Desizing in textile
Download as PPTX, PDF25 likes22,733 views
Desizing removes starch sizing agents from warp yarns that were applied before weaving to improve the weaving process. The main objectives of desizing are to remove this non-water-soluble starch so the fabric can undergo further wet processing like dyeing. Common desizing methods include rot steeping, which uses microbes to hydrolyze starch over 24 hours; acidic desizing, which uses dilute acid to hydrolyze starch in 8-12 hours; and enzymatic desizing, the most widely used modern method harnessing enzymes. Oxidative desizing can work on a variety of unknown sizes but may damage fibers if not carefully applied. The type of size, fabric construction, and desizing method
1 of 20
Downloaded 494 times

















Recommended
Chemicals and Auxiliaries used in Textile Wet Processing



Chemicals and Auxiliaries used in Textile Wet ProcessingMashrur Wasity
Ėý
This document discusses various chemicals and auxiliaries used in textile wet processing. It defines auxiliaries as chemicals that help processing operations like preparation, dyeing and printing work more efficiently. Some common auxiliaries mentioned include surfactants, wetting agents, sequestering agents, dispersing agents and emulsifiers. Basic chemicals used in wet processing like acids, bases, salts, oxidizing and reducing agents are also discussed. The roles and examples of various chemicals are provided in concise points.Mercerization



Mercerizationparmeet kaur
Ėý
The document discusses the process of mercerizing cotton fabrics. Mercerizing involves treating cotton yarns or fabrics with a cold or hot solution of sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) under tension to improve properties like strength, luster, and dye affinity. Specifically, swelling the cotton fibers in the caustic soda solution changes their cross-sectional shape and increases luster when the tension is maintained during washing. There are different methods for mercerizing yarns, knits, and woven fabrics either as batches or continuously. The advantages of mercerizing include brighter dye colors, better color retention after washing, and increased strength, smoothness, and resistance to damage.Resin finishing



Resin finishingMohan Pegu
Ėý
This document discusses resin finishing, which is a process that adds crease resistance and recovery properties to cotton fabrics. It involves applying cross-linking resins like DMDHEU to the fabric using a chemical finishing process with water and heat. The resins chemically bond to the cotton fibers and prevent creasing during wear and laundering. The document covers the types of resins used, the objectives of resin finishing, its advantages and disadvantages, how resin concentration and curing temperature affect properties, and provides an example resin finishing recipe.Pretreatment of textile materials



Pretreatment of textile materialsRinku Shemar
Ėý
The document discusses the process of singeing textiles. Singeing involves burning off protruding fibers from fabric surfaces to improve smoothness and luster. It can be done using gas singeing machines, which pass fabric over flames, or hot plate/roller machines. Key factors that affect singeing include flame intensity, fabric speed and temperature, and fiber type. Singeing removes fuzz to create a uniform, lustrous surface that reflects light evenly.pretreatment is the heart of wet processing.



pretreatment is the heart of wet processing.Nazmul Islam
Ėý
Pretreatment is an essential process for textile materials prior to dyeing and printing. The key processes include singeing, desizing, scouring, bleaching, and mercerizing. Singeing burns off protruding fibers to smooth the surface. Desizing removes starch coatings from warp yarns. Scouring makes the fabric highly absorbent by removing natural oils and impurities. Bleaching removes natural colorants to whiten the fabric. Mercerizing improves luster, strength, and dye uptake of cotton fabrics. All pretreatment processes prepare textiles for downstream applications.Scouring



ScouringMd. Mazadul Hasan Shishir
Ėý
Scouring is a process that removes natural and added impurities from textiles to make them more absorbent and suitable for dyeing and finishing. It works by saponification, emulsification, and solubilization using alkalis, surfactants, and sometimes solvents. The document provides details on scouring of different natural and synthetic fibers like cotton, silk, wool, polyester/cotton blends. It also lists typical recipes and procedures for scouring cotton and polyester/cotton blend goods.Garment washing



Garment washingRajeev Sharan
Ėý
The document discusses different methods of finishing garments, including stone washing. Stone washing involves tumbling freshly dyed jeans with pumice stones to produce a pre-washed and faded look through abrasion. The degree of fading depends on factors like the garment to stone ratio, washing time, stone size and hardness. Stone washing can damage machinery and pollute water. It also risks uneven fading and back staining if dye is redeposited on fabrics.TEXTILE FINISHING



TEXTILE FINISHINGsweet saran
Ėý
ENTIRE NOTES FOR RECENT TEXTILE FINISHING
IT IS USEFUL FOR COLLEGE LEVEL STUDENTS, AND ALSO FOR INDUSTRIAL PEOPLES..,Introduction to dyeing



Introduction to dyeingRajeev Sharan
Ėý
The document provides an introduction to textile dyeing, including definitions of basic terms like dyestuff and pigment, an overview of dyeing processes and factors that influence dye choices, and descriptions of different types of dyes including direct dyes for cellulosic fibers, reactive dyes, vat dyes, sulfur dyes, and disperse dyes for synthetic fibers. Classification methods for dyes and dyeing conditions for various fiber and dye combinations are also outlined.Mercerization



MercerizationMd. Mazadul Hasan Shishir
Ėý
1. Mercerization is a finishing treatment for cotton that improves luster, hardness, and other properties by treating cotton with a strong alkaline solution.
2. It involves immersing cotton yarn or fabric under tension in a cold sodium hydroxide solution, then neutralizing it in acid. This causes swelling of the cotton fibers and increases their luster.
3. The ideal conditions for mercerization are a caustic concentration of 250-320 g/L at 18-20°C for 30-60 seconds, as this provides the best luster with minimal shrinkage.DIRECT DYE



DIRECT DYESayeed Ahmed
Ėý
This presentation discusses direct dyes, which are water-soluble dyes used to dye cellulosic materials like cotton directly. There are two major types of direct dyes: anionic direct dyes, which are used for paper coloring and shade correction, and cationic direct dyes. Direct dyes have properties like water solubility and being anionic in nature. They dye materials through weak hydrogen and van der Waals bonding in alkaline conditions. The dyeing process involves dissolving the dye in boiling water with electrolytes before applying it to materials and boiling for 30-45 minutes. Direct dyes provide duller colors than reactive dyes and have lower wash fastness. They are used for applications where high fastness isDesizing



DesizingMd. Mazadul Hasan Shishir
Ėý
1. Desizing is done to remove sizing agents like starch that were applied to warp yarns during weaving to facilitate the weaving process.
2. There are several methods of desizing including enzymatic, acid, and oxidative methods. Enzymatic desizing uses enzymes like amylase to break down starch into soluble sugars.
3. Proper control of factors like temperature, pH, and fabric speed are important for effective desizing when using the enzymatic method.Scouring process in textile processing



Scouring process in textile processingFarhan ullah baig
Ėý
The document discusses the scouring process used to clean fabrics prior to dyeing or finishing. Scouring removes natural and mechanical impurities through processes like saponification, solubilization, and emulsification. Saponification converts oils and fats to soap and glycerin. Solubilization and emulsification remove other impurities like pectins, proteins, waxes, and minerals by making them water soluble or dispersing them. Selection of scouring agents depends on fiber type, fabric properties, and impurity level. Effectiveness is tested through measures like absorbency, weight loss, and residual wax content.Direct dye



Direct dyeRinku Shemar
Ėý
Direct dyes are water-soluble aromatic compounds that have an affinity for cellulose fibers like cotton. They are applied as aqueous solutions and bond to fibers physically through hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces. Direct dyes generally have poor fastness properties but these can be improved through after-treatments using metallic salts like copper or chromium compounds, or formaldehyde, which increase the dye's molecular weight and bonding strength to the fibers. Key factors that influence direct dye uptake include electrolyte concentration, temperature, liquor ratio, and dye class.Mercerisation



MercerisationVasanth Kumar
Ėý
Mercerization is a treatment of cotton yarn or fabric with a strong caustic soda solution that improves several qualities of the cotton. It increases luster and dye affinity, improves strength and stability, and results in smoother, rounder fibers. The process involves immersing cotton in a high concentration sodium hydroxide solution under tension control and then washing to neutralize the fabric. This summarizes the key points about mercerization from the provided document.Bleaching process in textile processing



Bleaching process in textile processingFarhan ullah baig
Ėý
Natural fibers contain coloring compounds that make them appear off-white. The objective of bleaching is to remove these color bodies and produce a white fabric using oxidizing bleaching agents while minimizing fiber damage. Hydrogen peroxide is the most widely used bleaching agent for cotton and blends. It works through its decomposition product, perhydroxyl ion, which breaks the double bonds in color compounds at an optimal pH of 10-11. Proper regulation of perhydroxyl ions through stabilizers prevents rapid decomposition of the bleach and fiber degradation. Temperature, time, concentration, and liquor ratio must be optimized to achieve effective bleaching with minimal impact on strength properties. Yarn count



Yarn countAmit Biswas
Ėý
This document discusses yarn count and its measurement. It defines yarn count as the numerical expression of the coarseness or fineness of yarn. There are several systems used to express yarn count, including indirect, direct, and universal systems. The most common systems are the indirect system used for cotton, wool, and linen, where higher count means finer yarn, and the direct system used for jute and silk, where higher count means coarser yarn. The universal Tex system introduced by ISO is a direct system where count indicates the weight in grams of 1000 meters of yarn. There are several instruments that can be used to measure yarn count, including quadrant balances, Knowles balances, and measuring drums forPresentation on mercerization



Presentation on mercerizationFranco Majigoi
Ėý
this slide in mercerization is prepared in chemical processing in textile and it could help a lot of students or lecturers who might be looking for web handout, presentation or seminar. it is openly accessible for all.scouring and bleaching 



scouring and bleaching Azmir Latif Beg
Ėý
Comparative study between bio scouring bleaching and traditional scouring and bleaching and cotton fabric dyeing with reactive dye. Softening Finishes 



Softening Finishes Asaye Dessie
Ėý
Softening finishes are important textile treatments that make fabrics feel softer. Chemical softeners allow fabrics to have a soft, smooth hand. The main types of softeners are cationic, anionic, non-ionic, and amphoteric softeners. Cationic softeners provide excellent softening but can cause yellowing, while anionic softeners have lower softening ability but better compatibility. Silicone softeners provide unique softness and properties like durability and heat stability, but can be expensive. Softener selection depends on the desired properties like fastness, compatibility with other chemicals, and effect on processes like seam slippage or drying.Wet processing-I



Wet processing-IAhmad Sakib
Ėý
This document contains information about Shuvo Brahma, a lecturer at BUTEX. It includes his contact details, education background of BSc and ongoing MSc from BUTEX, and previous job experience at Epyllion Knitex Ltd and as a lecturer at NITER.
It also includes the syllabus for the course WPE 243 Wet Processing-1 which covers topics like water and its importance in textile processing, detergents and auxiliaries, and pretreatment.
Finally, it discusses water treatment processes in the textile industry, including different water sources, hardness types, units of hardness measurement, effects of hardness on textile processing, and problems associated with hard water like scale formation inExhaust dyeing process



Exhaust dyeing processInterloop Limited
Ėý
Batch dyeing involves dyeing fabric in a stationary dye bath. There are three main types of batch dyeing machines. Jigger dyeing machines transfer fabric back and forth between rollers through a dye bath, applying tension. Winch dyeing machines pass rope-formed fabric over rollers through a stationary dye bath with little tension. Jet dyeing machines eliminate rollers and use jet nozzles to circulate fabric through a closed tubular system at high temperatures and pressures.Polyester fiber processing



Polyester fiber processingMd. Mazadul Hasan Shishir
Ėý
Polyester is a polymer made from a condensation reaction between small molecules to form ester groups. It is commonly made from a dibasic acid and a dihydric alcohol. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) fibers are widely produced today and modified forms also exist. PET polyester fabric can be finished through various sequences including scouring, heat-setting, and dyeing. Heat-setting is important to stabilize the fabric against shrinkage during further processing and use. Dyeing is typically done with disperse dyes at high temperature for an even application.Auxiliaries & chemicals required in dyeing and finishing



Auxiliaries & chemicals required in dyeing and finishingMd. Mazadul Hasan Shishir
Ėý
The document discusses various auxiliaries and chemicals used in dyeing and finishing processes in the textile industry. It defines textile auxiliaries as chemicals that help processing operations like dyeing and printing by speeding them up or making them more efficient. It provides examples of common auxiliaries like sequestering agents, wetting agents, levelling agents, and discusses their functions. It also discusses chemicals used in specific processes like bleaching, mercerizing, soaping and printing.Finishing



FinishingPrateek Nigam
Ėý
The document discusses textile finishing processes. It begins by introducing textiles and their basic components and materials. It then describes the major departments of textiles - spinning, weaving, and wet-processing. Wet-processing involves pretreatments like scouring and bleaching, dyeing and printing, and finishing treatments like calendaring to impart properties like softness and durability. Specific mechanical finishing processes are also outlined, including sueding, raising, shearing, and decating. Calendaring is discussed in detail as a process that smoothes fabrics and modifies properties.Scouring



ScouringMainul Morshed
Ėý
Scouring is the process of removing natural and added impurities from textiles using alkali solutions. It makes fabrics hydrophilic and absorbent. There are two main methods - batch/discontinuous scouring using kier boilers, and continuous scouring using J-boxes. Key steps involve saponification of oils and emulsification of waxes. Souring neutralizes residual alkali on scoured fabrics using acids.singeing process



singeing processparmeet kaur
Ėý
Singeing is a process that burns off loose fibers protruding from fabric or yarn surfaces. The fabric or yarn passes over a heated plate, cylinder or open flame, which singes the loose fibers without damaging the rest of the material. This process produces a smooth, clean surface and reduces pilling, soiling, and issues with subsequent dyeing or printing. Common singeing machines include plate singeing machines, rotary cylinder singeing machines, and gas singeing machines. Singeing improves the appearance, hand, and functionality of many textile materials.Plasma technology In Textile



Plasma technology In TextileNafiz Antu
Ėý
This presentation summarizes the use of plasma technology in textile processing. It discusses how plasma is created through heating and ionizing gas, and its classification. The presentation then outlines various plasma systems used in textiles and how plasma works to modify fabric surfaces at a nano scale. Specific textile applications of plasma technology discussed include desizing, dyeing, improving wettability and printability. The presentation notes the advantages of plasma treatment as being more environmentally friendly and providing properties like abrasion resistance and faster dyeing. It concludes that plasma technology is an interesting alternative to conventional wet processing methods.Textile Desizing šÝšÝßĢ.pptx



Textile Desizing šÝšÝßĢ.pptxTextileDetails
Ėý
Desizing is the process of removing starch sizes from warp yarns after weaving. The key methods are rot steeping, acidic desizing using dilute acid, enzymatic desizing using starch-hydrolyzing enzymes, and oxidative desizing using oxidizing agents. Rot steeping is the oldest method but is slow, while enzymatic desizing is now widely used as it efficiently removes sizes under mild conditions without damaging fibers. Acidic and oxidative desizing can also work but may damage fibers if not properly controlled. The Tegewa violet scale is commonly used to assess desizing efficiency by checking for color changes from starch residues on fabrics.The object is to remove size from the grey fabric that has been applied durin...



The object is to remove size from the grey fabric that has been applied durin...NadirRind1
Ėý
To remove the starch material from the fabric.
To increase the absorbency power of the fabric.
To increase the affinity of the fabric to the dry chemicals.
To make the fabric suitable for the next process.
To increase the luster of the fabric, increase of dyeing and printing.Ėý
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Introduction to dyeing



Introduction to dyeingRajeev Sharan
Ėý
The document provides an introduction to textile dyeing, including definitions of basic terms like dyestuff and pigment, an overview of dyeing processes and factors that influence dye choices, and descriptions of different types of dyes including direct dyes for cellulosic fibers, reactive dyes, vat dyes, sulfur dyes, and disperse dyes for synthetic fibers. Classification methods for dyes and dyeing conditions for various fiber and dye combinations are also outlined.Mercerization



MercerizationMd. Mazadul Hasan Shishir
Ėý
1. Mercerization is a finishing treatment for cotton that improves luster, hardness, and other properties by treating cotton with a strong alkaline solution.
2. It involves immersing cotton yarn or fabric under tension in a cold sodium hydroxide solution, then neutralizing it in acid. This causes swelling of the cotton fibers and increases their luster.
3. The ideal conditions for mercerization are a caustic concentration of 250-320 g/L at 18-20°C for 30-60 seconds, as this provides the best luster with minimal shrinkage.DIRECT DYE



DIRECT DYESayeed Ahmed
Ėý
This presentation discusses direct dyes, which are water-soluble dyes used to dye cellulosic materials like cotton directly. There are two major types of direct dyes: anionic direct dyes, which are used for paper coloring and shade correction, and cationic direct dyes. Direct dyes have properties like water solubility and being anionic in nature. They dye materials through weak hydrogen and van der Waals bonding in alkaline conditions. The dyeing process involves dissolving the dye in boiling water with electrolytes before applying it to materials and boiling for 30-45 minutes. Direct dyes provide duller colors than reactive dyes and have lower wash fastness. They are used for applications where high fastness isDesizing



DesizingMd. Mazadul Hasan Shishir
Ėý
1. Desizing is done to remove sizing agents like starch that were applied to warp yarns during weaving to facilitate the weaving process.
2. There are several methods of desizing including enzymatic, acid, and oxidative methods. Enzymatic desizing uses enzymes like amylase to break down starch into soluble sugars.
3. Proper control of factors like temperature, pH, and fabric speed are important for effective desizing when using the enzymatic method.Scouring process in textile processing



Scouring process in textile processingFarhan ullah baig
Ėý
The document discusses the scouring process used to clean fabrics prior to dyeing or finishing. Scouring removes natural and mechanical impurities through processes like saponification, solubilization, and emulsification. Saponification converts oils and fats to soap and glycerin. Solubilization and emulsification remove other impurities like pectins, proteins, waxes, and minerals by making them water soluble or dispersing them. Selection of scouring agents depends on fiber type, fabric properties, and impurity level. Effectiveness is tested through measures like absorbency, weight loss, and residual wax content.Direct dye



Direct dyeRinku Shemar
Ėý
Direct dyes are water-soluble aromatic compounds that have an affinity for cellulose fibers like cotton. They are applied as aqueous solutions and bond to fibers physically through hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces. Direct dyes generally have poor fastness properties but these can be improved through after-treatments using metallic salts like copper or chromium compounds, or formaldehyde, which increase the dye's molecular weight and bonding strength to the fibers. Key factors that influence direct dye uptake include electrolyte concentration, temperature, liquor ratio, and dye class.Mercerisation



MercerisationVasanth Kumar
Ėý
Mercerization is a treatment of cotton yarn or fabric with a strong caustic soda solution that improves several qualities of the cotton. It increases luster and dye affinity, improves strength and stability, and results in smoother, rounder fibers. The process involves immersing cotton in a high concentration sodium hydroxide solution under tension control and then washing to neutralize the fabric. This summarizes the key points about mercerization from the provided document.Bleaching process in textile processing



Bleaching process in textile processingFarhan ullah baig
Ėý
Natural fibers contain coloring compounds that make them appear off-white. The objective of bleaching is to remove these color bodies and produce a white fabric using oxidizing bleaching agents while minimizing fiber damage. Hydrogen peroxide is the most widely used bleaching agent for cotton and blends. It works through its decomposition product, perhydroxyl ion, which breaks the double bonds in color compounds at an optimal pH of 10-11. Proper regulation of perhydroxyl ions through stabilizers prevents rapid decomposition of the bleach and fiber degradation. Temperature, time, concentration, and liquor ratio must be optimized to achieve effective bleaching with minimal impact on strength properties. Yarn count



Yarn countAmit Biswas
Ėý
This document discusses yarn count and its measurement. It defines yarn count as the numerical expression of the coarseness or fineness of yarn. There are several systems used to express yarn count, including indirect, direct, and universal systems. The most common systems are the indirect system used for cotton, wool, and linen, where higher count means finer yarn, and the direct system used for jute and silk, where higher count means coarser yarn. The universal Tex system introduced by ISO is a direct system where count indicates the weight in grams of 1000 meters of yarn. There are several instruments that can be used to measure yarn count, including quadrant balances, Knowles balances, and measuring drums forPresentation on mercerization



Presentation on mercerizationFranco Majigoi
Ėý
this slide in mercerization is prepared in chemical processing in textile and it could help a lot of students or lecturers who might be looking for web handout, presentation or seminar. it is openly accessible for all.scouring and bleaching 



scouring and bleaching Azmir Latif Beg
Ėý
Comparative study between bio scouring bleaching and traditional scouring and bleaching and cotton fabric dyeing with reactive dye. Softening Finishes 



Softening Finishes Asaye Dessie
Ėý
Softening finishes are important textile treatments that make fabrics feel softer. Chemical softeners allow fabrics to have a soft, smooth hand. The main types of softeners are cationic, anionic, non-ionic, and amphoteric softeners. Cationic softeners provide excellent softening but can cause yellowing, while anionic softeners have lower softening ability but better compatibility. Silicone softeners provide unique softness and properties like durability and heat stability, but can be expensive. Softener selection depends on the desired properties like fastness, compatibility with other chemicals, and effect on processes like seam slippage or drying.Wet processing-I



Wet processing-IAhmad Sakib
Ėý
This document contains information about Shuvo Brahma, a lecturer at BUTEX. It includes his contact details, education background of BSc and ongoing MSc from BUTEX, and previous job experience at Epyllion Knitex Ltd and as a lecturer at NITER.
It also includes the syllabus for the course WPE 243 Wet Processing-1 which covers topics like water and its importance in textile processing, detergents and auxiliaries, and pretreatment.
Finally, it discusses water treatment processes in the textile industry, including different water sources, hardness types, units of hardness measurement, effects of hardness on textile processing, and problems associated with hard water like scale formation inExhaust dyeing process



Exhaust dyeing processInterloop Limited
Ėý
Batch dyeing involves dyeing fabric in a stationary dye bath. There are three main types of batch dyeing machines. Jigger dyeing machines transfer fabric back and forth between rollers through a dye bath, applying tension. Winch dyeing machines pass rope-formed fabric over rollers through a stationary dye bath with little tension. Jet dyeing machines eliminate rollers and use jet nozzles to circulate fabric through a closed tubular system at high temperatures and pressures.Polyester fiber processing



Polyester fiber processingMd. Mazadul Hasan Shishir
Ėý
Polyester is a polymer made from a condensation reaction between small molecules to form ester groups. It is commonly made from a dibasic acid and a dihydric alcohol. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) fibers are widely produced today and modified forms also exist. PET polyester fabric can be finished through various sequences including scouring, heat-setting, and dyeing. Heat-setting is important to stabilize the fabric against shrinkage during further processing and use. Dyeing is typically done with disperse dyes at high temperature for an even application.Auxiliaries & chemicals required in dyeing and finishing



Auxiliaries & chemicals required in dyeing and finishingMd. Mazadul Hasan Shishir
Ėý
The document discusses various auxiliaries and chemicals used in dyeing and finishing processes in the textile industry. It defines textile auxiliaries as chemicals that help processing operations like dyeing and printing by speeding them up or making them more efficient. It provides examples of common auxiliaries like sequestering agents, wetting agents, levelling agents, and discusses their functions. It also discusses chemicals used in specific processes like bleaching, mercerizing, soaping and printing.Finishing



FinishingPrateek Nigam
Ėý
The document discusses textile finishing processes. It begins by introducing textiles and their basic components and materials. It then describes the major departments of textiles - spinning, weaving, and wet-processing. Wet-processing involves pretreatments like scouring and bleaching, dyeing and printing, and finishing treatments like calendaring to impart properties like softness and durability. Specific mechanical finishing processes are also outlined, including sueding, raising, shearing, and decating. Calendaring is discussed in detail as a process that smoothes fabrics and modifies properties.Scouring



ScouringMainul Morshed
Ėý
Scouring is the process of removing natural and added impurities from textiles using alkali solutions. It makes fabrics hydrophilic and absorbent. There are two main methods - batch/discontinuous scouring using kier boilers, and continuous scouring using J-boxes. Key steps involve saponification of oils and emulsification of waxes. Souring neutralizes residual alkali on scoured fabrics using acids.singeing process



singeing processparmeet kaur
Ėý
Singeing is a process that burns off loose fibers protruding from fabric or yarn surfaces. The fabric or yarn passes over a heated plate, cylinder or open flame, which singes the loose fibers without damaging the rest of the material. This process produces a smooth, clean surface and reduces pilling, soiling, and issues with subsequent dyeing or printing. Common singeing machines include plate singeing machines, rotary cylinder singeing machines, and gas singeing machines. Singeing improves the appearance, hand, and functionality of many textile materials.Plasma technology In Textile



Plasma technology In TextileNafiz Antu
Ėý
This presentation summarizes the use of plasma technology in textile processing. It discusses how plasma is created through heating and ionizing gas, and its classification. The presentation then outlines various plasma systems used in textiles and how plasma works to modify fabric surfaces at a nano scale. Specific textile applications of plasma technology discussed include desizing, dyeing, improving wettability and printability. The presentation notes the advantages of plasma treatment as being more environmentally friendly and providing properties like abrasion resistance and faster dyeing. It concludes that plasma technology is an interesting alternative to conventional wet processing methods.Similar to Desizing in textile (20)
Textile Desizing šÝšÝßĢ.pptx



Textile Desizing šÝšÝßĢ.pptxTextileDetails
Ėý
Desizing is the process of removing starch sizes from warp yarns after weaving. The key methods are rot steeping, acidic desizing using dilute acid, enzymatic desizing using starch-hydrolyzing enzymes, and oxidative desizing using oxidizing agents. Rot steeping is the oldest method but is slow, while enzymatic desizing is now widely used as it efficiently removes sizes under mild conditions without damaging fibers. Acidic and oxidative desizing can also work but may damage fibers if not properly controlled. The Tegewa violet scale is commonly used to assess desizing efficiency by checking for color changes from starch residues on fabrics.The object is to remove size from the grey fabric that has been applied durin...



The object is to remove size from the grey fabric that has been applied durin...NadirRind1
Ėý
To remove the starch material from the fabric.
To increase the absorbency power of the fabric.
To increase the affinity of the fabric to the dry chemicals.
To make the fabric suitable for the next process.
To increase the luster of the fabric, increase of dyeing and printing.Ėý
Desizing 140503101043-phpapp01



Desizing 140503101043-phpapp01Abdullah Al Mamun
Ėý
1. The document discusses different methods of desizing fabrics, which is the process of removing starch coatings called "size" that are applied during weaving.
2. Enzymatic desizing using amylase enzymes is the most common method as it can break down starch without damaging cellulose fibers.
3. Other oxidative methods can also be used to desize fabrics by oxidizing and breaking down starch into soluble products using oxidizing agents like sodium bromite.Class desizing



Class desizingghoshb
Ėý
The document discusses different methods for desizing cotton fabric, which is the process of removing starch-based "size" added during weaving. The three main methods are:
1. Rot steeping, the oldest method, uses microorganisms in water to secrete enzymes that break down starch over 24 hours. It is cheap but slow.
2. Acid desizing uses dilute sulfuric or hydrochloric acid to hydrolyze starch in 8-12 hours. It is faster but the acid can damage fibers if not properly handled.
3. Enzyme desizing uses specific enzymes at optimal temperatures and pH to rapidly liquefy starch for removal. It is the fastest method if conditions are carefullyPresentation on Textile Desizing



Presentation on Textile DesizingAmanuzzaman Aman
Ėý
Desizing is the process of removing size material from warp yarns in woven fabrics to facilitate weaving. Size is applied before weaving to prevent breakage on the loom but must be removed before dyeing and finishing. There are two main methods of desizing - hydrolytic and oxidative. Hydrolytic methods like enzymatic desizing use enzymes like amylase to hydrolyze and reduce the molecular weight of starch size. Oxidative desizing uses oxidizing agents like bromides but risks damaging the cellulose fibers. Complete removal of size is important for effective dyeing and is tested by checking for color change or measuring weight loss in the fabric.Presentation on Textile Desizing



Presentation on Textile DesizingAmanuzzaman Aman
Ėý
This document describes different methods of desizing fabrics. Desizing is necessary to remove starch-based sizing agents applied to warp yarns before weaving. The key methods discussed are hydrolytic desizing using water and microorganisms, acid desizing using dilute acid solutions, and enzymatic desizing using enzymes like malt extract. Oxidative desizing using oxidizing agents like sodium bromite is also covered, which oxidizes and depolymerizes the starch sizing agents. The document provides details on the processes and chemicals involved in each desizing method.02 - Process sequence of wet processing.pdf



02 - Process sequence of wet processing.pdfVinaleeSeneviratne
Ėý
The document describes various wet processing steps involved in textile manufacturing, including preparation, pretreatment, and finishing processes. Some key points:
- Preparation steps include grey inspection, stitching, shearing, cropping, and singeing to smooth fabric surfaces and remove loose fibers.
- Pretreatment aims to remove natural and added impurities through desizing, scouring, bleaching, and optional mercerization. This makes fabrics more absorbent and receptive to dyes.
- Common pretreatment methods include desizing to remove starches added during weaving, scouring using alkalis to remove natural waxes and oils, and bleaching to further whiten fabrics using oxidizing agents likeScouring



ScouringMd. Mazadul Hasan Shishir
Ėý
The document discusses the scouring process, which involves removing natural and added impurities from textile fibers. There are three main methods for removing impurities: saponification, emulsification, and solubilization. Saponification converts impurities like oils and fats into water-soluble soaps. Emulsification forms suspensions of non-saponifiable impurities. Solubilization dissolves substances like pectin and proteins into soluble salts. The scouring process aims to remove all impurities and leave the fibers highly absorbent without damage. Common scouring agents include alkaline solutions, surfactants, and sometimes organic solvents.eco friendly textile processing



eco friendly textile processingOmkar S Parmaj
Ėý
www.textilecore.com
The presentation gives you the information about new eco friendly textile processing. All steps of preparation of fabric for dyeing.



All steps of preparation of fabric for dyeing.Amit kumar
Ėý
The document describes various wet processing steps for textiles, including:
- Pretreatment processes like singeing, shearing, and cropping to remove surface fibers and impurities.
- Preparation steps like greige inspection and stitching before wet processing.
- Desizing to remove starch coatings from warp yarns.
- Scouring to remove natural and added impurities using alkalis.
- Bleaching to whiten fibers using oxidizing agents.
The summary highlights the key goal of pretreatment, preparation steps, and common wet processing steps like desizing, scouring, and bleaching that are used to clean and treat textiles.DESIZING



DESIZINGRahulRoy482
Ėý
1. Desizing is the process of removing size material from warp yarns in woven fabrics to facilitate weaving. Sizing agents are selected based on fabric type.
2. Size comes from coating warp yarns with sizing agents before weaving to decrease breakage and improve productivity. However, sizing agents resist dyes and chemicals used in textile processing, so must be removed before wet processing.
3. Common desizing methods include acid desizing using dilute acids, enzymatic desizing using enzymes to degrade starch size, and desizing on a jigger using hot water and amylase in an impregnation stage followed by washing.Advecofreindlypretrtrt 160421074340



Advecofreindlypretrtrt 160421074340shihabj
Ėý
The document discusses various eco-friendly textile processing techniques. It describes preparatory processes like singeing, desizing, and scouring that use enzymes instead of harsh chemicals to remove impurities. For desizing, it discusses enzymatic, solvent, ultrasonic, and plasma methods. It also covers enzymatic scouring and bleaching techniques using enzymes like amylases, catalases, laccases, and glucose oxidases. Other eco-friendly techniques discussed are liquid ammonia mercerization, ozone bleaching, and peracetic acid bleaching. The document emphasizes that new sustainable technologies are needed in textile processing to be environmentally compliant with increasing regulations.Desizing lecture 3



Desizing lecture 3robellegese1
Ėý
The document discusses the desizing process of cotton fabric. Desizing involves removing the size material that was applied to warp yarns during weaving to prevent breakage. This is done to increase the fabric's absorbency and affinity for chemicals in subsequent processing. Common methods of desizing include acid desizing using dilute acids, enzymatic desizing using amylase enzymes to hydrolyze starch, and oxidative desizing using oxidizing agents. The key objectives of desizing are to remove the size material, increase wettability and absorbency of the fabric to prepare it for downstream processes like dyeing and printing.Project Work nahid



Project Work nahidNahid Morshed
Ėý
The document describes a study comparing a traditional scouring process to a bio-scouring process for textiles. It finds that bio-scouring using the enzyme Scourzyme L is more environmentally friendly and reduces costs compared to traditional caustic scouring. Specifically, bio-scouring reduces water, energy and chemical usage, lowers BOD, COD and TDS in wastewater, and avoids the health and safety risks of harsh chemicals. However, it provides slightly less whiteness for light and white fabrics compared to traditional scouring. Overall, bio-scouring is shown to be a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative.Desizing



DesizingAjinkya Mule
Ėý
This document discusses various methods for desizing fabric after weaving to remove starch paste. It describes the objectives of desizing as removing starch paste to increase fabric absorbency, affinity for dry chemicals, and suitability for downstream processes. The key desizing methods discussed are rot steeping, acidic desizing using hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, alkaline desizing using caustic soda, enzymatic desizing using amylase enzymes, and oxidative desizing using chlorine or bromine. Each method is explained in terms of its process, advantages, and disadvantages. Enzymatic desizing is noted as requiring less time and avoiding fibre damage compared to other methods. Proper control of temperature, pH, and time is important forApplications of enzymes in textiles



Applications of enzymes in textileshema upadhayay
Ėý
Enzymes have been used for over 2,000 years in textile processing. Their use has increased in the past century, especially for processing natural fibers, as enzymes are more environmentally friendly and specific than chemicals. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts to accelerate chemical reactions without being altered. Common enzymes used in textiles include amylases, cellulases, lipases, and proteases. Enzymes are measured in activity units and mediate synthetic and degradative reactions in living organisms.Wool treatment & enzyme finishing.pptx



Wool treatment & enzyme finishing.pptxMdAliujjaman
Ėý
The document discusses various wet processing techniques for wool fabric treatment, including scouring, bleaching, carbonizing, milling, decatising, crabbing, and enzyme finishing processes like bio-polishing. It provides details on the objectives, recipes, and process conditions for each technique. For example, it explains that scouring aims to remove contaminants from wool fabrics using recipes with sodium carbonate, wetting agents, and soap at temperatures of 35-40 degrees Celsius. Bleaching uses hydrogen peroxide to lighten wool fabrics at pH 8.0-8.5. Carbonizing removes vegetable matter impurities from wool using sulfuric acid.Garments washing



Garments washingMd. Mazadul Hasan Shishir
Ėý
Garment washing is a process used to modify the appearance, comfort, and fashion of garments. There are various types of washes that produce different effects on fabrics, such as vintage, cloud, and acid washes. The type of wash depends on the product - for example, denim requires heavy enzyme washes while knit tees may only need a light softener wash. Common garment washing steps include a desizing process, washing with chemicals like detergent and enzymes, rinsing, drying, and quality checking. Washing introduces effects like fading and increases garment softness and comfort for customers.ECO FRIENDLY TEXTILE PROCESSING: âBio Scouringâ



ECO FRIENDLY TEXTILE PROCESSING: âBio ScouringâFahim Zauwad Reloaded
Ėý
Though the conventional scouring process is extremely using now-a-days, it has great bad effect on environment.
Many of the developed countries are avoiding the conventional scouring process replacing enzymatic,ecofriendly, scouring processes.
Bioscouring is an eco-friendly scouring process it has great future.
The new enzymatic procedure is corresponding with a significant role in minimizing the de-mand of energy, water, chemicals, time and costs.
Recent advances in desizing, scouring and bleaching



Recent advances in desizing, scouring and bleachingBahirdar University
Ėý
The slide contains advances (recent developments) in textile pretreatment called desizing, scouring, and bleaching. Different advances such as an enzyme, ozone, and plasma treatments are included for each pretreatment process.Recently uploaded (20)
The Golden Gate Bridge a structural marvel inspired by mother nature.pptx



The Golden Gate Bridge a structural marvel inspired by mother nature.pptxAkankshaRawat75
Ėý
The Golden Gate Bridge is a 6 lane suspension bridge spans the Golden Gate Strait, connecting the city of San Francisco to Marin County, California.
It provides a vital transportation link between the Pacific Ocean and the San Francisco Bay.
Best KNow Hydrogen Fuel Production in the World The cost in USD kwh for H2



Best KNow Hydrogen Fuel Production in the World The cost in USD kwh for H2Daniel Donatelli
Ėý
The cost in USD/kwh for H2
Daniel Donatelli
Secure Supplies Group
Index
âĒ Introduction - Page 3
âĒ The Need for Hydrogen Fueling - Page 5
âĒ Pure H2 Fueling Technology - Page 7
âĒ Blend Gas Fueling: A Transition Strategy - Page 10
âĒ Performance Metrics: H2 vs. Fossil Fuels - Page 12
âĒ Cost Analysis and Economic Viability - Page 15
âĒ Innovations Driving Leadership - Page 18
âĒ Laminar Flame Speed Adjustment
âĒ Heat Management Systems
âĒ The Donatelli Cycle
âĒ Non-Carnot Cycle Applications
âĒ Case Studies and Real-World Applications - Page 22
âĒ Conclusion: Secure Suppliesâ Leadership in Hydrogen Fueling - Page 27
G8 mini project for alcohol detection and engine lock system with GPS tracki...



G8 mini project for alcohol detection and engine lock system with GPS tracki...sahillanjewar294
Ėý
b.tech final year projects report for cseIntroduction to Safety, Health & Environment



Introduction to Safety, Health & Environmentssuserc606c7
Ėý
Introduction to
Safety, Health &EnvironmentUS Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
Ėý
Preface: The ReGenX Generator innovation operates with a US Patented Frequency Dependent Load Current Delay which delays the creation and storage of created Electromagnetic Field Energy around the exterior of the generator coil. The result is the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs any magnitude of Positive Electro-Mechanical Work at infinite efficiency on the generator's Rotating Magnetic Field, increasing its Kinetic Energy and increasing the Kinetic Energy of an EV or ICE Vehicle to any magnitude without requiring any Externally Supplied Input Energy. In Electricity Generation applications the ReGenX Generator innovation now allows all electricity to be generated at infinite efficiency requiring zero Input Energy, zero Input Energy Cost, while producing zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions, zero Air Pollution and zero Nuclear Waste during the Electricity Generation Phase. In Electric Motor operation the ReGen-X Quantum Motor now allows any magnitude of Work to be performed with zero Electric Input Energy.
Demonstration Protocol: The demonstration protocol involves three prototypes;
1. Protytpe #1, demonstrates the ReGenX Generator's Load Current Time Delay when compared to the instantaneous Load Current Sine Wave for a Conventional Generator Coil.
2. In the Conventional Faraday Generator operation the created Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Negative Work at infinite efficiency and it reduces the Kinetic Energy of the system.
3. The Magnitude of the Negative Work / System Kinetic Energy Reduction (in Joules) is equal to the Magnitude of the created Electromagnetic Field Energy (also in Joules).
4. When the Conventional Faraday Generator is placed On-Load, Negative Work is performed and the speed of the system decreases according to Lenz's Law of Induction.
5. In order to maintain the System Speed and the Electric Power magnitude to the Loads, additional Input Power must be supplied to the Prime Mover and additional Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft.
6. For example, if 100 Watts of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >100 Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
7. If 1 MW of Electric Power is delivered to the Load by the Faraday Generator, an additional >1 MW Watts of Mechanical Input Power must be supplied to the Generator's Drive Shaft by the Prime Mover.
8. Generally speaking the ratio is 2 Watts of Mechanical Input Power to every 1 Watt of Electric Output Power generated.
9. The increase in Drive Shaft Mechanical Input Power is provided by the Prime Mover and the Input Energy Source which powers the Prime Mover.
10. In the Heins ReGenX Generator operation the created and Time Delayed Electromagnetic Field Energy performs Positive Work at infinite efficiency and it increases the Kinetic Energy of the system.Taykon-Kalite belgeleri



Taykon-Kalite belgeleriTAYKON
Ėý
Kalite PolitikamÄąz
Taykon Ãelik için kalite, hayallerinizi bizlerle paylaÅtÄąÄÄąnÄąz an baÅlar. Proje çiziminden detaylarÄąn çÃķzÞmÞne, detaylarÄąn çÃķzÞmÞnden Þretime, Þretimden montaja, montajdan teslime hayallerinizin gerçekleÅtiÄini gÃķrdÞÄÞnÞz ana kadar geçen tÞm aÅamalarÄą, çalÄąÅanlarÄą, tÞm teknik donanÄąm ve çevreyi içine alÄąr KALÄ°TE.Integration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...



Integration of Additive Manufacturing (AM) with IoT : A Smart Manufacturing A...ASHISHDESAI85
Ėý
Combining 3D printing with Internet of Things (IoT) enables the creation of smart, connected, and customizable objects that can monitor, control, and optimize their performance, potentially revolutionizing various industries. oT-enabled 3D printers can use sensors to monitor the quality of prints during the printing process. If any defects or deviations from the desired specifications are detected, the printer can adjust its parameters in real time to ensure that the final product meets the required standards.Industrial Valves, Instruments Products Profile



Industrial Valves, Instruments Products Profilezebcoeng
Ėý
Weâre excited to share our product profile, showcasing our expertise in Industrial Valves, Instrumentation, and Hydraulic & Pneumatic Solutions.
We also supply API-approved valves from globally trusted brands, ensuring top-notch quality and internationally certified solutions. Letâs explore valuable business opportunities together!
We specialize in:
âĒ Industrial Valves (Gate, Globe, Ball, Butterfly, Check)
âĒ Instrumentation (Pressure Gauges, Transmitters, Flow Meters)
âĒ Pneumatic Products (Cylinders, Solenoid Valves, Fittings)
As authorized partners of trusted global brands, we deliver high-quality solutions tailored to meet your industrial needs with seamless support.Frankfurt University of Applied Science urkunde



Frankfurt University of Applied Science urkundeLisa Emerson
Ėý
Duplicate Frankfurt University of Applied Science urkunde, make a Frankfurt UAS degree.US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...



US Patented ReGenX Generator, ReGen-X Quatum Motor EV Regenerative Accelerati...Thane Heins NOBEL PRIZE WINNING ENERGY RESEARCHER
Ėý
Desizing in textile
- 1. DESIZING Prepared by Karamat Ali Saif
- 2. Desizing Introduction: ï§ Desizing is done in order to removes the size from warp yarn of the woven fabric. Warp yarn are coated with sizing agents period to weaving in order to reduce their fractional properties, decrease yarn breakage in loom and improve weaving productivity by increasing weft insertion speed. ï§ The sizing materials present on warp yarn acts as a resist toward dye and chemicals in textile wet processing. it must therefore be removed before any subsequent wet processing of the fabric.
- 3. Factors on which the desizing efficiency depends The factors on which the efficiency of size removal depends are as follow... ï§ Type and the amount of size applied ï§ Viscosity of the size in solution ï§ Ease of dissolution of the size film on the yarn ï§ The nature and the amount of the plasticizer ï§ Fabric construction ï§ Method of desizing and ï§ Method of washing off
- 4. Objectives of desizing ï§ The object is to remove from the grey fabric the size that has been applied during weaving and thus to make the fabric ready for further processes. ï§ The main ingredient in size that is not water-soluble is usually starch. ï§ Chemically starch is poly-glucopyranose in which straight chain and branched chain polymers are present. ï§ .
- 5. Objectives of desizing contd ï§ Both the constituents of starch are insoluble in water but they can be made soluble by hydrolysis of these long chain compounds to shorter ones ï§ Grey cotton fabric contains both natural impurities as well as âadded matterâ. ï§ The added matter is called âsizeâ. It is added by man in a process called âsizingâ, as it facilitates weaving.
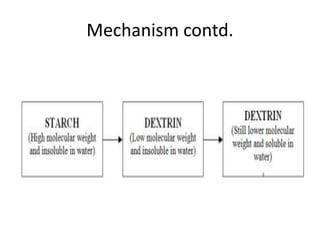
- 6. Mechanism âĒ The main ingredient in size that is not water-soluble is usually starch. âĒ Chemically starch is poly-glucopyranose in which straight chain and branched chain polymers are present. âĒ Both the constituents of starch are insoluble in water but they can be made soluble by hydrolysis of these long chain compounds to shorter ones. âĒ Thus, under suitable conditions, the following steps show the progressive hydrolysis of starch. âĒ However, in desizing, the hydrolysis of starch is carried out only up to the soluble dextrin stage, as this can be removed off the desized fabric by means of an aqueous wash.
- 8. Methods of desizing ï§ Rot steeping ï§ Enzymatic desizing ï§ Acidic desizing ï§ Oxidative desizing
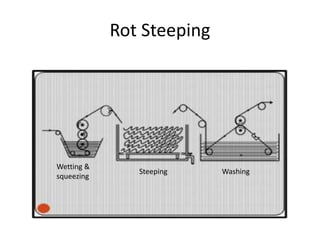
- 9. Rot Steep ï§ This is the oldest and cheapest method of desizing. ï§ Here no special chemical is used. ï§ The cloth is first passed through warm water at 40C in a padding mangle where the cloth is squeezed to about 100% expression. ï§ The cloth is then allowed to stand for 24 hours. ï§ The microorganisms, naturally present in water, multiply and secrete starch-liquefying (hydrolysing) enzymes, which break down the starch present in the size to w ater-soluble products ï§ The cloth is then washed to remove these products.
- 10. Rot Steeping Wetting & squeezing Steeping Washing
- 11. Rot steep Advantages ï§ Rot steeping is the cheapest of all the desizing methods. ï§ No chemicals are required. Disadvantages ï§ A large floor space is required for this process. ï§ The process is slow, so desizing time is long. ï§ Mildew may attack the cloth during steeping ï§ and cause stains on the fabric.
- 12. Acid Desizing ï§ âDilute sulphuric acid or hydrochloric acid may be used to hydrolyse the starch from the sized fabric. ï§ âA 0.25% - 0.5 % solution of the acid at room temperature (30o C) is suitable for this process. ï§ âThe cloth is impregnated with the dilute acid solution in a two-bowl or three- bowl padding mangle and then stored for 8- 12 hours in a closed concrete pit
- 13. Acid Desizing Advantages ï§ Acid desizing is an economical process. ï§ The process is effective and gives fairly uniform desizing, as it is a chemical- based process. It does not require specific conditions of pH and can be done at room temperature. ï§ It is a much quicker process than rot steep desizing.
- 14. Acid desizing Disadvantage ï§ The main disadvantage of the process is that mineral acid is harmful to cellulose fibres if proper care is not taken. ï§ Especially during the storage stage, the acid-wet fabric must not be allowed to dry. ï§ This would cause the formation of hydrocellulose, which will weaken the fibre.
- 15. Enzymatic Desizing âĒ The hydrolysis of starch using enzymes under particular concentration, temperature and duration is called enzymatic desizing. âĒ Enzymatic desizing is the most widely experienced method to desize the starch.
- 16. Enzymatic desizing Advantages ï§ Time required for the desizing process is less. ï§ It is continuous process, so greater production can be achieved. ï§ Closely constructed fabric can be easily desized, due to the effective enzyme action. ï§ There is no chance for the cellulose to get hydrolysed, as in acid desizing.
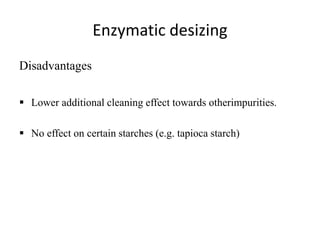
- 17. Enzymatic desizing Disadvantages ï§ Lower additional cleaning effect towards otherimpurities. ï§ No effect on certain starches (e.g. tapioca starch)
- 18. Oxidative desizing Desizing with Oxidizing agents ï§ Though the use of oxidants for desizing of cotton fabric is widely accepted but their large scale industrial application is yet to be exploited. ï§ The most important aspects of oxidizing agents are that they can be applicable to wide range of fabrics, the size content of which is often not known.
- 19. Oxidative desizing Advantages âĒ The advantages of oxidative desizing are supplementary cleaning effect, effectiveness for tapioca starches but oxidizing agents may damage to fibres.
- 20. THE END











