Dialysis
Download as PPTX, PDF7 likes1,066 views
Dialysis refers to the diffusion of molecules through a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. It serves to maintain fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance and remove toxins as a substitute for some kidney functions. The two main types are hemodialysis, which cleans the blood using an external dialysis machine, and peritoneal dialysis, which uses the peritoneal membrane. Hemodialysis requires vascular access via an arteriovenous fistula, graft, or catheter and involves passing blood through a dialyzer to remove waste using countercurrent dialysate flow. Nursing care focuses on monitoring patients during and after treatment and educating on access care.
1 of 27
Downloaded 21 times


















Recommended
Dialysis 



Dialysis supreet rupam
Ėý
The document discusses the kidneys and dialysis. It describes the kidneys' location and functions, including filtering the blood and regulating electrolytes. It then explains dialysis as a technique used when the kidneys fail, involving diffusion and osmosis across a semipermeable membrane. It provides details on hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, including procedures, equipment, complications, and lifestyle considerations for patients undergoing chronic dialysis.Dialysis seminar by Kiran Bhardwaj



Dialysis seminar by Kiran BhardwajKiran Bhardwaj
Ėý
Dilaysis, Types, Hemodialysis, Principal, Indication, Contraindication, Types of hemodialysis, Technique, Complication, Peritoneal dialysis, Nursing responsibilityDialysis complications dr A elbeally



Dialysis complications dr A elbeallyFarragBahbah
Ėý
The document discusses several potential complications of hemodialysis, including intradialytic hypotension, dialyzer reactions, disequilibrium syndrome, cramping, air embolism, hemolysis, cardiac arrhythmias, hemorrhage, pruritus, febrile reactions, and hypokalemia. For each complication, the document outlines the etiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies.Peritoneal dialysis



Peritoneal dialysisMahesh Sivaji
Ėý
Peritoneal dialysis is a treatment for kidney failure that uses the lining of your abdomen, or belly, to filter your blood inside your body. Health care providers call this lining the peritoneum. A more convenient method of dialysis in home itself. History of dialysis



History of dialysisIPMS- KMU KPK PAKISTAN
Ėý
This document discusses the history of hemodialysis. It describes how Thomas Graham first presented principles of solute transport across membranes in 1854. Willem Kolff constructed the first working dialyzer in 1943 and successfully treated a patient in renal failure in 1945, though it was initially only intended for acute cases. By the 1960s, dialysis was being used to treat chronic renal failure but demand exceeded capacity, requiring decisions on patient selection.Hemodialysis



HemodialysisJyoti1801
Ėý
Various aspects of hemodialysis has been covered along with detailed explanation of machine using Fresenius 2008T Hemodialysis in children



Hemodialysis in childrenFarragBahbah
Ėý
Hemodialysis in children has some differences from adults. Dialysis should start when the estimated GFR is below 15 mL/min/1.73m2 with symptoms of uremia, fluid overload, or malnutrition despite medical management, or below 6 mL/min/1.73m2 without symptoms. Clinical factors like growth, development, and nutrition are also important considerations. Hemodialysis facilities for children should be located within 30 minutes of patients' homes and have age-appropriate decorations to create a comfortable environment. Vascular access may include temporary catheters or arteriovenous fistulas created 6-12 months before dialysis. Hemodialysis prescriptions consider factors like dry weight estimation, dialADEQUACY OF HEMODIALYSIS



ADEQUACY OF HEMODIALYSISsaihari17
Ėý
1. Dialysis adequacy refers to removing sufficient toxins and waste from the blood to prevent adverse health outcomes and is measured by urea clearance and nutritional intake.
2. Urea clearance is the standard measure and is expressed as Kt/V, with a target single pool Kt/V of at least 1.2 per session for patients receiving hemodialysis 3 times a week.
3. Other factors that determine adequacy include residual kidney function, nutrition as measured by normalized protein catabolic rate, and controlling symptoms like anemia, acidosis, and blood pressure.AN OVERVIEW OF DIALYSIS



AN OVERVIEW OF DIALYSISMAHESWARI JAIKUMAR
Ėý
This document provides an overview of dialysis, including:
- Dialysis removes waste and excess water from the bloodstream for those with kidney failure through diffusion or ultrafiltration across a semi-permeable membrane.
- The two primary types of dialysis are hemodialysis, which uses an external dialyzer, and peritoneal dialysis, which uses the peritoneum.
- Hemofiltration works via convection rather than diffusion to filter blood and remove larger solutes less cleared by hemodialysis.Complications of hemodialysis



Complications of hemodialysisReynel Dan
Ėý
This document discusses common and less common complications that can occur during dialysis treatment. It provides details on the causes, symptoms, and management of various complications including hypotension, cramps, nausea/vomiting, headaches, and others. Potential complications are grouped as either common (occurring in 5-60% of treatments) or less common. Treatment approaches focus on prevention through careful fluid management and addressing underlying causes of complications when they arise.Dialysis machines.pptx



Dialysis machines.pptxDarshanS239776
Ėý
The document describes the key components and functions of a dialysis machine. It discusses the three main compartments, features like the blood pump and dialysate delivery system, safety monitors including pressure monitors, and options like bicarbonate and variable sodium. It provides details on how each component works, such as how the blood pump circulates blood and how safety monitors detect issues like high pressure or air bubbles. The document also covers system disinfection and how to respond to common alarm situations during dialysis treatment.Seminar on CRRT



Seminar on CRRTJinumol Jacob
Ėý
This seminar presentation provides an overview of continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). CRRT is a slow, continuous blood purification therapy that mimics kidney function for patients with kidney failure who are hemodynamically unstable. The presentation defines CRRT and discusses its principles, indications, features, types including CVVH, CVVHD and CVVHDF, vascular access requirements, dialysate fluids, the CRRT process, nursing management, complications and conclusions. A research study is also summarized that found comparable survival outcomes between acute peritoneal dialysis and CRRT for hemodynamically unstable patients requiring renal replacement therapy.Basic principles of hemodialysis final



Basic principles of hemodialysis finalFarragBahbah
Ėý
This document discusses the basic principles of hemodialysis. It covers:
1) Hemodialysis aims to remove waste, correct electrolytes, and remove excess fluids via diffusion, convection, and ultrafiltration across a semi-permeable membrane.
2) Countercurrent blood-dialysate flow maintains the concentration gradient to increase solute removal efficiency.
3) Clearance depends on factors like molecular weight, blood/dialysate flow rates, and dialyzer properties. Higher blood flows and matching dialysate flows can improve clearance.Continuous renal replacement therapy crrt



Continuous renal replacement therapy crrtMEEQAT HOSPITAL
Ėý
CRRT is a continuous renal replacement therapy that provides a gentler form of dialysis for critically ill patients. It works through slow, continuous removal of waste and fluid over multiple days rather than the typical 4 hour sessions of hemodialysis. This puts less stress on the heart. CRRT can be delivered through various modes including continuous venovenous hemofiltration, hemodialysis, or hemodiafiltration that utilize diffusion, convection, or both to clean the blood. Anticoagulation is required to prevent clotting of the dialysis circuit and can include regional citrate or low-dose heparin.Principles of-hemodialysis



Principles of-hemodialysisFarragBahbah
Ėý
This document discusses the basics of hemodialysis, including the main principles of diffusion, osmosis, filtration, and convection that hemodialysis is based on. It also describes the technique of hemodialysis, varieties of hemodialysis methods like conventional hemodialysis and online hemodiafiltration, and provides details on assessing hemodialysis treatment adequacy using Kt/V.Hemodialysis



HemodialysisAnjita Khadka
Ėý
Hemodialysis is a medical procedure that removes waste and excess fluid from the blood of patients with kidney failure. It uses a hemodialysis machine and an artificial kidney called a dialyzer to filter the blood outside of the body. Blood flows through the dialyzer where diffusion and ultrafiltration remove waste and regulate electrolytes, and is then returned to the patient. Hemodialysis is usually done three times a week for four hours each session through an arteriovenous fistula, graft, or catheter. Potential complications include hypotension, muscle cramps, nausea, and disequilibrium syndrome.Dialysis



DialysisRoanna Martin
Ėý
This is a presentation that I created for my Medical Nutrition Therapy course during graduate school.Dialysis machine (2)



Dialysis machine (2)Bew Melesse
Ėý
Kidney dialysis is a treatment for kidney failure that involves removing waste and excess water from the blood. There are two main types - hemodialysis which uses a dialysis machine to filter the blood outside the body, and peritoneal dialysis which uses the lining of the abdominal cavity. The dialysis machine works via diffusion and ultrafiltration across a semi-permeable membrane, allowing toxins and water to pass out of the bloodstream and be replaced by clean dialysate fluid. Researchers are developing wearable artificial kidneys to allow for more continuous dialysis treatment and improved patient mobility and quality of life.Hemodialysis and care of patients.



Hemodialysis and care of patients.Sachin Dwivedi
Ėý
It is the removal of solutes and water from body across a semipermeable membrane (dialyzer)
care during and after the dialysis is very important to prevent the entry of pathogens in to the body.Hemodialysis procedure



Hemodialysis procedureIPMS- KMU KPK PAKISTAN
Ėý
The document discusses factors to consider for a patient's first dialysis session for end-stage renal disease including using heparin-free anticoagulation, limiting fluid removal to 2 liters, using a bicarbonate dialysate, and having skilled medical staff present. It also provides guidelines for initial settings for a first session such as a blood flow rate of 150-200 ml/min, a dialysis time of 60-90 minutes, and a dialysate potassium level of 4-4.5 mmol/L. Precautions are recommended when initiating and terminating dialysis to ensure patient safety.Dialysis



DialysisNursing Hi Nursing
Ėý
This document discusses dialysis and renal failure. It provides information on the causes of renal failure, diagnosis of renal failure, treatment options which include dialysis and transplantation, and types of dialysis including hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. It describes how each type of dialysis works, factors in selecting between them, and their effects on lifestyle.Hemodialysis



HemodialysisSurendran Radjou
Ėý
Hemodialysis is a process that uses a dialyzer to remove wastes like urea from the blood and restore electrolyte balance and fluid levels. It is indicated for conditions like renal failure, acidosis, electrolyte imbalance, and fluid overload. Hemodialysis works through diffusion, osmosis, and ultrafiltration. Vascular access can be a catheter, arteriovenous fistula, or graft. Nursing considerations include pre, during, and post dialysis care to monitor for complications related to access or the dialysis machine itself.14 peritoneal dialysis



14 peritoneal dialysisyogesh tiwari
Ėý
Peritoneal dialysis is a treatment for kidney failure that uses the peritoneal membrane in the abdomen as a filter. It involves infusing dialysate fluid into the abdomen through a catheter for diffusion and osmosis to occur. There are various types of peritoneal dialysis including continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis, automated peritoneal dialysis, and intermittent peritoneal dialysis. Nursing management focuses on preventing infections, monitoring for fluid overload, managing pain, and providing education on catheter care and lifestyle adjustments. Peritoneal dialysis offers patients greater independence compared to hemodialysis.Discussion of dialyzer reuse



Discussion of dialyzer reuseAnup Singh
Ėý
The document discusses guidelines for reusing dialyzers, including labeling dialyzers with patient names, testing dialyzers after each use, and monitoring patients for reactions. It outlines requirements for reprocessing dialyzers, including using ultrapure water and specific cleaning/disinfecting agents like sodium hypochlorite, hydrogen peroxide, formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde, and peracetic acid. It also covers reprocessing blood tubings and testing their performance.Peritoneal dialysis by Dr. Basil Tumaini



Peritoneal dialysis by Dr. Basil TumainiBasil Tumaini
Ėý
Peritoneal dialysis by Dr. Basil Tumaini, prepared for nephrology lecture during the residency in Internal medicine at Muhimbili University of Health and Allied Sciences CRRT



CRRTmarwa Mahrous
Ėý
CRRT (continuous renal replacement therapy) involves using an extracorporeal circuit connected to the patient via catheters to slowly remove fluid and toxins over 24 hours, mimicking the function of the kidneys. It was developed for critically ill patients who cannot tolerate the fluid shifts of intermittent hemodialysis. CRRT uses a semipermeable membrane to filter fluids and small molecules from the blood based on hydrostatic pressure gradients. It provides more hemodynamic stability than intermittent hemodialysis and allows for better nutrition support by preventing fluid overload. CRRT is indicated for patients who cannot tolerate intermittent dialysis due to hemodynamic instability from their critical illness.Dialysis basics



Dialysis basicsDr Ashutosh Ojha
Ėý
Dialysis is used to treat kidney failure and manage its complications. There are different modalities including peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, and continuous renal replacement therapy. Hemodialysis uses a dialyzer, tubing, and machine to remove waste and fluid by diffusion and ultrafiltration as blood and dialysate flow countercurrently. Vascular access includes catheters, arteriovenous grafts, and arteriovenous fistulas. Complications can include infections, thrombosis, and fluid overload.Acute renal failure nursing care plan & management



Acute renal failure nursing care plan & managementNursing Path
Ėý
Is a sudden decline in renal function, usually marked by increased concentrations of blood urea nitrogen (BUN; azotemia) and creatinine; oliguria (less than 500 ml of urine in 24 hours); hyperkalemia; and sodium retention.Diaysis john



Diaysis johnJohny Wilbert
Ėý
The document discusses dialysis as a renal replacement therapy for patients with kidney failure or injury. It describes the process of diffusion and ultrafiltration that occurs during hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis to remove waste and excess fluid. Complications related to each type of dialysis are also outlined. Nursing considerations are provided for pre-dialysis assessment, monitoring patients during treatment, and post-dialysis care.5_Nursing_management_for_patients_with_replacement_therapy_Dialysis.pptx



5_Nursing_management_for_patients_with_replacement_therapy_Dialysis.pptxssuser47b89a
Ėý
Nursing College More Related Content
What's hot (20)
AN OVERVIEW OF DIALYSIS



AN OVERVIEW OF DIALYSISMAHESWARI JAIKUMAR
Ėý
This document provides an overview of dialysis, including:
- Dialysis removes waste and excess water from the bloodstream for those with kidney failure through diffusion or ultrafiltration across a semi-permeable membrane.
- The two primary types of dialysis are hemodialysis, which uses an external dialyzer, and peritoneal dialysis, which uses the peritoneum.
- Hemofiltration works via convection rather than diffusion to filter blood and remove larger solutes less cleared by hemodialysis.Complications of hemodialysis



Complications of hemodialysisReynel Dan
Ėý
This document discusses common and less common complications that can occur during dialysis treatment. It provides details on the causes, symptoms, and management of various complications including hypotension, cramps, nausea/vomiting, headaches, and others. Potential complications are grouped as either common (occurring in 5-60% of treatments) or less common. Treatment approaches focus on prevention through careful fluid management and addressing underlying causes of complications when they arise.Dialysis machines.pptx



Dialysis machines.pptxDarshanS239776
Ėý
The document describes the key components and functions of a dialysis machine. It discusses the three main compartments, features like the blood pump and dialysate delivery system, safety monitors including pressure monitors, and options like bicarbonate and variable sodium. It provides details on how each component works, such as how the blood pump circulates blood and how safety monitors detect issues like high pressure or air bubbles. The document also covers system disinfection and how to respond to common alarm situations during dialysis treatment.Seminar on CRRT



Seminar on CRRTJinumol Jacob
Ėý
This seminar presentation provides an overview of continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). CRRT is a slow, continuous blood purification therapy that mimics kidney function for patients with kidney failure who are hemodynamically unstable. The presentation defines CRRT and discusses its principles, indications, features, types including CVVH, CVVHD and CVVHDF, vascular access requirements, dialysate fluids, the CRRT process, nursing management, complications and conclusions. A research study is also summarized that found comparable survival outcomes between acute peritoneal dialysis and CRRT for hemodynamically unstable patients requiring renal replacement therapy.Basic principles of hemodialysis final



Basic principles of hemodialysis finalFarragBahbah
Ėý
This document discusses the basic principles of hemodialysis. It covers:
1) Hemodialysis aims to remove waste, correct electrolytes, and remove excess fluids via diffusion, convection, and ultrafiltration across a semi-permeable membrane.
2) Countercurrent blood-dialysate flow maintains the concentration gradient to increase solute removal efficiency.
3) Clearance depends on factors like molecular weight, blood/dialysate flow rates, and dialyzer properties. Higher blood flows and matching dialysate flows can improve clearance.Continuous renal replacement therapy crrt



Continuous renal replacement therapy crrtMEEQAT HOSPITAL
Ėý
CRRT is a continuous renal replacement therapy that provides a gentler form of dialysis for critically ill patients. It works through slow, continuous removal of waste and fluid over multiple days rather than the typical 4 hour sessions of hemodialysis. This puts less stress on the heart. CRRT can be delivered through various modes including continuous venovenous hemofiltration, hemodialysis, or hemodiafiltration that utilize diffusion, convection, or both to clean the blood. Anticoagulation is required to prevent clotting of the dialysis circuit and can include regional citrate or low-dose heparin.Principles of-hemodialysis



Principles of-hemodialysisFarragBahbah
Ėý
This document discusses the basics of hemodialysis, including the main principles of diffusion, osmosis, filtration, and convection that hemodialysis is based on. It also describes the technique of hemodialysis, varieties of hemodialysis methods like conventional hemodialysis and online hemodiafiltration, and provides details on assessing hemodialysis treatment adequacy using Kt/V.Hemodialysis



HemodialysisAnjita Khadka
Ėý
Hemodialysis is a medical procedure that removes waste and excess fluid from the blood of patients with kidney failure. It uses a hemodialysis machine and an artificial kidney called a dialyzer to filter the blood outside of the body. Blood flows through the dialyzer where diffusion and ultrafiltration remove waste and regulate electrolytes, and is then returned to the patient. Hemodialysis is usually done three times a week for four hours each session through an arteriovenous fistula, graft, or catheter. Potential complications include hypotension, muscle cramps, nausea, and disequilibrium syndrome.Dialysis



DialysisRoanna Martin
Ėý
This is a presentation that I created for my Medical Nutrition Therapy course during graduate school.Dialysis machine (2)



Dialysis machine (2)Bew Melesse
Ėý
Kidney dialysis is a treatment for kidney failure that involves removing waste and excess water from the blood. There are two main types - hemodialysis which uses a dialysis machine to filter the blood outside the body, and peritoneal dialysis which uses the lining of the abdominal cavity. The dialysis machine works via diffusion and ultrafiltration across a semi-permeable membrane, allowing toxins and water to pass out of the bloodstream and be replaced by clean dialysate fluid. Researchers are developing wearable artificial kidneys to allow for more continuous dialysis treatment and improved patient mobility and quality of life.Hemodialysis and care of patients.



Hemodialysis and care of patients.Sachin Dwivedi
Ėý
It is the removal of solutes and water from body across a semipermeable membrane (dialyzer)
care during and after the dialysis is very important to prevent the entry of pathogens in to the body.Hemodialysis procedure



Hemodialysis procedureIPMS- KMU KPK PAKISTAN
Ėý
The document discusses factors to consider for a patient's first dialysis session for end-stage renal disease including using heparin-free anticoagulation, limiting fluid removal to 2 liters, using a bicarbonate dialysate, and having skilled medical staff present. It also provides guidelines for initial settings for a first session such as a blood flow rate of 150-200 ml/min, a dialysis time of 60-90 minutes, and a dialysate potassium level of 4-4.5 mmol/L. Precautions are recommended when initiating and terminating dialysis to ensure patient safety.Dialysis



DialysisNursing Hi Nursing
Ėý
This document discusses dialysis and renal failure. It provides information on the causes of renal failure, diagnosis of renal failure, treatment options which include dialysis and transplantation, and types of dialysis including hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. It describes how each type of dialysis works, factors in selecting between them, and their effects on lifestyle.Hemodialysis



HemodialysisSurendran Radjou
Ėý
Hemodialysis is a process that uses a dialyzer to remove wastes like urea from the blood and restore electrolyte balance and fluid levels. It is indicated for conditions like renal failure, acidosis, electrolyte imbalance, and fluid overload. Hemodialysis works through diffusion, osmosis, and ultrafiltration. Vascular access can be a catheter, arteriovenous fistula, or graft. Nursing considerations include pre, during, and post dialysis care to monitor for complications related to access or the dialysis machine itself.14 peritoneal dialysis



14 peritoneal dialysisyogesh tiwari
Ėý
Peritoneal dialysis is a treatment for kidney failure that uses the peritoneal membrane in the abdomen as a filter. It involves infusing dialysate fluid into the abdomen through a catheter for diffusion and osmosis to occur. There are various types of peritoneal dialysis including continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis, automated peritoneal dialysis, and intermittent peritoneal dialysis. Nursing management focuses on preventing infections, monitoring for fluid overload, managing pain, and providing education on catheter care and lifestyle adjustments. Peritoneal dialysis offers patients greater independence compared to hemodialysis.Discussion of dialyzer reuse



Discussion of dialyzer reuseAnup Singh
Ėý
The document discusses guidelines for reusing dialyzers, including labeling dialyzers with patient names, testing dialyzers after each use, and monitoring patients for reactions. It outlines requirements for reprocessing dialyzers, including using ultrapure water and specific cleaning/disinfecting agents like sodium hypochlorite, hydrogen peroxide, formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde, and peracetic acid. It also covers reprocessing blood tubings and testing their performance.Peritoneal dialysis by Dr. Basil Tumaini



Peritoneal dialysis by Dr. Basil TumainiBasil Tumaini
Ėý
Peritoneal dialysis by Dr. Basil Tumaini, prepared for nephrology lecture during the residency in Internal medicine at Muhimbili University of Health and Allied Sciences CRRT



CRRTmarwa Mahrous
Ėý
CRRT (continuous renal replacement therapy) involves using an extracorporeal circuit connected to the patient via catheters to slowly remove fluid and toxins over 24 hours, mimicking the function of the kidneys. It was developed for critically ill patients who cannot tolerate the fluid shifts of intermittent hemodialysis. CRRT uses a semipermeable membrane to filter fluids and small molecules from the blood based on hydrostatic pressure gradients. It provides more hemodynamic stability than intermittent hemodialysis and allows for better nutrition support by preventing fluid overload. CRRT is indicated for patients who cannot tolerate intermittent dialysis due to hemodynamic instability from their critical illness.Dialysis basics



Dialysis basicsDr Ashutosh Ojha
Ėý
Dialysis is used to treat kidney failure and manage its complications. There are different modalities including peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, and continuous renal replacement therapy. Hemodialysis uses a dialyzer, tubing, and machine to remove waste and fluid by diffusion and ultrafiltration as blood and dialysate flow countercurrently. Vascular access includes catheters, arteriovenous grafts, and arteriovenous fistulas. Complications can include infections, thrombosis, and fluid overload.Acute renal failure nursing care plan & management



Acute renal failure nursing care plan & managementNursing Path
Ėý
Is a sudden decline in renal function, usually marked by increased concentrations of blood urea nitrogen (BUN; azotemia) and creatinine; oliguria (less than 500 ml of urine in 24 hours); hyperkalemia; and sodium retention.Similar to Dialysis (20)
Diaysis john



Diaysis johnJohny Wilbert
Ėý
The document discusses dialysis as a renal replacement therapy for patients with kidney failure or injury. It describes the process of diffusion and ultrafiltration that occurs during hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis to remove waste and excess fluid. Complications related to each type of dialysis are also outlined. Nursing considerations are provided for pre-dialysis assessment, monitoring patients during treatment, and post-dialysis care.5_Nursing_management_for_patients_with_replacement_therapy_Dialysis.pptx



5_Nursing_management_for_patients_with_replacement_therapy_Dialysis.pptxssuser47b89a
Ėý
Nursing College Presentazione dialisi.pdf



Presentazione dialisi.pdfandreamanzione1
Ėý
Dialysis is a process that removes waste and excess water from the blood when the kidneys fail. It uses diffusion and osmosis across a semi-permeable membrane as an artificial replacement for kidney function. There are two main types: hemodialysis which cleanses the blood directly by passing it through a dialyzer, and peritoneal dialysis which uses the peritoneal membrane in the abdomen as a filter. Both aim to maintain fluid, electrolyte and acid-base balance by removing toxins when the kidneys are unable to do so.Dialysis ppt



Dialysis pptjasmineshimnas
Ėý
This document provides information about dialysis including hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. It defines dialysis as a procedure that substitutes for kidney function by filtering and cleaning the blood. It discusses the types of dialysis as well as the principles, indications, equipment, procedures, complications, nursing management and lifestyle considerations for patients undergoing hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.Renal replacement therapy



Renal replacement therapyDr Amrit Parihar
Ėý
Dr. Amrit parihar
IKDRC ITS college of physiotherapy, Ahmedabad
amritparihar94@yahoo.com
8233341883HEMODIALYSIS MACHINE



HEMODIALYSIS MACHINEteja bayapalli
Ėý
The document summarizes the key components and functioning of a hemodialysis machine. It describes how the machine works by circulating blood outside the body through a dialyzer to remove waste and excess water. The blood flows through the dialyzer in one direction while dialysate flows counter-currently to maximize concentration gradients and removal of toxins like urea and creatinine from the blood. The machine monitors various parameters like blood pressure and temperature during the dialysis process to ensure patient safety.DIALYSIS- HEMODIALYSIS AND PERITONEAL DIALYSIS, INDICATIONS, PRINCIPLES & COM...



DIALYSIS- HEMODIALYSIS AND PERITONEAL DIALYSIS, INDICATIONS, PRINCIPLES & COM...SURENDRA K JOGPAL
Ėý
HEMODIALYSIS AND PERITONEAL DIALYSISCrf and dialysis



Crf and dialysisDarya Daoud
Ėý
This document provides an overview of chronic kidney disease (CKF), end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and different types of dialysis used to treat kidney failure. It discusses that CKF is usually asymptomatic until advanced stages and is common in individuals with hypertension, diabetes, or a family history of chronic kidney disease. Dialysis is indicated when benefits of relieving uremic symptoms outweigh risks. The two main types are hemodialysis, which uses a machine to filter blood outside the body, and peritoneal dialysis, which uses the peritoneal membrane in the abdomen. Hemofiltration is also discussed as a variant of hemodialysis that uses convection rather than diffusion to remove waste from theDialysis



Dialysisabhilasha chaudhary
Ėý
This document provides an overview of dialysis, including the types (hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis), process, principles, indications, and nursing care both before and after the procedure. It explains that dialysis uses a semipermeable membrane to remove waste and excess fluid from the blood of patients with kidney failure, but does not correct all kidney functions. Hemodialysis typically takes place three times a week for 2-4 hours each session using a dialyzer with hollow fibers to filter the blood, while peritoneal dialysis uses the peritoneal membrane and repeated exchanges of fluid into the abdominal cavity. Complications and the nursing care required for patients undergoing either type of dialysis are also outlined.Hemodialysis



HemodialysisJinumol Jacob
Ėý
Hemodialysis is a medical procedure that uses a machine to filter waste and excess fluid from the blood of patients with kidney failure or injury. During hemodialysis, the patient's blood is pumped through a dialyzer filter to remove toxins and regulate electrolyte and mineral levels before being returned. It helps control symptoms but is not a cure for kidney disease. Vascular access is required, either through an arteriovenous fistula, graft, or temporary catheter placed in the subclavian, jugular, or femoral vein. Precise regulation of dialysate solutions, blood flow rates, and treatment time is needed to safely remove waste while avoiding complications.Intravenous Medications Administration



Intravenous Medications AdministrationAhmed Fathy
Ėý
Hospital Pharmacy Seminar about IV medications and their methods of administration
Clinical Pharmacy
Mansoura UniversityCardiology with pharmacology for nurses



Cardiology with pharmacology for nursestentance
Ėý
A complete overview of the most common cardiac and vascular conditions affecting Americans today. While designed for nurses and nursing students, the pharmacology and pathophysiology included is a useful refresher for paramedics and other healthcare.Dialysis



DialysisMenthy Pandiangan
Ėý
Based on the information provided:
- Mr. Jackson was admitted for hypotension during dialysis and now has a fever
- This raises concern for possible infection, such as line infection
- As the intern on call, I would:
1. Review the admission note and labs/cultures drawn so far
2. Perform a focused exam looking for signs of infection
3. Draw blood cultures and consider changing the line
4. Start empiric antibiotics for line infection
5. Notify the nephrology team and discuss management
The key issues are evaluating for possible infection as the cause of fever, reviewing previous workup, examining the patient, and involving the nephrology team for guidance on next steps.Artificial kidney , dialysis and renal transplant by Pandian M 



Artificial kidney , dialysis and renal transplant by Pandian M Dr. Pandian M
Ėý
INDICATIONS OF DIALYSIS
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF DIALYSIS WITH AN ARTIFICIAL KIDNRY
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
INDICATIONS OF RENAL TRANSPLANTION
Artificial kidney , dialysis and renal transplant By Pandian M



Artificial kidney , dialysis and renal transplant By Pandian MDr. Pandian M
Ėý
INDICATIONS OF DIALYSIS
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF DIALYSIS WITH AN ARTIFICIAL KIDNRY
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
INDICATIONS OF RENAL TRANSPLANTION
Dialysis



DialysisGayathri R
Ėý
Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are two types of dialysis used to replicate kidney function for patients with kidney failure. Hemodialysis uses a machine to filter waste from the blood outside of the body through a semipermeable membrane, while peritoneal dialysis introduces fluid into the abdomen to draw waste from the blood vessels within. Both aim to control fluid balance and remove toxins when the kidneys are unable to do so, helping to correct conditions like fluid overload, electrolyte imbalances, and metabolic acidosis. Key differences between the two include that hemodialysis requires vascular access while peritoneal dialysis uses a permanent catheter, and that hemodialysis is done at a center several times a weekARTIFICIAL KIDNEY , DIALYSIS AND RENAL TRANSPLANT.ppt



ARTIFICIAL KIDNEY , DIALYSIS AND RENAL TRANSPLANT.pptDr. Pandian M
Ėý
This document discusses dialysis, artificial kidneys, and renal transplantation. It begins by outlining the objectives and providing definitions of dialysis and indications for when it is needed, both acutely and chronically. It then describes the two main types of dialysis - hemodialysis, which uses an artificial kidney machine, and peritoneal dialysis, which uses the peritoneum. The principles, procedures, requirements, compositions and potential complications of each type of dialysis are explained in detail. Finally, the document covers renal transplantation as the treatment of choice for end-stage renal disease, outlining the benefits, risks, types of donors, compatibility testing, immunosuppressant drugs used, and the transplantation procedure and potentialRecently uploaded (20)
Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...



Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
Ėý
Co-Chairs and Presenters, Gerald Appel, MD, and Dana V. Rizk, MD, discuss kidney disease in this CME activity titled âAdvancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Pathway Therapies.â For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/48UHvVM. CME credit will be available until February 25, 2026.Dr. Jaymee Shellâs Perspective on COVID-19



Dr. Jaymee Shellâs Perspective on COVID-19Jaymee Shell
Ėý
Dr. Jaymee Shell views the COVID-19 pandemic as both a crisis that exposed weaknesses and an opportunity to build stronger systems. She emphasizes that the pandemic revealed critical healthcare inequities while demonstrating the power of collaboration and adaptability.
Shell highlights that organizations with gender-diverse executive teams are 25% more likely to experience above-average profitability, positioning diversity as a business necessity rather than just a moral imperative. She notes that the pandemic disproportionately affected women of color, with one in three women considering leaving or downshifting their careers.
To combat inequality, Shell recommends implementing flexible work policies, establishing clear metrics for diversity in leadership, creating structured virtual collaboration spaces, and developing comprehensive wellness programs. For healthcare providers specifically, she advocates for multilingual communication systems, mobile health units, telehealth services with alternatives for those lacking internet access, and cultural competency training.
Shell emphasizes the importance of mental health support through culturally appropriate resources, employee assistance programs, and regular check-ins. She calls for diverse leadership teams that reflect the communities they serve and community-centered care models that address social determinants of health.
In her words: "The COVID-19 pandemic didn't create healthcare inequalities â it illuminated them." She urges building systems that reach every community and provide dignified care to all.Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.pptx



Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.pptxKafrELShiekh University
Ėý
Eye assessment in polytrauma for undergraduates.Restoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy W...



Restoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy W...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
Ėý
Chair, Shaji K. Kumar, MD, prepared useful Practice Aids pertaining to multiple myeloma for this CME/NCPD/AAPA/IPCE activity titled âRestoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy With GPRC5D-Targeting Options.â For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/NCPD/AAPA/IPCE information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/4fYDKkj. CME/NCPD/AAPA/IPCE credit will be available until February 23, 2026.TunesKit Spotify Converter Crack With Registration Code 2025 Free



TunesKit Spotify Converter Crack With Registration Code 2025 Freedfsdsfs386
Ėý
TunesKit Spotify Converter is a software tool that allows users to convert and download Spotify music to various formats, such as MP3, AAC, FLAC, or WAV. It is particularly useful for Spotify users who want to keep their favorite tracks offline and have them in a more accessible format, especially if they wish to listen to them on devices that do not support the Spotify app.
https://shorturl.at/LDQ9c
Copy Above link & paste in New TabDigestive Powerhouses: Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas for Nursing Students



Digestive Powerhouses: Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas for Nursing StudentsViresh Mahajani
Ėý
This educational PowerPoint presentation is designed to equip GNM students with a solid understanding of the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. It explores the anatomical structures, physiological processes, and clinical significance of these vital organs. Key topics include:
Liver functions: detoxification, metabolism, and bile synthesis.
Gallbladder: bile storage and release.
Pancreas: exocrine and endocrine functions, including digestive enzyme and hormone production. This presentation is ideal for GNM students seeking a clear and concise review of these important digestive system components."IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINE



IMMUNO-ONCOLOGY DESCOVERING THE IMPORTANCE OF CLINICAL IMUNOLOGY IN MEDICINERelianceNwosu
Ėý
This presentation emphasizes the role of immunodiagnostics and Immunotherapy. Neurologic Manifestations of Infective Endocarditis.pptx



Neurologic Manifestations of Infective Endocarditis.pptxdribnibrahem164
Ėý
neurological complications of infective endocarditisEnzyme Induction and Inhibition: Mechanisms, Examples, and Clinical Significance



Enzyme Induction and Inhibition: Mechanisms, Examples, and Clinical SignificanceSumeetSharma591398
Ėý
This presentation explains the concepts of enzyme induction and enzyme inhibition in drug metabolism. It covers the mechanisms, examples, clinical significance, and factors affecting enzyme activity, with a focus on CYP450 enzymes. Learn how these processes impact drug interactions, efficacy, and toxicity. Essential for pharmacy, pharmacology, and medical students.Strategies for Promoting Innovation in Healthcare Like Akiva Greenfield.pdf



Strategies for Promoting Innovation in Healthcare Like Akiva Greenfield.pdfakivagreenfieldus
Ėý
Healthcare innovation has been greatly aided by leaders like Akiva Greenfield, CEO of Nexus, particularly in fields like operational efficiency, revenue cycle management (RCM), and client engagement. In order to ensure both operational success and better patient experiences, Akiva's approach combines technological advancements with an emphasis on improving the human side of healthcare.
Understanding Trauma: Causes, Effects, and Healing Strategies



Understanding Trauma: Causes, Effects, and Healing StrategiesBecoming Institute
Ėý
Trauma affects millions of people worldwide, shaping their emotional, psychological, and even physical well-being. This presentation delves into the root causes of trauma, its profound effects on mental health, and practical strategies for healing. Whether you are seeking to understand your own experiences or support others on their journey, this guide offers insights into coping mechanisms, therapy approaches, and self-care techniques. Explore how trauma impacts the brain, body, and relationships, and discover pathways to resilience and recovery.
Perfect for mental health advocates, therapists, educators, and anyone looking to foster emotional well-being. Watch now and take the first step toward healing!Research Hyopthesis and Research Assumption



Research Hyopthesis and Research AssumptionDr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy
Ėý
Research Hyopthesis and AssumptionSAPIENT Medi-trivia Quiz (Prelims) | TRI-ORTA 2025



SAPIENT Medi-trivia Quiz (Prelims) | TRI-ORTA 2025Anindya Das Adhikary
Ėý
Preliminary Round of SAPIENT Medi-trivia quiz | part of TRI-ORTA 2025Role of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Microbiology.pptx



Role of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Microbiology.pptxDr Punith Kumar
Ėý
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing clinical microbiology by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, automating workflows, and improving patient outcomes. This presentation explores the key applications of AI in microbial identification, antimicrobial resistance detection, and laboratory automation. Learn how machine learning, deep learning, and data-driven analytics are transforming the field, leading to faster and more efficient microbiological diagnostics. Whether you're a researcher, clinician, or healthcare professional, this presentation provides valuable insights into the future of AI in microbiology.BLEEDING IN EARLY PREGNANCY HYDATIDIFORM MOLE.pptx



BLEEDING IN EARLY PREGNANCY HYDATIDIFORM MOLE.pptxSREEVIDYA UMMADISETTI
Ėý
PROLIFERATION OF CHORIONIC VILLIRabies Bali 2008-2020_WRD Webinar_WSAVA 2020_Final.pptx



Rabies Bali 2008-2020_WRD Webinar_WSAVA 2020_Final.pptxWahid Husein
Ėý
A decade of rabies control programmes in Bali with support from FAO ECTAD Indonesia with Mass Dog Vaccination, Integrated Bite Case Management, Dog Population Management, and Risk Communication as the backbone of the programmesAddressing Unmet Needs for Better Outcomes in DLBCL: Leveraging Prognostic As...



Addressing Unmet Needs for Better Outcomes in DLBCL: Leveraging Prognostic As...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
Ėý
Chair, Grzegorz (Greg) S. Nowakowski, MD, FASCO, discusses diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in this CME activity titled âAddressing Unmet Needs for Better Outcomes in DLBCL: Leveraging Prognostic Assessment and Off-the-Shelf Immunotherapy Strategies.â For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aid, and complete CME information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/49JdxV4. CME credit will be available until February 27, 2026.
Distribution of Drugs â Plasma Protein Binding and Blood-Brain Barrier



Distribution of Drugs â Plasma Protein Binding and Blood-Brain BarrierSumeetSharma591398
Ėý
This presentation provides a detailed overview of drug distribution, focusing on plasma protein binding and the blood-brain barrier (BBB). It explains the factors affecting drug distribution, the role of plasma proteins in drug binding, and how drugs penetrate the BBB. Key topics include the significance of protein-bound vs. free drug concentration, drug interactions, and strategies to enhance drug permeability across the BBB. Ideal for students, researchers, and healthcare professionals in pharmacology and drug development.Public health 101 x health disinformation.pptx



Public health 101 x health disinformation.pptxTina Purnat
Ėý
Public health approaches to health disinformation Increased Clinical Trial Complexity | Dr. Ulana Rey | MindLumina



Increased Clinical Trial Complexity | Dr. Ulana Rey | MindLuminaUlana Rey PharmD
Ėý
Increased Clinical Trial Complexity. By Ulana Rey PharmD for MindLumina. Dr. Ulana Rey discusses how clinical trial complexityâendpoints, procedures, eligibility criteria, countriesâhas increased over a 20-year period.Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...



Advancements in IgA Nephropathy: Discovering the Potential of Complement Path...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
Ėý
Restoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy W...



Restoring Remission in RRMM: Present and Future of Sequential Immunotherapy W...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
Ėý
Enzyme Induction and Inhibition: Mechanisms, Examples, and Clinical Significance



Enzyme Induction and Inhibition: Mechanisms, Examples, and Clinical SignificanceSumeetSharma591398
Ėý
Addressing Unmet Needs for Better Outcomes in DLBCL: Leveraging Prognostic As...



Addressing Unmet Needs for Better Outcomes in DLBCL: Leveraging Prognostic As...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
Ėý
Dialysis
- 1. DIALYSIS
- 2. Introduction Dialysis refers to diffusion of solid molecules through semipermeable membrane passing from higher concentration to lower concentration. The main purpose is to : ï§ Maintain fluid , electrolyte and acid base balance. ï§ To remove endogenous and exogenous toxins. It is substitute for some kidney excretory function but does not replace the kidneys endocrine function.
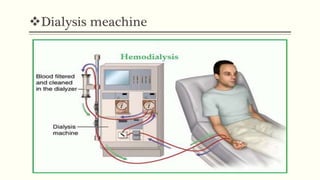
- 4. Haemodialysis ï§ Hemo = blood , dialysis = seprate ï§ It is the process of cleaning the blood of accumulated waste product. ï§ It is used for the patient who is acutely ill and and require short term dialysis (days to week ) and for the patients with advanced CKD and ESRD who required longterm or permanent treatment. It prevent death but donât cure disease. ï§ 3 times a week with an average 3-4 hours in outpatient settings.
- 5. Indication ï§ Clinical ïFluid overloads not responding to diuretics . ïUremic convulsion. ïPersistent dyspnea , vomiting and restlessness. ïSigns of pericarditis , pericardial effusion and ï pericardial frictional rub.
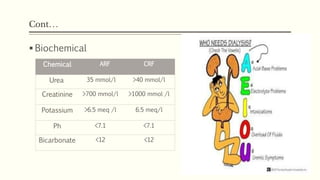
- 6. ContâĶ ï§ Biochemical Chemical ARF CRF Urea 35 mmol/l >40 mmol/l Creatinine >700 mmol/l >1000 mmol /l Potassium >6.5 meq /l 6.5 meq/l Ph <7.1 <7.1 Bicarbonate <12 <12
- 7. Requirements of hemodialysis ï§ Access to patient circulation . ï§ Dialysis machine . ï§ Dialyzer . ï§ Appropriate dialysate bath .
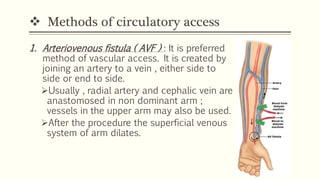
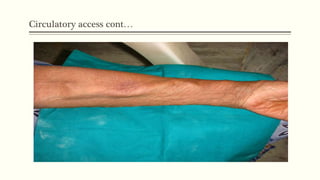
- 8. ïķ Methods of circulatory access 1. Arteriovenous fistula ( AVF ) : It is preferred method of vascular access. It is created by joining an artery to a vein , either side to side or end to side. ïUsually , radial artery and cephalic vein are anastomosed in non dominant arm ; vessels in the upper arm may also be used. ïAfter the procedure the superficial venous system of arm dilates.
- 9. Circulatory access contâĶ ïBy the means of 2 large bore needles inserted into the dilated venous system, blood may be obtained and passed thrugh the dialyzer. ïThe arterial end is used for arterial flow and the distal end is used for reinfusion of dialysed blood. ïHealing of AVF requires at least 6 to 8 weeks ; the centre vain is used for interim.
- 10. ContâĶ 2. Arteriovenous Graft : Arteriovenous connection consisting of a tube graft made from autologous saphenous vein or from polytetrafluoroethylene . Usually graft is created when the patientâs vessels are not suitable for creation of an AV fistula. Patient with compromised vascular system ( e.g. diabetes ) will graft because their native vessels are not suitable for creation of fistula. Ready to use in 3 to 4 weeks.
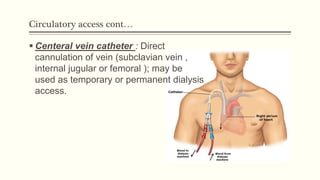
- 12. Circulatory access contâĶ ï§ Centeral vein catheter : Direct cannulation of vein (subclavian vein , internal jugular or femoral ); may be used as temporary or permanent dialysis access.
- 14. ïķDialyser ï§ It is hollow fiber devices containing thousand of tiny straw like tubes that carry the blood through the dialyzer. ï§ The tube are porous and act as semipermeable membrane allowing toxins fluid and electrolytes to pass through. ï§ The constant flow of solution maintain the concentration gradient to to facilate the exchange of wastes from the blood through semi permeable membrane into the dialysate solution where they are removed and discard.
- 15. ïķ Dialysate ï§ It is a solution made up of all the important electrolyte in their extracellular concentration. ï§ Dialysis solution is: ïžHighly purified water ïžNa,K, Ca, Mg, Cl, & dextrose ïžEither bicarbonate or acetate, to maintain a proper pH
- 16. Physiological principles 1. Diffusion : The toxins and wastes in blood are removed by diffusion i.e they move from an area of higher concentration in blood to an area of lower concentration in the dialysate. 2. Osmosis : Excess water I removed from blood by osmosis , in which water move from an area of lower concentration potential to an area of high concentration potential. 3. Ultrafiltration : Created by increased pressure in the blood compartment or a decreased pressure in the dialysate compartment. In this water moves under high pressure to an area of low pressure.
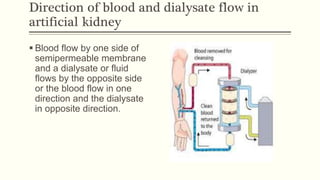
- 17. Direction of blood and dialysate flow in artificial kidney ï§ Blood flow by one side of semipermeable membrane and a dialysate or fluid flows by the opposite side or the blood flow in one direction and the dialysate in opposite direction.
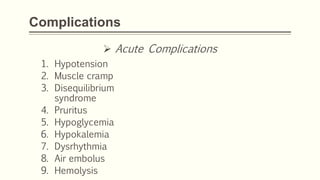
- 18. Complications ï Acute Complications 1. Hypotension 2. Muscle cramp 3. Disequilibrium syndrome 4. Pruritus 5. Hypoglycemia 6. Hypokalemia 7. Dysrhythmia 8. Air embolus 9. Hemolysis
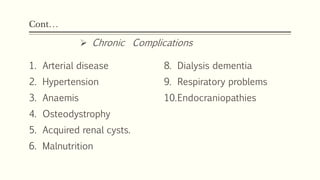
- 19. ContâĶ 1. Arterial disease 2. Hypertension 3. Anaemis 4. Osteodystrophy 5. Acquired renal cysts. 6. Malnutrition 8. Dialysis dementia 9. Respiratory problems 10.Endocraniopathies ï Chronic Complications
- 20. Care of blood access fistula or graft 1. Proper exercise by squeezing of hand . 2. Avoid heavy lifting . 3. Avoid pressure while sleeping . 4. Avoid any pricks . 5. Avoid taking BP on access hand. 6. Keep access clean all time, do not use any cream or lotions on the vascular site . 7. Avoid wearing jewellery and tight clothes .
- 21. ContâĶ 8. Listen for bruit at the site by placing the diaphragm of stethoscope gently on the site . 9. Check the functioning of vascular access several times a day by palpating the site for a thrill , which is buzzing or pulsing feeling that indicates good blood flow through the access site . 10.Assess the vascular site for any signs of infection such as redness , warmth , tenderness ,open sores and swelling .
- 23. Before dialysis 1. Explanation about the procedure /duration ,expected outcomes and possible complications . 2. Informed consent . 3. Collect all the investigations report . 4. Check vital signs :BP for hypo and hypertension; temperature for sepsis; respiration for fluid overload. 5. Weight: Determines amount of fluid to be removed during dialysis and patientâs clinical conditioning before starting . 6. Check efficiency of AV fistula .
- 24. ContâĶ 7. Review Medications : Hold drugs that pass through the dialysis membrane, such as piperacillin, folic acid, and other water-soluble vitamins. Hold antihypertensive drugs, especially if systolic pressure is below 100, per physician order . 8. Preparation of dialyzer âarterial venous tubing 9. Preparation of dialysis sets/area . 10.Setting of emergency cart . 11.Preparation of procedure area . 12.Start dialysis .
- 25. During dialysis 1. Monitor vital signs in every 15 minutes . 2. Provide comfortable position , diversional activities to promote comfort and help to pass time . 3. Assess for dialysis disequilibrium syndrome , with headache , nausea and vomiting , altered LOC , and hypertension .Rapid change in the BUN and electrolytes level lead to cerebral edema and increased ICP .
- 26. ContâĶ 4. Assess for the other responses to dialysis such as dehydration , nausea , vomiting , muscle cramps or seizure activity . 5. If a transfusion is given during dialysis , monitor for the possible transfusion reaction . 6. Assess for bleeding at the access site or elsewhere. Heparinization during dialysis increases the risk for bleeding.
- 27. After dialysis 1. Positioning of patient as comfortable . 2. Monitor vital signs and status of patient . 3. Carefully removing of arterial and venous tubing and apply effective pressure on that area to prevent bleeding . 4. Record the outcome . 5. Inform patient and visitors for next date of dialysis . 6. Explain about the home care including fistula care .

