevator Load Capacity Crates weight 250 Crate W Kg ’ĆĮ Number of Crates That Can Be Loaded Into the Elevator (N) 8 Total Crate W N W ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ WD P t ’ĆĮ Power Required : ( ) 588600 Total WD W g h J ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ 13.08 WD P Kw t ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ Motor Power 15.41 Motor P P Kw ’ü© ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ D P Bhaskar
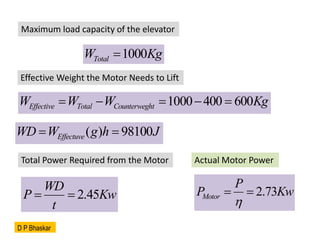
- 29. A counterweight elevator is designed to lift both passengers and goods in a commercial building. The elevator has the following specifications: ŌĆó Load Capacity: 1,000 kg (for passengers and goods combined) ŌĆó Counterweight: 600 kg ŌĆó Height of Lift: 25 meters ŌĆó Time to Lift Load: 40 seconds ŌĆó Efficiency of the Motor: 90% ŌĆó Each passenger weighs approximately 75 kg Calculate: ŌĆó The total weight of the load being lifted when the elevator is at maximum capacity. ŌĆó The effective weight the motor needs to lift, considering the counterweight. ŌĆó The work done in lifting the maximum load to the specified height. ŌĆó The total power required from the motor to lift the maximum load. ŌĆó The actual power output of the motor considering its efficiency. ŌĆó The maximum number of passengers that can be loaded into the elevator when operating at maximum capacity. D P Bhaskar
- 30. Maximum load capacity of the elevator 1000 Total W Kg ’ĆĮ Effective Weight the Motor Needs to Lift 1000 400 600 Effective Total Counterweght W W W Kg ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ( ) 98100 Effectuve WD W g h J ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ 2.45 WD P Kw t ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ Total Power Required from the Motor Actual Motor Power 2.73 Motor P P Kw ’ü© ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ D P Bhaskar
- 31. Maximum Number of Passengers That Can Be Loaded Into the Elevator (N) 13.33 Total Passenger W N W N ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ D P Bhaskar