Design Thinking : An Introduction for Engineering Students
- 1. Principles of Design Thinking Presented by : Prof. Vikramjit Kakati
- 2. Roll Name Branch Innovative Idea Novelty Justification Reason for Selection DC2020BTE0183 Arnab Acharjee EEE A machine to measure brain pressure. A device that does not yet exist in the medical field, potentially providing important health insights by measuring brain pressure. Potentially groundbreaking in medical diagnostics, filling a gap for monitoring brain health in real time. DC2024BTE0010 Sadananda Das CVE Bio-sensing wearable for real-time health monitoring using non- invasive sweat analysis. Introduces non-invasive real-time health monitoring using sweat analysis, which is more convenient than traditional blood tests. Revolutionizes health tracking for chronic conditions like diabetes through non-invasive, real-time monitoring. DC2024BTE0004 Noulevi Yhor CVE Smart Solar Roads combining renewable energy and transportation. Innovates road infrastructure by integrating solar energy generation and smart transportation systems. Creates sustainable infrastructure while simultaneously generating energy, addressing multiple challenges in urban environments. DC2024BTE0058 Yaikhom Bishwaraj CVE Self-healing road infrastructure system using smart concrete and embedded nanomaterials. A smart road infrastructure system that repairs itself, minimizing the need for frequent maintenance and reducing costs. Offers a sustainable solution to road maintenance, extending road lifespan and reducing disruptions from frequent repairs. DC2024BTE0012 Dondor James Duia AI & ML AI-driven price forecasting for vegetables and pulses to aid farming and trade. Uses AI for precise, data-driven price forecasting in agriculture, supporting better decisions for farmers and traders. Improves decision-making in agriculture with high accuracy, positively impacting food security and market stability. BC2024BTE0025 Dolimhangba MNE Replacement of charging plugs with electromagnetism-based wall energy system. This idea revolutionizes charging by eliminating the need for traditional outlets and allows power access through the entire wall. Innovative approach to convenience in power usage, which could have widespread applications in homes and public places. DC2024BTE0002 Longsela Juliana Sangtam CVE Windmills that run on solar energy where there's no wind, generating electricity. Combines renewable energy sources (solar and wind), offering a solution for areas where wind energy is unavailable. Utilizes dual renewable energy sources, increasing efficiency and applicability in diverse environmental conditions. DC2024BTE0003 MERIBENI KIKON CVE Umbrella with air cooler attached. A novel way to make an umbrella more functional by adding cooling, making it useful in hot climates and multifunctional. A practical solution to a common problem, enhancing the utility of an everyday object with a simple innovation. DC2024BTE0038 Rongsennungshi Pongen CVE Nanobots that detect damage (scratches or tears) and autonomously repair materials. Autonomously repairing nanobots can revolutionize material maintenance by detecting and fixing damages, extending product life. A futuristic idea that could be applied in various fields, reducing the need for human intervention in repairs. DB2024BTE0106 Ningthoujam Pamheiba Singh CVE Virtual reality therapy for those afraid to go to the doctor. Uses virtual reality to provide healthcare solutions to patients without the need to visit hospitals, reducing anxiety and discomfort. Addresses a specific mental health issue by using emerging technology, providing a unique solution to doctor-phobia.
- 3. Introduction to Design Thinking
- 4. Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that combines creative and analytical thinking. It aims to solve complex problems by deeply understanding the user’s needs and iterating solutions.
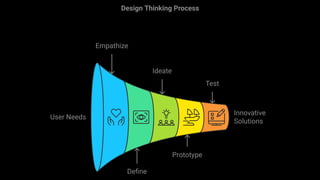
- 6. The Five Phases of Design Thinking
- 8. Empathize Goal Understand the user’s needs and experiences. How to Conduct interviews, observations, and user surveys. Example A team designing a new mobile app for elderly users starts by interviewing senior citizens about their daily tech usage and struggles.
- 9. Define Goal Clearly articulate the problem based on insights from the Empathize phase. How to Synthesize research into a problem statement or "Point of View" (POV). Example Elderly users struggle with small text and complex navigation in mobile apps, making it hard for them to stay connected with family.
- 10. Ideate Goal Brainstorm a wide range of creative solutions. How to Use techniques like brainstorming, mind mapping, or SCAMPER to generate ideas. Example The team generates ideas for larger fonts, simplified navigation, and voice-activated commands for the mobile app.
- 11. Prototype Goal Build quick, low-cost prototypes of the ideas. [A prototype is a basic, working model of a product or idea used to test and improve it before the final version is made.] How to Create physical models, wireframes, or mock-ups to explore different solutions. Example The team builds wireframes of the app with large buttons, voice commands, and simplified screens.
- 12. Test Goal Test the prototypes with real users and gather feedback. How to Conduct user testing sessions and refine the solution based on feedback. Example The elderly users test the app prototype, and the team refines the design based on their feedback—like adding an emergency button and making the font even larger.
- 13. Iteration is Key Goal Keep improving the solution through feedback loops. How to After each testing phase, return to ideation or prototyping if necessary. Example The app team continues to iterate on the design, making small improvements after each round of user testing.
- 14. Example Case Study: Airbnb Example Airbnb used Design Thinking to transform their website experience. After empathizing with hosts and guests, they redefined the problem and redesigned their platform with more visual listings and user-friendly navigation. As a result, their business grew exponentially.
- 15. Design Thinking • User-Centred Solutions • Encourages Innovation • Reduces Risk of Failure • Fosters Collaboration and Creativity
- 16. Design Thinking helps create innovative solutions by focusing on user needs and iterating through feedback. The iterative, flexible approach makes it applicable across industries. Conclusion
- 17. THANK YOU










![Prototype Goal
Build quick, low-cost prototypes of the ideas.
[A prototype is a basic, working model of a product or idea
used to test and improve it before the final version is made.]
How to
Create physical models, wireframes, or mock-ups to
explore different solutions.
Example
The team builds wireframes of the app with large
buttons, voice commands, and simplified screens.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designthinkingvikramjitkakati-241027153259-7366ecba/85/Design-Thinking-An-Introduction-for-Engineering-Students-11-320.jpg)





